Abstract
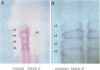
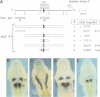
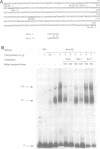
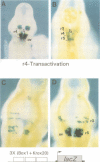
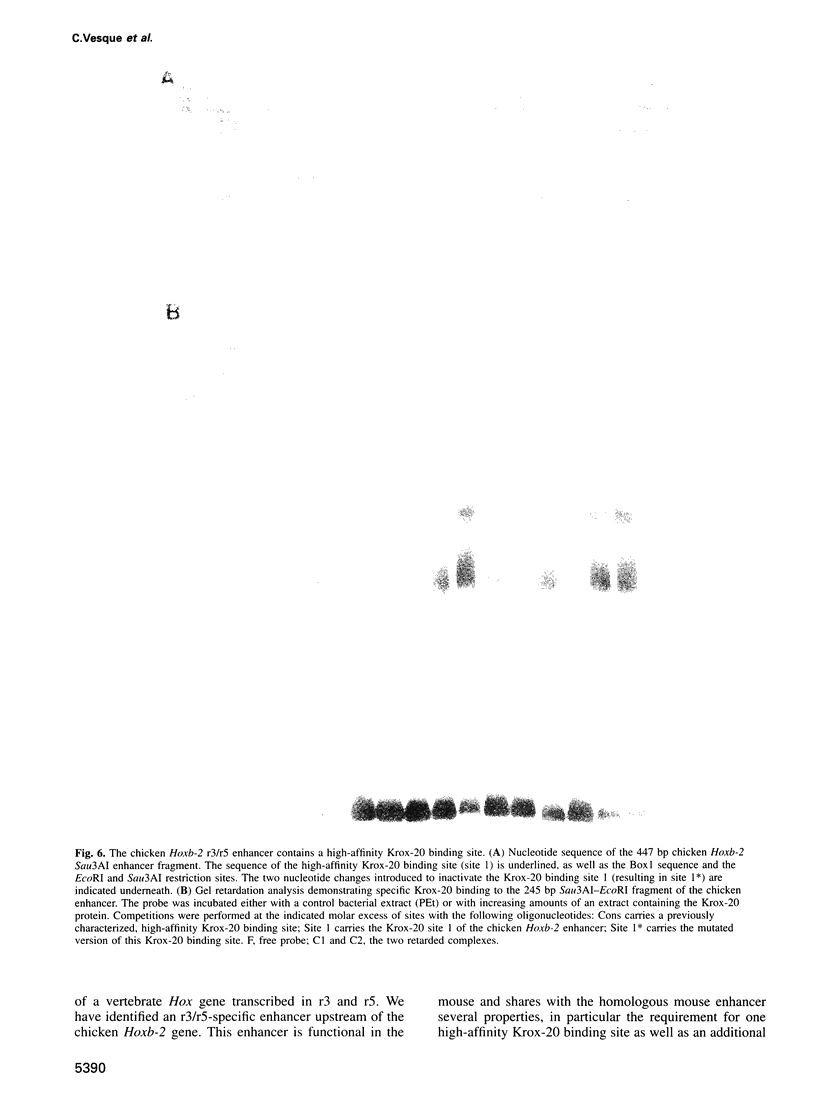
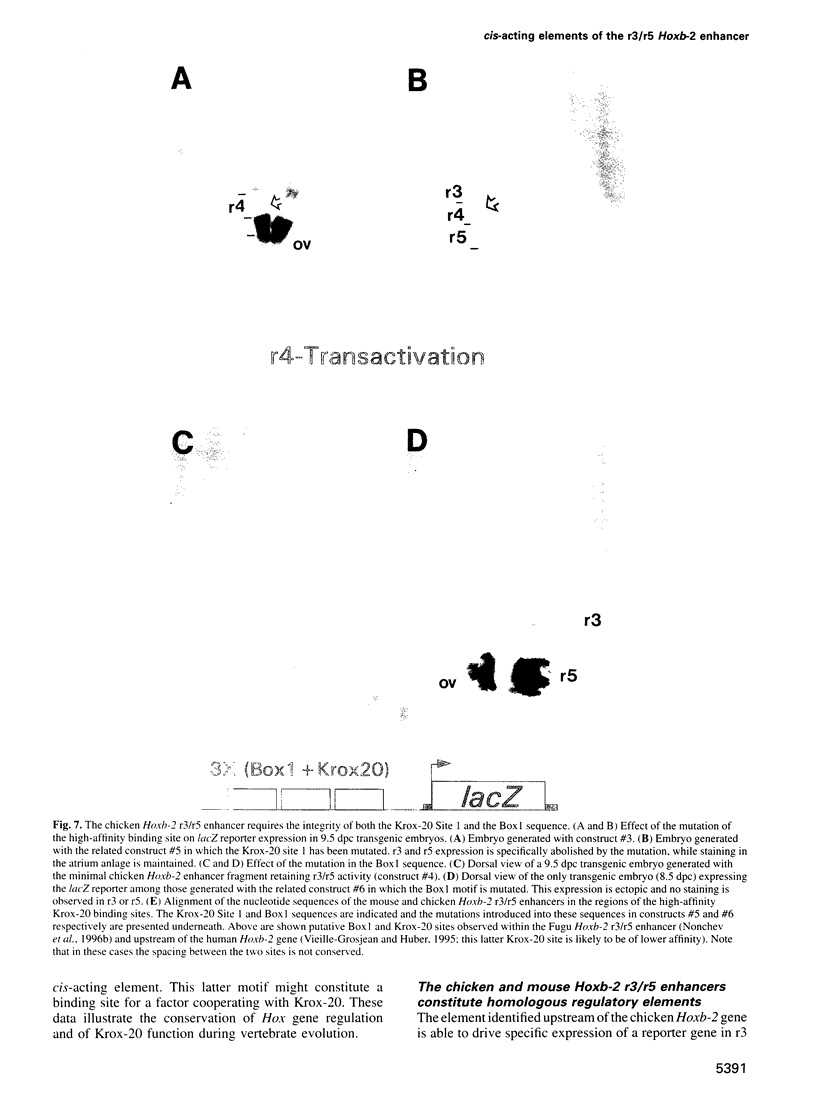
Segmentation is a key feature of the development of the vertebrate hindbrain where it involves the generation of repetitive morphological units termed rhombomeres (r). Hox genes are likely to play an essential role in the specification of segmental identity and we have been investigating their regulation. We show here that the mouse and chicken Hoxb-2 genes are dependent for their expression in r3 and r5 on homologous enhancer elements and on binding to this enhancer of the r3/r5-specific transcriptional activator Krox-20. Among the three Krox-20 binding sites of the mouse Hoxb-2 enhancer, only the high-affinity site is absolutely necessary for activity. In contrast, we have identified an additional cis-acting element, Box1, essential for r3/r5 enhancer activity. It is conserved both in sequence and in position respective to the high-affinity Krox-20 binding site within the mouse and chicken enhancers. Furthermore, a short 44 bp sequence spanning the Box1 and Krox-20 sites can act as an r3/r5 enhancer when oligomerized. Box1 may therefore constitute a recognition sequence for another factor cooperating with Krox-20. Taken together, these data demonstrate the conservation of Hox gene regulation and of Krox-20 function during vertebrate evolution.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aparicio S., Morrison A., Gould A., Gilthorpe J., Chaudhuri C., Rigby P., Krumlauf R., Brenner S. Detecting conserved regulatory elements with the model genome of the Japanese puffer fish, Fugu rubripes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1684–1688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Awgulewitsch A., Jacobs D. Deformed autoregulatory element from Drosophila functions in a conserved manner in transgenic mice. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):341–344. doi: 10.1038/358341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker N., Seitanidou T., Murphy P., Mattéi M. G., Topilko P., Nieto M. A., Wilkinson D. G., Charnay P., Gilardi-Hebenstreit P. Several receptor tyrosine kinase genes of the Eph family are segmentally expressed in the developing hindbrain. Mech Dev. 1994 Jul;47(1):3–17. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(94)90091-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgbauer E., Fraser S. E. Violation of cell lineage restriction compartments in the chick hindbrain. Development. 1994 Jun;120(6):1347–1356. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.6.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birgbauer E., Sechrist J., Bronner-Fraser M., Fraser S. Rhombomeric origin and rostrocaudal reassortment of neural crest cells revealed by intravital microscopy. Development. 1995 Apr;121(4):935–945. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.4.935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter E. M., Goddard J. M., Chisaka O., Manley N. R., Capecchi M. R. Loss of Hox-A1 (Hox-1.6) function results in the reorganization of the murine hindbrain. Development. 1993 Aug;118(4):1063–1075. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.4.1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Vesque C., Galliot B., Vigneron M., Dollé P., Duboule D., Charnay P. The segment-specific gene Krox-20 encodes a transcription factor with binding sites in the promoter region of the Hox-1.4 gene. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1209–1218. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08228.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Zerial M., Lemaire P., Almendral J., Bravo R., Charnay P. A gene encoding a protein with zinc fingers is activated during G0/G1 transition in cultured cells. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02780.