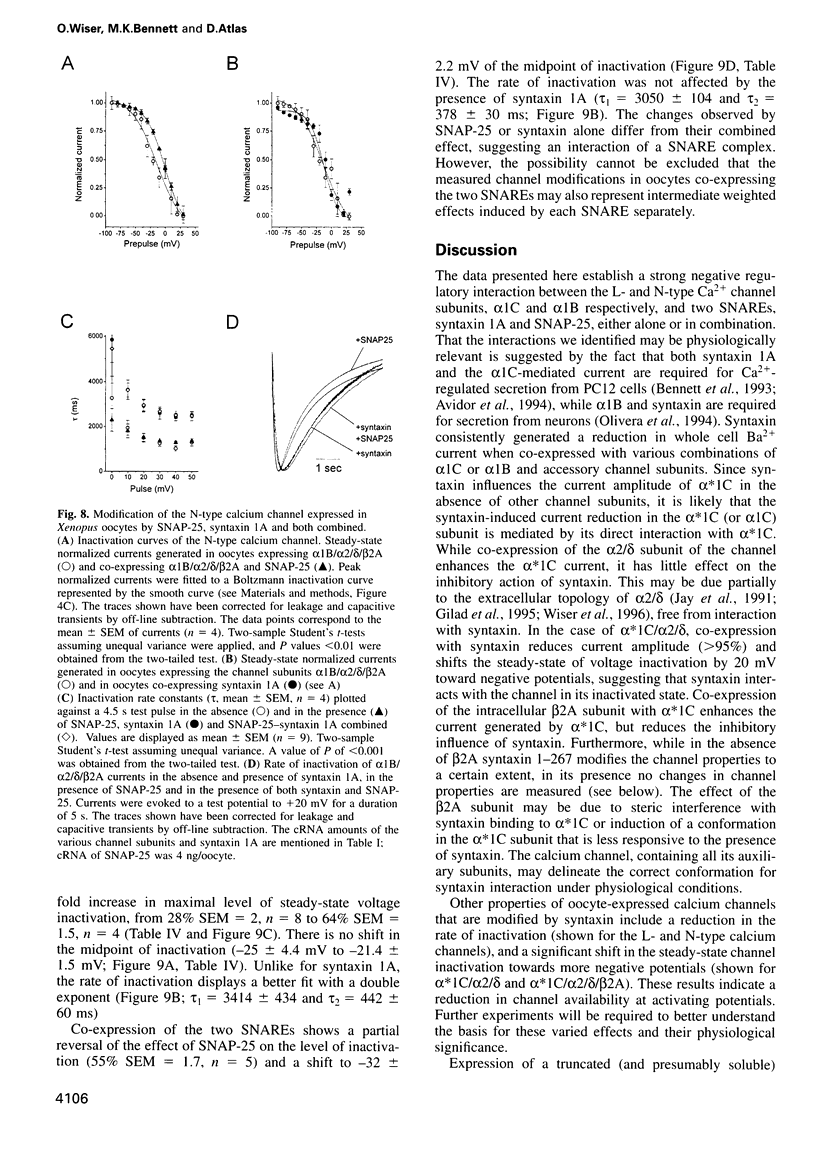
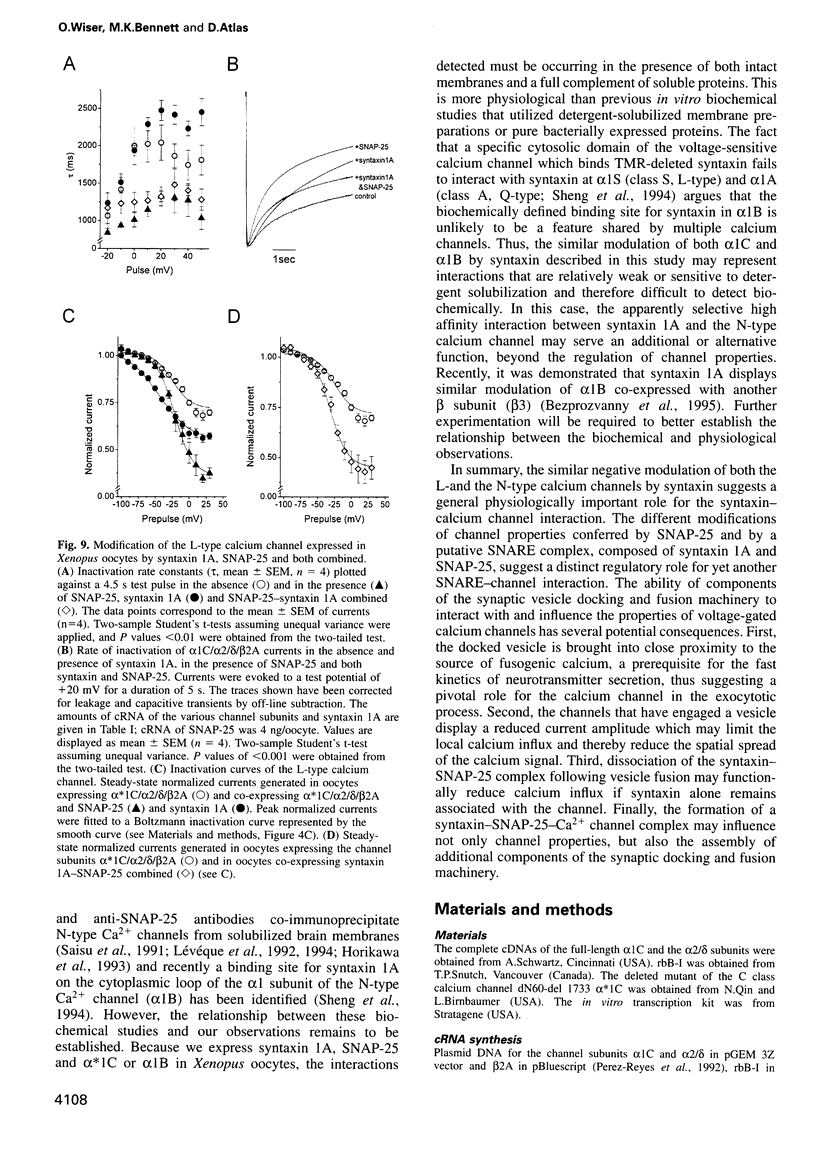
Abstract
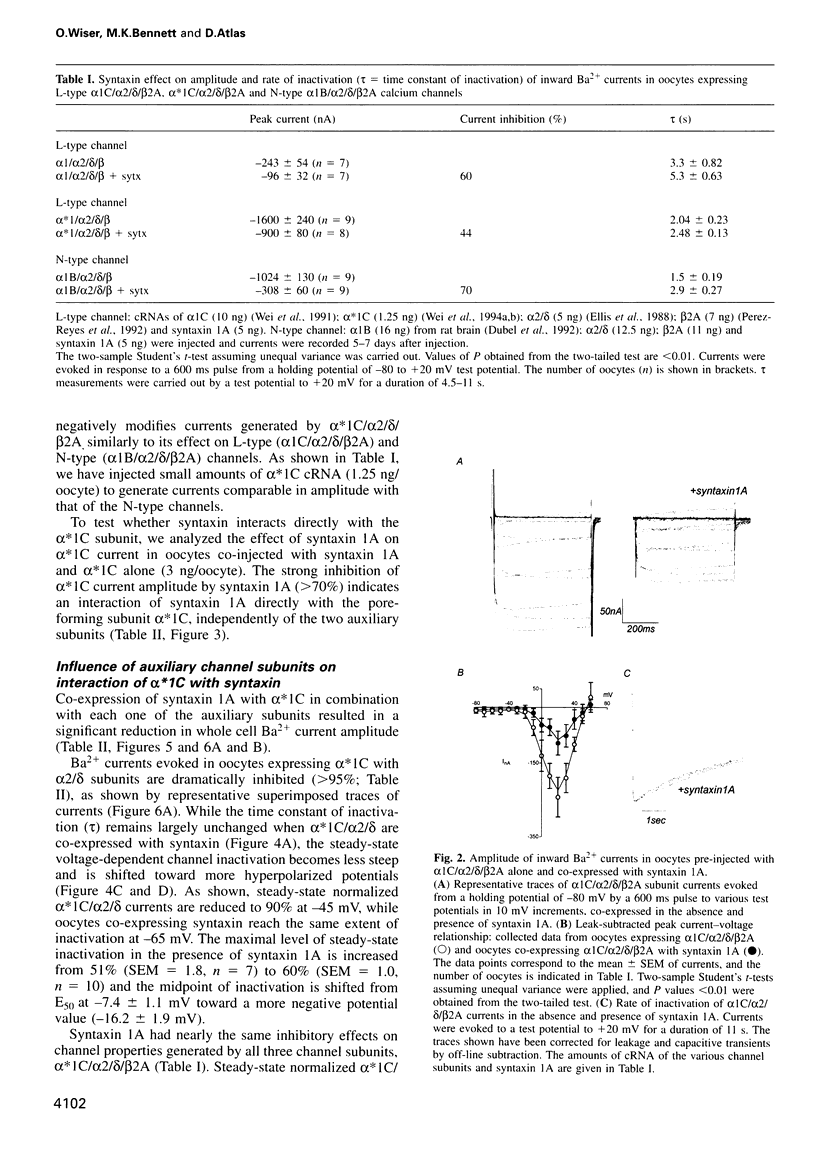
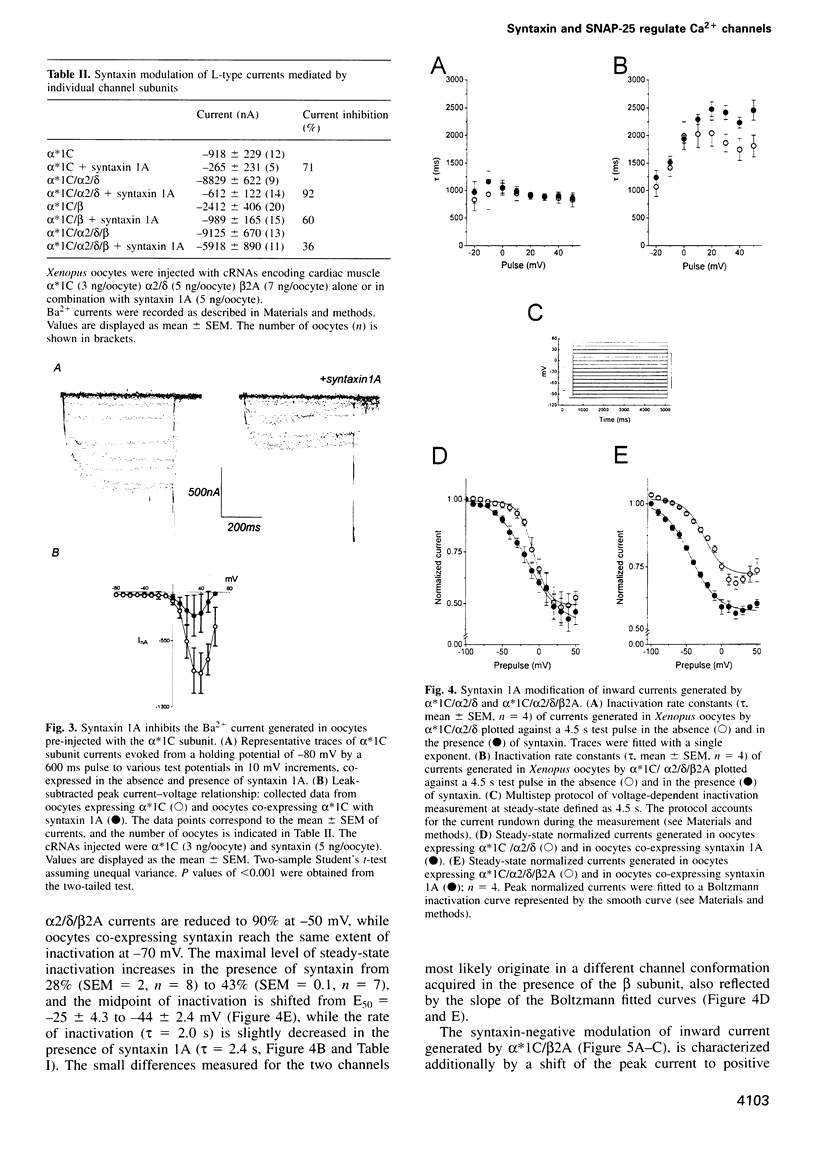
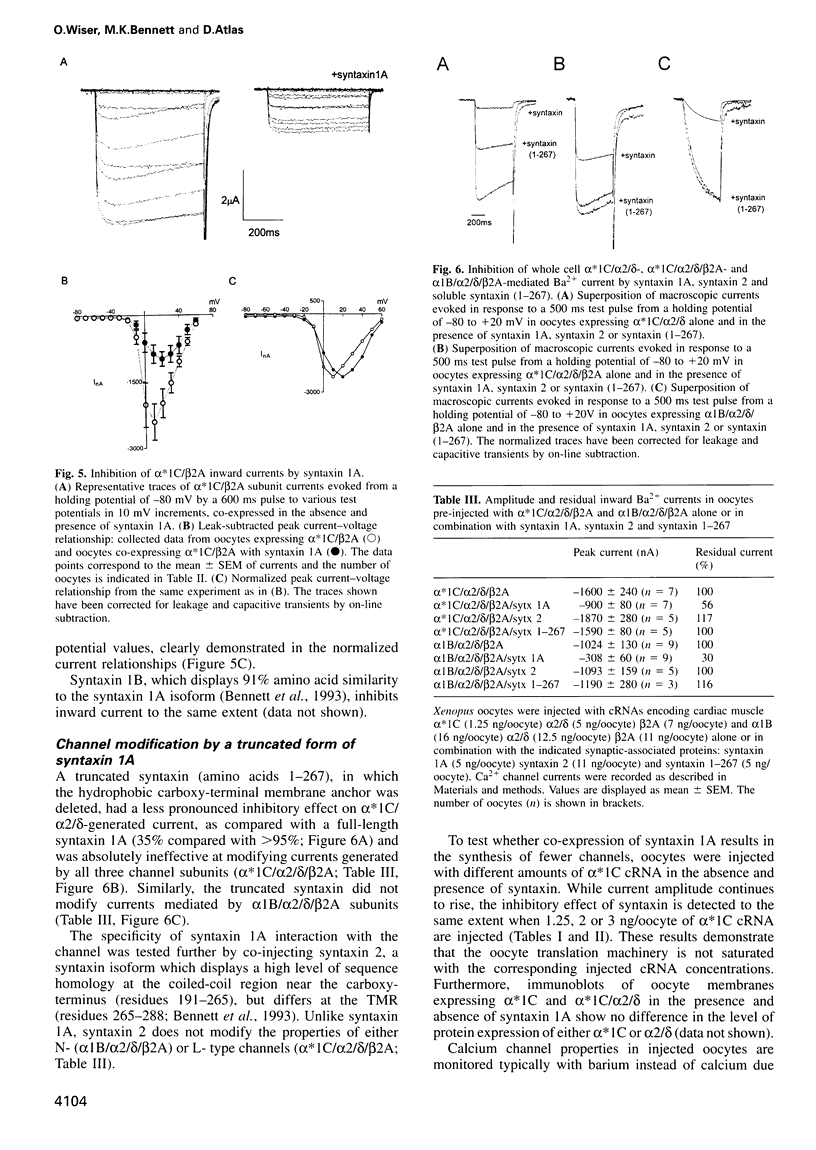
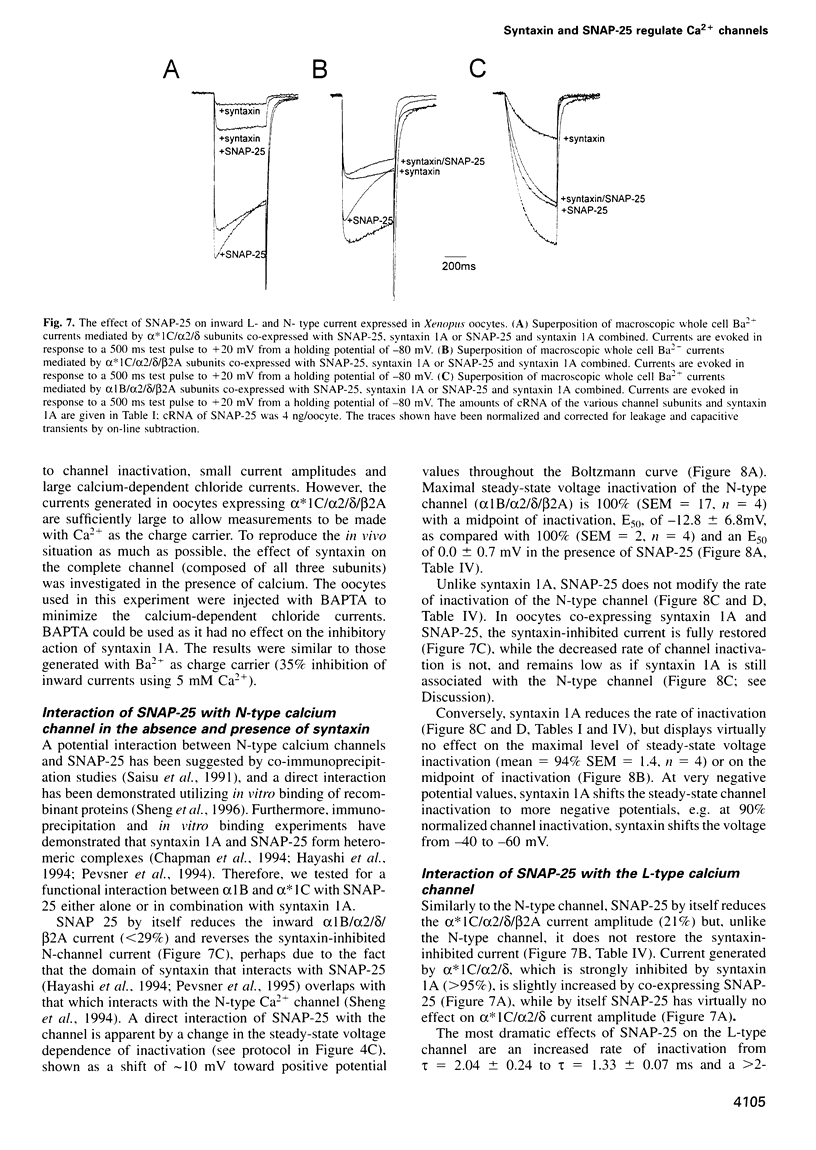
We have used an electrophysiological assay to investigate the functional interaction of syntaxin 1A and SNAP-25 with the class C, L-type, and the class B, N-type, voltage-sensitive calcium channels. Co-expression of syntaxin 1A with the pore-forming subunits of the L- and N-type channels in Xenopus oocytes generates a dramatic inhibition of inward currents (>60%) and modifies the rate of inactivation (tau) and steady-state voltage dependence of inactivation. Syntaxin 1-267, which lacks the transmembrane region (TMR), and syntaxin 2 do not modify channel properties, suggesting that the syntaxin 1A interaction site resides predominantly in the TMR. Co-expression of SNAP-25 significantly modifies the gating properties of L- and N-type channels and displays modest inhibition of current amplitude. Syntaxin 1A and SNAP-25 combined restore the syntaxin-inhibited N-type inward current but not the reduced rate of inactivation. Hence, a distinct interaction of a putative syntaxin 1A-SNAP-25 complex with the channel is apparent, consistent with the formation of a synaptosomal SNAP receptors (SNAREs) complex. The in vivo functional reconstitution: (i) establishes the proximity of the SNAREs to calcium channels; (ii) provides new insight into a potential regulatory role for the two SNAREs in controlling calcium influx through N- and L-type channels; and (iii) may suggest a pivotal role for calcium channels in the secretion process.