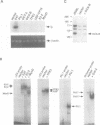
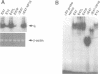
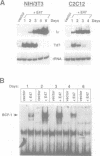
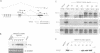Abstract
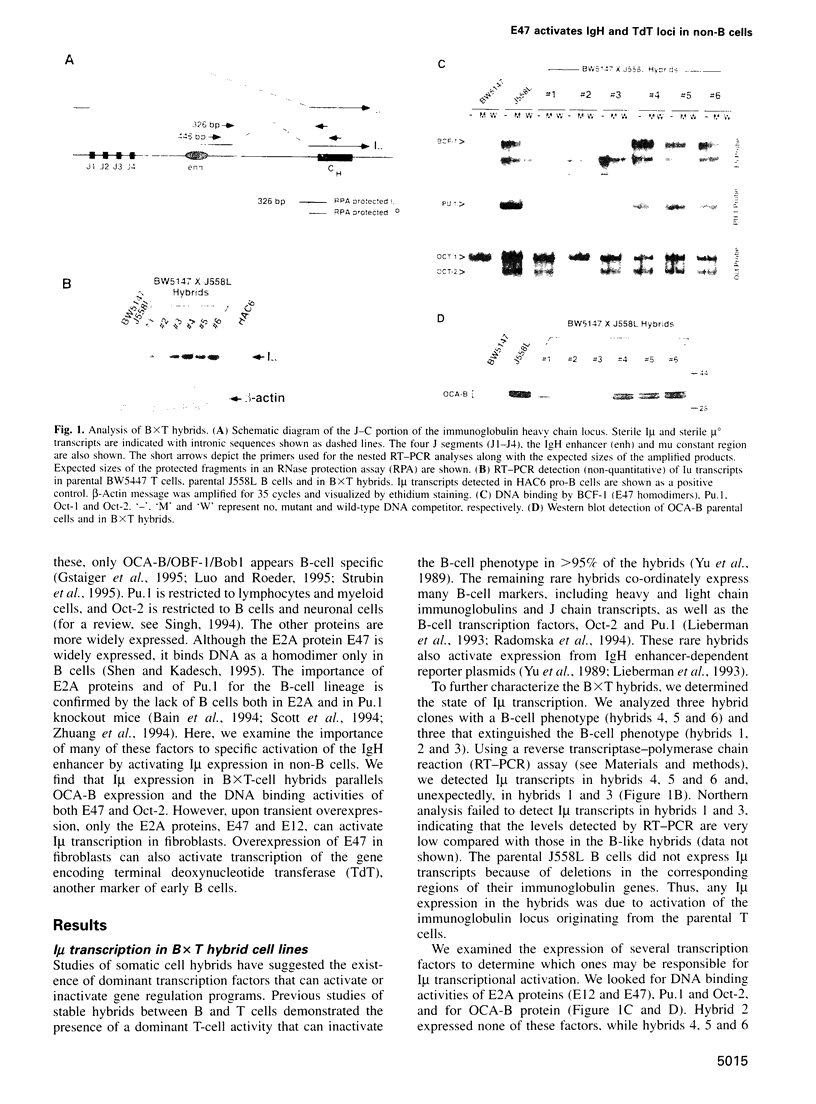
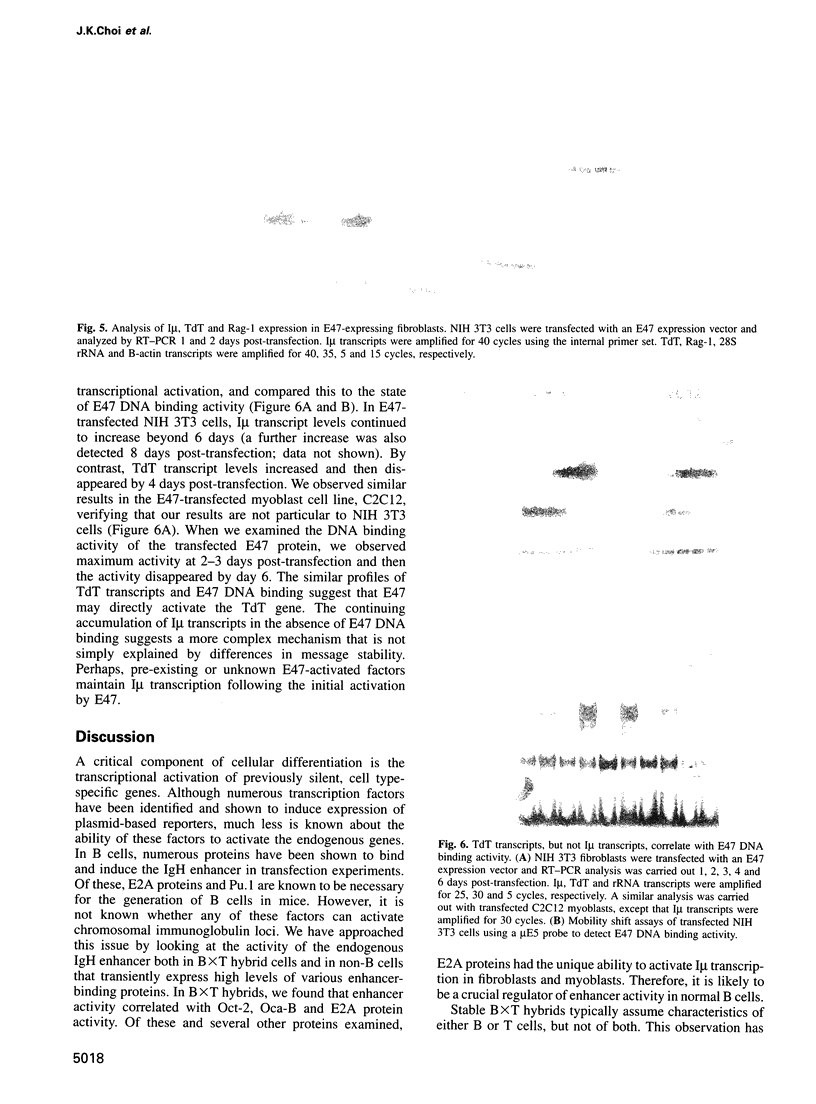
The E2A proteins, E12 and E47, are basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins essential for the B-cell lineage. Initially identified as immunoglobulin enhancer-binding proteins, they have also been shown to activate immunoglobulin enhancer-based reporters in transient transfection assays. Here, we examine the relationship between E2A DNA binding activity and activation of the endogenous, chromosomal immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) locus. Using sterile I(mu) transcription as an indicator of IgH enhancer activity, we see a direct correlation between E2A DNA binding activity and I(mu) transcription in stable BxT hybrids. We also observe a 1000-fold stimulation of endogenous I(mu) transcription in fibroblasts that express high levels of E47 and less stimulation in cells that express E12. By contrast, none of the other IgH enhancer-binding proteins tested (E2-2, Pu.1, Oct-2, OCA-B, TFE3 and USF) were able to activate I(mu) transcription. E47 overexpression also resulted in transcriptional activation of the endogenous gene encoding TdT, indicating that it, too, is a target of E2A proteins early in the B-cell lineage. Our results indicate that E2A proteins have the distinctive property of activating silent, chromatin-embedded B-cell-specific genes, underscoring their crucial role in B-cell development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bain G., Maandag E. C., Izon D. J., Amsen D., Kruisbeek A. M., Weintraub B. C., Krop I., Schlissel M. S., Feeney A. J., van Roon M. E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):885–892. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron M. H., Farrington S. M. Positive regulators of the lineage-specific transcription factor GATA-1 in differentiating erythroid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3108–3114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Strich B., Sharir H., Ber R., Laskov R. Extinction of Ig genes expression in myeloma x fibroblast somatic cell hybrids is accompanied by repression of the oct-2 gene encoding a B-cell specific transcription factor. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):849–855. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08182.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burk O., Mink S., Ringwald M., Klempnauer K. H. Synergistic activation of the chicken mim-1 gene by v-myb and C/EBP transcription factors. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2027–2038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J., Young F., Bottaro A., Stewart V., Smith R. K., Alt F. W. Mutations of the intronic IgH enhancer and its flanking sequences differentially affect accessibility of the JH locus. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4635–4645. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06152.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cserjesi P., Olson E. N. Myogenin induces the myocyte-specific enhancer binding factor MEF-2 independently of other muscle-specific gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):4854–4862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.4854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorshkind K. Transcriptional control points during lymphopoiesis. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):751–753. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst P., Smale S. T. Combinatorial regulation of transcription II: The immunoglobulin mu heavy chain gene. Immunity. 