Abstract
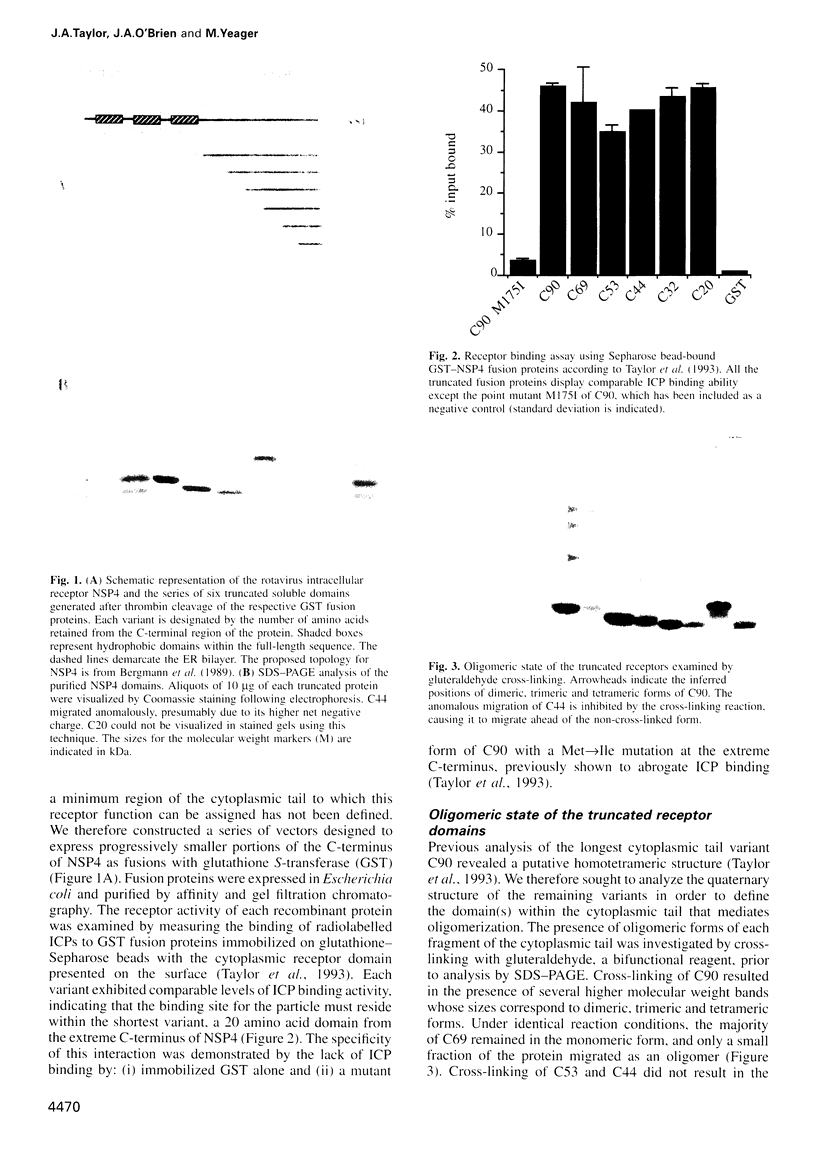
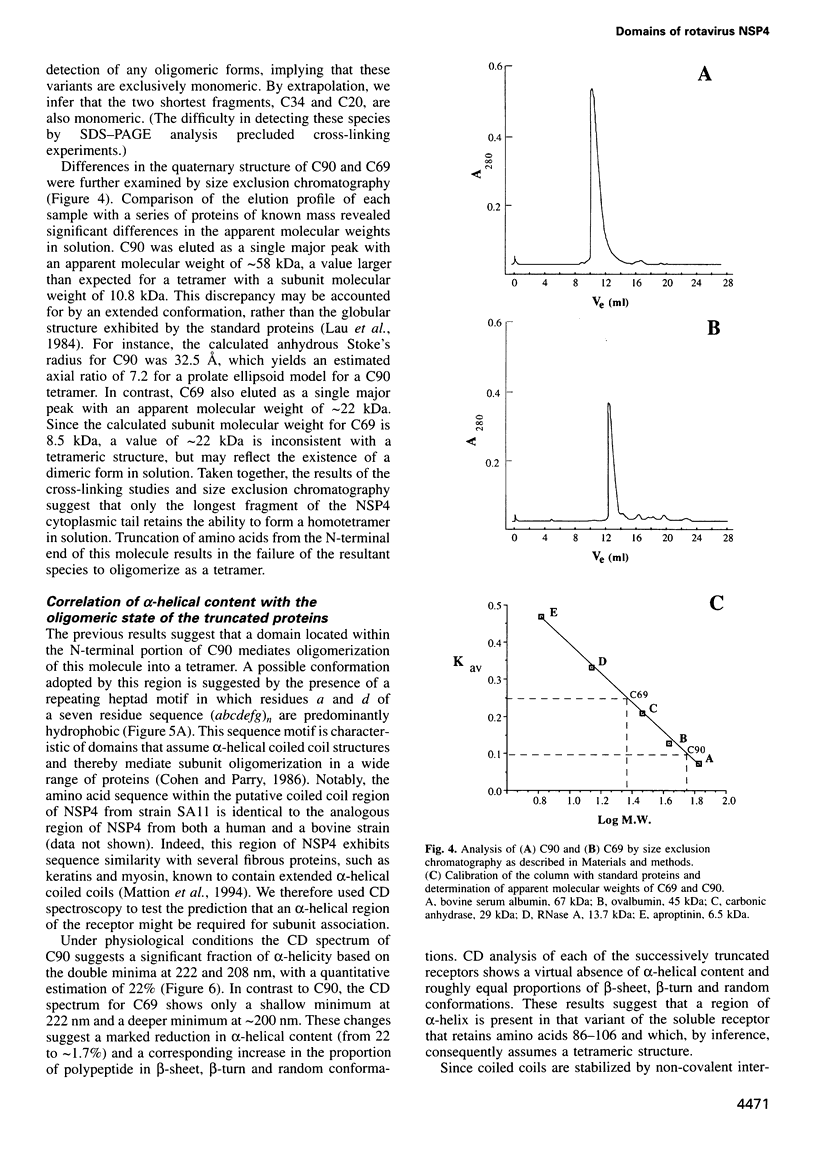
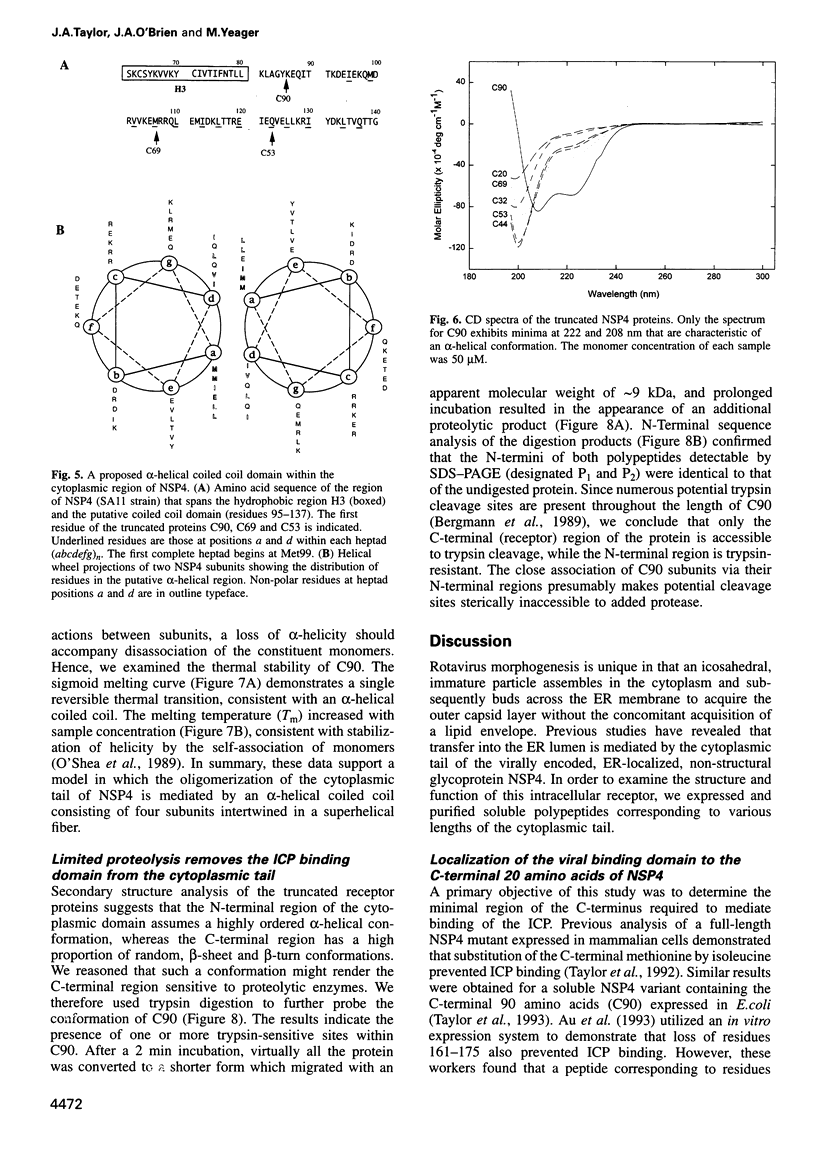
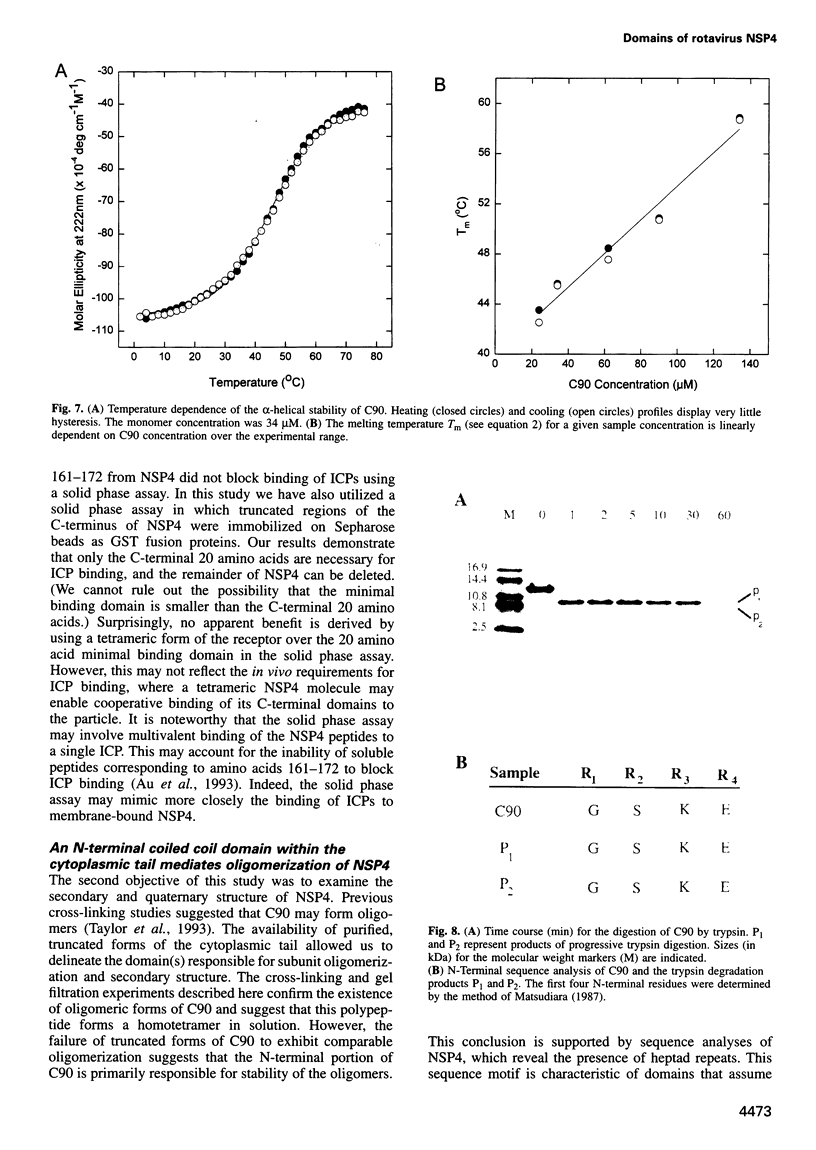
The final steps in the assembly of rotavirus occur in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Targeting of the immature inner capsid particle (ICP) to this compartment is mediated by the cytoplasmic tail of NSP4, a non-structural virus glycoprotein located in the ER membrane. To delineate structural and functional features of NSP4, soluble fragments of the cytoplasmic tail have been expressed and purified. Our analysis combines a functional assay for ICP binding with biochemical and CD spectroscopic studies to examine the secondary and quaternary structure. The ICP-binding domain is located within the C-terminal 20 amino acids of the polypeptide. A second region, distinct from this receptor domain, adopts an alpha-helical coiled coil structure and mediates the oligomerization of the virus binding domains into a homotetramer. The domain organization of the cytoplasmic fragments of NSP4 suggests a novel structure for an icosahedral virus receptor protein in which C-terminal binding sites for immature rotavirus particles are connected to an alpha-helical coiled coil stalk which projects from the ER membrane.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Au K. S., Chan W. K., Burns J. W., Estes M. K. Receptor activity of rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4553–4562. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4553-4562.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Au K. S., Mattion N. M., Estes M. K. A subviral particle binding domain on the rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NS28. Virology. 1993 Jun;194(2):665–673. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Both G. W. Molecular biology of rotaviruses. Adv Virus Res. 1990;38:1–43. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60858-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergmann C. C., Maass D., Poruchynsky M. S., Atkinson P. H., Bellamy A. R. Topology of the non-structural rotavirus receptor glycoprotein NS28 in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1695–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03561.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascio M., Gogol E., Wallace B. A. The secondary structure of gap junctions. Influence of isolation methods and proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):2358–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chambers T. J., Hahn C. S., Galler R., Rice C. M. Flavivirus genome organization, expression, and replication. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:649–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.003245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. T., Wu C. S., Yang J. T. Circular dichroic analysis of protein conformation: inclusion of the beta-turns. Anal Biochem. 1978 Nov;91(1):13–31. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90812-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbury P. B., Zhang T., Kim P. S., Alber T. A switch between two-, three-, and four-stranded coiled coils in GCN4 leucine zipper mutants. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1401–1407. doi: 10.1126/science.8248779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenicke R., Rudolph R. Refolding and association of oligomeric proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;131:218–250. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)31043-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau S. Y., Taneja A. K., Hodges R. S. Synthesis of a model protein of defined secondary and quaternary structure. Effect of chain length on the stabilization and formation of two-stranded alpha-helical coiled-coils. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13253–13261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maass D. R., Atkinson P. H. Rotavirus proteins VP7, NS28, and VP4 form oligomeric structures. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2632–2641. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2632-2641.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metsikkö K., Garoff H. Oligomers of the cytoplasmic domain of the p62/E2 membrane protein of Semliki Forest virus bind to the nucleocapsid in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):4678–4683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.4678-4683.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitra A. K., van Hoek A. N., Wiener M. C., Verkman A. S., Yeager M. The CHIP28 water channel visualized in ice by electron crystallography. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Sep;2(9):726–729. doi: 10.1038/nsb0995-726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Nakamura G. R., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D., Brands R. Intracellular assembly and packaging of hepatitis B surface antigen particles occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.884-892.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrie B. L., Estes M. K., Graham D. Y. Effects of tunicamycin on rotavirus morphogenesis and infectivity. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):270–274. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.270-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poruchynsky M. S., Maass D. R., Atkinson P. H. Calcium depletion blocks the maturation of rotavirus by altering the oligomerization of virus-encoded proteins in the ER. J Cell Biol. 1991 Aug;114(4):651–656. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.4.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabara M., Babiuk L. A., Gilchrist J., Misra V. Effect of tunicamycin on rotavirus assembly and infectivity. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1082–1090. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1082-1090.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Garoff H. The budding mechanisms of enveloped animal viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 Sep;50(1):1–21. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-50-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suomalainen M., Liljeström P., Garoff H. Spike protein-nucleocapsid interactions drive the budding of alphaviruses. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4737–4747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4737-4747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. A., Meyer J. C., Legge M. A., O'Brien J. A., Street J. E., Lord V. J., Bergmann C. C., Bellamy A. R. Transient expression and mutational analysis of the rotavirus intracellular receptor: the C-terminal methionine residue is essential for ligand binding. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3566–3572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3566-3572.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. A., O'Brien J. A., Lord V. J., Meyer J. C., Bellamy A. R. The RER-localized rotavirus intracellular receptor: a truncated purified soluble form is multivalent and binds virus particles. Virology. 1993 Jun;194(2):807–814. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tian P., Estes M. K., Hu Y., Ball J. M., Zeng C. Q., Schilling W. P. The rotavirus nonstructural glycoprotein NSP4 mobilizes Ca2+ from the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1995 Sep;69(9):5763–5772. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.9.5763-5772.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson I. A., Skehel J. J., Wiley D. C. Structure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3 A resolution. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):366–373. doi: 10.1038/289366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]