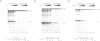Abstract
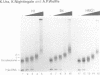
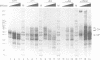
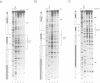
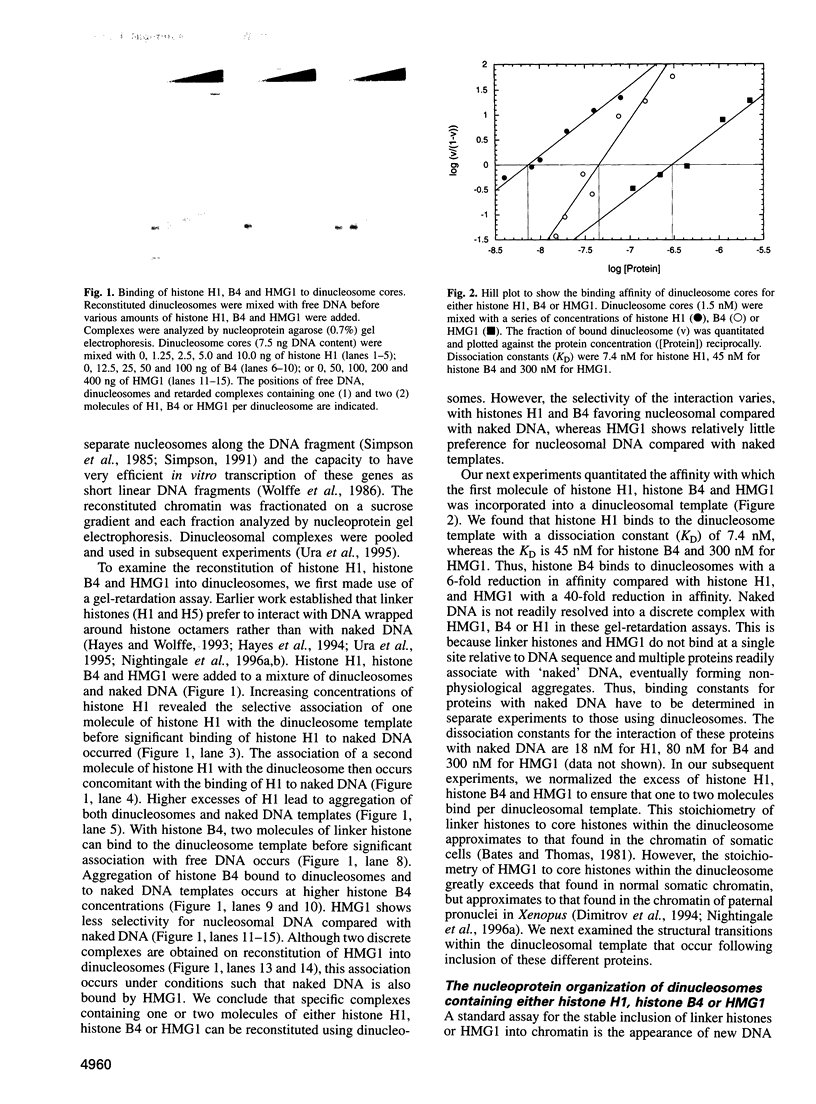
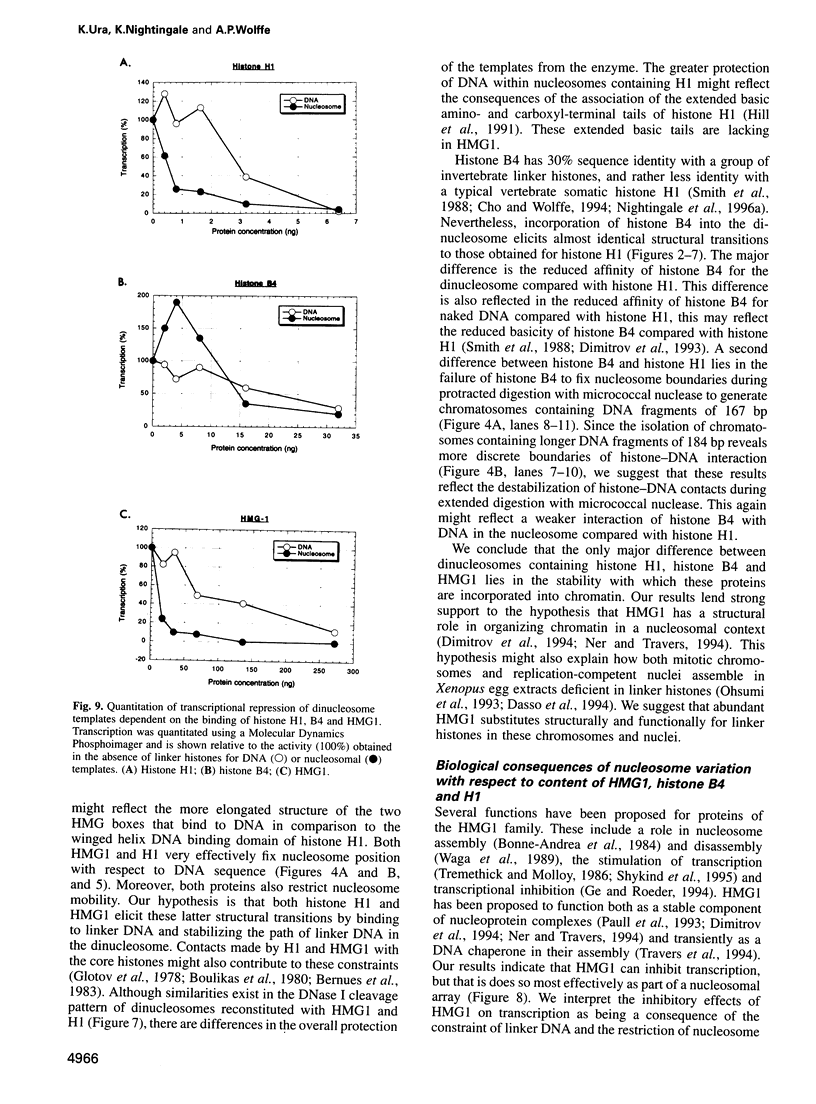
We examined the structural and functional consequences of incorporating either histone H1, histone B4 or HMG1 into a synthetic dinucleosome containing two 5S rRNA genes. We found that all three proteins bind to linker DNA, stabilizing an additional 20 bp from micrococcal nuclease digestion and restrict nucleosome mobility. Histone H1 has the highest-affinity interaction with the dinucleosome; histone B4 and HMG1 associate with significantly reduced affinities. We found that histone H1 binds to the dinucleosome template with a dissociation constant (KD) of 7.4 nM, whereas the KD is 45 nM for histone B4 and 300 nM for HMG1. The KDs for the interaction of these proteins with naked DNA are 18 nM for H1, 80 nM for B4 and 300 nM for HMG1. The differences in association of these proteins with the dinucleosome are reflected in the efficiency with which the different proteins repress transcription from the 5S rRNA genes. Thus, although all three proteins can contribute to the organization of chromatin, the stability of the structures they assemble will vary. Our results provide a molecular explanation for the transcriptional promiscuity of Xenopus early embryonic chromatin, which is enriched in HMG1 and linker histone B4, but deficient in histone H1.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan J., Hartman P. G., Crane-Robinson C., Aviles F. X. The structure of histone H1 and its location in chromatin. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):675–679. doi: 10.1038/288675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almouzni G., Wolffe A. P. Constraints on transcriptional activator function contribute to transcriptional quiescence during early Xenopus embryogenesis. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1752–1765. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates D. L., Thomas J. O. Histones H1 and H5: one or two molecules per nucleosome? Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):5883–5894. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.5883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bavykin S. G., Usachenko S. I., Zalensky A. O., Mirzabekov A. D. Structure of nucleosomes and organization of internucleosomal DNA in chromatin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 5;212(3):495–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90328-J. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernués J., Querol E., Martinez P., Barris A., Espel E., Lloberas J. Detection by chemical cross-linking of interaction between high mobility group protein 1 and histone oligomers in free solution. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11020–11024. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi M. E. Prokaryotic HU and eukaryotic HMG1: a kinked relationship. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Oct;14(1):1–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb01261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne-Andrea C., Harper F., Sobczak J., De Recondo A. M. Rat liver HMG1: a physiological nucleosome assembly factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulikas T., Wiseman J. M., Garrard W. T. Points of contact between histone H1 and the histone octamer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):127–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvet P., Dimitrov S., Wolffe A. P. Specific regulation of Xenopus chromosomal 5S rRNA gene transcription in vivo by histone H1. Genes Dev. 1994 May 15;8(10):1147–1159. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustin M., Lehn D. A., Landsman D. Structural features of the HMG chromosomal proteins and their genes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90092-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chipev C. C., Wolffe A. P. Chromosomal organization of Xenopus laevis oocyte and somatic 5S rRNA genes in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;12(1):45–55. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.1.