1995 May;2(5):427–438. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernex C., Capone M., Ferrier P. The V(D)J recombinational and transcriptional activities of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain intronic enhancer can be mediated through distinct protein-binding sites in a transgenic substrate. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3217–3226. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genetta T., Ruezinsky D., Kadesch T. Displacement of an E-box-binding repressor by basic helix-loop-helix proteins: implications for B-cell specificity of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6153–6163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gstaiger M., Knoepfel L., Georgiev O., Schaffner W., Hovens C. M. A B-cell coactivator of octamer-binding transcription factors. Nature. 1995 Jan 26;373(6512):360–362. doi: 10.1038/373360a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. W., Adami G. R., Wei N., Keyomarsi K., Elledge S. J. The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):805–816. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90499-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junker S., Pedersen S., Schreiber E., Matthias P. Extinction of an immunoglobulin kappa promoter in cell hybrids is mediated by the octamer motif and correlates with suppression of Oct-2 expression. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):467–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90528-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Harris A. W., Adams J. M. Transcripts of the immunoglobulin C mu gene vary in structure and splicing during lymphoid development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7400–7404. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- König H., Pfisterer P., Corcoran L. M., Wirth T. Identification of CD36 as the first gene dependent on the B-cell differentiation factor Oct-2. Genes Dev. 1995 Jul 1;9(13):1598–1607. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.13.1598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. S., Hayakawa K., Hardy R. R. The regulated expression of B lineage associated genes during B cell differentiation in bone marrow and fetal liver. J Exp Med. 1993 Sep 1;178(3):951–960. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.3.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman S. A., Hines M. D., Bergsagel P. L., Kuehl W. M., Eckhardt L. A. Coordinate silencing of myeloma-specific genes in myeloma x T lymphoma hybrids. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2588–2600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H., Grosschedl R. Failure of B-cell differentiation in mice lacking the transcription factor EBF. Nature. 1995 Jul 20;376(6537):263–267. doi: 10.1038/376263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Roeder R. G. Cloning, functional characterization, and mechanism of action of the B-cell-specific transcriptional coactivator OCA-B. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):4115–4124. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.8.4115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers F., Rolink A., Grawunder U., Winkler T. H., Karasuyama H., Ghia P., Andersson J. Positive and negative selection events during B lymphopoiesis. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Apr;7(2):214–227. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melotti P., Calabretta B. Ets-2 and c-Myb act independently in regulating expression of the hematopoietic stem cell antigen CD34. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25303–25309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molkentin J. D., Black B. L., Martin J. F., Olson E. N. Cooperative activation of muscle gene expression by MEF2 and myogenic bHLH proteins. Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1125–1136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90139-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Characterization of productive and sterile transcripts from the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: processing of micron and muS mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1317–1332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ness S. A., Kowenz-Leutz E., Casini T., Graf T., Leutz A. Myb and NF-M: combinatorial activators of myeloid genes in heterologous cell types. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):749–759. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peverali F. A., Ramqvist T., Saffrich R., Pepperkok R., Barone M. V., Philipson L. Regulation of G1 progression by E2A and Id helix-loop-helix proteins. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4291–4301. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06749.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quong M. W., Massari M. E., Zwart R., Murre C. A new transcriptional-activation motif restricted to a class of helix-loop-helix proteins is functionally conserved in both yeast and mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;13(2):792–800. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.2.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radomska H. S., Shen C. P., Kadesch T., Eckhardt L. A. Constitutively expressed Oct-2 prevents immunoglobulin gene silencing in myeloma x T cell hybrids. Immunity. 1994 Nov;1(8):623–634. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(94)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M. S., Corcoran L. M., Baltimore D. Virus-transformed pre-B cells show ordered activation but not inactivation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangement and transcription. J Exp Med. 1991 Mar 1;173(3):711–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M., Voronova A., Baltimore D. Helix-loop-helix transcription factor E47 activates germ-line immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene transcription and rearrangement in a pre-T-cell line. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1367–1376. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer B. W., Blakely B. T., Darlington G. J., Blau H. M. Effect of cell history on response to helix-loop-helix family of myogenic regulators. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):454–458. doi: 10.1038/344454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott E. W., Simon M. C., Anastasi J., Singh H. Requirement of transcription factor PU.1 in the development of multiple hematopoietic lineages. Science. 1994 Sep 9;265(5178):1573–1577. doi: 10.1126/science.8079170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serwe M., Sablitzky F. V(D)J recombination in B cells is impaired but not blocked by targeted deletion of the immunoglobulin heavy chain intron enhancer. EMBO J. 1993 Jun;12(6):2321–2327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05886.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen C. P., Kadesch T. B-cell-specific DNA binding by an E47 homodimer. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):4518–4524. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.8.4518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Lieberman S., Eckhardt L. A. The octamer/mu E4 region of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer mediates gene repression in myeloma x T-lymphoma hybrids. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3530–3540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H. Genetic analysis of transcription factors implicated in B lymphocyte development. Immunol Res. 1994;13(4):280–290. doi: 10.1007/BF02935619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strubin M., Newell J. W., Matthias P. OBF-1, a novel B cell-specific coactivator that stimulates immunoglobulin promoter activity through association with octamer-binding proteins. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90500-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su L. K., Kadesch T. The immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer functions as the promoter for I mu sterile transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2619–2624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo T., Nishikawa S., Ohno N., Akiyama N., Tamakoshi M., Yoshida H., Nishikawa S. Expression and function of the interleukin 7 receptor in murine lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9125–9129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun X. H., Baltimore D. An inhibitory domain of E12 transcription factor prevents DNA binding in E12 homodimers but not in E12 heterodimers. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):459–470. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90653-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapscott S. J., Thayer M. J., Weintraub H. Deficiency in rhabdomyosarcomas of a factor required for MyoD activity and myogenesis. Science. 1993 Mar 5;259(5100):1450–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.8383879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tontonoz P., Hu E., Spiegelman B. M. Stimulation of adipogenesis in fibroblasts by PPAR gamma 2, a lipid-activated transcription factor. Cell. 1994 Dec 30;79(7):1147–1156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechsler D. S., Papoulas O., Dang C. V., Kingston R. E. Differential binding of c-Myc and Max to nucleosomal DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4097–4107. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Genetta T., Kadesch T. Tissue-specific gene activation by MyoD: determination of specificity by cis-acting repression elements. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 15;8(18):2203–2211. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.18.2203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. B., Kiledjian M., Shen C. P., Benezra R., Zwollo P., Dymecki S. M., Desiderio S. V., Kadesch T. Repression of immunoglobulin enhancers by the helix-loop-helix protein Id: implications for B-lymphoid-cell development. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;11(12):6185–6191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.12.6185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Workman J. L., Taylor I. C., Kingston R. E. Activation domains of stably bound GAL4 derivatives alleviate repression of promoters by nucleosomes. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90237-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Z., Xie Y., Bucher N. L., Farmer S. R. Conditional ectopic expression of C/EBP beta in NIH-3T3 cells induces PPAR gamma and stimulates adipogenesis. Genes Dev. 1995 Oct 1;9(19):2350–2363. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.19.2350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Porton B., Shen L. Y., Eckhardt L. A. Role of the octamer motif in hybrid cell extinction of immunoglobulin gene expression: extinction is dominant in a two enhancer system. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Soriano P., Weintraub H. The helix-loop-helix gene E2A is required for B cell formation. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):875–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]