Abstract
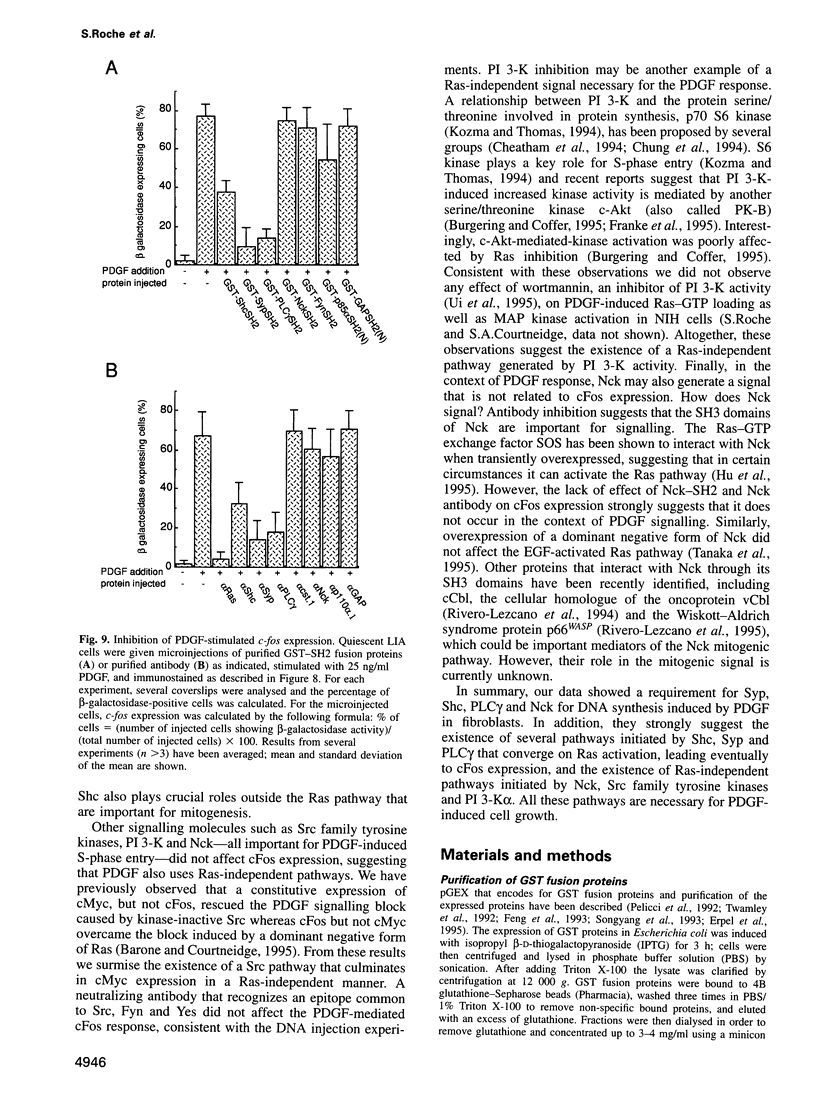
We have investigated the roles of the phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp (also called SH-PTP2), phospholipase C (PLC) gamma1, rasGTPase Activating Protein (rasGAP) and the adapter molecules Nck and Shc in the mitogenic response induced by PDGF in fibroblasts. Two separate approaches were used to inhibit the biological activity of these signalling proteins in vivo. Either glutathione S-transferase (GST) fusion proteins containing the SH2 domains of these proteins, or antibodies specific for these polypeptides, were microinjected into cells. GST-SH2 fusion proteins are expected to act as dominant inhibitors by competing for physiological SH2-mediated interactions, while microinjected antibodies can directly block protein functions. Inhibition of PLCgamma, Syp, Shc and Nck signals blocked PDGF-stimulated cells in G1 showing a requirement for these proteins for S-phase entry. Inhibition of rasGAP, in contrast, had no effect on S-phase entry. We next examined which of these signals were required for PDGF-induced cFos expression, a Ras-dependent event important for signalling. By using the same approaches with cells expressing beta-galactosidase under the control of a c-fos promoter, we showed that PLCgamma, Syp and Shc were necessary for ligand-induced cFos expression whereas Nck and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha were not. From these results we concluded that PDGF generates Ras-dependent and Ras-independent pathways important for DNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barone M. V., Courtneidge S. A. Myc but not Fos rescue of PDGF signalling block caused by kinase-inactive Src. Nature. 1995 Nov 30;378(6556):509–512. doi: 10.1038/378509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biro S., Fu Y. M., Yu Z. X., Epstein S. E. Inhibitory effects of antisense oligodeoxynucleotides targeting c-myc mRNA on smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):654–658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgering B. M., Coffer P. J. Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature. 1995 Aug 17;376(6541):599–602. doi: 10.1038/376599a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheatham B., Vlahos C. J., Cheatham L., Wang L., Blenis J., Kahn C. R. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation is required for insulin stimulation of pp70 S6 kinase, DNA synthesis, and glucose transporter translocation. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4902–4911. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Grall D., Salcini A. E., Pelicci P. G., Pouysségur J., Van Obberghen-Schilling E. Shc adaptor proteins are key transducers of mitogenic signaling mediated by the G protein-coupled thrombin receptor. EMBO J. 1996 Mar 1;15(5):1037–1044. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Grammer T. C., Lemon K. P., Kazlauskas A., Blenis J. PDGF- and insulin-dependent pp70S6k activation mediated by phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase. Nature. 1994 Jul 7;370(6484):71–75. doi: 10.1038/370071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikic I., Schlessinger J., Lax I. PC12 cells overexpressing the insulin receptor undergo insulin-dependent neuronal differentiation. Curr Biol. 1994 Aug 1;4(8):702–708. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00155-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erpel T., Superti-Furga G., Courtneidge S. A. Mutational analysis of the Src SH3 domain: the same residues of the ligand binding surface are important for intra- and intermolecular interactions. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 1;14(5):963–975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07077.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Hui C. C., Pawson T. SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase as a target of protein-tyrosine kinases. Science. 1993 Mar 12;259(5101):1607–1611. doi: 10.1126/science.8096088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke T. F., Yang S. I., Chan T. O., Datta K., Kazlauskas A., Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Tsichlis P. N. The protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):727–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90534-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt J. T., Gopal T. V., Moulton A. D., Nienhuis A. W. Inducible production of c-fos antisense RNA inhibits 3T3 cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4794–4798. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hordijk P. L., Verlaan I., van Corven E. J., Moolenaar W. H. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation induced by lysophosphatidic acid in Rat-1 fibroblasts. Evidence that phosphorylation of map kinase is mediated by the Gi-p21ras pathway. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):645–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q., Milfay D., Williams L. T. Binding of NCK to SOS and activation of ras-dependent gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1169–1174. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Thomas G. p70s6k/p85s6k: mechanism of activation and role in mitogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 1994 Aug;5(4):255–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai N., Morii N., Fujisawa K., Yoshimasa T., Nakao K., Narumiya S. Lysophosphatidic acid induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of MAP-kinase and focal adhesion kinase in cultured Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1993 Aug 30;329(3):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80236-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lev S., Moreno H., Martinez R., Canoll P., Peles E., Musacchio J. M., Plowman G. D., Rudy B., Schlessinger J. Protein tyrosine kinase PYK2 involved in Ca(2+)-induced regulation of ion channel and MAP kinase functions. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):737–745. doi: 10.1038/376737a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGlade J., Brunkhorst B., Anderson D., Mbamalu G., Settleman J., Dedhar S., Rozakis-Adcock M., Chen L. B., Pawson T. The N-terminal region of GAP regulates cytoskeletal structure and cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3073–3081. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori S., Rönnstrand L., Yokote K., Engström A., Courtneidge S. A., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Identification of two juxtamembrane autophosphorylation sites in the PDGF beta-receptor; involvement in the interaction with Src family tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2257–2264. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05879.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikura K., Murray J. M. Antisense RNA of proto-oncogene c-fos blocks renewed growth of quiescent 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):639–649. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura R., Li W., Kashishian A., Mondino A., Zhou M., Cooper J., Schlessinger J. Two signaling molecules share a phosphotyrosine-containing binding site in the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):6889–6896. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nori M., Vogel U. S., Gibbs J. B., Weber M. J. Inhibition of v-src-induced transformation by a GTPase-activating protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2812–2818. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelicci G., Lanfrancone L., Grignani F., McGlade J., Cavallo F., Forni G., Nicoletti I., Grignani F., Pawson T., Pelicci P. G. A novel transforming protein (SHC) with an SH2 domain is implicated in mitogenic signal transduction. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):93–104. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90536-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivard N., McKenzie F. R., Brondello J. M., Pouysségur J. The phosphotyrosine phosphatase PTP1D, but not PTP1C, is an essential mediator of fibroblast proliferation induced by tyrosine kinase and G protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):11017–11024. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.11017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivero-Lezcano O. M., Marcilla A., Sameshima J. H., Robbins K. C. Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein physically associates with Nck through Src homology 3 domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;15(10):5725–5731. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.10.5725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivero-Lezcano O. M., Sameshima J. H., Marcilla A., Robbins K. C. Physical association between Src homology 3 elements and the protein product of the c-cbl proto-oncogene. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 1;269(26):17363–17366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche S., Dhand R., Waterfield M. D., Courtneidge S. A. The catalytic subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase is a substrate for the activated platelet-derived growth factor receptor, but not for middle-T antigen-pp60c-src complexes. Biochem J. 1994 Aug 1;301(Pt 3):703–711. doi: 10.1042/bj3010703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche S., Koegl M., Barone M. V., Roussel M. F., Courtneidge S. A. DNA synthesis induced by some but not all growth factors requires Src family protein tyrosine kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;15(2):1102–1109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.2.1102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roche S., Koegl M., Courtneidge S. A. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase alpha is required for DNA synthesis induced by some, but not all, growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Sep 13;91(19):9185–9189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.19.9185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rönnstrand L., Mori S., Arridsson A. K., Eriksson A., Wernstedt C., Hellman U., Claesson-Welsh L., Heldin C. H. Identification of two C-terminal autophosphorylation sites in the PDGF beta-receptor: involvement in the interaction with phospholipase C-gamma. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3911–3919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaoka T., Rose D. W., Jhun B. H., Saltiel A. R., Draznin B., Olefsky J. M. Evidence for a functional role of Shc proteins in mitogenic signaling induced by insulin, insulin-like growth factor-1, and epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 6;269(18):13689–13694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schilling K., Luk D., Morgan J. I., Curran T. Regulation of a fos-lacZ fusion gene: a paradigm for quantitative analysis of stimulus-transcription coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5665–5669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. R., Liu Y. L., Kim H., Rhee S. G., Kung H. F. Inhibition of serum- and ras-stimulated DNA synthesis by antibodies to phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1074–1077. doi: 10.1126/science.2408147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studzinski G. P., Brelvi Z. S., Feldman S. C., Watt R. A. Participation of c-myc protein in DNA synthesis of human cells. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.3532322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Gupta R., Mayer B. J. Differential inhibition of signaling pathways by dominant-negative SH2/SH3 adapter proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;15(12):6829–6837. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.12.6829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse S., Seedorf K., Paterson H., Marshall C. J., Cohen P., Ullrich A. EGF triggers neuronal differentiation of PC12 cells that overexpress the EGF receptor. Curr Biol. 1994 Aug 1;4(8):694–701. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00154-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Ternary complex factors: growth factor regulated transcriptional activators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twamley-Stein G. M., Pepperkok R., Ansorge W., Courtneidge S. A. The Src family tyrosine kinases are required for platelet-derived growth factor-mediated signal transduction in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7696–7700. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twamley G. M., Kypta R. M., Hall B., Courtneidge S. A. Association of Fyn with the activated platelet-derived growth factor receptor: requirements for binding and phosphorylation. Oncogene. 1992 Oct;7(10):1893–1901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ui M., Okada T., Hazeki K., Hazeki O. Wortmannin as a unique probe for an intracellular signalling protein, phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Aug;20(8):303–307. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Bazenet C., Kazlauskas A. Tyrosines 1021 and 1009 are phosphorylation sites in the carboxy terminus of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta subunit and are required for binding of phospholipase C gamma and a 64-kilodalton protein, respectively. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;13(1):133–143. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valius M., Kazlauskas A. Phospholipase C-gamma 1 and phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase are the downstream mediators of the PDGF receptor's mitogenic signal. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):321–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90232-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickstrom E. L., Bacon T. A., Gonzalez A., Freeman D. L., Lyman G. H., Wickstrom E. Human promyelocytic leukemia HL-60 cell proliferation and c-myc protein expression are inhibited by an antisense pentadecadeoxynucleotide targeted against c-myc mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(4):1028–1032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.4.1028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao S., Rose D. W., Sasaoka T., Maegawa H., Burke T. R., Jr, Roller P. P., Shoelson S. E., Olefsky J. M. Syp (SH-PTP2) is a positive mediator of growth factor-stimulated mitogenic signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21244–21248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokote K., Mori S., Hansen K., McGlade J., Pawson T., Heldin C. H., Claesson-Welsh L. Direct interaction between Shc and the platelet-derived growth factor beta-receptor. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):15337–15343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J., Rozengurt E. Bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Identification of a novel tyrosine kinase as a major substrate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19031–19034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Geer P., Hunter T., Lindberg R. A. Receptor protein-tyrosine kinases and their signal transduction pathways. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1994;10:251–337. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.10.110194.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]