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avidor B., Avidor T., Schwartz L., De Jongh K. S., Atlas D. Cardiac L-type Ca2+ channel triggers transmitter release in PC12 cells. FEBS Lett. 1994 Apr 4;342(2):209–213. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80502-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumert M., Maycox P. R., Navone F., De Camilli P., Jahn R. Synaptobrevin: an integral membrane protein of 18,000 daltons present in small synaptic vesicles of rat brain. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):379–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03388.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Syntaxin: a synaptic protein implicated in docking of synaptic vesicles at presynaptic active zones. Science. 1992 Jul 10;257(5067):255–259. doi: 10.1126/science.1321498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., García-Arrarás J. E., Elferink L. A., Peterson K., Fleming A. M., Hazuka C. D., Scheller R. H. The syntaxin family of vesicular transport receptors. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):863–873. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. The molecular machinery for secretion is conserved from yeast to neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bezprozvanny I., Scheller R. H., Tsien R. W. Functional impact of syntaxin on gating of N-type and Q-type calcium channels. Nature. 1995 Dec 7;378(6557):623–626. doi: 10.1038/378623a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasi J., Chapman E. R., Yamasaki S., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R. Botulinum neurotoxin C1 blocks neurotransmitter release by means of cleaving HPC-1/syntaxin. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4821–4828. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06171.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Scheller R. H. Vesicle-associated membrane protein and synaptophysin are associated on the synaptic vesicle. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 7;269(40):24534–24537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman E. R., An S., Barton N., Jahn R. SNAP-25, a t-SNARE which binds to both syntaxin and synaptobrevin via domains that may form coiled coils. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 4;269(44):27427–27432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubel S. J., Starr T. V., Hell J., Ahlijanian M. K., Enyeart J. J., Catterall W. A., Snutch T. P. Molecular cloning of the alpha-1 subunit of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive calcium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5058–5062. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis S. B., Williams M. E., Ways N. R., Brenner R., Sharp A. H., Leung A. T., Campbell K. P., McKenna E., Koch W. J., Hui A. Sequence and expression of mRNAs encoding the alpha 1 and alpha 2 subunits of a DHP-sensitive calcium channel. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1661–1664. doi: 10.1126/science.2458626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilad B., Shenkar N., Halevi S., Trus M., Atlas D. Identification of the alternative spliced form of the alpha 2/delta subunit of voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels expressed in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Jul 7;193(3):157–160. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11689-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi T., McMahon H., Yamasaki S., Binz T., Hata Y., Südhof T. C., Niemann H. Synaptic vesicle membrane fusion complex: action of clostridial neurotoxins on assembly. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5051–5061. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06834.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikawa H. P., Saisu H., Ishizuka T., Sekine Y., Tsugita A., Odani S., Abe T. A complex of rab3A, SNAP-25, VAMP/synaptobrevin-2 and syntaxins in brain presynaptic terminals. FEBS Lett. 1993 Sep 13;330(2):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Obata K., Akagawa K. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for a neuronal cell membrane antigen, HPC-1. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10613–10619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay S. D., Sharp A. H., Kahl S. D., Vedvick T. S., Harpold M. M., Campbell K. P. Structural characterization of the dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel alpha 2-subunit and the associated delta peptides. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 15;266(5):3287–3293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushima Y., Fujiwara T., Morimoto T., Akagawa K. Involvement of HPC-1/syntaxin-1A antigen in transmitter release from PC12h cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jul 6;212(1):97–103. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leveque C., Hoshino T., David P., Shoji-Kasai Y., Leys K., Omori A., Lang B., el Far O., Sato K., Martin-Moutot N. The synaptic vesicle protein synaptotagmin associates with calcium channels and is a putative Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3625–3629. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévêque C., el Far O., Martin-Moutot N., Sato K., Kato R., Takahashi M., Seagar M. J. Purification of the N-type calcium channel associated with syntaxin and synaptotagmin. A complex implicated in synaptic vesicle exocytosis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 4;269(9):6306–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon H. T., Ushkaryov Y. A., Edelmann L., Link E., Binz T., Niemann H., Jahn R., Südhof T. C. Cellubrevin is a ubiquitous tetanus-toxin substrate homologous to a putative synaptic vesicle fusion protein. Nature. 1993 Jul 22;364(6435):346–349. doi: 10.1038/364346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochida S., Saisu H., Kobayashi H., Abe T. Impairment of syntaxin by botulinum neurotoxin C1 or antibodies inhibits acetylcholine release but not Ca2+ channel activity. Neuroscience. 1995 Apr;65(3):905–915. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)00508-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niemann H., Blasi J., Jahn R. Clostridial neurotoxins: new tools for dissecting exocytosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90203-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olivera B. M., Miljanich G. P., Ramachandran J., Adams M. E. Calcium channel diversity and neurotransmitter release: the omega-conotoxins and omega-agatoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:823–867. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Reyes E., Castellano A., Kim H. S., Bertrand P., Baggstrom E., Lacerda A. E., Wei X. Y., Birnbaumer L. Cloning and expression of a cardiac/brain beta subunit of the L-type calcium channel. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1792–1797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pevsner J., Hsu S. C., Braun J. E., Calakos N., Ting A. E., Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. Specificity and regulation of a synaptic vesicle docking complex. Neuron. 