Abstract
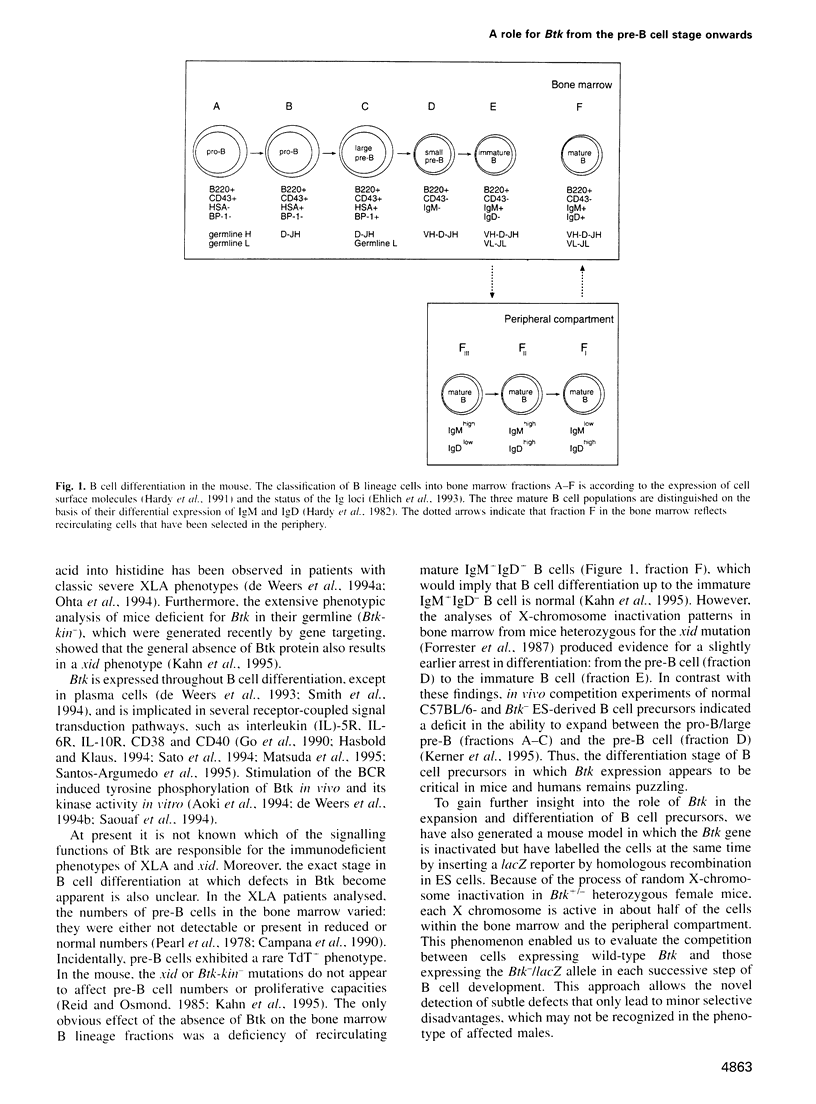
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) is a cytoplasmic protein kinase that is defective in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia in man and in X-linked immunodeficiency in the mouse. There is controversy regarding the stages of B cell development that are dependent on Btk function. To determine the point in B cell differentiation at which defects in Btk become apparent, we generated a mouse model by inactivating the Btk gene through an in-frame insertion of a lacZ reporter by homologous recombination in embryonic stem cells. The phenomenon of X-chromosome inactivation in Btk+/- heterozygous female mice enabled us to evaluate the competition between B cell progenitors expressing wild-type Btk and those expressing the Btk-/lacZ allele in each successive step of development. Although Btk was already expressed in pro-B cells, the first selective disadvantage only became apparent at the transition from small pre-B cells to immature B cells in the bone marrow. A second differentiation arrest was found during the maturation from IgD(low)IgM(high) to IgD(high)IgM(low) stages in the periphery. Our results show that Btk expression is essential at two distinct differentiation steps, both past the pre-B cell stage.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alt F. W., Blackwell T. K., Yancopoulos G. D. Development of the primary antibody repertoire. Science. 1987 Nov 20;238(4830):1079–1087. doi: 10.1126/science.3317825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki Y., Isselbacher K. J., Pillai S. Bruton tyrosine kinase is tyrosine phosphorylated and activated in pre-B lymphocytes and receptor-ligated B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10606–10609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUTON O. C. Agammaglobulinemia. Pediatrics. 1952 Jun;9(6):722–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campana D., Farrant J., Inamdar N., Webster A. D., Janossy G. Phenotypic features and proliferative activity of B cell progenitors in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Immunol. 1990 Sep 15;145(6):1675–1680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E. B cells in patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Immunol. 1985 May;134(5):3070–3074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Brown P., Pickard A. R., Buckley R. H., Miller D. S., Raskind W. H., Singer J. W., Fialkow P. J. Expression of the gene defect in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. N Engl J Med. 1986 Aug 28;315(9):564–567. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198608283150907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley M. E., Parolini O., Rohrer J., Campana D. X-linked agammaglobulinemia: new approaches to old questions based on the identification of the defective gene. Immunol Rev. 1994 Apr;138:5–21. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00844.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehlich A., Schaal S., Gu H., Kitamura D., Müller W., Rajewsky K. Immunoglobulin heavy and light chain genes rearrange independently at early stages of B cell development. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):695–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90398-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester L. M., Ansell J. D., Micklem H. S. Development of B lymphocytes in mice heterozygous for the X-linked immunodeficiency (xid) mutation. xid inhibits development of all splenic and lymph node B cells at a stage subsequent to their initial formation in bone marrow. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):949–958. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu S. M., Hurley J. N., McCune J. M., Kunkel H. G., Good R. A. Pre-B cells and other possible precursor lymphoid cell lines derived from patients with X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1519–1526. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genevier H. C., Hinshelwood S., Gaspar H. B., Rigley K. P., Brown D., Saeland S., Rousset F., Levinsky R. J., Callard R. E., Kinnon C. Expression of Bruton's tyrosine kinase protein within the B cell lineage. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Dec;24(12):3100–3105. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go N. F., Castle B. E., Barrett R., Kastelein R., Dang W., Mosmann T. R., Moore K. W., Howard M. Interleukin 10, a novel B cell stimulatory factor: unresponsiveness of X chromosome-linked immunodeficiency B cells. J Exp Med. 1990 Dec 1;172(6):1625–1631. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.6.1625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Carmack C. E., Shinton S. A., Kemp J. D., Hayakawa K. Resolution and characterization of pro-B and pre-pro-B cell stages in normal mouse bone marrow. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1213–1225. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Haaijman J., Herzenberg L. A. B-cell subpopulations identified by two-colour fluorescence analysis. Nature. 1982 Jun 17;297(5867):589–591. doi: 10.1038/297589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy R. R., Hayakawa K., Parks D. R., Herzenberg L. A. Demonstration of B-cell maturation in X-linked immunodeficient mice by simultaneous three-colour immunofluorescence. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):270–272. doi: 10.1038/306270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasbold J., Klaus G. G. B cells from CBA/N mice do not proliferate following ligation of CD40. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Jan;24(1):152–157. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Rolink A., Shinkai Y., Young F., Alt F. W., Melchers F. The expression of Vpre-B/lambda 5 surrogate light chain in early bone marrow precursor B cells of normal and B cell-deficient mutant mice. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. E., Lovering R. C., Bradley L. A., Rigley K. P., Brown D., Cotter F., Chessells J. M., Levinsky R. J., Kinnon C. Expression of the X-linked agammaglobulinemia gene, btk in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia. 1994 Apr;8(4):574–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski C., Evans D. I. Neutropenia associated with X-linked agammaglobulinaemia. J Clin Pathol. 1991 May;44(5):388–390. doi: 10.1136/jcp.44.5.388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassoued K., Nuñez C. A., Billips L., Kubagawa H., Monteiro R. C., LeBlen T. W., Cooper M. D. Expression of surrogate light chain receptors is restricted to a late stage in pre-B cell differentiation. Cell. 1993 Apr 9;73(1):73–86. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90161-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. S., Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R. The regulated expression of B lineage associated genes during B cell differentiation in bone marrow and fetal liver. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):951–960. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda T., Takahashi-Tezuka M., Fukada T., Okuyama Y., Fujitani Y., Tsukada S., Mano H., Hirai H., Witte O. N., Hirano T. Association and activation of Btk and Tec tyrosine kinases by gp130, a signal transducer of the interleukin-6 family of cytokines. Blood. 1995 Feb 1;85(3):627–633. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyama-Inaba M., Kuma S., Inaba K., Ogata H., Iwai H., Yasumizu R., Muramatsu S., Steinman R. M., Ikehara S. Unusual phenotype of B cells in the thymus of normal mice. J Exp Med. 1988 Aug 1;168(2):811–816. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.2.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musacchio A., Gibson T., Rice P., Thompson J., Saraste M. The PH domain: a common piece in the structural patchwork of signalling proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Sep;18(9):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90071-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Fiering S., Nicolas J. F., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell analysis and sorting of viable mammalian cells based on beta-D-galactosidase activity after transduction of Escherichia coli lacZ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2603–2607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuez B., Michalovich D., Bygrave A., Ploemacher R., Grosveld F. Defective haematopoiesis in fetal liver resulting from inactivation of the EKLF gene. Nature. 