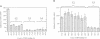Abstract
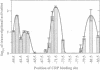
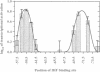
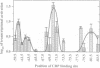
Transcription from many Escherichia coli promoters can be activated by the cAMP-CRP complex bound at different locations upstream of the promoter. At some locations the mechanism of activation involves direct protein-protein contacts between CRP and the RNA polymerase. We positioned the CRP binding site at various distances from the transcription start site of the malT promoter and measured the in vivo activities of these promoter variants. From the activation profiles we deduce that the protein-protein interactions involved in transcriptional activation are rather rigid. A heterologous protein (IHF) that bends the DNA to a similar degree as does CRP activates transcription when bound at sites equivalent to activating positions for CRP. DNA geometry makes a major contribution to the process of transcriptional activation and DNA upstream of the activator binding site participates in this process. Removal of this DNA decreases the capacity of the malT promoter to be activated by CRP in vitro. We conclude that both DNA topology and direct protein-protein contacts contribute to transcriptional activation and that the relative importance of these two modes of activation depends on the nature of the activator and on the location of the activator binding site.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba H., Fujimoto S., Ozaki N. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequencing of the gene for E. coli cAMP receptor protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1345–1361. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell A., Gaston K., Williams R., Chapman K., Kolb A., Buc H., Minchin S., Williams J., Busby S. Mutations that alter the ability of the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein to activate transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7243–7250. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Selection of DNA binding sites by regulatory proteins. II. The binding specificity of cyclic AMP receptor protein to recognition sites. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):709–723. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90482-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter E. E., Ross W., Tang H., Gourse R. L., Ebright R. H. Domain organization of RNA polymerase alpha subunit: C-terminal 85 amino acids constitute a domain capable of dimerization and DNA binding. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):889–896. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90682-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bracco L., Kotlarz D., Kolb A., Diekmann S., Buc H. Synthetic curved DNA sequences can act as transcriptional activators in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4289–4296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle M., Buc H., Travers A. A. DNA deformation in nucleoprotein complexes between RNA polymerase, cAMP receptor protein and the lac UV5 promoter probed by singlet oxygen. EMBO J. 1992 Jul;11(7):2619–2625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05327.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapon C. Expression of malT, the regulator gene of the maltose region in Escherichia coli, is limited both at transcription and translation. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):369–374. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapon C., Kolb A. Action of CAP on the malT promoter in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1135–1143. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1135-1143.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Identification of the target of a transcription activator protein by protein-protein photocrosslinking. Science. 1994 Jul 1;265(5168):90–92. doi: 10.1126/science.8016656. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole S. T., Raibaud O. The nucleotide sequence of the malT gene encoding the positive regulator of the Escherichia coli maltose regulon. Gene. 1986;42(2):201–208. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebright R. H. Transcription activation at Class I CAP-dependent promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01626.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger T., Behnke D., Bujard H., Gralla J. D. Stalling of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase in the +6 to +12 region in vivo is associated with tight binding to consensus promoter elements. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jun 17;239(4):455–465. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhorn M., Boccard F., Murtin C., Prentki P., Geiselmann J. In vivo interaction of the Escherichia coli integration host factor with its specific binding sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Aug 11;23(15):2959–2965. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenlauer A. C., Reznikoff W. S. Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein mutants defective in positive control of lac operon transcription. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5024–5029. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5024-5029.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman D. I. Integration host factor: a protein for all reasons. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):545–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90213-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Eggert M., Waterman M. S. Rigorous pattern-recognition methods for DNA sequences. Analysis of promoter sequences from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1985 Nov 5;186(1):117–128. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90262-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamas P., Burger A. C., Churchward G., Caro L., Galas D., Chandler M. Replication of pSC101: effects of mutations in the E. coli DNA binding protein IHF. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Jul;204(1):85–89. doi: 10.1007/BF00330192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. Synthetic DNA bending sequences increase the rate of in vitro transcription initiation at the Escherichia coli lac promoter. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):217–230. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90563-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaston K., Bell A., Kolb A., Buc H., Busby S. Stringent spacing requirements for transcription activation by CRP. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):733–743. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90118-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Gottesman M., Oppenheim A. B. Integration host factor stimulates the phage lambda pL promoter. J Mol Biol. 1990 May 5;213(1):109–121. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80124-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Oppenheim A. B. Stimulation of the phage lambda pL promoter by integration host factor requires the carboxy terminus of the alpha-subunit of RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):985–990. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90514-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giladi H., Koby S., Gottesman M. E., Oppenheim A. B. Supercoiling, integration host factor, and a dual promoter system, participate in the control of the bacteriophage lambda pL promoter. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90461-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goosen N., van de Putte P. The regulation of transcription initiation by integration host factor. Mol Microbiol. 1995 Apr;16(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granston A. E., Nash H. A. Characterization of a set of integration host factor mutants deficient for DNA binding. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 5;234(1):45–59. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., McClure W. R. Compilation and analysis of Escherichia coli promoter DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2237–2255. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert M., Kolb A., Buc H. Overlapping promoters and their control in Escherichia coli: the gal case. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2807–2811. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Bipartite functional map of the E. coli RNA polymerase alpha subunit: involvement of the C-terminal region in transcription activation by cAMP-CRP. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1015–1022. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90553-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihama A. Protein-protein communication within the transcription apparatus. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.9.2483-2489.