1994 Aug;13(2):353–361. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90352-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiavo G., Shone C. C., Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H., Montecucco C. Botulinum neurotoxin type C cleaves a single Lys-Ala bond within the carboxyl-terminal region of syntaxins. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10566–10570. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreibmayer W., Lester H. A., Dascal N. Voltage clamping of Xenopus laevis oocytes utilizing agarose-cushion electrodes. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Mar;426(5):453–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00388310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng Z. H., Rettig J., Cook T., Catterall W. A. Calcium-dependent interaction of N-type calcium channels with the synaptic core complex. Nature. 1996 Feb 1;379(6564):451–454. doi: 10.1038/379451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng Z. H., Rettig J., Takahashi M., Catterall W. A. Identification of a syntaxin-binding site on N-type calcium channels. Neuron. 1994 Dec;13(6):1303–1313. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90417-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Bennett M. K., Whiteheart S. W., Scheller R. H., Rothman J. E. A protein assembly-disassembly pathway in vitro that may correspond to sequential steps of synaptic vesicle docking, activation, and fusion. Cell. 1993 Nov 5;75(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Söllner T., Whiteheart S. W., Brunner M., Erdjument-Bromage H., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Rothman J. E. SNAP receptors implicated in vesicle targeting and fusion. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):318–324. doi: 10.1038/362318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble W. S., Cowan D. M., Scheller R. H. VAMP-1: a synaptic vesicle-associated integral membrane protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4538–4542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X. Y., Perez-Reyes E., Lacerda A. E., Schuster G., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. Heterologous regulation of the cardiac Ca2+ channel alpha 1 subunit by skeletal muscle beta and gamma subunits. Implications for the structure of cardiac L-type Ca2+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21943–21947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei X., Neely A., Lacerda A. E., Olcese R., Stefani E., Perez-Reyes E., Birnbaumer L. Modification of Ca2+ channel activity by deletions at the carboxyl terminus of the cardiac alpha 1 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1635–1640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiser O., Trus M., Tobi D., Halevi S., Giladi E., Atlas D. The alpha 2/delta subunit of voltage sensitive Ca2+ channels is a single transmembrane extracellular protein which is involved in regulated secretion. FEBS Lett. 1996 Jan 22;379(1):15–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01475-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida A., Oho C., Omori A., Kuwahara R., Ito T., Takahashi M. HPC-1 is associated with synaptotagmin and omega-conotoxin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 Dec 15;267(35):24925–24928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


