Abstract
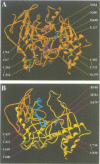
Neurotactin (Nrt), a Drosophila transmembrane glycoprotein which is expressed in neuronal and epithelial tissues during embryonic and larval stages, exhibits heterophilic adhesive properties. The extracellular domain is composed of a catalytically inactive cholinesterase-like domain. A three-dimensional model deduced from the crystal structure of Torpedo acetylcholinesterase (AChE) has been constructed for Nrt and suggests that its extracellular domain is composed of two sub-domains organized around a gorge: an N-terminal region, whose three-dimensional structure is almost identical to that of Torpedo AChE, and a less conserved C-terminal region. By using truncated Nrt molecules and a homotypic cell aggregation assay which involves a soluble ligand activity, it has been possible to show that the adhesive function is localized in the N-terminal region of the extracellular domain comprised between His347 and His482. The C-terminal region of the protein can be removed without impairing Nrt adhesive properties, suggesting that the two sub-domains are structurally independent. Chimeric molecules in which the Nrt cholinesterase-like domain has been replaced by homologous domains from Drosophila AChE, Torpedo AChE or Drosophila glutactin (Glt), share similar adhesive properties. These properties may require the presence of Nrt cytoplasmic and transmembrane domains since authentic Drosophila AChE does not behave as an adhesive molecule when transfected in S2 cells.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auld V. J., Fetter R. D., Broadie K., Goodman C. S. Gliotactin, a novel transmembrane protein on peripheral glia, is required to form the blood-nerve barrier in Drosophila. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90537-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axelsen P. H., Harel M., Silman I., Sussman J. L. Structure and dynamics of the active site gorge of acetylcholinesterase: synergistic use of molecular dynamics simulation and X-ray crystallography. Protein Sci. 1994 Feb;3(2):188–197. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
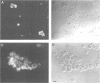
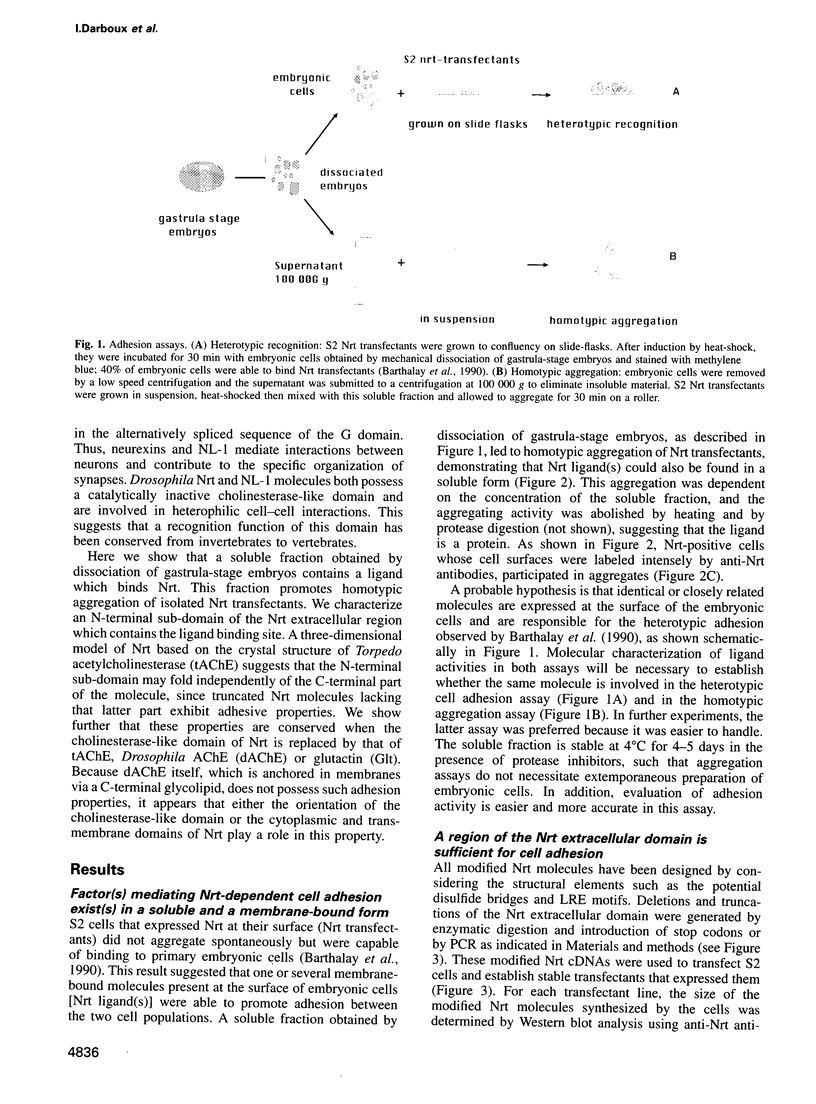
- Barthalay Y., Hipeau-Jacquotte R., de la Escalera S., Jiménez F., Piovant M. Drosophila neurotactin mediates heterophilic cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3603–3609. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07571.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne Y., Taylor P., Marchot P. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition by fasciculin: crystal structure of the complex. Cell. 1995 Nov 3;83(3):503–512. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cousin X., Hotelier T., Liévin P., Toutant J. P., Chatonnet A. A cholinesterase genes server (ESTHER): a database of cholinesterase-related sequences for multiple alignments, phylogenetic relationships, mutations and structural data retrieval. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Jan 1;24(1):132–136. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.1.132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cygler M., Schrag J. D., Sussman J. L., Harel M., Silman I., Gentry M. K., Doctor B. P. Relationship between sequence conservation and three-dimensional structure in a large family of esterases, lipases, and related proteins. Protein Sci. 1993 Mar;2(3):366–382. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Lauro R., Obici S., Condliffe D., Ursini V. M., Musti A., Moscatelli C., Avvedimento V. E. The sequence of 967 amino acids at the carboxyl-end of rat thyroglobulin. Location and surroundings of two thyroxine-forming sites. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Apr 1;148(1):7–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLMAN G. L., COURTNEY K. D., ANDRES V., Jr, FEATHER-STONE R. M. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961 Jul;7:88–95. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(61)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenningloh G., Bieber A. J., Rehm E. J., Snow P. M., Traquina Z. R., Hortsch M., Patel N. H., Goodman C. S. Molecular genetics of neuronal recognition in Drosophila: evolution and function of immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1990;55:327–340. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1990.055.01.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Spierer P. The Ace locus of Drosophila melanogaster: structural gene for acetylcholinesterase with an unusual 5' leader. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2949–2954. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04591.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hortsch M., Patel N. H., Bieber A. J., Traquina Z. R., Goodman C. S. Drosophila neurotactin, a surface glycoprotein with homology to serine esterases, is dynamically expressed during embryogenesis. Development. 