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke J. D., Lumsden A. Segmental repetition of neuronal phenotype sets in the chick embryo hindbrain. Development. 1993 May;118(1):151–162. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook M., Gould A., Brand N., Davies J., Strutt P., Shaknovich R., Licht J., Waxman S., Chen Z., Gluecksohn-Waelsch S. Expression of the zinc-finger gene PLZF at rhombomere boundaries in the vertebrate hindbrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2249–2253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordes S. P., Barsh G. S. The mouse segmentation gene kr encodes a novel basic domain-leucine zipper transcription factor. Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):1025–1034. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Lufkin T., Krumlauf R., Mark M., Duboule D., Chambon P. Local alterations of Krox-20 and Hox gene expression in the hindbrain suggest lack of rhombomeres 4 and 5 in homozygote null Hoxa-1 (Hox-1.6) mutant embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 15;90(16):7666–7670. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.16.7666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch M., Chen X., Lufkin T. Evolutionary-conserved enhancers direct region-specific expression of the murine Hoxa-1 and Hoxa-2 loci in both mice and Drosophila. Development. 1995 Apr;121(4):957–974. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.4.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser S., Keynes R., Lumsden A. Segmentation in the chick embryo hindbrain is defined by cell lineage restrictions. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):431–435. doi: 10.1038/344431a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Fernández J., Holland P. W. Archetypal organization of the amphioxus Hox gene cluster. Nature. 1994 Aug 18;370(6490):563–566. doi: 10.1038/370563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilardi-Hebenstreit P., Nieto M. A., Frain M., Mattéi M. G., Chestier A., Wilkinson D. G., Charnay P. An Eph-related receptor protein tyrosine kinase gene segmentally expressed in the developing mouse hindbrain. Oncogene. 1992 Dec;7(12):2499–2506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyman I., Faissner A., Lumsden A. Cell and matrix specialisations of rhombomere boundaries. Dev Dyn. 1995 Nov;204(3):301–315. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002040308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R. Hox genes in vertebrate development. Cell. 1994 Jul 29;78(2):191–201. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90290-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden A., Keynes R. Segmental patterns of neuronal development in the chick hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):424–428. doi: 10.1038/337424a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumsden A., Sprawson N., Graham A. Segmental origin and migration of neural crest cells in the hindbrain region of the chick embryo. Development. 1991 Dec;113(4):1281–1291. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.4.1281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin M., Nehlin J. O., Ronne H. Importance of a flanking AT-rich region in target site recognition by the GC box-binding zinc finger protein MIG1. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1979–1985. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Horton C., Graham A., Leonard L., Pizzey J., Siegenthaler G., Lumsden A., Eriksson U. Domains of cellular retinoic acid-binding protein I (CRABP I) expression in the hindbrain and neural crest of the mouse embryo. Mech Dev. 1992 Mar;37(1-2):13–23. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(92)90011-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maden M., Hunt P., Eriksson U., Kuroiwa A., Krumlauf R., Summerbell D. Retinoic acid-binding protein, rhombomeres and the neural crest. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):35–43. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood R., Kiefer P., Guthrie S., Dickson C., Mason I. Multiple roles for FGF-3 during cranial neural development in the chicken. Development. 1995 May;121(5):1399–1410. doi: 10.1242/dev.121.5.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malicki J., Cianetti L. C., Peschle C., McGinnis W. A human HOX4B regulatory element provides head-specific expression in Drosophila embryos. Nature. 1992 Jul 23;358(6384):345–347. doi: 10.1038/358345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mark M., Lufkin T., Vonesch J. L., Ruberte E., Olivo J. C., Dollé P., Gorry P., Lumsden A., Chambon P. Two rhombomeres are altered in Hoxa-1 mutant mice. Development. 1993 Oct;119(2):319–338. doi: 10.1242/dev.119.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall H., Studer M., Pöpperl H., Aparicio S., Kuroiwa A., Brenner S., Krumlauf R. A conserved retinoic acid response element required for early expression of the homeobox gene Hoxb-1. Nature. 1994 Aug 18;370(6490):567–571. doi: 10.1038/370567a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A., Chaudhuri C., Ariza-McNaughton L., Muchamore I., Kuroiwa A., Krumlauf R. Comparative analysis of chicken Hoxb-4 regulation in transgenic mice. Mech Dev. 1995 Sep;53(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(95)00423-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy P., Davidson D. R., Hill R. E. Segment-specific expression of a homoeobox-containing gene in the mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Sep 14;341(6238):156–159. doi: 10.1038/341156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T. J., Vesque C., Charnay P. Base sequence discrimination by zinc-finger DNA-binding domains. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):175–178. doi: 10.1038/349175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardelli J., Gibson T., Charnay P. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: analysis of base specificity by site-directed mutagenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4137–4144. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonchev S., Vesque C., Maconochie M., Seitanidou T., Ariza-McNaughton L., Frain M., Marshall H., Sham M. H., Krumlauf R., Charnay P. Segmental expression of Hoxa-2 in the hindbrain is directly regulated by Krox-20. Development. 1996 Feb;122(2):543–554. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.2.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Pabo C. O. Zinc finger-DNA recognition: crystal structure of a Zif268-DNA complex at 2.1 A. Science. 1991 May 10;252(5007):809–817. doi: 10.1126/science.2028256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöpperl H., Bienz M., Studer M., Chan S. K., Aparicio S., Brenner S., Mann R. S., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hoxb-1 is controlled by a highly conserved autoregulatory loop dependent upon exd/pbx. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1031–1042. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Dolle P., Chambon P., Morriss-Kay G. Retinoic acid receptors and cellular retinoid binding proteins. II. Their differential pattern of transcription during early morphogenesis in mouse embryos. Development. 1991 Jan;111(1):45–60. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruberte E., Friederich V., Morriss-Kay G., Chambon P. Differential distribution patterns of CRABP I and CRABP II transcripts during mouse embryogenesis. Development. 1992 Aug;115(4):973–987. doi: 10.1242/dev.115.4.973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo M. W., Sevetson B. R., Milbrandt J. Identification of NAB1, a repressor of NGFI-A- and Krox20-mediated transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6873–6877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider-Maunoury S., Topilko P., Seitandou T., Levi G., Cohen-Tannoudji M., Pournin S., Babinet C., Charnay P. Disruption of Krox-20 results in alteration of rhombomeres 3 and 5 in the developing hindbrain. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1199–1214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90329-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sechrist J., Serbedzija G. N., Scherson T., Fraser S. E., Bronner-Fraser M. Segmental migration of the hindbrain neural crest does not arise from its segmental generation. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):691–703. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serbedzija G. N., Bronner-Fraser M., Fraser S. E. Vital dye analysis of cranial neural crest cell migration in the mouse embryo. Development. 1992 Oct;116(2):297–307. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.2.297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sham M. H., Hunt P., Nonchev S., Papalopulu N., Graham A., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. Analysis of the murine Hox-2.7 gene: conserved alternative transcripts with differential distributions in the nervous system and the potential for shared regulatory regions. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1825–1836. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05234.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sham M. H., Vesque C., Nonchev S., Marshall H., Frain M., Gupta R. D., Whiting J., Wilkinson D., Charnay P., Krumlauf R. The zinc finger gene Krox20 regulates HoxB2 (Hox2.8) during hindbrain segmentation. Cell. 1993 Jan 29;72(2):183–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90659-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studer M., Pöpperl H., Marshall H., Kuroiwa A., Krumlauf R. Role of a conserved retinoic acid response element in rhombomere restriction of Hoxb-1. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1728–1732. doi: 10.1126/science.7916164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O. H., Eichele G. A homeo domain protein reveals the metameric nature of the developing chick hindbrain. Genes Dev. 1990 Aug;4(8):1267–1276. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.8.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swirnoff A. H., Milbrandt J. DNA-binding specificity of NGFI-A and related zinc finger transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Apr;15(4):2275–2287. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.4.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieille-Grosjean I., Huber P. Transcription factor GATA-1 regulates human HOXB2 gene expression in erythroid cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4544–4550. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiting J., Marshall H., Cook M., Krumlauf R., Rigby P. W., Stott D., Allemann R. K. Multiple spatially specific enhancers are required to reconstruct the pattern of Hox-2.6 gene expression. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2048–2059. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Chavrier P., Bravo R., Charnay P. Segment-specific expression of a zinc-finger gene in the developing nervous system of the mouse. Nature. 1989 Feb 2;337(6206):461–464. doi: 10.1038/337461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G., Bhatt S., Cook M., Boncinelli E., Krumlauf R. Segmental expression of Hox-2 homoeobox-containing genes in the developing mouse hindbrain. Nature. 1989 Oct 5;341(6241):405–409. doi: 10.1038/341405a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson D. G. Molecular mechanisms of segmental patterning in the vertebrate hindbrain. Perspect Dev Neurobiol. 1993;1(3):117–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee S. P., Rigby P. W. The regulation of myogenin gene expression during the embryonic development of the mouse. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1277–1289. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer A., Zimmer A. Induction of a RAR beta 2-lacZ transgene by retinoic acid reflects the neuromeric organization of the central nervous system. Development. 1992 Dec;116(4):977–983. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.4.977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]