1995 May 25;375(6529):316–318. doi: 10.1038/375316a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearl E. R., Vogler L. B., Okos A. J., Crist W. M., Lawton A. R., 3rd, Cooper M. D. B lymphocyte precursors in human bone marrow: an analysis of normal individuals and patients with antibody-deficiency states. J Immunol. 1978 Apr;120(4):1169–1175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings D. J., Saffran D. C., Tsukada S., Largaespada D. A., Grimaldi J. C., Cohen L., Mohr R. N., Bazan J. F., Howard M., Copeland N. G. Mutation of unique region of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in immunodeficient XID mice. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):358–361. doi: 10.1126/science.8332901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings D. J., Witte O. N. Bruton's tyrosine kinase is a key regulator in B-cell development. Immunol Rev. 1994 Apr;138:105–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00849.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigley K. P., Harnett M. M., Phillips R. J., Klaus G. G. Analysis of signaling via surface immunoglobulin receptors on B cells from CBA/N mice. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Nov;19(11):2081–2086. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830191117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A., ten Boekel E., Melchers F., Fearon D. T., Krop I., Andersson J. A subpopulation of B220+ cells in murine bone marrow does not express CD19 and contains natural killer cell progenitors. J Exp Med. 1996 Jan 1;183(1):187–194. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos-Argumedo L., Lund F. E., Heath A. W., Solvason N., Wu W. W., Grimaldi J. C., Parkhouse R. M., Howard M. CD38 unresponsiveness of xid B cells implicates Bruton's tyrosine kinase (btk) as a regular of CD38 induced signal transduction. Int Immunol. 1995 Feb;7(2):163–170. doi: 10.1093/intimm/7.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saouaf S. J., Mahajan S., Rowley R. B., Kut S. A., Fargnoli J., Burkhardt A. L., Tsukada S., Witte O. N., Bolen J. B. Temporal differences in the activation of three classes of non-transmembrane protein tyrosine kinases following B-cell antigen receptor surface engagement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 27;91(20):9524–9528. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.20.9524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Katagiri T., Takaki S., Kikuchi Y., Hitoshi Y., Yonehara S., Tsukada S., Kitamura D., Watanabe T., Witte O. IL-5 receptor-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of SH2/SH3-containing proteins and activation of Bruton's tyrosine and Janus 2 kinases. J Exp Med. 1994 Dec 1;180(6):2101–2111. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.6.2101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savelkoul H. F., Lebman D. A., Benner R., Coffman R. L. Increase of precursor frequency and clonal size of murine IgE-secreting cells by IL-4. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):749–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher I. The CBA/N mouse strain: an experimental model illustrating the influence of the X-chromosome on immunity. Adv Immunol. 1982;33:1–71. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
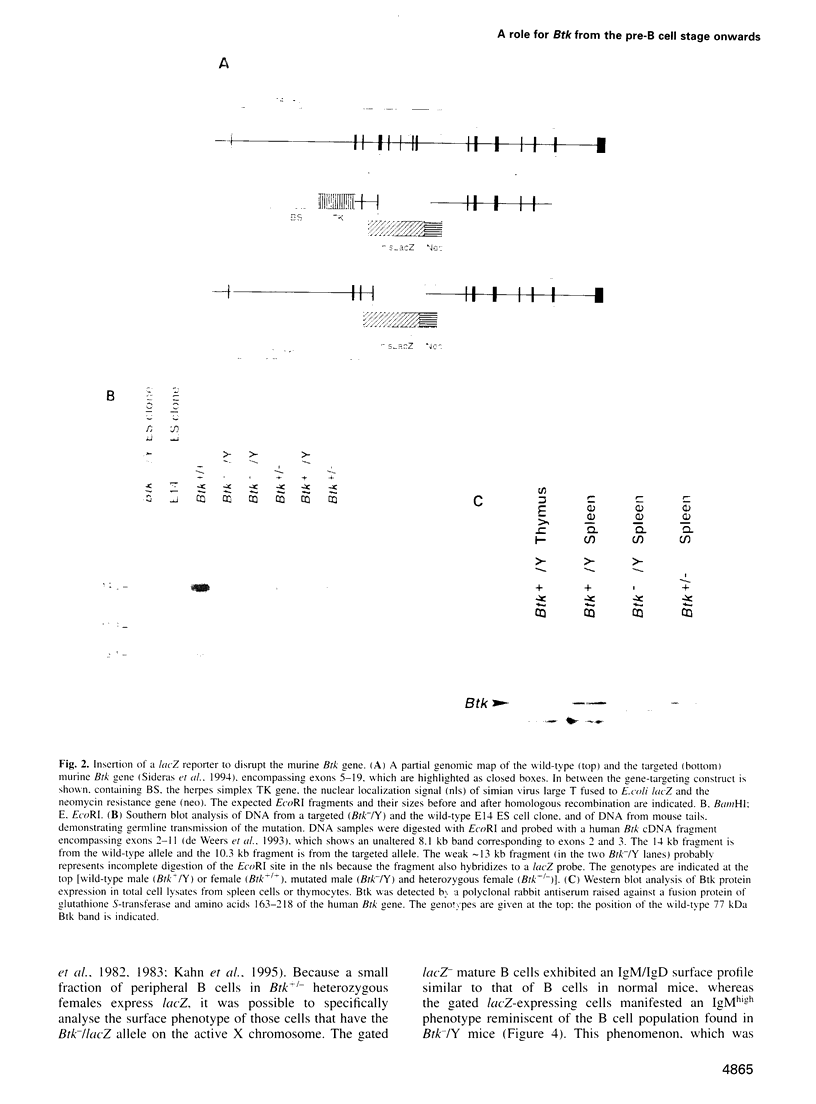