1990 Dec;110(4):1327–1340. doi: 10.1242/dev.110.4.1327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichtchenko K., Hata Y., Nguyen T., Ullrich B., Missler M., Moomaw C., Südhof T. C. Neuroligin 1: a splice site-specific ligand for beta-neurexins. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90396-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen K. M., Fehon R. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The notch gene product is a glycoprotein expressed on the cell surface of both epidermal and neuronal precursor cells during Drosophila development. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2427–2440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokerst R. S., Weeks J. R., Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. Analysis of the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):266–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00339727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krantz D. E., Zipursky S. L. Drosophila chaoptin, a member of the leucine-rich repeat family, is a photoreceptor cell-specific adhesion molecule. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1969–1977. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08325.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krejci E., Duval N., Chatonnet A., Vincens P., Massoulié J. Cholinesterase-like domains in enzymes and structural proteins: functional and evolutionary relationships and identification of a catalytically essential aspartic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6647–6651. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson P. F., Fessler L. I., Nelson R. E., Sterne R. E., Campbell A. G., Fessler J. H. Glutactin, a novel Drosophila basement membrane-related glycoprotein with sequence similarity to serine esterases. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08229.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piovant M., Léna P. Membrane glycoproteins immunologically related to the human insulin receptor are associated with presumptive neuronal territories and developing neurones in Drosophila melanogaster. Development. 1988 May;103(1):145–156. doi: 10.1242/dev.103.1.145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider I. Cell lines derived from late embryonic stages of Drosophila melanogaster. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1972 Apr;27(2):353–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneuwly S., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Redesigning the body plan of Drosophila by ectopic expression of the homoeotic gene Antennapedia. 1987 Feb 26-Mar 4Nature. 325(6107):816–818. doi: 10.1038/325816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger M. A., Haffley L., Kaufman T. C. Characterization of amalgam: a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily from Drosophila. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):589–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Krejci E., Massoulié J. cDNA sequences of Torpedo marmorata acetylcholinesterase: primary structure of the precursor of a catalytic subunit; existence of multiple 5'-untranslated regions. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):1865–1873. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02445.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. L., Harel M., Frolow F., Oefner C., Goldman A., Toker L., Silman I. Atomic structure of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo californica: a prototypic acetylcholine-binding protein. Science. 1991 Aug 23;253(5022):872–879. doi: 10.1126/science.1678899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeichi M. Morphogenetic roles of classic cadherins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;7(5):619–627. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. D., Higgins D. G., Gibson T. J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Nov 11;22(22):4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thummel C. S., Boulet A. M., Lipshitz H. D. Vectors for Drosophila P-element-mediated transformation and tissue culture transfection. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):445–456. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toutant J. P., Arpagaus M., Fournier D. Native molecular forms of head acetylcholinesterase from adult Drosophila melanogaster: quaternary structure and hydrophobic character. J Neurochem. 1988 Jan;50(1):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb13251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Escalera S., Bockamp E. O., Moya F., Piovant M., Jiménez F. Characterization and gene cloning of neurotactin, a Drosophila transmembrane protein related to cholinesterases. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3593–3601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07570.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]