Abstract
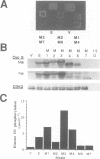
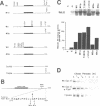
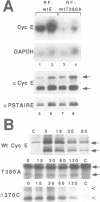
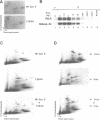
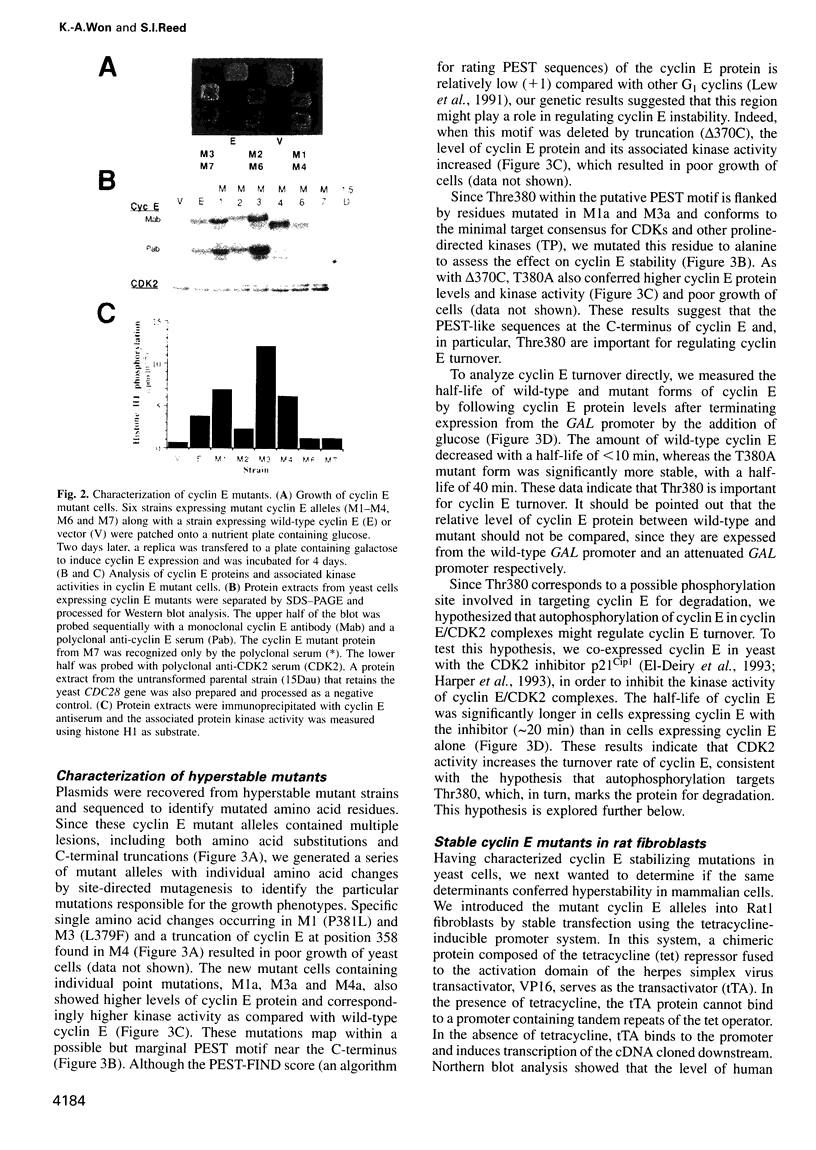
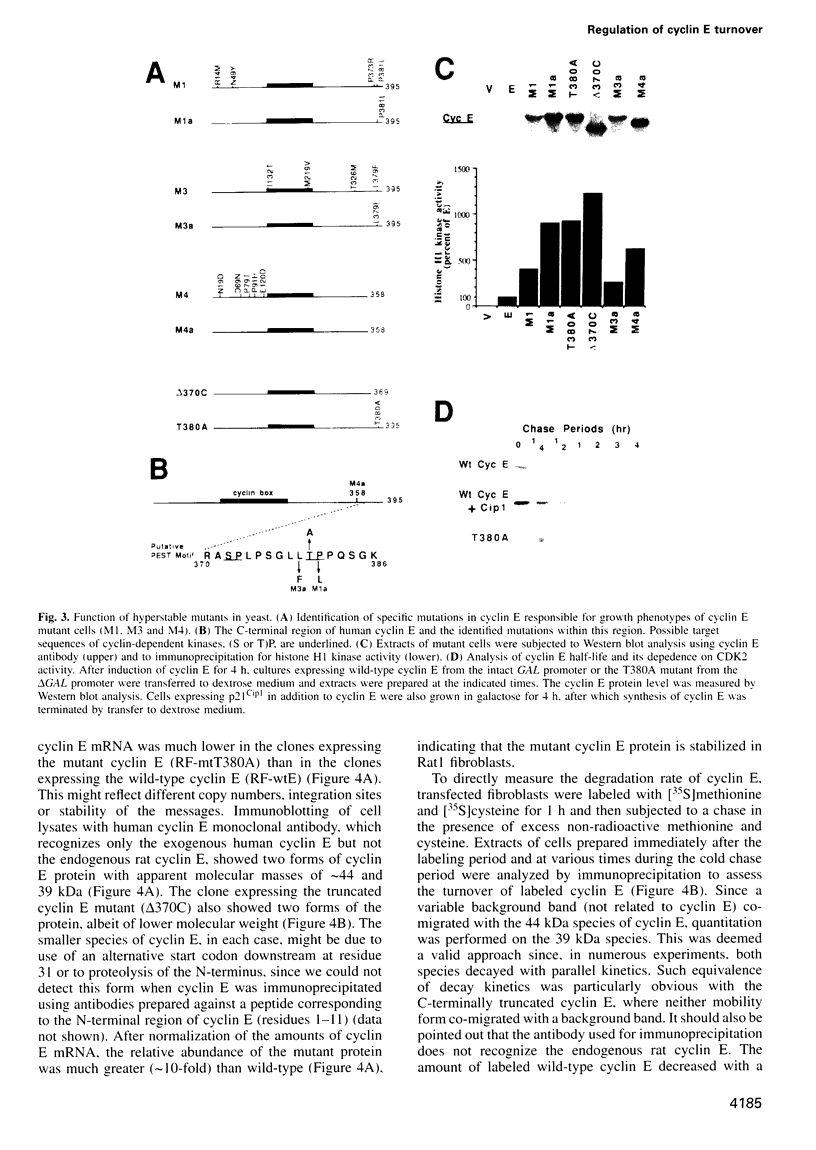
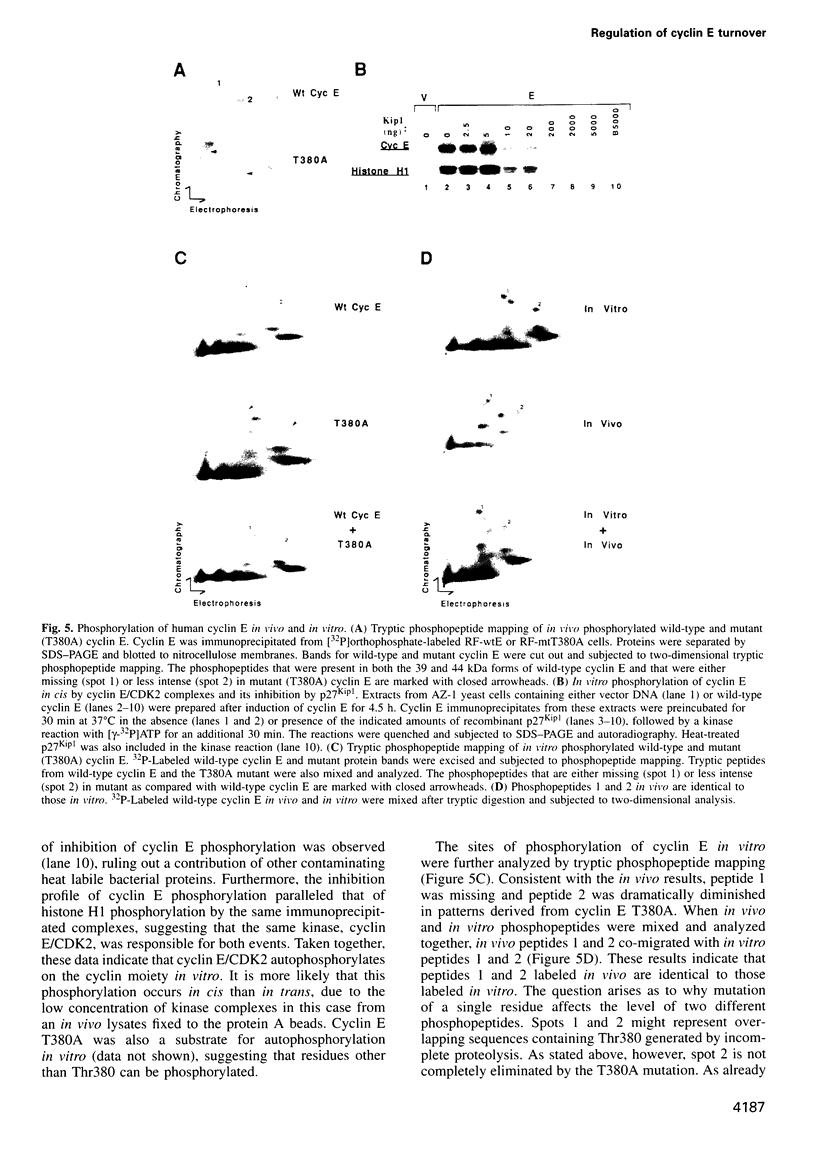
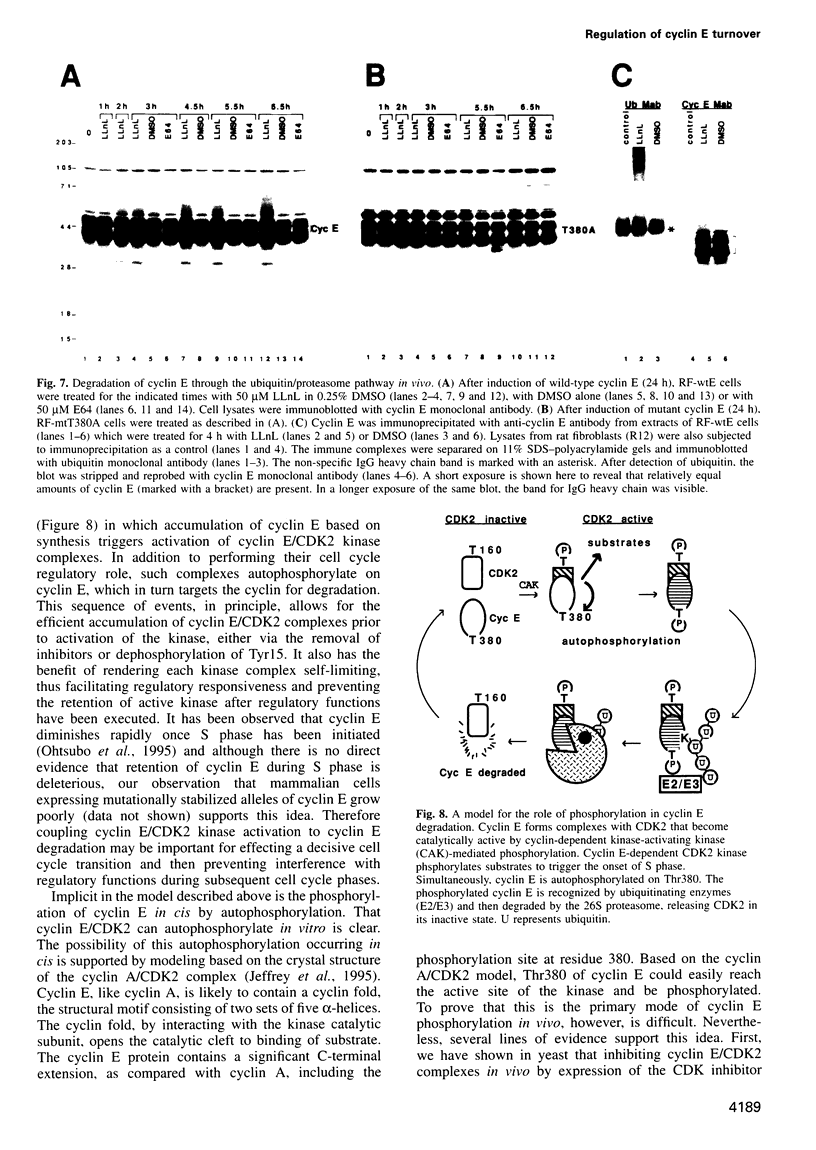
A yeast screen was developed to identify mutations in human cyclin E that lead to stabilization of the protein in order to identify determinants important for cyclin E turnover. Both C-terminal truncations and missense mutations near the C-terminus of cyclin E conferred hyperstability in vivo, suggesting that sequences in this region were critical for turnover. The following observations indicate that autophosphorylation of CDK2/cyclin E on Thr380 of the cyclin regulates cyclin E destruction: (i) mutation of Thr380 to Ala stabilizes cyclin E in yeast and mammalian cells; (ii) cyclin E/CDK2 autophosphorylates on cyclin E in vitro and cyclin E is a phosphoprotein in vivo in mammalian cells; (iii) the T380A mutation eliminates phosphorylation on the same site in mammalian cells and in vitro; (iv) inhibiting CDK2 activity in vivo stabilizes cyclin E; (v) the T380A mutation prevents ubiquitination of cyclin E. These results suggest a model where activation of cyclinE/CDK2 is coupled to cyclin E turnover via site-specific phosphorylation, which acts as a signal for ubiquitination and proteasome processing.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajchenbaum F., Ando K., DeCaprio J. A., Griffin J. D. Independent regulation of human D-type cyclin gene expression during G1 phase in primary human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 25;268(6):4113–4119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockman J. A., Scherer D. C., McKinsey T. A., Hall S. M., Qi X., Lee W. Y., Ballard D. W. Coupling of a signal response domain in I kappa B alpha to multiple pathways for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2809–2818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K., Gerstberger S., Carlson L., Franzoso G., Siebenlist U. Control of I kappa B-alpha proteolysis by site-specific, signal-induced phosphorylation. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1485–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.7878466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley M. F., Sweeney K. J., Hamilton J. A., Sini R. L., Manning D. L., Nicholson R. I., deFazio A., Watts C. K., Musgrove E. A., Sutherland R. L. Expression and amplification of cyclin genes in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 1993 Aug;8(8):2127–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau V., Tobias J. W., Bachmair A., Marriott D., Ecker D. J., Gonda D. K., Varshavsky A. A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1576–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.2538923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Hagler J., Palombella V. J., Melandri F., Scherer D., Ballard D., Maniatis T. Signal-induced site-specific phosphorylation targets I kappa B alpha to the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Genes Dev. 1995 Jul 1;9(13):1586–1597. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.13.1586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole G. M., Stone D. E., Reed S. I. Stoichiometry of G protein subunits affects the Saccharomyces cerevisiae mating pheromone signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):510–517. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Blake C. M. The yeast Cln3 protein is an unstable activator of Cdc28. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3266–3271. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshaies R. J., Chau V., Kirschner M. Ubiquitination of the G1 cyclin Cln2p by a Cdc34p-dependent pathway. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 16;14(2):303–312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Kaufmann W. K., Wilson S. J., Tlsty T. D., Lees E., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Reed S. I. p53-dependent inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase activities in human fibroblasts during radiation-induced G1 arrest. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1013–1023. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulić V., Lees E., Reed S. I. Association of human cyclin E with a periodic G1-S phase protein kinase. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1958–1961. doi: 10.1126/science.1329201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossen M., Bujard H. Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5547–5551. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengst L., Reed S. I. Translational control of p27Kip1 accumulation during the cell cycle. Science. 1996 Mar 29;271(5257):1861–1864. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5257.1861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:761–807. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.003553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser M. Ubiquitin, proteasomes, and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;7(2):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80031-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. D., Russo A. A., Polyak K., Gibbs E., Hurwitz J., Massagué J., Pavletich N. P. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):313–320. doi: 10.1038/376313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., Schlenker S. Selective protein degradation: a journey's end within the proteasome. Cell. 1995 Sep 22;82(6):881–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S. The ubiquitin-conjugation system. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:179–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyomarsi K., Conte D., Jr, Toyofuku W., Fox M. P. Deregulation of cyclin E in breast cancer. Oncogene. 1995 Sep 7;11(5):941–950. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keyomarsi K., Pardee A. B. Redundant cyclin overexpression and gene amplification in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. W., Jackson P. K., Kirschner M. W. Mitosis in transition. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):563–571. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90542-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koff A., Giordano A., Desai D., Yamashita K., Harper J. W., Elledge S., Nishimoto T., Morgan D. O., Franza B. R., Roberts J. M. Formation and activation of a cyclin E-cdk2 complex during the G1 phase of the human cell cycle. Science. 1992 Sep 18;257(5077):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.1388288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanker S., Valdivieso M. H., Wittenberg C. Rapid degradation of the G1 cyclin Cln2 induced by CDK-dependent phosphorylation. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1597–1601. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew D. J., Dulić V., Reed S. I. Isolation of three novel human cyclins by rescue of G1 cyclin (Cln) function in yeast. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1197–1206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90042-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo K. X., Hurley T. R., Sefton B. M. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and proteolytic peptide mapping of proteins immobilized to membranes. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:149–152. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01014-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Roussel M. F., Ashmun R. A., Sherr C. J. Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):701–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. Cyclin ubiquitination: the destructive end of mitosis. Cell. 1995 Apr 21;81(2):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Control of the yeast cell cycle by the Cdc28 protein kinase. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):166–179. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90099-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya-Tsuji J., Nomoto S., Yasuda H., Reed S. I., Matsumoto K. Cloning of a human cDNA encoding a CDC2-related kinase by complementation of a budding yeast cdc28 mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9006–9010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Roberts J. M. Cyclin-dependent regulation of G1 in mammalian fibroblasts. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1908–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.8384376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Theodoras A. M., Schumacher J., Roberts J. M., Pagano M. Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2612–2624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombella V. J., Rando O. J., Goldberg A. L., Maniatis T. The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway is required for processing the NF-kappa B1 precursor protein and the activation of NF-kappa B. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):773–785. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90482-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polyak K., Lee M. H., Erdjument-Bromage H., Koff A., Roberts J. M., Tempst P., Massagué J. Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90572-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I. The role of p34 kinases in the G1 to S-phase transition. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:529–561. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Gossen M., Bujard H., Reed S. I. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1669–1679. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson H. E., Wittenberg C., Cross F., Reed S. I. An essential G1 function for cyclin-like proteins in yeast. Cell. 1989 Dec 22;59(6):1127–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90768-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock K. L., Gramm C., Rothstein L., Clark K., Stein R., Dick L., Hwang D., Goldberg A. L. Inhibitors of the proteasome block the degradation of most cell proteins and the generation of peptides presented on MHC class I molecules. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):761–771. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90462-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers S., Wells R., Rechsteiner M. Amino acid sequences common to rapidly degraded proteins: the PEST hypothesis. Science. 1986 Oct 17;234(4774):364–368. doi: 10.1126/science.2876518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. M., Finley D. Proteolysis. The proteasome: a protein-degrading organelle? Curr Biol. 1995 Aug 1;5(8):854–858. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00172-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Kishi M., Saito M., Tanaka T., Higuchi N., Kominami E., Katunuma N., Murachi T. Inhibitory effect of di- and tripeptidyl aldehydes on calpains and cathepsins. J Enzyme Inhib. 