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H., Wolffe A. P. Xenopus laevis B4, an intron-containing oocyte-specific linker histone-encoding gene. Gene. 1994 Jun 10;143(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(94)90102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Churchill M. E., Jones D. N., Glaser T., Hefner H., Searles M. A., Travers A. A. HMG-D is an architecture-specific protein that preferentially binds to DNA containing the dinucleotide TG. EMBO J. 1995 Mar 15;14(6):1264–1275. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M., Dimitrov S., Wolffe A. P. Nuclear assembly is independent of linker histones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Dec 20;91(26):12477–12481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov S., Almouzni G., Dasso M., Wolffe A. P. Chromatin transitions during early Xenopus embryogenesis: changes in histone H4 acetylation and in linker histone type. Dev Biol. 1993 Nov;160(1):214–227. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrov S., Dasso M. C., Wolffe A. P. Remodeling sperm chromatin in Xenopus laevis egg extracts: the role of core histone phosphorylation and linker histone B4 in chromatin assembly. J Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;126(3):591–601. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong F., Hansen J. C., van Holde K. E. DNA and protein determinants of nucleosome positioning on sea urchin 5S rRNA gene sequences in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5724–5728. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin-Rastl E., Kandolf H., Smith R. C. The maternal histone H1 variant, H1M (B4 protein), is the predominant H1 histone in Xenopus pregastrula embryos. Dev Biol. 1994 Feb;161(2):425–439. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1994.1042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsenfeld G., McGhee J. D. Structure of the 30 nm chromatin fiber. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):375–377. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90456-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ge H., Roeder R. G. The high mobility group protein HMG1 can reversibly inhibit class II gene transcription by interaction with the TATA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 24;269(25):17136–17140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotov B. O., Itkes A. V., Nikolaev L. G., Severin E. S. Evidence for the close proximity of histones H1 and H3 in chromatin of intact nuclei. FEBS Lett. 1978 Jul 1;91(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(78)80037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godde J. S., Wolffe A. P. Disruption of reconstituted nucleosomes. The effect of particle concentration, MgCl2 and KCl concentration, the histone tails, and temperature. J Biol Chem. 1995 Nov 17;270(46):27399–27402. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.46.27399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin G. H., Woodhead L., Johns E. W. The presence of high mobility group non-histone chromatin proteins in isolated nucleosomes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jan 15;73(1):85–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Pruss D., Wolffe A. P. Contacts of the globular domain of histone H5 and core histones with DNA in a "chromatosome". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7817–7821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes J. J., Wolffe A. P. Preferential and asymmetric interaction of linker histones with 5S DNA in the nucleosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6415–6419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Rimmer J. M., Green B. N., Finch J. T., Thomas J. O. Histone-DNA interactions and their modulation by phosphorylation of -Ser-Pro-X-Lys/Arg- motifs. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1939–1948. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock R., Moorman A., Fischer D., Scheer U. Absence of somatic histone H1 in oocytes and preblastula embryos of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1993 Aug;158(2):510–522. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Maric C., Méchali M. Transition in specification of embryonic metazoan DNA replication origins. Science. 1995 Nov 10;270(5238):994–997. