Abstract
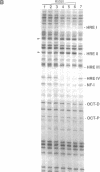
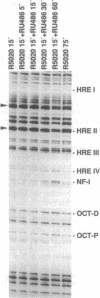
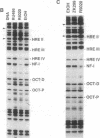
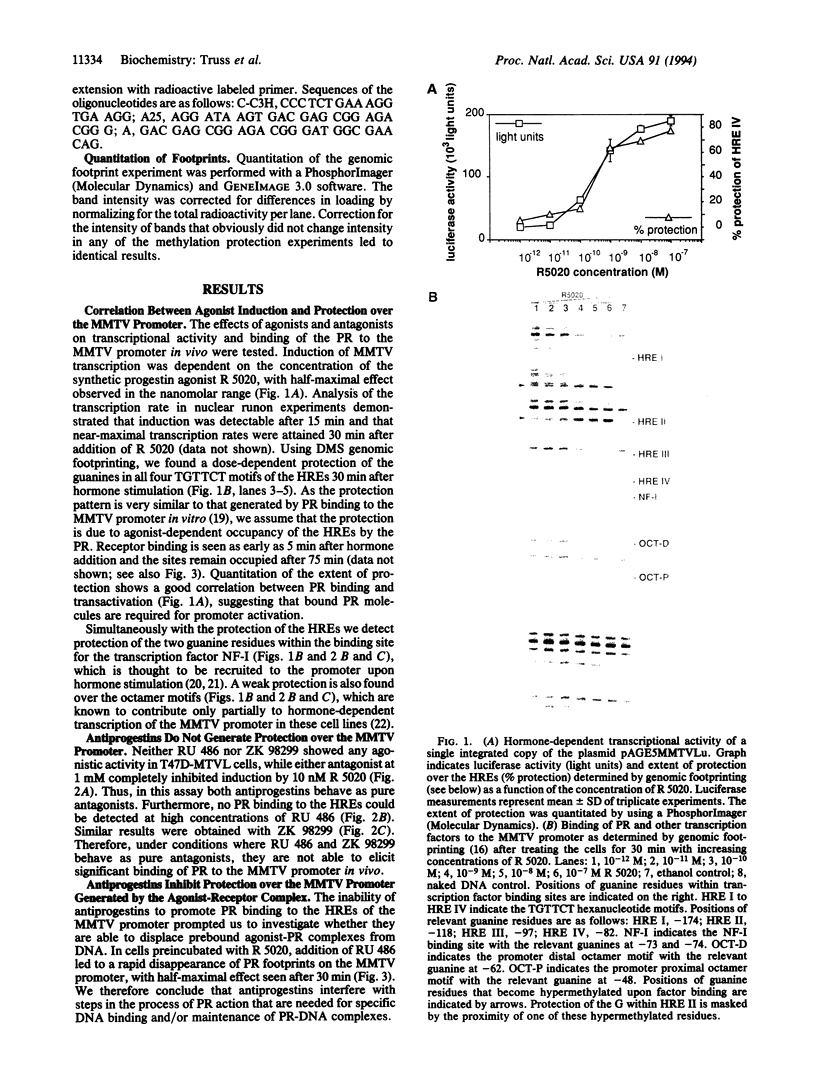
Antiprogestins inhibit progesterone action by competing for binding to the progesterone receptor and are potentially important pharmaceuticals in fertility control and cancer therapy. Why the complex of antiprogestins and progesterone receptor is functionally inactive is unclear. Present models are based on indirect evidence, such as transfection competition assays and in vitro DNA binding studies, partly because of difficulties in visualizing the receptor bound to DNA in vivo. Here we used genomic footprinting analysis to show ligand-dependent binding of endogenous progesterone receptor to the hormone responsive elements (HREs) of a chromosomally integrated mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat in a human mammary carcinoma cell line. The antiprogestins RU 486 and ZK 98299 do not promote binding of the progesterone receptor to this natural HRE in vivo, even at concentrations that completely inhibit the agonistic effects of potent synthetic progestins. Moreover, antiprogestins cause a rapid disappearance of the agonist-induced progesterone receptor footprint. We conclude that antiprogestins interfere with receptor function by preventing its specific DNA binding.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allan G. F., Leng X., Tsai S. Y., Weigel N. L., Edwards D. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Hormone and antihormone induce distinct conformational changes which are central to steroid receptor activation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19513–19520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagchi M. K., Elliston J. F., Tsai S. Y., Edwards D. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Steroid hormone-dependent interaction of human progesterone receptor with its target enhancer element. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1221–1229. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. A., Weigel N. L., Edwards D. P. Effects of hormone and cellular modulators of protein phosphorylation on transcriptional activity, DNA binding, and phosphorylation of human progesterone receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Apr;6(4):607–620. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.4.1316549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. A., Weigel N. L., Moyer M. L., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. The progesterone antagonist RU486 acquires agonist activity upon stimulation of cAMP signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4441–4445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck C. A., Weigel N. L., Moyer M. L., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. The progesterone antagonist RU486 acquires agonist activity upon stimulation of cAMP signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4441–4445. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkenstam A., Glaumann H., Gustafsson J. A. Unspecific and sequence-specific deoxyribonucleic acid binding of the partially purified human progesterone receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jun;2(6):571–578. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-6-571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Kalff M., Franke S., Scheidereit C., Beato M. Ubiquitous transcription factor OTF-1 mediates induction of the MMTV promoter through synergistic interaction with hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):565–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90240-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemeier U., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L., Beato M. Nuclear factor I acts as a transcription factor on the MMTV promoter but competes with steroid hormone receptors for DNA binding. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2233–2239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalepakis G., Arnemann J., Slater E., Brüller H. J., Gross B., Beato M. Differential gene activation by glucocorticoids and progestins through the hormone regulatory element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):371–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90157-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Riegel A. T., Hager G. L. Steroid-dependent interaction of transcription factors with the inducible promoter of mouse mammary tumor virus in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):261–270. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90429-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMarzo A. M., Oñate S. A., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. Effects of the steroid antagonist RU486 on dimerization of the human progesterone receptor. Biochemistry. 1992 Nov 3;31(43):10491–10501. doi: 10.1021/bi00158a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delabre K., Guiochon-Mantel A., Milgrom E. In vivo evidence against the existence of antiprogestins disrupting receptor binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4421–4425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards D. P., Kühnel B., Estes P. A., Nordeen S. K. Human progesterone receptor binding to mouse mammary tumor virus deoxyribonucleic acid: dependence on hormone and nonreceptor nuclear factor(s). Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Feb;3(2):381–391. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-2-381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronemeyer H., Meyer M. E., Bocquel M. T., Kastner P., Turcotte B., Chambon P. Progestin receptors: isoforms and antihormone action. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1991;40(1-3):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(91)90192-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groyer A., Schweizer-Groyer G., Cadepond F., Mariller M., Baulieu E. E. Antiglucocorticosteroid effects suggest why steroid hormone is required for receptors to bind DNA in vivo but not in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):624–626. doi: 10.1038/328624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiochon-Mantel A., Loosfelt H., Ragot T., Bailly A., Atger M., Misrahi M., Perricaudet M., Milgrom E. Receptors bound to antiprogestin from abortive complexes with hormone responsive elements. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):695–698. doi: 10.1038/336695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Zava D. T., Thilagar A. K., Jensen E. M., McGuire W. L. Steroid receptor analyses of nine human breast cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2434–2437. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klehr D., Maass K., Bode J. Scaffold-attached regions from the human interferon beta domain can be used to enhance the stable expression of genes under the control of various promoters. Biochemistry. 1991 Feb 5;30(5):1264–1270. doi: 10.1021/bi00219a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Cato A. C., Henderson D., Ryffel G. U. Two types of antiprogestins identified by their differential action in transcriptionally active extracts from T47D cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 25;19(6):1227–1234. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.6.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M. E., Pornon A., Ji J. W., Bocquel M. T., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Agonistic and antagonistic activities of RU486 on the functions of the human progesterone receptor. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3923–3932. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordeen S. K., Bona B. J., Moyer M. L. Latent agonist activity of the steroid antagonist, RU486, is unmasked in cells treated with activators of protein kinase A. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Jun;7(6):731–742. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.6.8395651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer G. P., Steigerwald S. D., Mueller P. R., Wold B., Riggs A. D. Genomic sequencing and methylation analysis by ligation mediated PCR. Science. 1989 Nov 10;246(4931):810–813. doi: 10.1126/science.2814502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Power R. F., Mani S. K., Codina J., Conneely O. M., O'Malley B. W. Dopaminergic and ligand-independent activation of steroid hormone receptors. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1636–1639. doi: 10.1126/science.1749936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Dull T. J., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. A chimaeric receptor allows insulin to stimulate tyrosine kinase activity of epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1986 Nov 6;324(6092):68–70. doi: 10.1038/324068a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaud G., Roux J., Pictet R., Grange T. In vivo footprinting of rat TAT gene: dynamic interplay between the glucocorticoid receptor and a liver-specific factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90370-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sartorius C. A., Tung L., Takimoto G. S., Horwitz K. B. Antagonist-occupied human progesterone receptors bound to DNA are functionally switched to transcriptional agonists by cAMP. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9262–9266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer M., Chalepakis G., Willmann T., Beato M. Binding of hormone accelerates the kinetics of glucocorticoid and progesterone receptor binding to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1123–1127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemshedini L., Ji J. W., Brou C., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. In vitro activity of the transcription activation functions of the progesterone receptor. Evidence for intermediary factors. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1834–1839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Archer T. K., Hamlin-Green G., Hager G. L. Newly expressed progesterone receptor cannot activate stable, replicated mouse mammary tumor virus templates but acquires transactivation potential upon continuous expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11202–11206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Conneely O. M., O'Malley B. W. Modulation of the ligand-independent activation of the human estrogen receptor by hormone and antihormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6120–6124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truss M., Beato M. Steroid hormone receptors: interaction with deoxyribonucleic acid and transcription factors. Endocr Rev. 1993 Aug;14(4):459–479. doi: 10.1210/edrv-14-4-459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung L., Mohamed M. K., Hoeffler J. P., Takimoto G. S., Horwitz K. B. Antagonist-occupied human progesterone B-receptors activate transcription without binding to progesterone response elements and are dominantly inhibited by A-receptors. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Oct;7(10):1256–1265. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.10.8123133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vegeto E., Allan G. F., Schrader W. T., Tsai M. J., McDonnell D. P., O'Malley B. W. The mechanism of RU486 antagonism is dependent on the conformation of the carboxy-terminal tail of the human progesterone receptor. Cell. 1992 May 15;69(4):703–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90234-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vegeto E., Shahbaz M. M., Wen D. X., Goldman M. E., O'Malley B. W., McDonnell D. P. Human progesterone receptor A form is a cell- and promoter-specific repressor of human progesterone receptor B function. Mol Endocrinol. 1993 Oct;7(10):1244–1255. doi: 10.1210/mend.7.10.8264658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weigel N. L., Beck C. A., Estes P. A., Prendergast P., Altmann M., Christensen K., Edwards D. P. Ligands induce conformational changes in the carboxyl-terminus of progesterone receptors which are detected by a site-directed antipeptide monoclonal antibody. Mol Endocrinol. 1992 Oct;6(10):1585–1597. doi: 10.1210/mend.6.10.1448113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willmann T., Beato M. Steroid-free glucocorticoid receptor binds specifically to mouse mammary tumour virus DNA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):688–691. doi: 10.1038/324688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Ashry D., Oñate S. A., Nordeen S. K., Edwards D. P. Human progesterone receptor complexed with the antagonist RU 486 binds to hormone response elements in a structurally altered form. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Oct;3(10):1545–1558. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-10-1545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]