1990;3(3):195–201. doi: 10.3109/14756369009035837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D., Brake A. J., Kiefer M. C., Young D., Barr P. J. Cloning of three human multifunctional de novo purine biosynthetic genes by functional complementation of yeast mutations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):2916–2920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.2916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Futcher B., Jentsch S. Role of a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme in degradation of S- and M-phase cyclins. Nature. 1995 Jan 5;373(6509):78–81. doi: 10.1038/373078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slingerland J. M., Hengst L., Pan C. H., Alexander D., Stampfer M. R., Reed S. I. A novel inhibitor of cyclin-Cdk activity detected in transforming growth factor beta-arrested epithelial cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):3683–3694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueland C. S., Lew D. J., Cismowski M. J., Reed S. I. Full activation of p34CDC28 histone H1 kinase activity is unable to promote entry into mitosis in checkpoint-arrested cells of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3744–3755. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Tamura T., Yoshimura T., Ichihara A. Proteasomes: protein and gene structures. New Biol. 1992 Mar;4(3):173–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima H., Hunter T. p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):67–74. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90573-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Stevenson J. K., Schwarz E. M., Van Antwerp D., Miyamoto S. Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 15;9(22):2723–2735. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.22.2723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinitsky A., Michaud C., Powers J. C., Orlowski M. Inhibition of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the pituitary multicatalytic proteinase complex. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 6;31(39):9421–9428. doi: 10.1021/bi00154a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside S. T., Ernst M. K., LeBail O., Laurent-Winter C., Rice N., Israël A. N- and C-terminal sequences control degradation of MAD3/I kappa B alpha in response to inducers of NF-kappa B activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;15(10):5339–5345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.10.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmel A., Lucibello F. C., Sewing A., Adolph S., Müller R. Inducible acceleration of G1 progression through tetracycline-regulated expression of human cyclin E. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):995–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaglom J., Linskens M. H., Sadis S., Rubin D. M., Futcher B., Finley D. p34Cdc28-mediated control of Cln3 cyclin degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):731–741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]