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5238.994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Debold W. A., Reeck G. R. Isolation and separation of chicken erythrocyte high mobility group non-histone chromatin proteins by chromatography on phosphocellulose. FEBS Lett. 1980 Oct 6;119(2):337–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80284-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Pollock J. M., Jr, Rill R. L. Chromatin fractionation procedure that yields nucleosomes containing near-stoichiometric amounts of high mobility group nonhistone chromosomal proteins. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3739–3748. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson J. B., Rill R. L. Circular dichroism, thermal denaturation, and deoxyribonuclease I digestion studies of nucleosomes highly enriched in high mobility group proteins HMG 1 and HMG 2. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):1042–1046. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kandolf H. The H1A histone variant is an in vivo repressor of oocyte-type 5S gene transcription in Xenopus laevis embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7257–7261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinschmidt J. A., Scheer U., Dabauvalle M. C., Bustin M., Franke W. W. High mobility group proteins of amphibian oocytes: a large storage pool of a soluble high mobility group-1-like protein and involvement in transcriptional events. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):838–848. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley D. M. DNA--protein interactions. HMG has DNA wrapped up. Nature. 1992 May 28;357(6376):282–283. doi: 10.1038/357282a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorch Y., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Nucleosomes inhibit the initiation of transcription but allow chain elongation with the displacement of histones. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):203–210. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90561-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losa R., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes in vitro through a nucleosome core without displacing it. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):801–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meersseman G., Pennings S., Bradbury E. M. Chromatosome positioning on assembled long chromatin. Linker histones affect nucleosome placement on 5 S rDNA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 5;220(1):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90383-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meersseman G., Pennings S., Bradbury E. M. Mobile nucleosomes--a general behavior. EMBO J. 1992 Aug;11(8):2951–2959. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirzabekov A. D., Pruss D. V., Ebralidse K. K. Chromatin superstructure-dependent crosslinking with DNA of the histone H5 residues Thr1, His25 and His62. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jan 20;211(2):479–491. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90366-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ner S. S., Travers A. A. HMG-D, the Drosophila melanogaster homologue of HMG 1 protein, is associated with early embryonic chromatin in the absence of histone H1. EMBO J. 1994 Apr 15;13(8):1817–1822. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newport J., Kirschner M. A major developmental transition in early Xenopus embryos: II. Control of the onset of transcription. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):687–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90273-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale K. P., Pruss D., Wolffe A. P. A single high affinity binding site for histone H1 in a nucleosome containing the Xenopus borealis 5 S ribosomal RNA gene. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 22;271(12):7090–7094. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.7090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nightingale K., Dimitrov S., Reeves R., Wolffe A. P. Evidence for a shared structural role for HMG1 and linker histones B4 and H1 in organizing chromatin. EMBO J. 1996 Feb 1;15(3):548–561. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M., Kornberg R. D. Action of micrococcal nuclease on chromatin and the location of histone H1. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jan 25;109(3):393–404. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsumi K., Katagiri C., Kishimoto T. Chromosome condensation in Xenopus mitotic extracts without histone H1. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2033–2035. doi: 10.1126/science.8266099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paull T. T., Haykinson M. J., Johnson R. C. The nonspecific DNA-binding and -bending proteins HMG1 and HMG2 promote the assembly of complex nucleoprotein structures. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1521–1534. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennings S., Meersseman G., Bradbury E. M. Linker histones H1 and H5 prevent the mobility of positioned nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10275–10279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierrou S., Hellqvist M., Samuelsson L., Enerbäck S., Carlsson P. Cloning and characterization of seven human forkhead proteins: binding site specificity and DNA bending. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):5002–5012. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06827.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prioleau M. N., Huet J., Sentenac A., Méchali M. Competition between chromatin and transcription complex assembly regulates gene expression during early development. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):439–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss D., Hayes J. J., Wolffe A. P. Nucleosomal anatomy--where are the histones? Bioessays. 1995 Feb;17(2):161–170. doi: 10.1002/bies.950170211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., Finch J. T., Graziano V., Lee P. L., Sweet R. M. Crystal structure of globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature. 1993 Mar 18;362(6417):219–223. doi: 10.1038/362219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read C. M., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C., Driscoll P. C., Norman D. G. Solution structure of a DNA-binding domain from HMG1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3427–3436. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read C. M., Cary P. D., Preston N. S., Lnenicek-Allen M., Crane-Robinson C. The DNA sequence specificity of HMG boxes lies in the minor wing of the structure. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5639–5646. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rupp R. A., Weintraub H. Ubiquitous MyoD transcription at the midblastula transition precedes induction-dependent MyoD expression in presumptive mesoderm of X. laevis. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90545-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild C., Claret F. X., Wahli W., Wolffe A. P. A nucleosome-dependent static loop potentiates estrogen-regulated transcription from the Xenopus vitellogenin B1 promoter in vitro. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):423–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Brown D. D. The transcriptional regulation of Xenopus 5s RNA genes in chromatin: the roles of active stable transcription complexes and histone H1. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):903–913. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90425-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröter H., Bode J. The binding sites for large and small high-mobility-group (HMG) proteins. Studies on HMG-nucleosome interactions in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Oct;127(2):429–436. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06890.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shykind B. M., Kim J., Sharp P. A. Activation of the TFIID-TFIIA complex with HMG-2. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 1;9(11):1354–1365. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.11.1354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Nucleosome positioning: occurrence, mechanisms, and functional consequences. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1991;40:143–184. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60841-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T. Structure of the chromatosome, a chromatin particle containing 160 base pairs of DNA and all the histones. Biochemistry. 