- Sideras P., Müller S., Shiels H., Jin H., Khan W. N., Nilsson L., Parkinson E., Thomas J. D., Brandén L., Larsson I. Genomic organization of mouse and human Bruton's agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase (Btk) loci. J Immunol. 1994 Dec 15;153(12):5607–5617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sideras P., Smith C. I. Molecular and cellular aspects of X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:135–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60631-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slieker W. A., de Rijk-de Bruijn M. F., Leenen P. J., van Ewijk W. ER-MP12 antigen, a new cell surface marker on mouse bone marrow cells with thymus-repopulating ability: I. Intrathymic repopulating ability of ER-MP12-positive bone marrow cells. Int Immunol. 1993 Sep;5(9):1093–1098. doi: 10.1093/intimm/5.9.1093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. I., Baskin B., Humire-Greiff P., Zhou J. N., Olsson P. G., Maniar H. S., Kjellén P., Lambris J. D., Christensson B., Hammarström L. Expression of Bruton's agammaglobulinemia tyrosine kinase gene, BTK, is selectively down-regulated in T lymphocytes and plasma cells. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 15;152(2):557–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprent J., Bruce J., Ron Y., Webb S. R. Physiology of B cells in mice with X-linked immunodeficiency. I. Size, migratory properties, and turnover of the B cell pool. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1442–1448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Sideras P., Smith C. I., Vorechovský I., Chapman V., Paul W. E. Colocalization of X-linked agammaglobulinemia and X-linked immunodeficiency genes. Science. 1993 Jul 16;261(5119):355–358. doi: 10.1126/science.8332900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada S., Saffran D. C., Rawlings D. J., Parolini O., Allen R. C., Klisak I., Sparkes R. S., Kubagawa H., Mohandas T., Quan S. Deficient expression of a B cell cytoplasmic tyrosine kinase in human X-linked agammaglobulinemia. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):279–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90667-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetrie D., Vorechovský I., Sideras P., Holland J., Davies A., Flinter F., Hammarström L., Kinnon C., Levinsky R., Bobrow M. The gene involved in X-linked agammaglobulinaemia is a member of the src family of protein-tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1993 Jan 21;361(6409):226–233. doi: 10.1038/361226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihinen M., Iwata T., Kinnon C., Kwan S. P., Ochs H. D., Vorechovský I., Smith C. I. BTKbase, mutation database for X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA). Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Jan 1;24(1):160–165. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vihinen M., Nilsson L., Smith C. I. Tec homology (TH) adjacent to the PH domain. FEBS Lett. 1994 Aug 22;350(2-3):263–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00783-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. Y., Morreau H., Rottier R., Davis D., Bonten E., Gillemans N., Wenger D., Grosveld F. G., Doherty P., Suzuki K. Mouse model for the lysosomal disorder galactosialidosis and correction of the phenotype with overexpressing erythroid precursor cells. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 1;9(21):2623–2634. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn M. F., Slieker W. A., van der Loo J. C., Voerman J. S., van Ewijk W., Leenen P. J. Distinct mouse bone marrow macrophage precursors identified by differential expression of ER-MP12 and ER-MP20 antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Oct;24(10):2279–2284. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weers M., Brouns G. S., Hinshelwood S., Kinnon C., Schuurman R. K., Hendriks R. W., Borst J. B-cell antigen receptor stimulation activates the human Bruton's tyrosine kinase, which is deficient in X-linked agammaglobulinemia. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 30;269(39):23857–23860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weers M., Mensink R. G., Kraakman M. E., Schuurman R. K., Hendriks R. W. Mutation analysis of the Bruton's tyrosine kinase gene in X-linked agammaglobulinemia: identification of a mutation which affects the same codon as is altered in immunodeficient xid mice. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Jan;3(1):161–166. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.1.161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]