Abstract
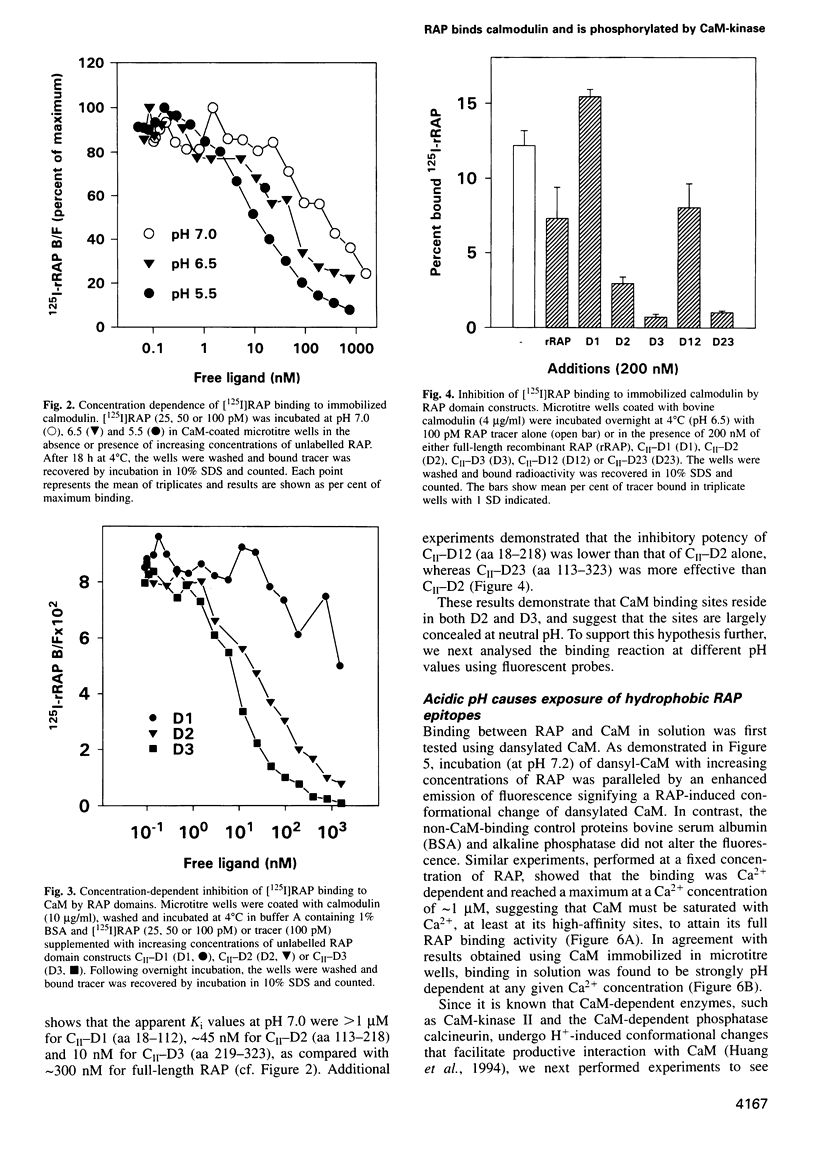
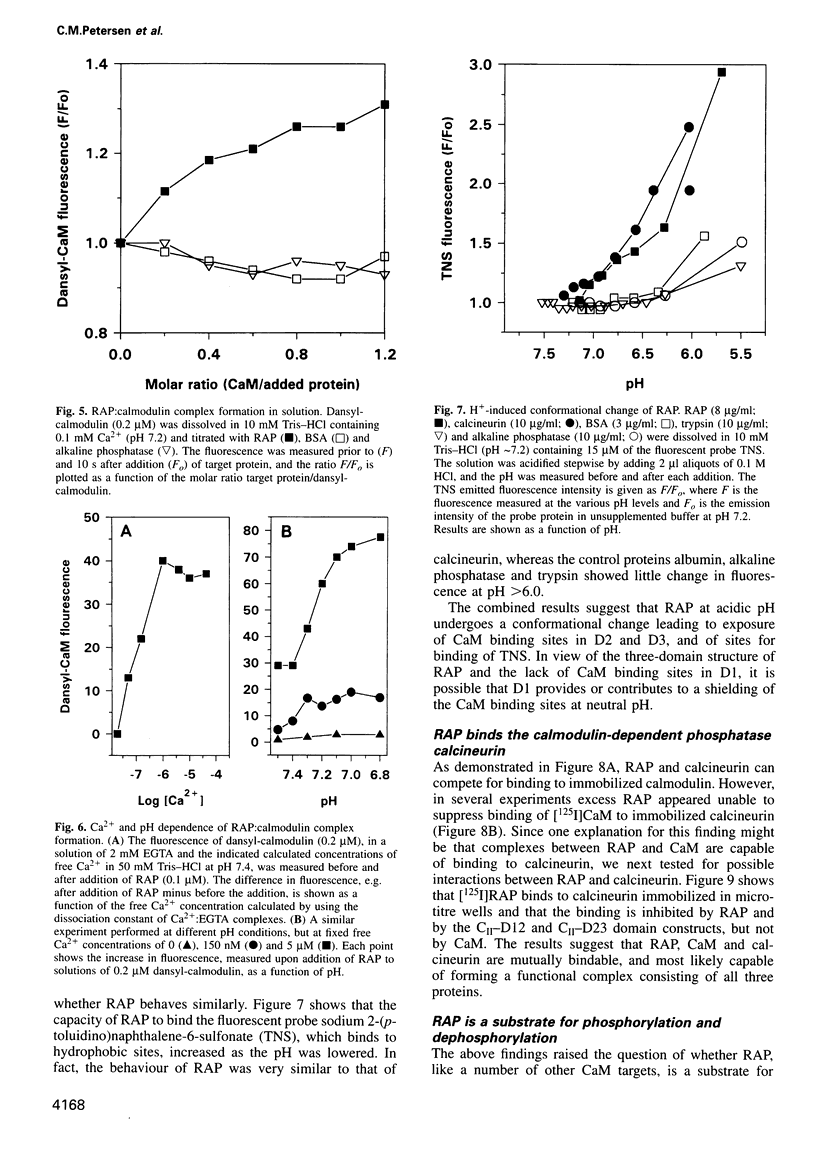
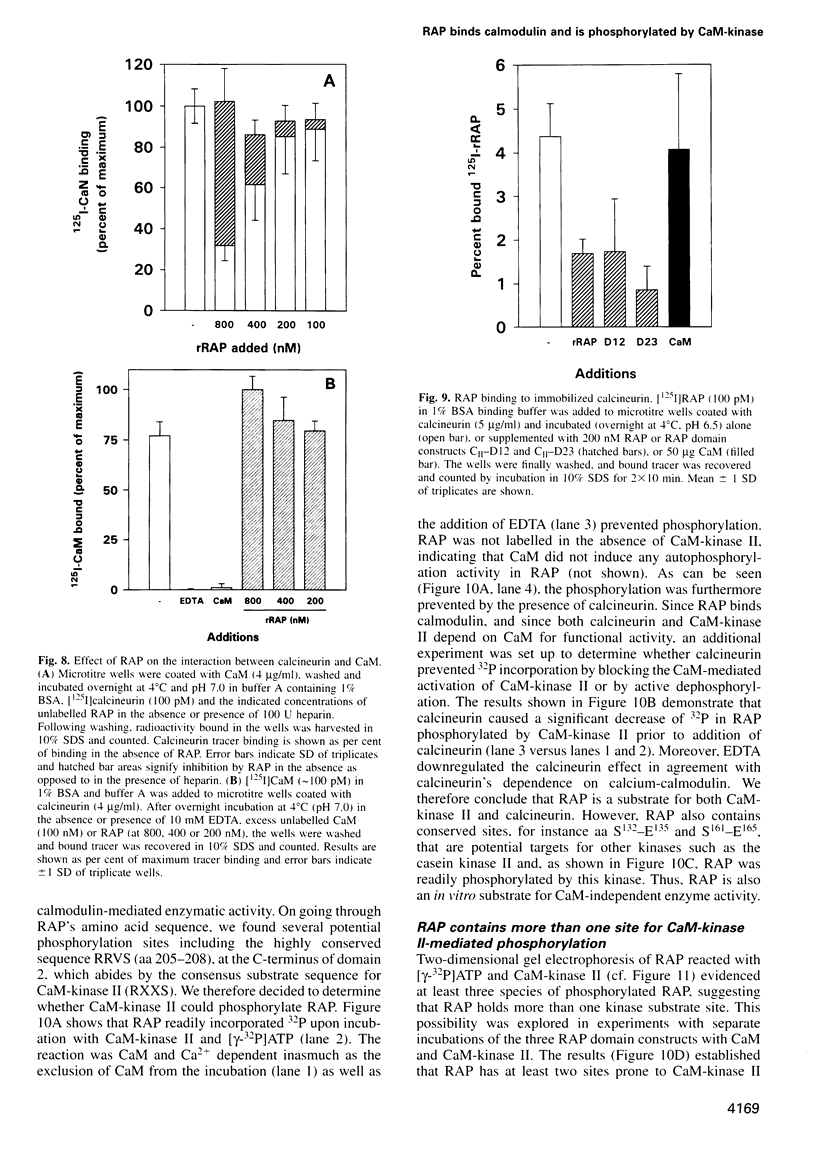
The receptor-associated protein, RAP, is an intracellular protein that may function as a chaperone for the LDL-receptor family receptors. Here we report calmodulin as the first identified RAP binding protein outside of the LDL-receptor family members. We demonstrate that RAP binds calmodulin in a Ca2+- and pH-dependent manner characteristic of calmodulin-dependent enzymes, and present evidence that RAP is a substrate for calmodulin-dependent enzymes. Thus, CaM-kinase II and calcineurin readily phosphorylate and dephosphorylate, respectively, serine residues in RAP, and in the individual RAP domains D2 (amino acids 113-218) and D3 (amino acids 219-323) which both contain sites for CaM-kinase II-mediated phosphorylation and for calmodulin binding. In addition, we provide evidence that RAP is phosphorylated by other kinases such as casein kinase II. Studies of 32[ortho]P-labelled cell cultures demonstrate that RAP is phosphorylated in vivo. Our results suggest that RAP may have hitherto unknown functions implicating phosphorylation and calmodulin-mediated modulation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbate M., Bachinsky D., Zheng G., Stamenkovic I., McLaughlin M., Niles J. L., McCluskey R. T., Brown D. Location of gp330/alpha 2-m receptor-associated protein (alpha 2-MRAP) and its binding sites in kidney: distribution of endogenous alpha 2-MRAP is modified by tissue processing. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;61(1):139–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey F. D., Gåfvels M. E., FitzGerald D. J., Argraves W. S., Chappell D. A., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Strickland D. K. The 39-kDa receptor-associated protein regulates ligand binding by the very low density lipoprotein receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 16;269(37):23268–23273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu G., Geuze H. J., Strous G. J., Schwartz A. L. 39 kDa receptor-associated protein is an ER resident protein and molecular chaperone for LDL receptor-related protein. EMBO J. 1995 May 15;14(10):2269–2280. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu G., Maksymovitch E. A., Geuze H., Schwartz A. L. Subcellular localization and endocytic function of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein in human glioblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 25;269(47):29874–29882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cala S. E., Jones L. R. GRP94 resides within cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles and is phosphorylated by casein kinase II. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):5926–5931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Rasmussen H. H., Gromov P., Olsen E., Madsen P., Leffers H., Honoré B., Dejgaard K., Vorum H., Kristensen D. B. The human keratinocyte two-dimensional gel protein database (update 1995): mapping components of signal transduction pathways. Electrophoresis. 1995 Dec;16(12):2177–2240. doi: 10.1002/elps.11501601355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin D. T., Goff S. A., Webster T., Smith T., Goldberg A. L. Sequence of the lon gene in Escherichia coli. A heat-shock gene which encodes the ATP-dependent protease La. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):11718–11728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Signal integration at the level of protein kinases, protein phosphatases and their substrates. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):408–413. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. J., Prendergast F. G., Ehrhardt M. R., Urbauer J. L., Wand A. J., Sedarous S. S., McCormick D. J., Buckley P. J. Calmodulin interacts with amphiphilic peptides composed of all D-amino acids. Nature. 1994 Apr 14;368(6472):651–653. doi: 10.1038/368651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinrichsen R. D. Calcium and calmodulin in the control of cellular behavior and motility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 23;1155(3):277–293. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90010-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S., Carlson G. M., Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin-dependent enzymes undergo a protein-induced conformational change that is associated with their interactions with calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7631–7638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida A., Kitani T., Okuno S., Fujisawa H. Inactivation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II by Ca2+/calmodulin. J Biochem. 1994 Jun;115(6):1075–1082. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a124460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James P., Vorherr T., Carafoli E. Calmodulin-binding domains: just two faced or multi-faceted? Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jan;20(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88949-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korenberg J. R., Argraves K. M., Chen X. N., Tran H., Strickland D. K., Argraves W. S. Chromosomal localization of human genes for the LDL receptor family member glycoprotein 330 (LRP2) and its associated protein RAP (LRPAP1). Genomics. 