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Busby S., Buc H., Garges S., Adhya S. Transcriptional regulation by cAMP and its receptor protein. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:749–795. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.003533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb A., Igarashi K., Ishihama A., Lavigne M., Buckle M., Buc H. E. coli RNA polymerase, deleted in the C-terminal part of its alpha-subunit, interacts differently with the cAMP-CRP complex at the lacP1 and at the galP1 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 25;21(2):319–326. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.2.319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosturko L. D., Daub E., Murialdo H. The interaction of E. coli integration host factor and lambda cos DNA: multiple complex formation and protein-induced bending. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):317–334. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. M., Bellomy G. R., Schlax P. J., Record M. T., Jr In vivo thermodynamic analysis of repression with and without looping in lac constructs. Estimates of free and local lac repressor concentrations and of physical properties of a region of supercoiled plasmid DNA in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1993 Mar 5;230(1):161–173. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu-Johnson H. N., Gartenberg M. R., Crothers D. M. The DNA binding domain and bending angle of E. coli CAP protein. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):995–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90814-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malan T. P., Kolb A., Buc H., McClure W. R. Mechanism of CRP-cAMP activation of lac operon transcription initiation activation of the P1 promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 25;180(4):881–909. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90262-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A. Bacterial bioluminescence: organization, regulation, and application of the lux genes. FASEB J. 1993 Aug;7(11):1016–1022. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.11.8370470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A. Molecular biology of bacterial bioluminescence. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Mar;55(1):123–142. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.1.123-142.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meighen E. A., Szittner R. B. Multiple repetitive elements and organization of the lux operons of luminescent terrestrial bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5371–5381. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5371-5381.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menendez M., Kolb A., Buc H. A new target for CRP action at the malT promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4227–4234. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02771.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niu W., Zhou Y., Dong Q., Ebright Y. W., Ebright R. H. Characterization of the activating region of Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein (CAP). I. Saturation and alanine-scanning mutagenesis. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 4;243(4):595–602. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90034-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Smith-Mungo L. I., Landy A. Single base-pair precision and structural rigidity in a small IHF-induced DNA loop. J Mol Biol. 1995 Oct 20;253(2):228–242. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parekh B. S., Hatfield G. W. Transcriptional activation by protein-induced DNA bending: evidence for a DNA structural transmission model. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 6;93(3):1173–1177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.3.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Vidal-Ingigliardi D., Kolb A. Genetic studies on the promoter of malT, the gene that encodes the activator of the Escherichia coli maltose regulon. Res Microbiol. 1991 Nov-Dec;142(9):937–942. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(91)90003-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao L., Ross W., Appleman J. A., Gaal T., Leirmo S., Schlax P. J., Record M. T., Jr, Gourse R. L. Factor independent activation of rrnB P1. An "extended" promoter with an upstream element that dramatically increases promoter strength. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 4;235(5):1421–1435. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1098. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross W., Gosink K. K., Salomon J., Igarashi K., Zou C., Ishihama A., Severinov K., Gourse R. L. A third recognition element in bacterial promoters: DNA binding by the alpha subunit of RNA polymerase. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1407–1413. doi: 10.1126/science.8248780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S., Garges S., Adhya S. An arcane role of DNA in transcription activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8582–8586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlax P. J., Capp M. W., Record M. T., Jr Inhibition of transcription initiation by lac repressor. J Mol Biol. 1995 Jan 27;245(4):331–350. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz A. Cyclic AMP receptor proteins interacts with lactose operator DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):277–292. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. C., Shields G. C., Steitz T. A. Crystal structure of a CAP-DNA complex: the DNA is bent by 90 degrees. Science. 1991 Aug 30;253(5023):1001–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1653449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Lubinsky-Mink S., Jackson C. G., Cassel A., Kuhn J. pHG165: a pBR322 copy number derivative of pUC8 for cloning and expression. Plasmid. 1986 May;15(3):172–181. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., O'Neill M., de Crombrugghe B. Interaction site of Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein on DNA of galactose operon promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5090–5094. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushida C., Aiba H. Helical phase dependent action of CRP: effect of the distance between the CRP site and the -35 region on promoter activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Nov 11;18(21):6325–6330. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.21.6325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West D., Williams R., Rhodius V., Bell A., Sharma N., Zou C., Fujita N., Ishihama A., Busby S. Interactions between the Escherichia coli cyclic AMP receptor protein and RNA polymerase at class II promoters. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Nov;10(4):789–797. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. M., Rhodius V. A., Bell A. I., Kolb A., Busby S. J. Orientation of functional activating regions in the Escherichia coli CRP protein during transcription activation at class II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1996 Mar 15;24(6):1112–1118. doi: 10.1093/nar/24.6.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R., Bell A., Sims G., Busby S. The role of two surface exposed loops in transcription activation by the Escherichia coli CRP and FNR proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 25;19(24):6705–6712. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.24.6705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang C. C., Nash H. A. The interaction of E. coli IHF protein with its specific binding sites. Cell. 1989 Jun 2;57(5):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90801-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Merkel T. J., Ebright R. H. Characterization of the activating region of Escherichia coli catabolite gene activator protein (CAP). II. Role at Class I and class II CAP-dependent promoters. J Mol Biol. 1994 Nov 4;243(4):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y., Zhang X., Ebright R. H. Identification of the activating region of catabolite gene activator protein (CAP): isolation and characterization of mutants of CAP specifically defective in transcription activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6081–6085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zou C., Fujita N., Igarashi K., Ishihama A. Mapping the cAMP receptor protein contact site on the alpha subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2599–2605. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01437.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rijn P. A., Goosen N., van de Putte P. Integration host factor of Escherichia coli regulates early- and repressor transcription of bacteriophage Mu by two different mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4595–4605. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]