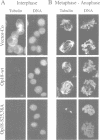
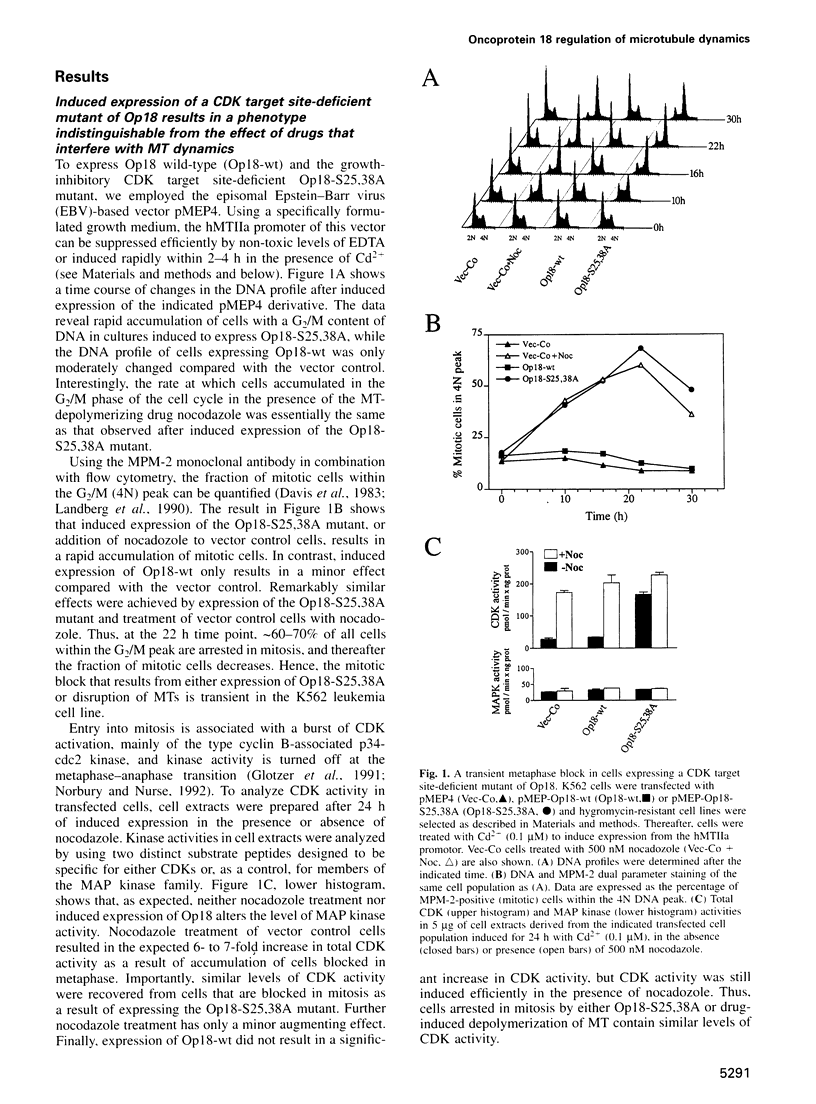
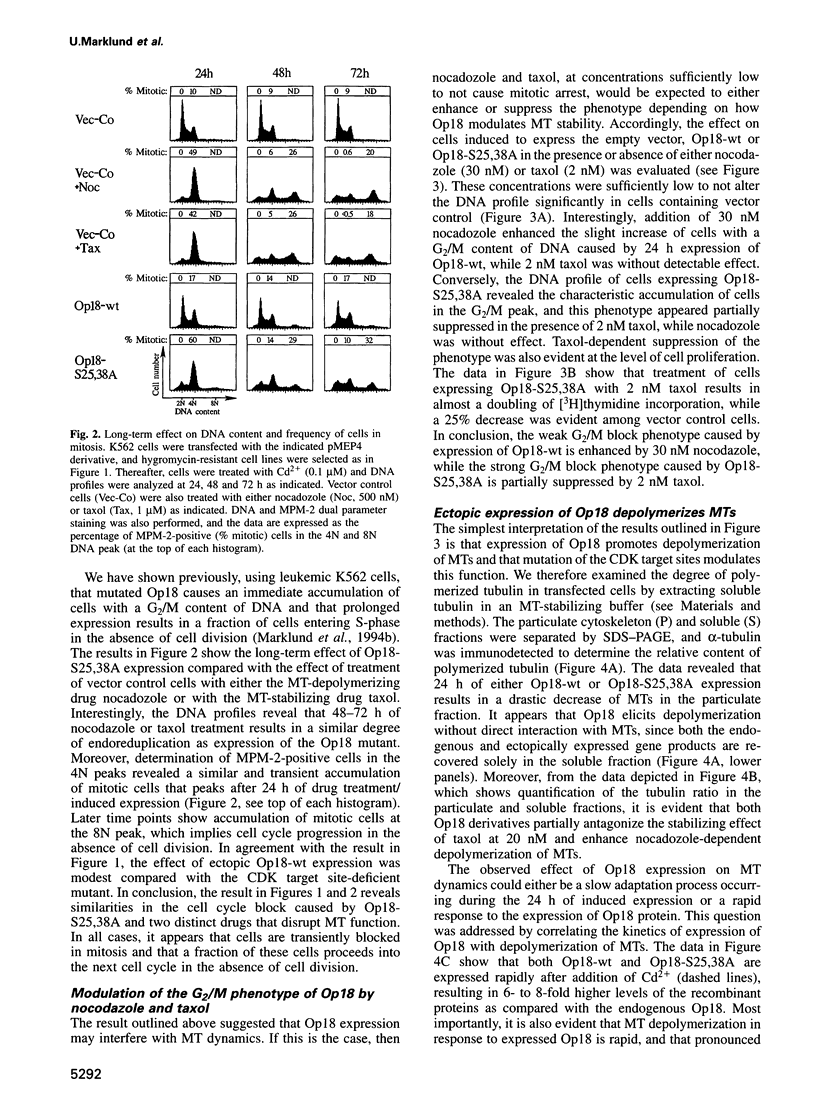
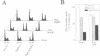Abstract
Oncoprotein 18 (Op18, also termed p19, p18, prosolin or stathmin) is a cytosolic protein of previously unknown function. Phosphorylation of Op18 is cell cycle regulated by cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs), and expression of a 'CDK target site-deficient mutant' results in a phenotype indicative of a role for Op18 during mitosis. This phenotype is compatible with the idea that Op18 is a phosphorylation-responsive regulator of microtubule (MT) dynamics. Therefore, in this study, we analyzed MTs in cells induced to express either wild-type or mutated Op18. The results showed that wild-type Op18 and a CDK target site mutant both efficiently elicited rapid depolymerization of MTs. This result contrasts with clear-cut differences in their cell cycle phenotypes. Morphological analysis of MTs explained this apparent discrepancy: while interphase MTs were depolymerized in cells expressing either Op18 derivative, apparently normal mitotic spindles were formed only in cells overexpressing wild-type Op18. This result correlates with our finding that only mutated Op18 causes a block during mitosis. Hence, we conclude that Op18 decreases MT stability and that this activity of Op18 is subject to cell cycle regulation by CDKs.
