Abstract
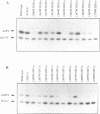
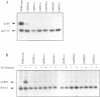
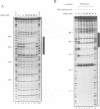
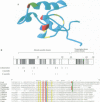
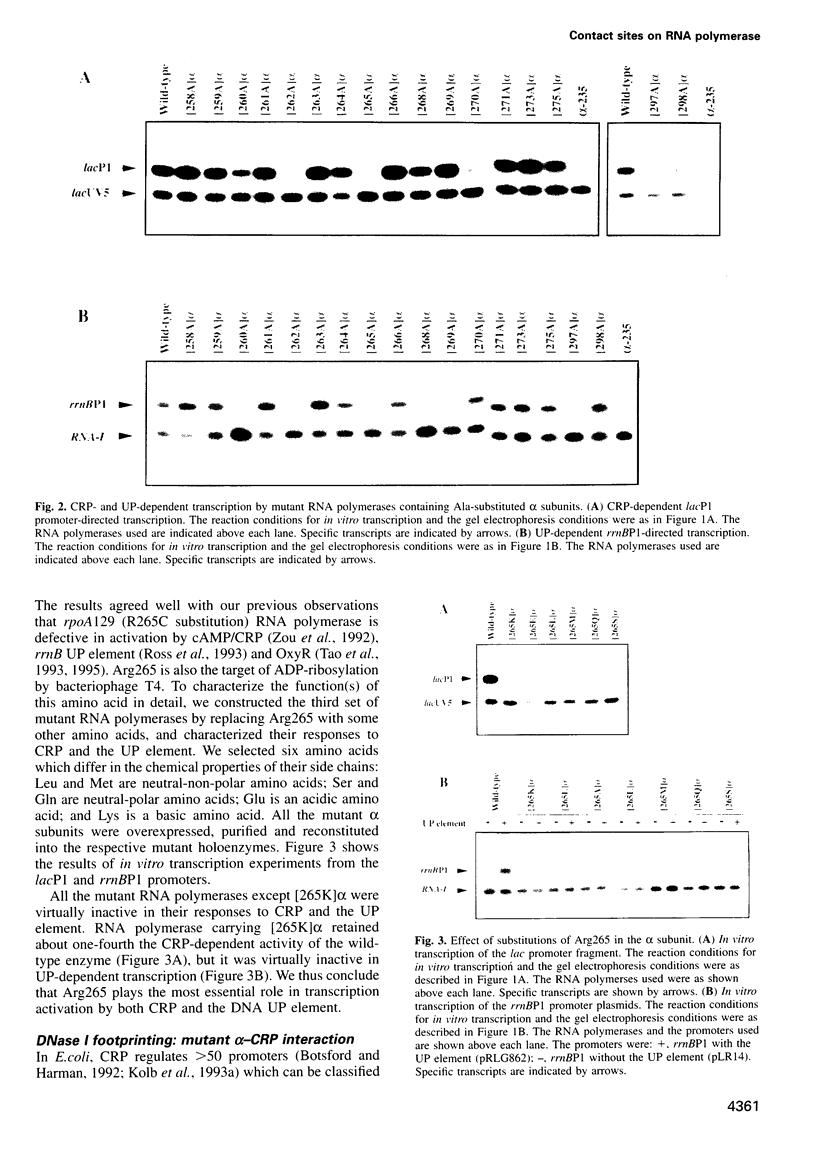
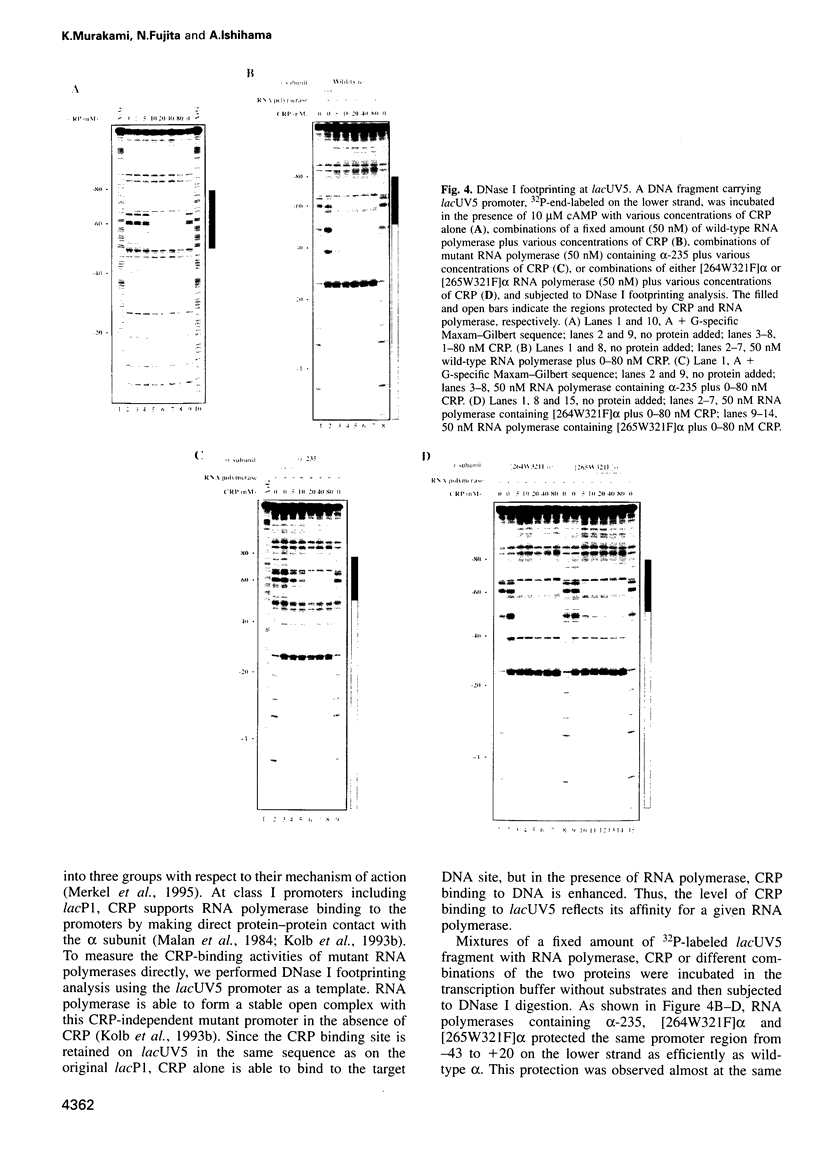
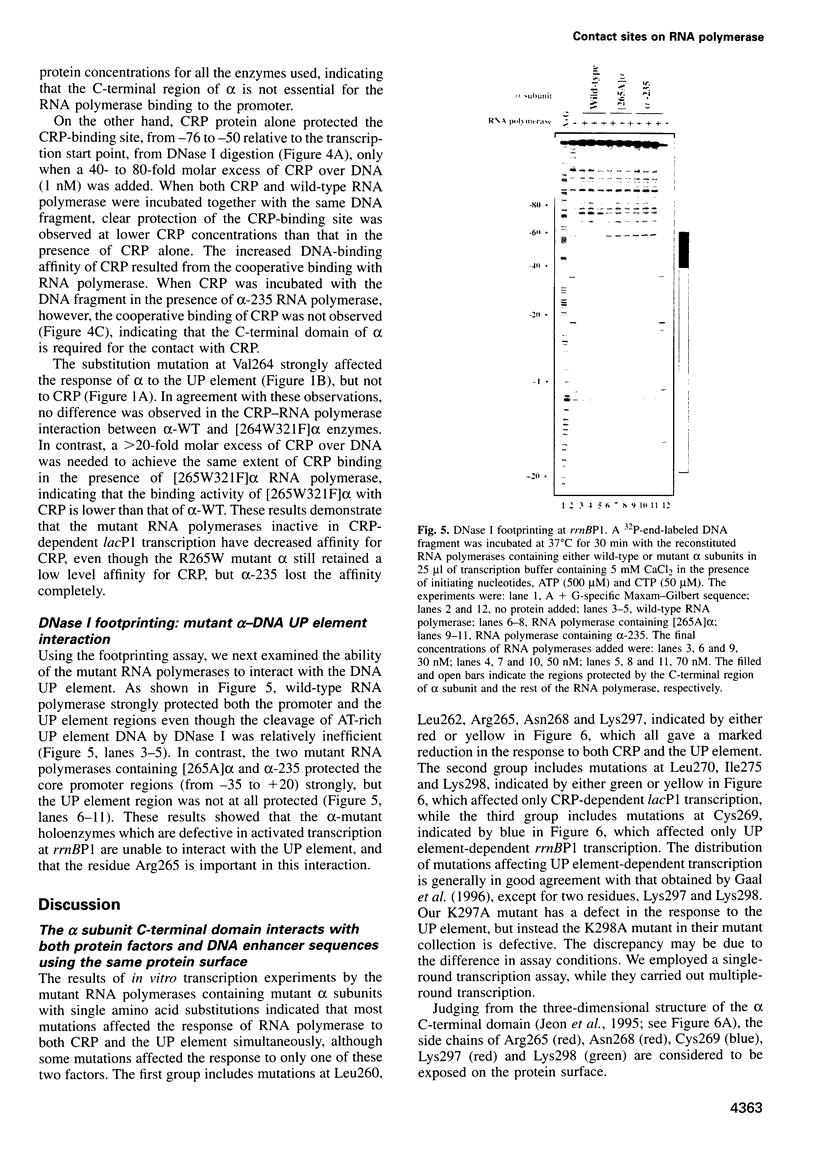
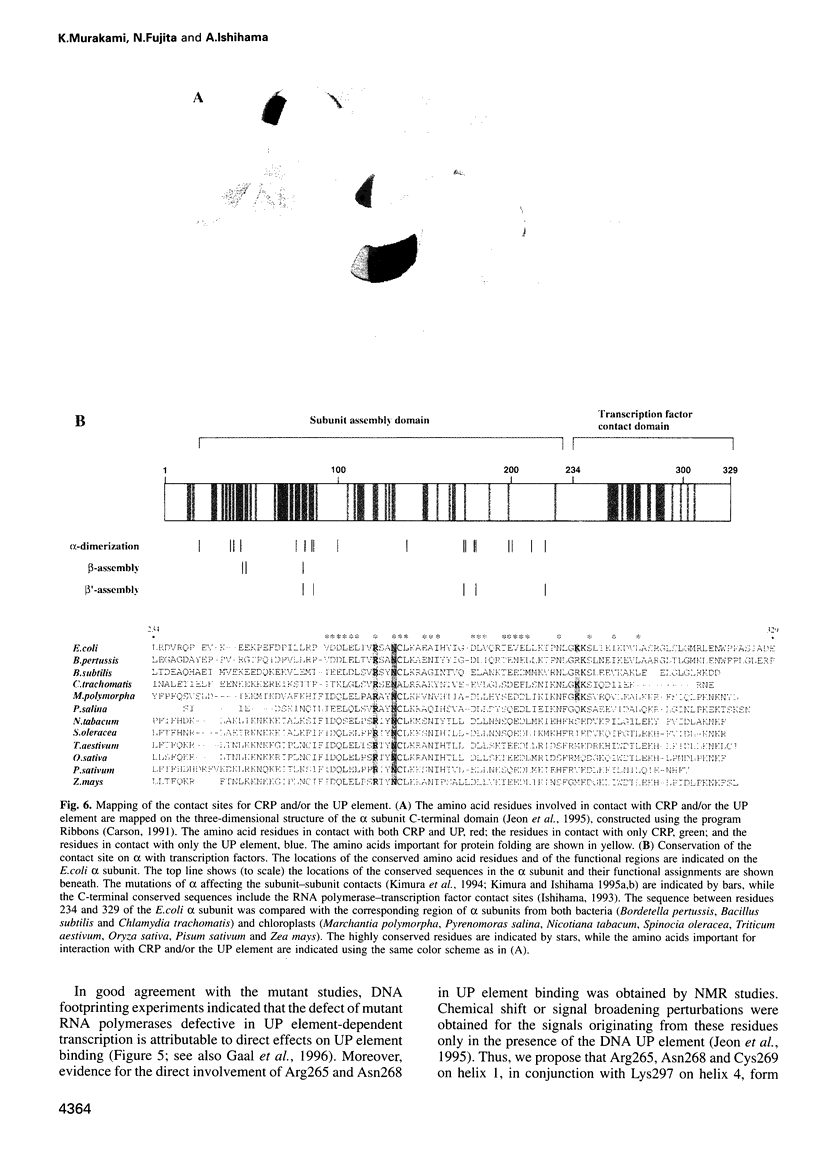
The carboxy-terminal one-third of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit plays a key role in transcription regulation by a group of protein transcription factors and DNA enhancer (UP) elements. The roles of individual amino acid residues within this regulatory domain of the alpha subunit were examined after systematic mutagenesis of the putative contact regions (residues 258-275 and 297-298) for the cAMP receptor protein (CRP). The reconstituted RNA polymerases containing the mutant alpha subunits were examined for their response to transcription activation by cAMP-CRP and the rrnBP1 UP element. Mutations affecting CRP responsiveness were located on the surface of the putative CRP contact helix and most of these mutations also influenced the response to the rrnB UP element. These observations raise the possibility that the CRP contact surface is also involved in contact with the DNA UP element, although some amino acid residues within this region play different roles in molecular communication with CRP and the UP element. Among the amino acid residues constituting the contact surface, Arg265 was found to play a major role in response to both CRP and the DNA UP element. Judged by DNase I footprinting analysis, alpha mutants defective in transcription from the CRP-dependent lacP1 promoter showed decreased activity in the cooperative binding of CRP. Likewise, mutants defective in rrnBP1 transcription showed decreased binding to the UP element. The amino acid residues important for contact with both CRP and DNA are conserved in the alpha subunits of not only bacterial, but also chloroplast RNA polymerases.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Botsford J. L., Harman J. G. Cyclic AMP in prokaryotes. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):100–122. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.100-122.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choy H. E., Park S. W., Aki T., Parrack P., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Adhya S. Repression and activation of transcription by Gal and Lac repressors: involvement of alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 1995 Sep 15;14(18):4523–4529. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00131.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. C., Wells J. A. High-resolution epitope mapping of hGH-receptor interactions by alanine-scanning mutagenesis. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1081–1085. doi: 10.1126/science.2471267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal T., Ross W., Blatter E. E., Tang H., Jia X., Krishnan V. V., Assa-Munt N., Ebright R. H., Gourse R. L. DNA-binding determinants of the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase: novel DNA-binding domain architecture. Genes Dev. 1996 Jan 1;10(1):16–26. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.1.16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward R. S., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Functional specialization within the alpha-subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80197-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Identification of a subunit assembly domain in the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 5;218(1):1–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Hanamura A., Makino K., Aiba H., Aiba H., Mizuno T., Nakata A., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: two modes of transcription activation by positive factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8958–8962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Protein-protein communication within the transcription apparatus. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2483-2489.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Role of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit in transcription activation. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Nov;6(22):3283–3288. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Subunit of assembly of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Adv Biophys. 1981;14:1–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeon Y. H., Negishi T., Shirakawa M., Yamazaki T., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Kyogoku Y. Solution structure of the activator contact domain of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1495–1497. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajitani M., Ishihama A. Determination of the promoter strength in the mixed transcription system. II. Promoters of ribosomal RNA, ribosomal protein S1 and recA protein operons from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 25;11(12):3873–3888. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.12.3873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajitani M., Ishihama A. Determination of the promoter strength in the mixed transcription system: promoters of lactose, tryptophan and ribosomal protein L10 operons from Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):671–686. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Deletion analysis of the amino-terminal assembly domain. J Mol Biol. 1994 Sep 16;242(2):107–115. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: amino acid substitution within the amino-terminal assembly domain. J Mol Biol. 1995 Dec 1;254(3):342–349. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Ishihama A. Functional map of the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase: insertion analysis of the amino-terminal assembly domain. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 12;248(4):756–767. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Buc H., Garges S., Adhya S. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:749–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Lavigne M., Buckle M., Buc H. E. coli RNA polymerase, deleted in the C-terminal part of its alpha-subunit, interacts differently with the cAMP-CRP complex at the lacP1 and at the galP1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Bebenek K., McClary J. Efficient site-directed mutagenesis using uracil-containing DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1991;204:125–139. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)04008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merkel T. J., Dahl J. L., Ebright R. H., Kadner R. J. Transcription activation at the Escherichia coli uhpT promoter by the catabolite gene activator protein. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(7):1712–1718. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.7.1712-1718.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagami H., Aiba H. Role of CRP in transcription activation at Escherichia coli lac promoter: CRP is dispensable after the formation of open complex. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Feb 25;23(4):599–605. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.4.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang H., Severinov K., Goldfarb A., Fenyo D., Chait B., Ebright R. H. Location, structure, and function of the target of a transcriptional activator protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):3058–3067. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.3058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao K., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Involvement of the RNA polymerase alpha subunit C-terminal region in co-operative interaction and transcriptional activation with OxyR protein. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):859–864. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao K., Zou C., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Mapping of the OxyR protein contact site in the C-terminal region of RNA polymerase alpha subunit. J Bacteriol. 1995 Dec;177(23):6740–6744. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.23.6740-6744.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou C., Fujita N., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Mapping the cAMP receptor protein contact site on the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2599–2605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]