Abstract
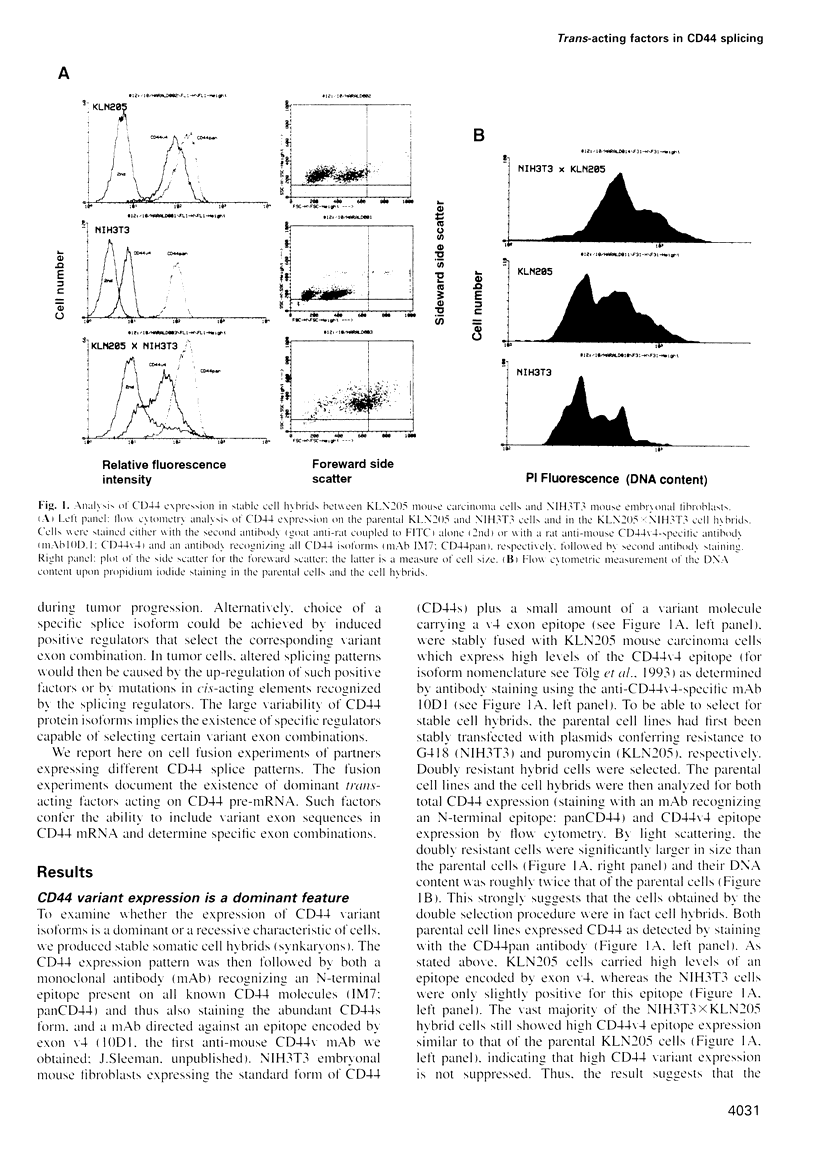
Variant isoforms of the cell surface glycoprotein CD44 (CD44v) are expressed during development, in selected adult tissues and in certain metastatic tumor cells. CD44v differ from the standard isoform (CD44s) by up to ten additional exon sequences included by alternative splicing. By cell fusion experiments, we have obtained evidence for the existence of cell-type specific trans-acting factors recruiting CD44 variant exon sequences. Stable cell hybrids of CD44s and CD44v expressing cells indicated a dominant mechanism for variant-exon inclusion. In transient interspecies heterokaryons of human keratinocytes and rat fibroblasts, the ability of the keratinocytes to include all variant exon sequences in CD44 was conferred completely on the rat fibroblast nucleus. Fusions of cells with complex CD44 splice patterns do not permit interpretation of splice control by the relative abundance of a single trans-acting factor, but rather by (a) positively acting factor(s) recruiting variant exon sequences in the 3' to 5' direction and additional factors selecting individual exons. Since the pancreatic carcinoma cell line BSp73ASML (in contrast to the cervix carcinoma cell lines SiHa and ME180) could not transfer its specific splice pattern in cell fusions, we conclude that in some tumors, splicing is also controlled by mutation of cis-acting recognition sites.
