Abstract
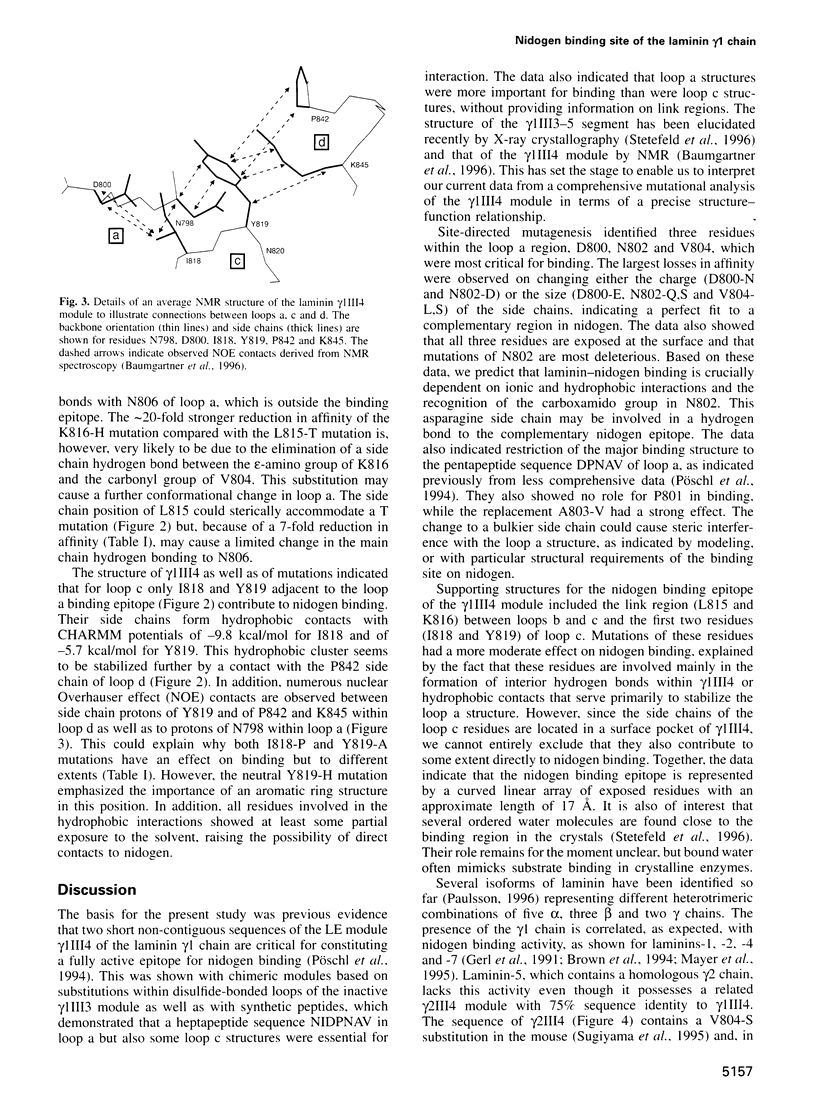
A precise molecular map of the nidogen binding site of laminins was obtained by site-directed mutagenesis and structural analysis of the 56 residue LE module gamma1III4 of their gamma1 chain. This demonstrated the crucial importance of the sequence DPNAV (position 800-804) in the disulfide-bonded loop a, with major contributions made by all residues except P801. Different substitutions of these residues emphasized the essential role of the negative charge (D800) and carboxamide group (N802) as well as their spacings and hydrophobic contacts (V804) for interaction, and predict direct contacts of these three residues with a complementary binding region of nidogen. An inactivating A803-V substitution, however, may lead to a distorted loop structure. A lower but still significant contribution originates from the non-contiguous link/loop c sequence LKCIY (positions 815-819) which is spatially close to the loop a sequence. The link residues (L815 and K816) provide main chain hydrogen bonds to N806 and a side chain hydrogen bond to the V804 carbonyl and thus stabilize the conformation of loop a. The side chains of I818 and Y819 together with P842 from loop d form hydrophobic contacts that provide further stability but could possibly also participate in direct ligation. The nidogen binding epitope is therefore localized on a narrow ridge and has a length of approximately 17 angstroms. The data also indicate a strong conservation of the epitope in the laminin gamma1 chains of several invertebrates.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumgartner R., Czisch M., Mayer U., Pöschl E., Huber R., Timpl R., Holak T. A. Structure of the nidogen binding LE module of the laminin gamma1 chain in solution. J Mol Biol. 1996 Apr 5;257(3):658–668. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. C., Wiedemann H., Timpl R. Protein binding and cell adhesion properties of two laminin isoforms (AmB1eB2e, AmB1sB2e) from human placenta. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):329–338. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covey T. R., Bonner R. F., Shushan B. I., Henion J. The determination of protein, oligonucleotide and peptide molecular weights by ion-spray mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 1988 Nov;2(11):249–256. doi: 10.1002/rcm.1290021111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M. Role of laminin-nidogen complexes in basement membrane formation during embryonic development. Experientia. 1995 Sep 29;51(9-10):901–913. doi: 10.1007/BF01921740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Ekblom M., Fecker L., Klein G., Zhang H. Y., Kadoya Y., Chu M. L., Mayer U., Timpl R. Role of mesenchymal nidogen for epithelial morphogenesis in vitro. Development. 1994 Jul;120(7):2003–2014. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fenn J. B., Mann M., Meng C. K., Wong S. F., Whitehouse C. M. Electrospray ionization for mass spectrometry of large biomolecules. Science. 1989 Oct 6;246(4926):64–71. doi: 10.1126/science.2675315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. W., Mayer U., Nischt R., Aumailley M., Reinhardt D., Wiedemann H., Mann K., Timpl R., Krieg T., Engel J. Recombinant nidogen consists of three globular domains and mediates binding of laminin to collagen type IV. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3137–3146. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerl M., Mann K., Aumailley M., Timpl R. Localization of a major nidogen-binding site to domain III of laminin B2 chain. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;202(1):167–174. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16358.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallunki P., Sainio K., Eddy R., Byers M., Kallunki T., Sariola H., Beck K., Hirvonen H., Shows T. B., Tryggvason K. A truncated laminin chain homologous to the B2 chain: structure, spatial expression, and chromosomal assignment. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):679–693. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer U., Aumailley M., Mann K., Timpl R., Engel J. Calcium-dependent binding of basement membrane protein BM-40 (osteonectin, SPARC) to basement membrane collagen type IV. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 23;198(1):141–150. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15996.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakae H., Sugano M., Ishimori Y., Endo T., Obinata T. Ascidian entactin/nidogen. Implication of evolution by shuffling two kinds of cysteine-rich motifs. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Apr 1;213(1):11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17729.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsson M., Aumailley M., Deutzmann R., Timpl R., Beck K., Engel J. Laminin-nidogen complex. Extraction with chelating agents and structural characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):11–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13476.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikkarainen T., Kallunki T., Tryggvason K. Human laminin B2 chain. Comparison of the complete amino acid sequence with the B1 chain reveals variability in sequence homology between different structural domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 15;263(14):6751–6758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöschl E., Fox J. W., Block D., Mayer U., Timpl R. Two non-contiguous regions contribute to nidogen binding to a single EGF-like motif of the laminin gamma 1 chain. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3741–3747. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06683.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Göhring W., Pan T. C., Chu M. L., Timpl R. Binding of mouse and human fibulin-2 to extracellular matrix ligands. J Mol Biol. 1995 Dec 15;254(5):892–899. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetefeld J., Mayer U., Timpl R., Huber R. Crystal structure of three consecutive laminin-type epidermal growth factor-like (LE) modules of laminin gamma1 chain harboring the nidogen binding site. J Mol Biol. 1996 Apr 5;257(3):644–657. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiyama S., Utani A., Yamada S., Kozak C. A., Yamada Y. Cloning and expression of the mouse laminin gamma 2 (B2t) chain, a subunit of epithelial cell laminin. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Feb 15;228(1):120–128. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20239.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vailly J., Verrando P., Champliaud M. F., Gerecke D., Wagman D. W., Baudoin C., Aberdam D., Burgeson R., Bauer E., Ortonne J. P. The 100-kDa chain of nicein/kalinin is a laminin B2 chain variant. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):209–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19932.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