1978 Dec 12;17(25):5524–5531. doi: 10.1021/bi00618a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. T., Thoma F., Brubaker J. M. Chromatin reconstituted from tandemly repeated cloned DNA fragments and core histones: a model system for study of higher order structure. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):799–808. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90276-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. C., Dworkin-Rastl E., Dworkin M. B. Expression of a histone H1-like protein is restricted to early Xenopus development. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1284–1295. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studitsky V. M., Clark D. J., Felsenfeld G. A histone octamer can step around a transcribing polymerase without leaving the template. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Van Holde K. E. Reconstitution of chromatin core particles. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 29;16(24):5295–5303. doi: 10.1021/bi00643a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travers A. A., Ner S. S., Churchill M. E. DNA chaperones: a solution to a persistence problem? Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):167–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90306-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tremethick D. J., Molloy P. L. High mobility group proteins 1 and 2 stimulate transcription in vitro by RNA polymerases II and III. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 25;261(15):6986–6992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ura K., Hayes J. J., Wolffe A. P. A positive role for nucleosome mobility in the transcriptional activity of chromatin templates: restriction by linker histones. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3752–3765. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00045.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga-Weisz P. D., Blank T. A., Becker P. B. Energy-dependent chromatin accessibility and nucleosome mobility in a cell-free system. EMBO J. 1995 May 15;14(10):2209–2216. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07215.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varga-Weisz P., Zlatanova J., Leuba S. H., Schroth G. P., van Holde K. Binding of histones H1 and H5 and their globular domains to four-way junction DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3525–3529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varshavsky A. J., Bakayev V. V., Georgiev G. P. Heterogeneity of chromatin subunits in vitro and location of histone H1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Feb;3(2):477–492. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waga S., Mizuno S., Yoshida M. Nonhistone proteins HMG1 and HMG2 suppress the nucleosome assembly at physiological ionic strength. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 1;1007(2):209–214. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(89)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall G., Varga-Weisz P. D., Sandaltzopoulos R., Becker P. B. Chromatin remodeling by GAGA factor and heat shock factor at the hypersensitive Drosophila hsp26 promoter in vitro. EMBO J. 1995 Apr 18;14(8):1727–1736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir H. M., Kraulis P. J., Hill C. S., Raine A. R., Laue E. D., Thomas J. O. Structure of the HMG box motif in the B-domain of HMG1. EMBO J. 1993 Apr;12(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner M. H., Huth J. R., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Molecular basis of human 46X,Y sex reversal revealed from the three-dimensional solution structure of the human SRY-DNA complex. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):705–714. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90532-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P. Dominant and specific repression of Xenopus oocyte 5S RNA genes and satellite I DNA by histone H1. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):527–537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Onset of 5 S RNA gene regulation during Xenopus embryogenesis. Dev Biol. 1983 Sep;99(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90273-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]