Full text
PDF

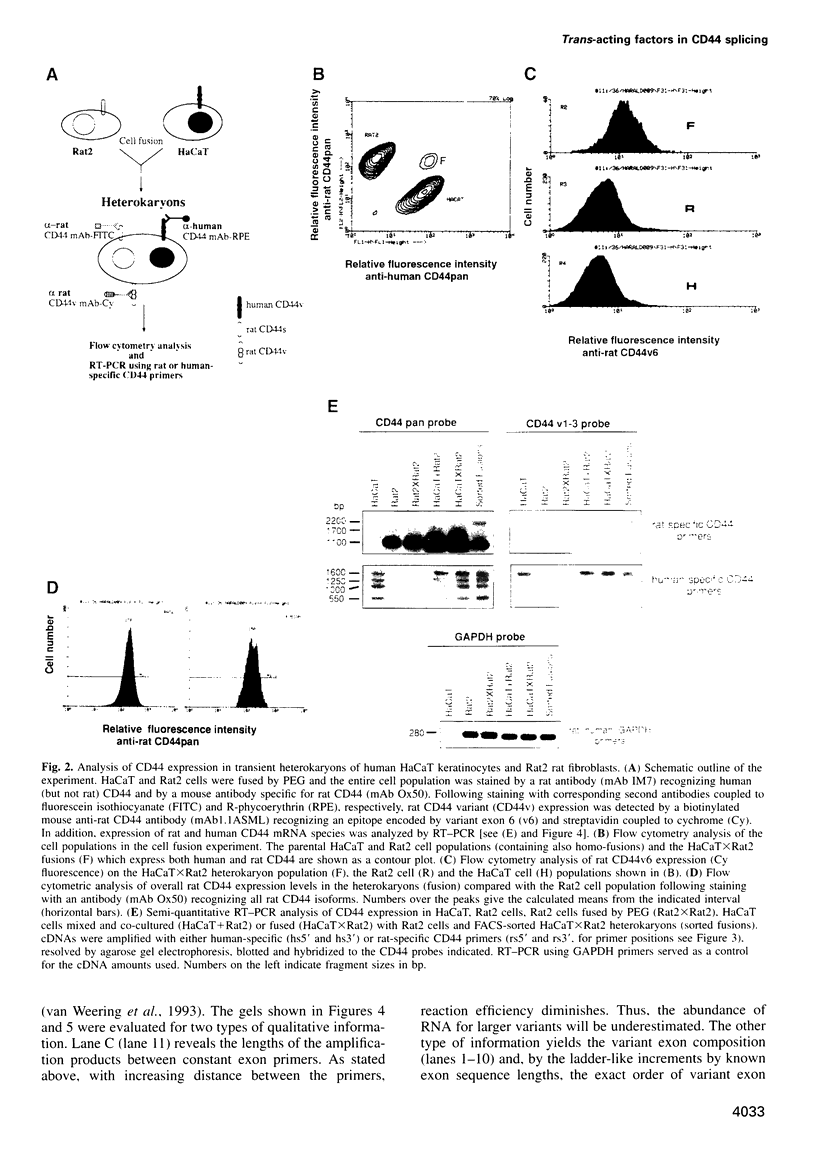

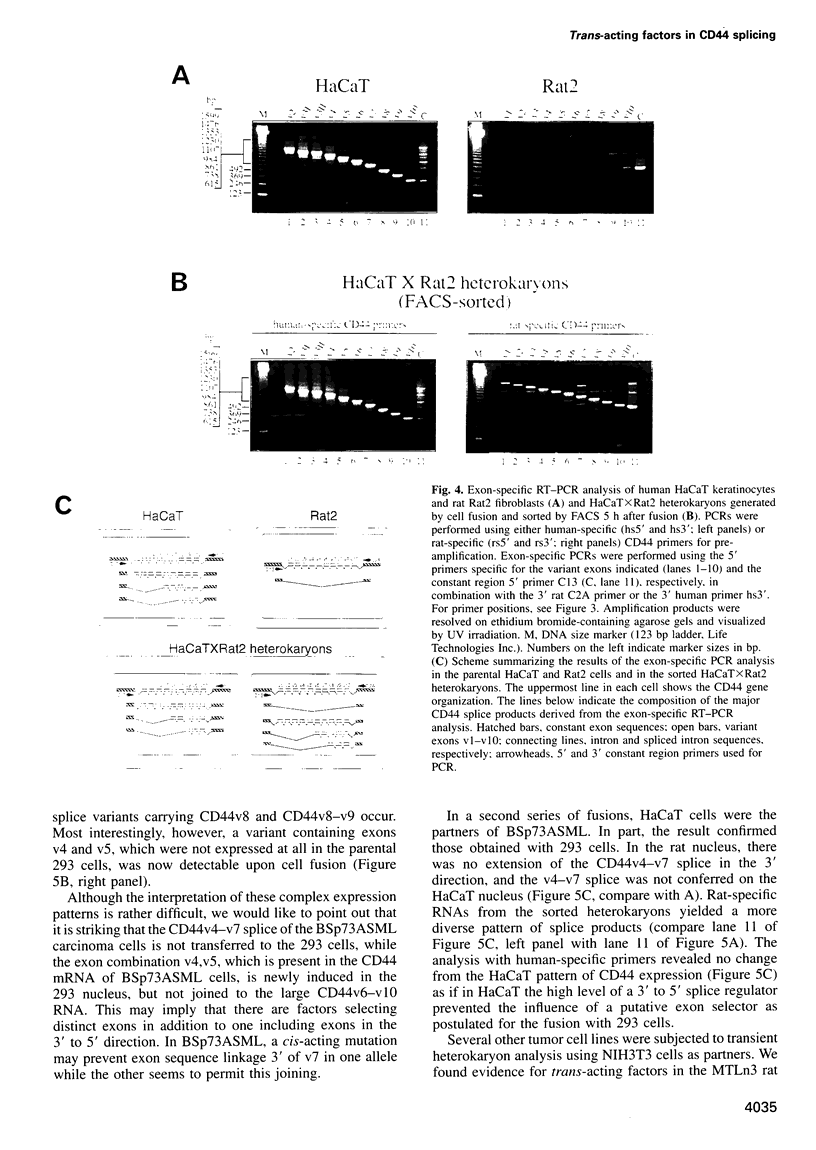
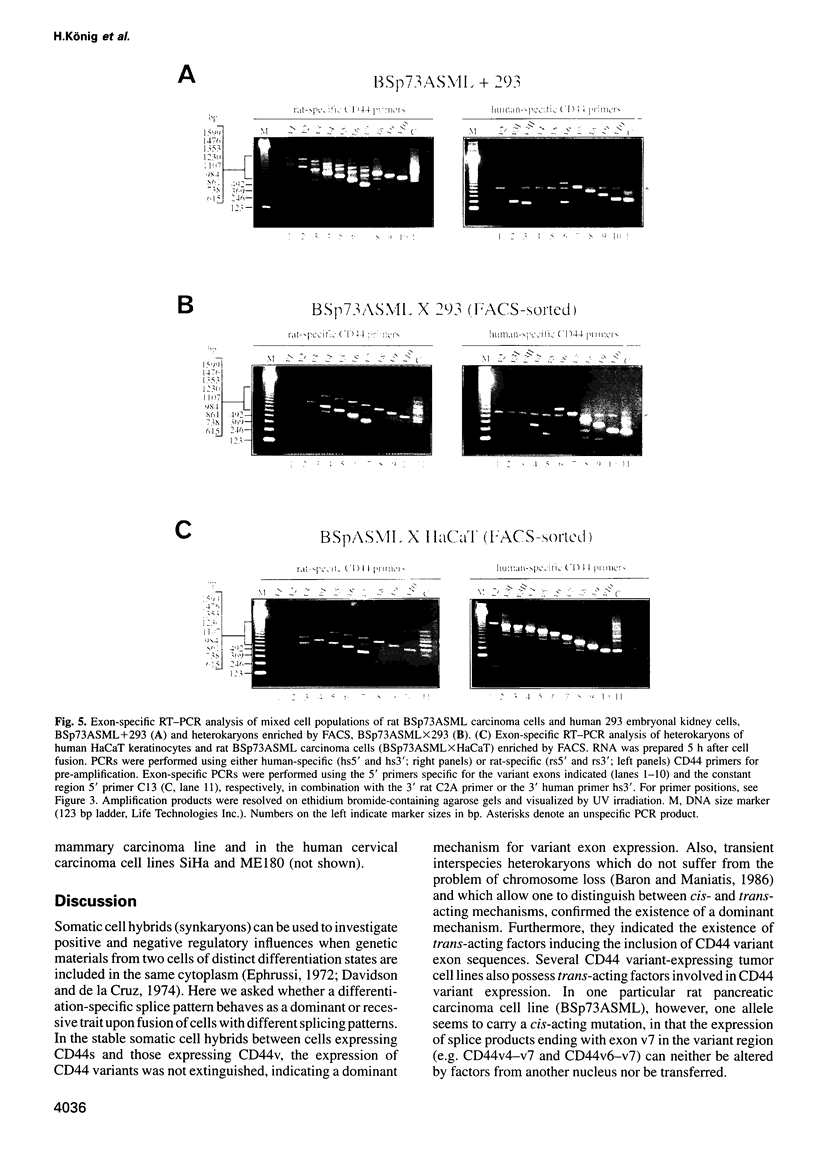



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arch R., Wirth K., Hofmann M., Ponta H., Matzku S., Herrlich P., Zöller M. Participation in normal immune responses of a metastasis-inducing splice variant of CD44. Science. 1992 Jul 31;257(5070):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.1496383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Maniatis T. Rapid reprogramming of globin gene expression in transient heterokaryons. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):591–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90885-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L. Activation of c-src neuron-specific splicing by an unusual RNA element in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):795–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90291-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. L. Does steric interference between splice sites block the splicing of a short c-src neuron-specific exon in non-neuronal cells? Genes Dev. 1991 Mar;5(3):389–402. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.3.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Chiu C. P., Webster C. Cytoplasmic activation of human nuclear genes in stable heterocaryons. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boukamp P., Petrussevska R. T., Breitkreutz D., Hornung J., Markham A., Fusenig N. E. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):761–771. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. A. In vitro splicing of cardiac troponin T precursors. Exon mutations disrupt splicing of the upstream intron. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 15;267(8):5330–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote G. J., Stolow D. T., Peleg S., Berget S. M., Gagel R. F. Identification of exon sequences and an exon binding protein involved in alternative RNA splicing of calcitonin/CGRP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 May 11;20(9):2361–2366. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.9.2361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deans J. P., Boyd A. W., Pilarski L. M. Transitions from high to low molecular weight isoforms of CD45 (T200) involve rapid activation of alternate mRNA splicing and slow turnover of surface CD45R. J Immunol. 1989 Aug 15;143(4):1233–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirksen W. P., Hampson R. K., Sun Q., Rottman F. M. A purine-rich exon sequence enhances alternative splicing of bovine growth hormone pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6431–6436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallego M. E., Balvay L., Brody E. cis-acting sequences involved in exon selection in the chicken beta-tropomyosin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5415–5425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham I. R., Hamshere M., Eperon I. C. Alternative splicing of a human alpha-tropomyosin muscle-specific exon: identification of determining sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;12(9):3872–3882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.9.3872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U. CD44: a multitude of isoforms with diverse functions. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1993;184:47–63. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78253-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günthert U., Hofmann M., Rudy W., Reber S., Zöller M., Haussmann I., Matzku S., Wenzel A., Ponta H., Herrlich P. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 1991 Apr 5;65(1):13–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90403-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampson R. K., La Follette L., Rottman F. M. Alternative processing of bovine growth hormone mRNA is influenced by downstream exon sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1604–1610. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haynes B. F., Liao H. X., Patton K. L. The transmembrane hyaluronate receptor (CD44): multiple functions, multiple forms. Cancer Cells. 1991 Sep;3(9):347–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedley M. L., Maniatis T. Sex-specific splicing and polyadenylation of dsx pre-mRNA requires a sequence that binds specifically to tra-2 protein in vitro. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):579–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90090-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heider K. H., Hofmann M., Hors E., van den Berg F., Ponta H., Herrlich P., Pals S. T. A human homologue of the rat metastasis-associated variant of CD44 is expressed in colorectal carcinomas and adenomatous polyps. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;120(1):227–233. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.1.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann M., Rudy W., Zöller M., Tölg C., Ponta H., Herrlich P., Günthert U. CD44 splice variants confer metastatic behavior in rats: homologous sequences are expressed in human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Oct 1;51(19):5292–5297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz D. S., Krainer A. R. Mechanisms for selecting 5' splice sites in mammalian pre-mRNA splicing. Trends Genet. 1994 Mar;10(3):100–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90233-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoshijima K., Inoue K., Higuchi I., Sakamoto H., Shimura Y. Control of doublesex alternative splicing by transformer and transformer-2 in Drosophila. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):833–836. doi: 10.1126/science.1902987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koopman G., Griffioen A. W., Ponta H., Herrlich P., van den Berg F., Manten-Horst E., Pals S. T. CD44 splice variants; expression on lymphocytes and in neoplasia. Res Immunol. 1993 Nov-Dec;144(9):750–762. doi: 10.1016/s0923-2494(93)80061-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavigueur A., La Branche H., Kornblihtt A. R., Chabot B. A splicing enhancer in the human fibronectin alternate ED1 exon interacts with SR proteins and stimulates U2 snRNP binding. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2405–2417. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesley J., Hyman R., Kincade P. W. CD44 and its interaction with extracellular matrix. Adv Immunol. 1993;54:271–335. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60537-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libri D., Goux-Pelletan M., Brody E., Fiszman M. Y. Exon as well as intron sequences are cis-regulating elements for the mutually exclusive alternative splicing of the beta tropomyosin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5036–5046. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch K. W., Maniatis T. Synergistic interactions between two distinct elements of a regulated splicing enhancer. Genes Dev. 1995 Feb 1;9(3):284–293. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.3.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay C. R., Terpe H. J., Stauder R., Marston W. L., Stark H., Günthert U. Expression and modulation of CD44 variant isoforms in humans. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):71–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzku S., Komitowski D., Mildenberger M., Zöller M. Characterization of BSp73, a spontaneous rat tumor and its in vivo selected variants showing different metastasizing capacities. Invasion Metastasis. 1983;3(2):109–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemeroff M. E., Utans U., Krämer A., Krug R. M. Identification of cis-acting intron and exon regions in influenza virus NS1 mRNA that inhibit splicing and cause the formation of aberrantly sedimenting presplicing complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):962–970. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neri A., Welch D., Kawaguchi T., Nicolson G. L. Development and biologic properties of malignant cell sublines and clones of a spontaneously metastasizing rat mammary adenocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Mar;68(3):507–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R., Maniatis T. A role for exon sequences and splice-site proximity in splice-site selection. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):681–690. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90343-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rio D. C. Splicing of pre-mRNA: mechanism, regulation and role in development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Aug;3(4):574–584. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90093-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein D. M., Saito H., Streuli M., Schlossman S. F., Morimoto C. The alternative splicing of the CD45 tyrosine phosphatase is controlled by negative regulatory trans-acting splicing factors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 5;267(10):7139–7147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy W., Hofmann M., Schwartz-Albiez R., Zöller M., Heider K. H., Ponta H., Herrlich P. The two major CD44 proteins expressed on a metastatic rat tumor cell line are derived from different splice variants: each one individually suffices to confer metastatic behavior. Cancer Res. 1993 Mar 15;53(6):1262–1268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Screaton G. R., Bell M. V., Bell J. I., Jackson D. G. The identification of a new alternative exon with highly restricted tissue expression in transcripts encoding the mouse Pgp-1 (CD44) homing receptor. Comparison of all 10 variable exons between mouse, human, and rat. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12235–12238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Screaton G. R., Bell M. V., Jackson D. G., Cornelis F. B., Gerth U., Bell J. I. Genomic structure of DNA encoding the lymphocyte homing receptor CD44 reveals at least 12 alternatively spliced exons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):12160–12164. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.12160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Screaton G. R., Cáceres J. F., Mayeda A., Bell M. V., Plebanski M., Jackson D. G., Bell J. I., Krainer A. R. Identification and characterization of three members of the human SR family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 1;14(17):4336–4349. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00108.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Sleeman J., Dall P., Hekele A., Moll J., Ponta H., Herrlich P. The CD44 proteins in embryonic development and in cancer. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1996;213(Pt 1):249–269. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-61107-0_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Sleeman J., Herrlich P., Ponta H. Hyaluronate receptors: key players in growth, differentiation, migration and tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;6(5):726–733. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90100-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebel C. W., Fresco L. D., Rio D. C. The mechanism of somatic inhibition of Drosophila P-element pre-mRNA splicing: multiprotein complexes at an exon pseudo-5' splice site control U1 snRNP binding. Genes Dev. 1992 Aug;6(8):1386–1401. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.8.1386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli M., Saito H. Regulation of tissue-specific alternative splicing: exon-specific cis-elements govern the splicing of leukocyte common antigen pre-mRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):787–796. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03439.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Watakabe A., Shimura Y. Polypurine sequences within a downstream exon function as a splicing enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1347–1354. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian M., Maniatis T. A splicing enhancer complex controls alternative splicing of doublesex pre-mRNA. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90298-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tölg C., Hofmann M., Herrlich P., Ponta H. Splicing choice from ten variant exons establishes CD44 variability. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1225–1229. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Underhill C. CD44: the hyaluronan receptor. J Cell Sci. 1992 Oct;103(Pt 2):293–298. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.2.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watakabe A., Tanaka K., Shimura Y. The role of exon sequences in splice site selection. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):407–418. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu R., Teng J., Cooper T. A. The cardiac troponin T alternative exon contains a novel purine-rich positive splicing element. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3660–3674. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahler A. M., Lane W. S., Stolk J. A., Roth M. B. SR proteins: a conserved family of pre-mRNA splicing factors. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):837–847. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Weering D. H., Baas P. D., Bos J. L. A PCR-based method for the analysis of human CD44 splice products. PCR Methods Appl. 1993 Oct;3(2):100–106. doi: 10.1101/gr.3.2.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]