Abstract
The product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene (Rb) controls the passage of mammalian cells through G1 phase. Animal virus oncoproteins interact with the Rb protein via an LXCXE motif and disrupt Rb-E2F complexes, driving cells into S-phase. Recently, we found that the RepA protein of a plant geminivirus contains an LXCXE motif that is essential for its function, a finding that predicts the existence of Rb-related proteins in plant cells. Here we report the isolation of a maize cDNA clone encoding a protein (ZmRb1) which, based on structural and functional studies, is closely related to the mammalian Rb family of growth regulatory proteins. ZmRb1 shows a high degree of amino acid conservation when compared with animal Rb members, particularly in the A/B 'pocket' domain, but ZmRb1 has a shorter N-terminal domain. ZmRb1 forms stable complexes with plant LXCXE-containing proteins, e.g. geminivirus RepA protein. Geminivirus DNA replication is reduced in plant cells transfected with plasmids encoding either ZmRb1 or human p130, a member of the Rb family. This suggests that ZmRb1 controls the G1/S transit in plant cells and is consistent with the fact that geminiviruses need an S-phase environment for DNA replication, as animal DNA tumor viruses do. Our results allow the extension of the Rb family of tumor suppressor proteins to plants and have implications on animal and plant strategies for cell growth control.
Full text
PDF




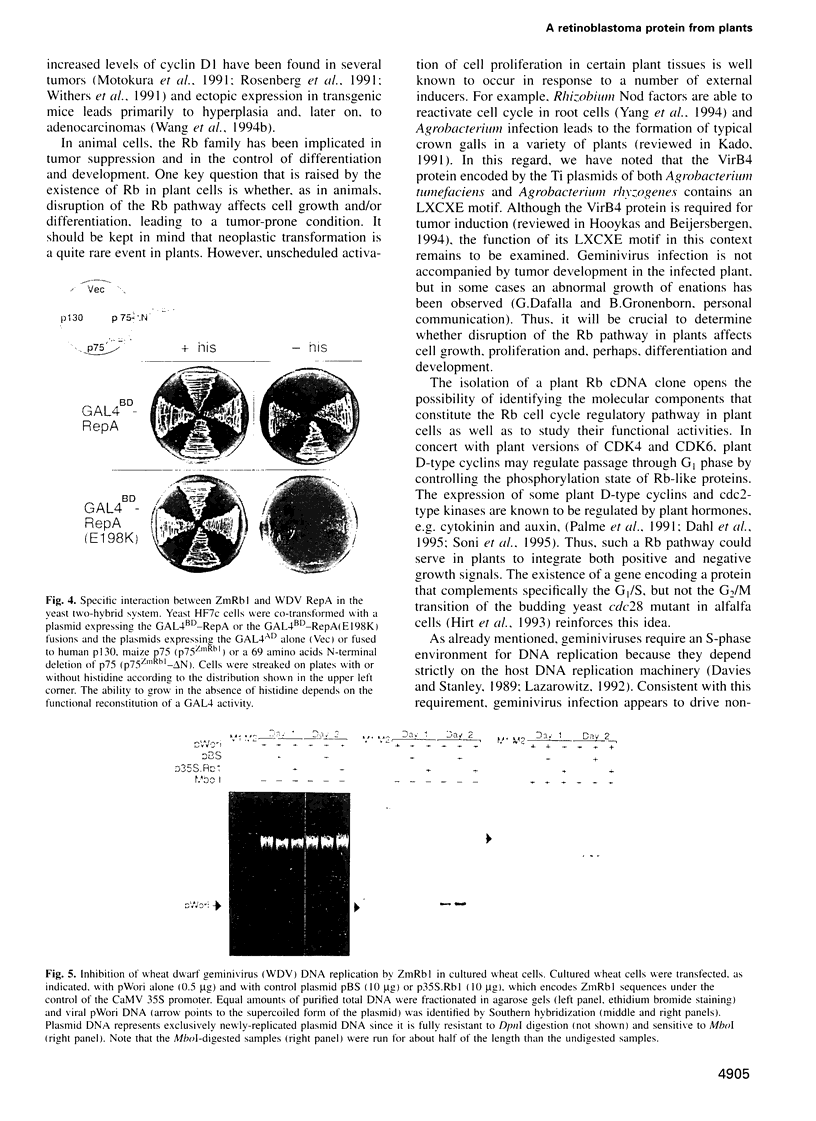



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartel P., Chien C. T., Sternglanz R., Fields S. Elimination of false positives that arise in using the two-hybrid system. Biotechniques. 1993 Jun;14(6):920–924. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Shackleford G. M., Schackleford G. M., Gerber M. R., Horowitz J. M., Friend S. H., Schartl M., Bogenmann E., Rapaport J. M., McGee T. Structure and expression of the murine retinoblastoma gene and characterization of its encoded protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6474–6478. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Regulation of the yeast HO gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:643–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherington V., Brown M., Paucha E., St Louis J., Spiegelman B. M., Roberts T. M. Separation of simian virus 40 large-T-antigen-transforming and origin-binding functions from the ability to block differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1380–1384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobrinik D., Whyte P., Peeper D. S., Jacks T., Weinberg R. A. Cell cycle-specific association of E2F with the p130 E1A-binding protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2392–2404. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl M., Meskiene I., Bögre L., Ha D. T., Swoboda I., Hubmann R., Hirt H., Heberle-Bors E. The D-type alfalfa cyclin gene cycMs4 complements G1 cyclin-deficient yeast and is induced in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Plant Cell. 1995 Nov;7(11):1847–1857. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.11.1847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. W., Stanley J. Geminivirus genes and vectors. Trends Genet. 1989 Mar;5(3):77–81. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90030-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day I. S., Reddy A. S. Cloning of a family of cyclins from Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 May 17;1218(1):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeCaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Figge J., Shew J. Y., Huang C. M., Lee W. H., Marsilio E., Paucha E., Livingston D. M. SV40 large tumor antigen forms a specific complex with the product of the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90559-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Destrée O. H., Lam K. T., Peterson-Maduro L. J., Eizema K., Diller L., Gryka M. A., Frebourg T., Shibuya E., Friend S. H. Structure and expression of the Xenopus retinoblastoma gene. Dev Biol. 1992 Sep;153(1):141–149. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerner P. W. Cell Cycle Regulation in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1994 Nov;106(3):823–827. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerner P., Jørgensen J. E., You R., Steppuhn J., Lamb C. Control of root growth and development by cyclin expression. Nature. 1996 Apr 11;380(6574):520–523. doi: 10.1038/380520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esumi M., Idutsu T., Kinugasa S., Ohno M., Nakabayashi H., Ikeda T., Shikata T. Isolation and sequence polymorphism of a rat retinoblastoma (RB) cDNA. Gene. 1995 Aug 19;161(2):231–235. