Abstract
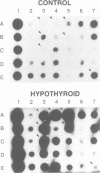
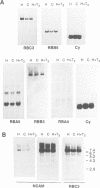
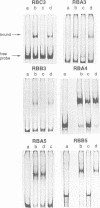
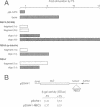
Thyroid hormone (T3) is a main regulator of brain development acting as a transcriptional modulator. However, only a few T3-regulated brain genes are known. Using an improved whole genome PCR approach, we have isolated seven clones encoding sequences expressed in neonatal rat brain which are under the transcriptional control of T3. Six of them, including the neural cell adhesion molecule NCAM, alpha-tubulin and four other unidentified sequences (RBA3, RBA4, RBB3 and RBB5) were found to be upregulated in the hypothyroid brain, whereas another (RBE7) was downregulated. Binding sites for the T3 receptor (T3R/c-erbA) were identified in the isolated clones by gel-shift and footprinting assays. Sites in the NCAM (in an intron), alpha-tubulin (in an exon) and RBA4 clones mediated transcriptional regulation by T3 when inserted upstream of a reporter construct. However, no effect of the NCAM clone was found when located downstream of another reporter gene. Northern blotting and in situ hybridization studies showed a higher expression of NCAM in the brain of postnatal hypothyroid rats. Since NCAM is an important morphoregulatory molecule, abnormal NCAM expression is likely to contribute to the alterations present in the brain of thyroid-deficient humans and experimental animals.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvarez-Dolado M., Iglesias T., Rodríguez-Peña A., Bernal J., Muñoz A. Expression of neurotrophins and the trk family of neurotrophin receptors in normal and hypothyroid rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1994 Dec;27(2):249–257. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(94)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aniello F., Couchie D., Gripois D., Nunez J. Regulation of five tubulin isotypes by thyroid hormone during brain development. J Neurochem. 1991 Nov;57(5):1781–1786. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb06381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atashi J. R., Klinz S. G., Ingraham C. A., Matten W. T., Schachner M., Maness P. F. Neural cell adhesion molecules modulate tyrosine phosphorylation of tubulin in nerve growth cone membranes. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):831–842. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90197-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baniahmad A., Ha I., Reinberg D., Tsai S., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Interaction of human thyroid hormone receptor beta with transcription factor TFIIB may mediate target gene derepression and activation by thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8832–8836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker C. G., Becker T., Schmidt A., Roth G. Polysialic acid expression in the salamander retina is inducible by thyroxine. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1994 May 13;79(1):140–146. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler J., Eisenman R. N. Isolation of a thyroid hormone-responsive gene by immunoprecipitation of thyroid hormone receptor-DNA complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7621–7632. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bigler J., Eisenman R. N. Novel location and function of a thyroid hormone response element. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 15;14(22):5710–5723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. J., Young W. S., 3rd, Weinberger C. Differential expression of alpha and beta thyroid hormone receptor genes in rat brain and pituitary. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7250–7254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caubín J., Iglesias T., Bernal J., Muñoz A., Márquez G., Barbero J. L., Zaballos A. Isolation of genomic DNA fragments corresponding to genes modulated in vivo by a transcription factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Oct 11;22(20):4132–4138. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.20.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Evans R. M. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):454–457. doi: 10.1038/377454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clos J., Legrand C. An interaction between thyroid hormone and nerve growth factor promotes the development of hippocampus, olfactory bulbs and cerebellum: a comparative biochemical study of normal and hypothyroid rats. Growth Factors. 1990;3(3):205–220. doi: 10.3109/08977199009043905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa-Giomi M. P., Gaub M. P., Chambon P., Abarzúa P. Characterization of a retinoic acid responsive element isolated by whole genome PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3223–3232. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A. Cell adhesion molecules as morphoregulators. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;7(5):628–633. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80103-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dussault J. H., Ruel J. Thyroid hormones and brain development. Annu Rev Physiol. 1987;49:321–334. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.49.030187.