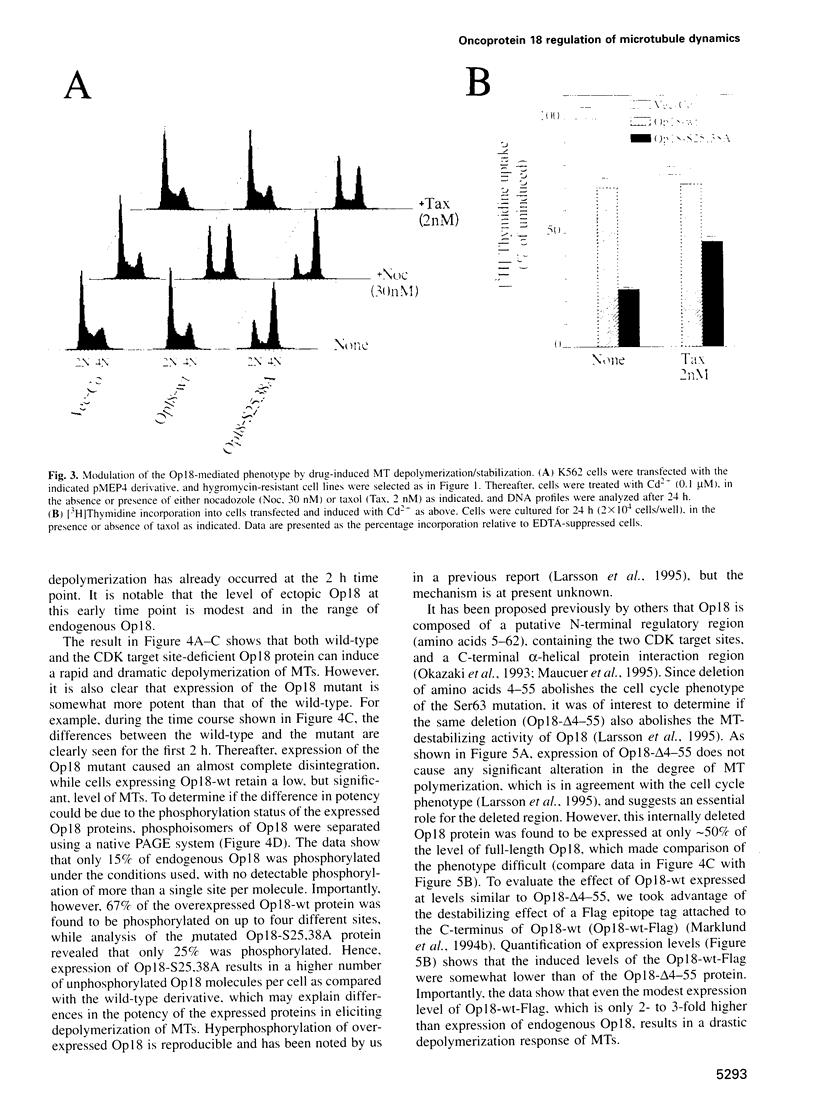
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belmont L. D., Mitchison T. J. Identification of a protein that interacts with tubulin dimers and increases the catastrophe rate of microtubules. Cell. 1996 Feb 23;84(4):623–631. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beretta L., Dobránsky T., Sobel A. Multiple phosphorylation of stathmin. Identification of four sites phosphorylated in intact cells and in vitro by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase and p34cdc2. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 25;268(27):20076–20084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brattsand G., Marklund U., Nylander K., Roos G., Gullberg M. Cell-cycle-regulated phosphorylation of oncoprotein 18 on Ser16, Ser25 and Ser38. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Mar 1;220(2):359–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb18632.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brattsand G., Roos G., Marklund U., Ueda H., Landberg G., Nånberg E., Sideras P., Gullberg M. Quantitative analysis of the expression and regulation of an activation-regulated phosphoprotein (oncoprotein 18) in normal and neoplastic cells. Leukemia. 1993 Apr;7(4):569–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H. L., Fuldner R., McDuffie E., Braverman R. A specific defect of prosolin phosphorylation in T cell leukemic lymphoblasts is associated with impaired down-regulation of DNA synthesis. J Immunol. 1990 Aug 15;145(4):1205–1213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis F. M., Tsao T. Y., Fowler S. K., Rao P. N. Monoclonal antibodies to mitotic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2926–2930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Boutterin M. C., Sobel A. Phosphorylation of stathmin and other proteins related to nerve growth factor-induced regulation of PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11650–11655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doye V., Soubrier F., Bauw G., Boutterin M. C., Beretta L., Koppel J., Vandekerckhove J., Sobel A. A single cDNA encodes two isoforms of stathmin, a developmentally regulated neuron-enriched phosphoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12134–12137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich B., Grönberg H., Landström M., Gullberg M., Bergh A. Differentiation-stage specific expression of oncoprotein 18 in human and rat prostatic adenocarcinoma. Prostate. 1995 Aug;27(2):102–109. doi: 10.1002/pros.2990270207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotzer M., Murray A. W., Kirschner M. W. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):132–138. doi: 10.1038/349132a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groger R. K., Morrow D. M., Tykocinski M. L. Directional antisense and sense cDNA cloning using Epstein-Barr virus episomal expression vectors. Gene. 1989 Sep 30;81(2):285–294. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90189-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg M., Noreus K., Brattsand G., Friedrich B., Shingler V. Purification and characterization of a 19-kilodalton intracellular protein. An activation-regulated putative protein kinase C substrate of T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17499–17505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanash S. M., Strahler J. R., Kuick R., Chu E. H., Nichols D. Identification of a polypeptide associated with the malignant phenotype in acute leukemia. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):12813–12815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kung A. L., Sherwood S. W., Schimke R. T. Cell line-specific differences in the control of cell cycle progression in the absence of mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9553–9557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labdon J. E., Nieves E., Schubart U. K. Analysis of phosphoprotein p19 by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Identification of two proline-directed serine phosphorylation sites and a blocked amino terminus. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3506–3513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landberg G., Tan E. M., Roos G. Flow cytometric multiparameter analysis of proliferating cell nuclear antigen/cyclin and Ki-67 antigen: a new view of the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Mar;187(1):111–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90124-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson N., Melander H., Marklund U., Osterman O., Gullberg M. G2/M transition requires multisite phosphorylation of oncoprotein 18 by two distinct protein kinase systems. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 9;270(23):14175–14183. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.14175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo X. N., Mookerjee B., Ferrari A., Mistry S., Atweh G. F. Regulation of phosphoprotein p18 in leukemic cells. Cell cycle regulated phosphorylation by p34cdc2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 8;269(14):10312–10318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund U., Brattsand G., Osterman O., Ohlsson P. I., Gullberg M. Multiple signal transduction pathways induce phosphorylation of serines 16, 25, and 38 of oncoprotein 18 in T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 5;268(34):25671–25680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund U., Brattsand G., Shingler V., Gullberg M. Serine 25 of oncoprotein 18 is a major cytosolic target for the mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):15039–15047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund U., Larsson N., Brattsand G., Osterman O., Chatila T. A., Gullberg M. Serine 16 of oncoprotein 18 is a major cytosolic target for the Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase-Gr. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Oct 1;225(1):53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.00053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund U., Osterman O., Melander H., Bergh A., Gullberg M. The phenotype of a "Cdc2 kinase target site-deficient" mutant of oncoprotein 18 reveals a role of this protein in cell cycle control. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 2;269(48):30626–30635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maucuer A., Camonis J. H., Sobel A. Stathmin interaction with a putative kinase and coiled-coil-forming protein domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3100–3104. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melhem R. F., Zhu X. X., Hailat N., Strahler J. R., Hanash S. M. Characterization of the gene for a proliferation-related phosphoprotein (oncoprotein 18) expressed in high amounts in acute leukemia. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17747–17753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minotti A. M., Barlow S. B., Cabral F. Resistance to antimitotic drugs in Chinese hamster ovary cells correlates with changes in the level of polymerized tubulin. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3987–3994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norbury C., Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–470. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.61.070192.002301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki T., Yoshida B. N., Avraham K. B., Wang H., Wuenschell C. W., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Anderson D. J., Mori N. Molecular diversity of the SCG10/stathmin gene family in the mouse. Genomics. 1993 Nov;18(2):360–373. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L., Palazzo R. E. Colcemid and the mitotic cycle. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jul;102(Pt 3):387–392. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.3.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos G., Brattsand G., Landberg G., Marklund U., Gullberg M. Expression of oncoprotein 18 in human leukemias and lymphomas. Leukemia. 1993 Oct;7(10):1538–1546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubart U. K., Banerjee M. D., Eng J. Homology between the cDNAs encoding phosphoprotein p19 and SCG10 reveals a novel mammalian gene family preferentially expressed in developing brain. DNA. 1989 Jul-Aug;8(6):389–398. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X. X., Kozarsky K., Strahler J. R., Eckerskorn C., Lottspeich F., Melhem R., Lowe J., Fox D. A., Hanash S. M., Atweh G. F. Molecular cloning of a novel human leukemia-associated gene. Evidence of conservation in animal species. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14556–14560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]