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(95)00154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Xing Y. G., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the cDNA for p107, a retinoblastoma gene product-related protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1155–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90038-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feilotter H. E., Hannon G. J., Ruddell C. J., Beach D. Construction of an improved host strain for two hybrid screening. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Apr 25;22(8):1502–1503. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.8.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein R., Bolton W. K., Quinones J. N., Mosialos G., Sif S., Huff J. L., Capobianco A. J., Gilmore T. D. Characterization of a chicken cDNA encoding the retinoblastoma gene product. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 May 17;1218(1):82–86. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90103-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fobert P. R., Coen E. S., Murphy G. J., Doonan J. H. Patterns of cell division revealed by transcriptional regulation of genes during the cell cycle in plants. EMBO J. 1994 Feb 1;13(3):616–624. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06299.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Demetrick D., Beach D. Isolation of the Rb-related p130 through its interaction with CDK2 and cyclins. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12A):2378–2391. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12a.2378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth R. E., Jr, Chen P. L., Lee W. H. Integration of cell cycle control with transcriptional regulation by the retinoblastoma protein. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90102-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Pines J. Cyclins and cancer. II: Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90543-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. Control of the cell cycle. Dev Biol. 1992 Sep;153(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90087-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye F. J., Kratzke R. A., Gerster J. L., Horowitz J. M. A single amino acid substitution results in a retinoblastoma protein defective in phosphorylation and oncoprotein binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6922–6926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. At least six nucleotides preceding the AUG initiator codon enhance translation in mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 20;196(4):947–950. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludlow J. W. Interactions between SV40 large-tumor antigen and the growth suppressor proteins pRB and p53. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):866–871. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meskiene I., Bögre L., Dahl M., Pirck M., Ha D. T., Swoboda I., Heberle-Bors E., Ammerer G., Hirt H. cycMs3, a novel B-type alfalfa cyclin gene, is induced in the G0-to-G1 transition of the cell cycle. Plant Cell. 1995 Jun;7(6):759–771. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.6.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E. Interaction of adenoviral proteins with pRB and p53. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):880–885. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8344487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran E., Zerler B., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. Identification of separate domains in the adenovirus E1A gene for immortalization activity and the activation of virus early genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3470–3480. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motokura T., Bloom T., Kim H. G., Jüppner H., Ruderman J. V., Kronenberg H. M., Arnold A. A novel cyclin encoded by a bcl1-linked candidate oncogene. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):512–515. doi: 10.1038/350512a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagar S., Pedersen T. J., Carrick K. M., Hanley-Bowdoin L., Robertson D. A geminivirus induces expression of a host DNA synthesis protein in terminally differentiated plant cells. Plant Cell. 1995 Jun;7(6):705–719. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.6.