1994 Jul 1;22(1):88–93. doi: 10.1006/geno.1994.1348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorent K., Overbergh L., Delabie J., Van Leuven F., Van den Berghe H. Distribution of mRNA coding for alpha-2-macroglobulin, the murinoglobulins, the alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor and the alpha-2-macroglobulin receptor associated protein during mouse embryogenesis and in adult tissues. Differentiation. 1994 Feb;55(3):213–223. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.1994.5530213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauxion F., Le Borgne R., Munier-Lehmann H., Hoflack B. A casein kinase II phosphorylation site in the cytoplasmic domain of the cation-dependent mannose 6-phosphate receptor determines the high affinity interaction of the AP-1 Golgi assembly proteins with membranes. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 26;271(4):2171–2178. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.4.2171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Cui S., Vorum H., Bregengård C., Bjørn S. E., Norris K., Gliemann J., Christensen E. I. Evidence that epithelial glycoprotein 330/megalin mediates uptake of polybasic drugs. J Clin Invest. 1995 Sep;96(3):1404–1413. doi: 10.1172/JCI118176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J. Analysis of ligand recognition by the purified alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor (low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein). Evidence that high affinity of alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complex is achieved by binding to adjacent receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14011–14017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K. The alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor and epithelial glycoprotein-330: two giant receptors mediating endocytosis of multiple ligands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 29;1197(2):197–213. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M. S., Nykjaer A., Warshawsky I., Schwartz A. L., Gliemann J. Analysis of ligand binding to the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor/low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Evidence that lipoprotein lipase and the carboxyl-terminal domain of the receptor-associated protein bind to the same site. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23713–23719. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Hanson P. I. Multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Neurochem Res. 1993 Jan;18(1):65–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00966924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H., Kuret J., Jefferson A. B., Nose P. S., Spitzer K. H. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent microtubule-associated protein 2 kinase: broad substrate specificity and multifunctional potential in diverse tissues. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5320–5327. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman H. The multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):247–253. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sfeir C., Veis A. Casein kinase localization in the endoplasmic reticulum of the ROS 17/2.8 cell line. J Bone Miner Res. 1995 Apr;10(4):607–615. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650100414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh N. K., Atreya C. D., Nakhasi H. L. Identification of calreticulin as a rubella virus RNA binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12770–12774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Battey F., Behre E., McTigue K., Battey J. F., Argraves W. S. Primary structure of alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor-associated protein. Human homologue of a Heymann nephritis antigen. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13364–13369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vorherr T., Chiesi M., Schwaller R., Carafoli E. Regulation of the calcium ion pump of sarcoplasmic reticulum: reversible inhibition by phospholamban and by the calmodulin binding domain of the plasma membrane calcium ion pump. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):371–376. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshawsky I., Bu G., Schwartz A. L. Binding analysis of amino-terminal and carboxyl-terminal regions of the 39-kDa protein to the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3325–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshawsky I., Bu G., Schwartz A. L. Identification of domains on the 39-kDa protein that inhibit the binding of ligands to the low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):22046–22054. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willnow T. E., Armstrong S. A., Hammer R. E., Herz J. Functional expression of low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein is controlled by receptor-associated protein in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 May 9;92(10):4537–4541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.10.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng G., Bachinsky D. R., Stamenkovic I., Strickland D. K., Brown D., Andres G., McCluskey R. T. Organ distribution in rats of two members of the low-density lipoprotein receptor gene family, gp330 and LRP/alpha 2MR, and the receptor-associated protein (RAP). J Histochem Cytochem. 1994 Apr;42(4):531–542. doi: 10.1177/42.4.7510321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