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M., Crossin K. L. Cell adhesion molecules: implications for a molecular histology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:155–190. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farsetti A., Mitsuhashi T., Desvergne B., Robbins J., Nikodem V. M. Molecular basis of thyroid hormone regulation of myelin basic protein gene expression in rodent brain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 5;266(34):23226–23232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo B. C., Almazan G., Ma Y., Tetzlaff W., Miller F. D., Cuello A. C. Gene expression in the developing cerebellum during perinatal hypo- and hyperthyroidism. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Mar;17(3-4):258–268. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90010-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figueiredo B. C., Otten U., Strauss S., Volk B., Maysinger D. Effects of perinatal hypo- and hyperthyroidism on the levels of nerve growth factor and its low-affinity receptor in cerebellum. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1993 Apr 16;72(2):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(93)90188-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fondell J. D., Roy A. L., Roeder R. G. Unliganded thyroid hormone receptor inhibits formation of a functional preinitiation complex: implications for active repression. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1400–1410. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D., Hallbök F., Persson H., Vennström B. Distinct functions for thyroid hormone receptors alpha and beta in brain development indicated by differential expression of receptor genes. EMBO J. 1991 Feb;10(2):269–275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07947.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest D. The erbA/thyroid hormone receptor genes in development of the central nervous system. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994 Apr;5(2):167–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- García-Fernández L. F., Iñiguez M. A., Rodríguez-Peña A., Muñoz A., Bernal J. Brain-specific prostaglandin D2 synthetase mRNA is dependent on thyroid hormone during rat brain development. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Oct 15;196(1):396–401. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegelashvili G., Andersson A. M., Schousboe A., Bock E. Cyclic AMP regulates NCAM expression and phosphorylation in cultured mouse astrocytes. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;62(2):343–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gennarini G., Hirsch M. R., He H. T., Hirn M., Finne J., Goridis C. Differential expression of mouse neural cell-adhesion molecule (N-CAM) mRNA species during brain development and in neural cell lines. J Neurosci. 1986 Jul;6(7):1983–1990. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-07-01983.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goridis C., Brunet J. F. NCAM: structural diversity, function and regulation of expression. Semin Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;3(3):189–197. doi: 10.1016/s1043-4682(10)80015-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goridis C., Hirn M., Santoni M. J., Gennarini G., Deagostini-Bazin H., Jordan B. R., Kiefer M., Steinmetz M. Isolation of mouse N-CAM-related cDNA: detection and cloning using monoclonal antibodies. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):631–635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03676.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husmann M., Görgen I., Weisgerber C., Bitter-Suermann D. Up-regulation of embryonic NCAM in an EC cell line by retinoic acid. Dev Biol. 1989 Nov;136(1):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörlein A. J., När A. M., Heinzel T., Torchia J., Gloss B., Kurokawa R., Ryan A., Kamei Y., Söderström M., Glass C. K. Ligand-independent repression by the thyroid hormone receptor mediated by a nuclear receptor co-repressor. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):397–404. doi: 10.1038/377397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iglesias T., Caubín J., Zaballos A., Bernal J., Muñoz A. Identification of the mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 (ND3) as a thyroid hormone regulated gene by whole genome PCR analysis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 May 25;210(3):995–1000. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1755. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iniguez M. A., De Lecea L., Guadano-Ferraz A., Morte B., Gerendasy D., Sutcliffe J. G., Bernal J. Cell-specific effects of thyroid hormone on RC3/neurogranin expression in rat brain. Endocrinology. 1996 Mar;137(3):1032–1041. doi: 10.1210/endo.137.3.8603571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue S., Kondo S., Hashimoto M., Kondo T., Muramatsu M. Isolation of estrogen receptor-binding sites in human genomic DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 11;19(15):4091–4096. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.15.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñiguez M. A., Rodriguez-Peña A., Ibarrola N., Aguilera M., Muñoz A., Bernal J. Thyroid hormone regulation of RC3, a brain-specific gene encoding a protein kinase-C substrate. Endocrinology. 1993 Aug;133(2):467–473. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.2.8344193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iñiguez M. A., Rodriguez-Peña A., Ibarrola N., Morreale de Escobar G., Bernal J. Adult rat brain is sensitive to thyroid hormone. Regulation of RC3/neurogranin mRNA. J Clin Invest. 1992 Aug;90(2):554–558. doi: 10.1172/JCI115894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Sasaki H., Suzawa M., Masushige S., Tora L., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Widely spaced, directly repeated PuGGTCA elements act as promiscuous enhancers for different classes of nuclear receptors. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;15(11):5858–5867. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.11.5858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Whole genome PCR: application to the identification of sequences bound by gene regulatory proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 25;17(10):3645–3653. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.10.3645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A. Thyroid hormone receptors: multiple forms, multiple possibilities. Endocr Rev. 1993 Apr;14(2):184–193. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-2-184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. W., Ryan F., Swaffield J. C., Johnston S. A., Moore D. D. Interaction of thyroid-hormone receptor with a conserved transcriptional mediator. Nature. 1995 Mar 2;374(6517):91–94. doi: 10.1038/374091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J. L., Kaplan M. M., Visser T. J., Silva J. E., Larsen P. R. Cerebral cortex responds rapidly to thyroid hormones. Science. 1981 Oct 30;214(4520):571–573. doi: 10.1126/science.7291997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi G., Broders F., Dunon D., Edelman G. M., Thiery J. P. Thyroxine-dependent modulations of the expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM during Xenopus laevis metamorphosis. Development. 1990 Apr;108(4):681–692. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.4.681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm D., Castrén E., Tsoulfas P., Kolbeck R., Berzaghi M. da P., Leingärtner A., Heisenberg C. P., Tessarollo L., Parada L. F., Thoenen H. Neurotrophin-3 induced by tri-iodothyronine in cerebellar granule cells promotes Purkinje cell differentiation. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(2):443–450. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.2.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linial M., Gunderson N., Groudine M. Enhanced transcription of c-myc in bursal lymphoma cells requires continuous protein synthesis. Science. 1985 Dec 6;230(4730):1126–1132. doi: 10.1126/science.2999973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellström B., Naranjo J. R., Santos A., Gonzalez A. M., Bernal J. Independent expression of the alpha and beta c-erbA genes in developing rat brain. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Sep;5(9):1339–1350. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-9-1339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller P. D., Chung W. W., Lagenaur C. F., DeKosky S. T. Regional distribution of neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) and L1 in human and rodent hippocampus. J Comp Neurol. 1993 Jan 15;327(3):341–349. doi: 10.1002/cne.903270303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montag D., Giese K. P., Bartsch U., Martini R., Lang Y., Blüthmann H., Karthigasan J., Kirschner D. A., Wintergerst E. S., Nave K. A. Mice deficient for the myelin-associated glycoprotein show subtle abnormalities in myelin. Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):229–246. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90472-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz A., Rodriguez-Peña A., Perez-Castillo A., Ferreiro B., Sutcliffe J. G., Bernal J. Effects of neonatal hypothyroidism on rat brain gene expression. Mol Endocrinol. 1991 Feb;5(2):273–280. doi: 10.1210/mend-5-2-273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Kypta R. Molecular genetics of neuronal adhesion. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Feb;5(1):36–41. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Näthke I. S., Hinck L. E., Nelson W. J. Epithelial cell adhesion and development of cell surface polarity: possible mechanisms for modulation of cadherin function, organization and distribution. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:139–145. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens G. C., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Organization of the neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) gene: alternative exon usage as the basis for different membrane-associated domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):294–298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perez-Castillo A., Bernal J., Ferreiro B., Pans T. The early ontogenesis of thyroid hormone receptor in the rat fetus. Endocrinology. 1985 Dec;117(6):2457–2461. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-6-2457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipaon C., Santos A., Perez-Castillo A. Thyroid hormone up-regulates NGFI-A gene expression in rat brain during development. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):21–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porterfield S. P., Hendrich C. E. The role of thyroid hormones in prenatal and neonatal neurological development--current perspectives. Endocr Rev. 1993 Feb;14(1):94–106. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-1-94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabié A., Patel A. J., Clavel M. C., Legrand J. Effect of thyroid deficiency on the growth of the hippocampus in the rat. A combined biochemical and morphological study. Dev Neurosci. 1979;2(4):183–194. doi: 10.1159/000112453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes A. A., Schulte S. V., Small S., Akeson R. Distinct NCAM splicing events are differentially regulated during rat brain development. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 1993 Mar;17(3-4):201–211. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(93)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez-Peña A., Ibarrola N., Iñiguez M. A., Muñoz A., Bernal J. Neonatal hypothyroidism affects the timely expression of myelin-associated glycoprotein in the rat brain. J Clin Invest. 1993 Mar;91(3):812–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI116301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosales C., O'Brien V., Kornberg L., Juliano R. Signal transduction by cell adhesion receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Jul 28;1242(1):77–98. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(95)00005-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudert F., Gronemeyer H. Retinoic acid-response elements with a highly repetitive structure isolated by immuno-selection from genomic DNA. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1993 Aug;46(2):121–133. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(93)90287-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutishauser U. Adhesion molecules of the nervous system. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1993 Oct;3(5):709–715. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(93)90142-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Stanley F., Casanova J. Depletion of L-3,5,3'-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine in euthyroid calf serum for use in cell culture studies of the action of thyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):80–85. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandaltzopoulos R., Becker P. B. Solid phase DNase I footprinting: quick and versatile. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1511–1512. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Schmitt J., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. Repression of transcription mediated at a thyroid hormone response element by the v-erb-A oncogene product. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):242–244. doi: 10.1038/340242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., de Magistris L., Stunnenberg H., Vennström B. A major thyroid hormone response element in the third intron of the rat growth hormone gene. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):887–896. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08186.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seelig S., Liaw C., Towle H. C., Oppenheimer J. H. Thyroid hormone attenuates and augments hepatic gene expression at a pretranslational level. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4733–4737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small S. J., Shull G. E., Santoni M. J., Akeson R. Identification of a cDNA clone that contains the complete coding sequence for a 140-kD rat NCAM polypeptide. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2335–2345. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Moore S. E., Walsh F. S. Thyroid hormones regulate expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule in adult skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jul 13;219(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosic M., Torch S., Comte V., Dolivo M., Honegger P., Matthieu J. M. Triiodothyronine has diverse and multiple stimulating effects on expression of the major myelin protein genes. J Neurochem. 1992 Nov;59(5):1770–1777. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb11009.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valcárcel R., Holz H., Jiménez C. G., Barettino D., Stunnenberg H. G. Retinoid-dependent in vitro transcription mediated by the RXR/RAR heterodimer. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):3068–3079. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Núez E., Menéndez-Hurtado A., Garesse R., Santos A., Perez-Castillo A. Thyroid hormone-regulated brain mitochondrial genes revealed by differential cDNA cloning. J Clin Invest. 1995 Aug;96(2):893–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI118136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W., Brooks R. L., Silversides D. W., West B. L., Leidig F., Baxter J. D., Eberhardt N. L. Negative thyroid hormone control of human growth hormone gene expression is mediated by 3'-untranslated/3'-flanking DNA. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15056–15063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou L., Hagen S. G., Strait K. A., Oppenheimer J. H. Identification of thyroid hormone response elements in rodent Pcp-2, a developmentally regulated gene of cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13346–13352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]