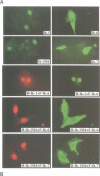
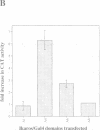
Abstract
The Ikaros gene, an essential regulator of lymphocyte differentiation, encodes, by means of differential splicing, protein isoforms with a distinct number of Kruppel-type zinc fingers organized in two domains. Deletion of the N-terminal zinc finger domain responsible for the sequence-specific DNA binding of the Ikaros proteins results in an early and complete arrest in lymphocyte development in homozygous mutant mice. In sharp contrast, heterozygotes reliably develop T cell leukemias and lymphomas. Here we show that the C-terminal zinc finger domain present in all of the Ikaros wild-type and mutant isoforms is responsible for their stable interactions off DNA and plays a pivotal role in determining their overall activity. Mutations in the C-terminal zinc fingers which ablate Ikaros protein interactions have a dramatic effect on the ability of these proteins to bind DNA and activate transcription. Therefore, interactions between Ikaros isoforms with an intact DNA binding domain are essential for their function. In contrast, interactions between isoforms with and without a DNA binding domain result in Ikaros complexes that do not bind DNA and, as a consequence, cannot activate transcription. Dominant-negative Ikaros isoforms are generated in smaller amounts by the wild-type Ikaros gene but are also produced exclusively by the N-terminally deleted Ikaros locus. Given these data, we propose that interactions between Ikaros isoforms are essential for normal progression through the lymphoid pathways. Mutations in the Ikaros gene that prevent Ikaros protein interactions or which change the relative ratio of DNA to non-DNA binding isoforms have profound effects in both lymphoid specification and homeostasis.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cavenee W. K., Dryja T. P., Phillips R. A., Benedict W. F., Godbout R., Gallie B. L., Murphree A. L., Strong L. C., White R. L. Expression of recessive alleles by chromosomal mechanisms in retinoblastoma. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):779–784. doi: 10.1038/305779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crossley M., Merika M., Orkin S. H. Self-association of the erythroid transcription factor GATA-1 mediated by its zinc finger domains. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2448–2456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dryja T. P., Rapaport J. M., Joyce J. M., Petersen R. A. Molecular detection of deletions involving band q14 of chromosome 13 in retinoblastomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7391–7394. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. K., Murphree A. L., T'Ang A., Qian J., Hinrichs S. H., Benedict W. F. Structural evidence for the authenticity of the human retinoblastoma gene. Science. 1987 Jun 26;236(4809):1657–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.2885916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., Bigby M., Wang J. H., Molnar A., Wu P., Winandy S., Sharpe A. The Ikaros gene is required for the development of all lymphoid lineages. Cell. 1994 Oct 7;79(1):143–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90407-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos K., Moore D. D., Derfler B. Ikaros, an early lymphoid-specific transcription factor and a putative mediator for T cell commitment. Science. 1992 Oct 30;258(5083):808–812. doi: 10.1126/science.1439790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gyuris J., Golemis E., Chertkov H., Brent R. Cdi1, a human G1 and S phase protein phosphatase that associates with Cdk2. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):791–803. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90498-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagman J., Gutch M. J., Lin H., Grosschedl R. EBF contains a novel zinc coordination motif and multiple dimerization and transcriptional activation domains. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 15;14(12):2907–2916. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07290.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahm K., Ernst P., Lo K., Kim G. S., Turck C., Smale S. T. The lymphoid transcription factor LyF-1 is encoded by specific, alternatively spliced mRNAs derived from the Ikaros gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;14(11):7111–7123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.11.7111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N. TBP, a universal eukaryotic transcription factor? Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1291–1308. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Härd T., Kellenbach E., Boelens R., Maler B. A., Dahlman K., Freedman L. P., Carlstedt-Duke J., Yamamoto K. R., Gustafsson J. A., Kaptein R. Solution structure of the glucocorticoid receptor DNA-binding domain. Science. 1990 Jul 13;249(4965):157–160. doi: 10.1126/science.2115209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klug A. Transcription. Opening the gateway. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):486–487. doi: 10.1038/365486a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. The mutational specificity of DNA polymerase-beta during in vitro DNA synthesis. Production of frameshift, base substitution, and deletion mutations. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5787–5796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Gippert G. P., Soman K. V., Case D. A., Wright P. E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):635–637. doi: 10.1126/science.2503871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bookstein R., Hong F., Young L. J., Shew J. Y., Lee E. Y. Human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene: cloning, identification, and sequence. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1394–1399. doi: 10.1126/science.3823889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mastrangelo I. A., Courey A. J., Wall J. S., Jackson S. P., Hough P. V. DNA looping and Sp1 multimer links: a mechanism for transcriptional synergism and enhancement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5670–5674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnár A., Georgopoulos K. The Ikaros gene encodes a family of functionally diverse zinc finger DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8292–8303. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnár A., Wu P., Largespada D. A., Vortkamp A., Scherer S., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Bruns G., Georgopoulos K. The Ikaros gene encodes a family of lymphocyte-restricted zinc finger DNA binding proteins, highly conserved in human and mouse. J Immunol. 1996 Jan 15;156(2):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pascal E., Tjian R. Different activation domains of Sp1 govern formation of multimers and mediate transcriptional synergism. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1646–1656. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of a five-finger GLI-DNA complex: new perspectives on zinc fingers. Science. 1993 Sep 24;261(5129):1701–1707. doi: 10.1126/science.8378770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Rangarajan P. N., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts S. G., Ha I., Maldonado E., Reinberg D., Green M. R. Interaction between an acidic activator and transcription factor TFIIB is required for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1993 Jun 24;363(6431):741–744. doi: 10.1038/363741a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruden D. M., Ma J., Li Y., Wood K., Ptashne M. Generating yeast transcriptional activators containing no yeast protein sequences. Nature. 1991 Mar 21;350(6315):250–252. doi: 10.1038/350250a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer F., Jäckle H. Dimerization and the control of transcription by Krüppel. Nature. 1993 Jul 29;364(6436):454–457. doi: 10.1038/364454a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su W., Jackson S., Tjian R., Echols H. DNA looping between sites for transcriptional activation: self-association of DNA-bound Sp1. Genes Dev. 1991 May;5(5):820–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.5.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis A., Hagman J., Hwang L., Grosschedl R. Purification of early-B-cell factor and characterization of its DNA-binding specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3392–3400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winandy S., Wu P., Georgopoulos K. A dominant mutation in the Ikaros gene leads to rapid development of leukemia and lymphoma. Cell. 1995 Oct 20;83(2):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zechel C., Shen X. Q., Chambon P., Gronemeyer H. Dimerization interfaces formed between the DNA binding domains determine the cooperative binding of RXR/RAR and RXR/TR heterodimers to DR5 and DR4 elements. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1414–1424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zervos A. S., Gyuris J., Brent R. Mxi1, a protein that specifically interacts with Max to bind Myc-Max recognition sites. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90662-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]