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palme K., Hesse T., Moore I., Campos N., Feldwisch J., Garbers C., Hesse F., Schell J. Hormonal modulation of plant growth: the role of auxin perception. Mech Dev. 1991 Feb;33(2):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(91)90076-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl A., Kless H., Blumenthal A., Galili G., Galun E. Improvement of plant regeneration and GUS expression in scutellar wheat calli by optimization of culture conditions and DNA-microprojectile delivery procedures. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Nov;235(2-3):279–284. doi: 10.1007/BF00279371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renaudin J. P., Colasanti J., Rime H., Yuan Z., Sundaresan V. Cloning of four cyclins from maize indicates that higher plants have three structurally distinct groups of mitotic cyclins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7375–7379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg C. L., Wong E., Petty E. M., Bale A. E., Tsujimoto Y., Harris N. L., Arnold A. PRAD1, a candidate BCL1 oncogene: mapping and expression in centrocytic lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9638–9642. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy N. K., Ballesteros A., Garte S. J. Cloning and sequence of the rat retinoblastoma (Rb) gene cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):170–170. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanford J. C., Smith F. D., Russell J. A. Optimizing the biolistic process for different biological applications. Methods Enzymol. 1993;217:483–509. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)17086-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. S., Scher C. D., Todaro G. J. Induction of cell division in medium lacking serum growth factor by SV40. Virology. 1971 May;44(2):359–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90267-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soni R., Carmichael J. P., Shah Z. H., Murray J. A. A family of cyclin D homologs from plants differentially controlled by growth regulators and containing the conserved retinoblastoma protein interaction motif. Plant Cell. 1995 Jan;7(1):85–103. doi: 10.1105/tpc.7.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staiger C., Doonan J. Cell division in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):226–231. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timmermans M. C., Das O. P., Messing J. Trans replication and high copy numbers of wheat dwarf virus vectors in maize cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 11;20(15):4047–4054. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.15.4047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzvolgyi E., Classon M., Henriksson M., Huang H. J., Szekely L., Lee W. H., Klein G., Sumegi J. Reintroduction of a normal retinoblastoma gene into retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma cells inhibits the replication associated function of SV40 large T antigen. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Jun;2(6):297–303. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. Interactions of human papillomavirus transforming proteins with the products of tumor suppressor genes. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):872–879. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8393818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Knudsen E. S., Welch P. J. The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor protein. Adv Cancer Res. 1994;64:25–85. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60834-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. C., Cardiff R. D., Zukerberg L., Lees E., Arnold A., Schmidt E. V. Mammary hyperplasia and carcinoma in MMTV-cyclin D1 transgenic mice. Nature. 1994 Jun 23;369(6482):669–671. doi: 10.1038/369669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Withers D. A., Harvey R. C., Faust J. B., Melnyk O., Carey K., Meeker T. C. Characterization of a candidate bcl-1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4846–4853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie Q., Suárez-López P., Gutiérrez C. Identification and analysis of a retinoblastoma binding motif in the replication protein of a plant DNA virus: requirement for efficient viral DNA replication. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 15;14(16):4073–4082. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W. C., de Blank C., Meskiene I., Hirt H., Bakker J., van Kammen A., Franssen H., Bisseling T. Rhizobium nod factors reactivate the cell cycle during infection and nodule primordium formation, but the cycle is only completed in primordium formation. Plant Cell. 1994 Oct;6(10):1415–1426. doi: 10.1105/tpc.6.10.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]