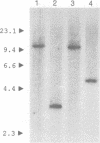
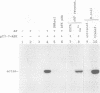
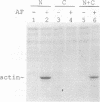
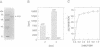Abstract
Actin-fragmin kinase (AFK) from Physarum polycephalum specifically phosphorylates actin in the EGTA-resistant 1:1 actin-fragmin complex. The cDNA deduced amino acid sequence reveals two major domains of approximately 35 kDa each that are separated by a hinge-like proline/serine-rich segment of 50 residues. Whereas the N-terminal domain does not show any significant similarity to protein sequences from databases, there are six complete kelch repeats in the protein that comprise almost the entire C-terminal half of the molecule. To prove the intrinsic phosphorylation activity of AFK, full-length or partial cDNA fragments were expressed both in a reticulocyte lysate and in Escherichia coli. In both expression systems, we obtained specific actin phosphorylation and located the catalytic domain in the N-terminal half. Interestingly, this region did not contain any of the known protein kinase consensus sequences. The only known sequence motif present that could have been involved in nucleotide binding was a nearly perfect phosphate binding loop (P-loop). However, introduction of two different point mutations into this putative P-loop sequence did not alter the catalytic activity of the kinase, which indicates an as yet unknown mechanism for phosphate transfer. Our data suggest that AFK belongs to a new class of protein kinases and that this actin phosphorylation might be the first example of a widely distributed novel type of regulation of the actin cytoskeleton in non-muscle cells.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alex L. A., Simon M. I. Protein histidine kinases and signal transduction in prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1994 Apr;10(4):133–138. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(94)90215-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvino C. G., Acquaviva A. M., Catanzano A. M., Tassi V. Evidence that thyroglobulin has an associated protein kinase activity correlated with the presence of an adenosine triphosphate binding site. Endocrinology. 1995 Aug;136(8):3179–3185. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.8.7628349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ampe C., Vandekerckhove J. The F-actin capping proteins of Physarum polycephalum: cap42(a) is very similar, if not identical, to fragmin and is structurally and functionally very homologous to gelsolin; cap42(b) is Physarum actin. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4149–4157. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- André E., Lottspeich F., Schleicher M., Noegel A. Severin, gelsolin, and villin share a homologous sequence in regions presumed to contain F-actin severing domains. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):722–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey J., Solnica-Krezel L., Lohman K., Dee J., Anderson R. W., Dove W. F. Cellular and molecular analysis of plasmodium development in Physarum. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1992 Nov;16(11):1083–1090. doi: 10.1016/s0309-1651(05)80033-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beeler J. F., LaRochelle W. J., Chedid M., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A. Prokaryotic expression cloning of a novel human tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):982–988. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bork P., Doolittle R. F. Drosophila kelch motif is derived from a common enzyme fold. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 11;236(5):1277–1282. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crennell S. J., Garman E. F., Laver W. G., Vimr E. R., Taylor G. L. Crystal structure of a bacterial sialidase (from Salmonella typhimurium LT2) shows the same fold as an influenza virus neuraminidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):9852–9856. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.9852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dikstein R., Ruppert S., Tjian R. TAFII250 is a bipartite protein kinase that phosphorylates the base transcription factor RAP74. Cell. 1996 Mar 8;84(5):781–790. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger L., Schleicher M. Characterization of actin- and lipid-binding domains in severin, a Ca(2+)-dependent F-actin fragmenting protein. Biochemistry. 1992 May 26;31(20):4779–4787. doi: 10.1021/bi00135a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber H. R., Groom C. R., Baker H. M., Morgan W. T., Smith A., Baker E. N. 1.8 A crystal structure of the C-terminal domain of rabbit serum haemopexin. Structure. 1995 Jun 15;3(6):551–559. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00189-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuhashi K., Hatano S. A fragmin-like protein from plasmodium of Physarum polycephalum that severs F-actin and caps the barbed end of F-actin in a Ca2+-sensitive way. J Biochem. 1989 Aug;106(2):311–318. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuhashi K., Hatano S. Actin kinase: a protein kinase that phosphorylates actin of fragmin-actin complex. J Biochem. 1992 Mar;111(3):366–370. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuhashi K., Hatano S., Ando S., Nishizawa K., Inagaki M. Phosphorylation by actin kinase of the pointed end domain on the actin molecule. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 5;267(13):9326–9330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuhashi K., Hatano S. Control of actin filament length by phosphorylation of fragmin-actin complex. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1081–1087. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futey L. M., Medley Q. G., Côté G. P., Egelhoff T. T. Structural analysis of myosin heavy chain kinase A from Dictyostelium. Evidence for a highly divergent protein kinase domain, an amino-terminal coiled-coil domain, and a domain homologous to the beta-subunit of heterotrimeric G proteins. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 13;270(2):523–529. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.2.523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gettemans J., De Ville Y., Vandekerckhove J., Waelkens E. Physarum actin is phosphorylated as the actin-fragmin complex at residues Thr203 and Thr202 by a specific 80 kDa kinase. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3185–3191. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05395.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gettemans J., De Ville Y., Vandekerckhove J., Waelkens E. Purification and partial amino acid sequence of the actin-fragmin kinase from Physarum polycephalum. Eur J Biochem. 1993 May 15;214(1):111–119. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17902.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gettemans J., De Ville Y., Waelkens E., Vandekerckhove J. The actin-binding properties of the Physarum actin-fragmin complex. Regulation by calcium, phospholipids, and phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 10;270(6):2644–2651. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.6.2644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinssen H. An actin-modulating protein from Physarum polycephalum. I. Isolation and purification. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;23(2):225–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes K. C., Popp D., Gebhard W., Kabsch W. Atomic model of the actin filament. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):44–49. doi: 10.1038/347044a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton R. M., Hunt H. D., Ho S. N., Pullen J. K., Pease L. R. Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene. 1989 Apr 15;77(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90359-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard P. K., Sefton B. M., Firtel R. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation of actin in Dictyostelium associated with cell-shape changes. Science. 1993 Jan 8;259(5092):241–244. doi: 10.1126/science.7678470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Phillips S. E., Yadav K. D., Knowles P. F. Crystal structure of a free radical enzyme, galactose oxidase. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 20;238(5):794–814. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungbluth A., Eckerskorn C., Gerisch G., Lottspeich F., Stocker S., Schweiger A. Stress-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of actin in Dictyostelium cells and localization of the phosphorylation site to tyrosine-53 adjacent to the DNase I binding loop. FEBS Lett. 1995 Nov 13;375(1-2):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01165-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jungbluth A., von Arnim V., Biegelmann E., Humbel B., Schweiger A., Gerisch G. Strong increase in the tyrosine phosphorylation of actin upon inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation: correlation with reversible rearrangements in the actin skeleton of Dictyostelium cells. J Cell Sci. 1994 Jan;107(Pt 1):117–125. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Mannherz H. G., Suck D., Pai E. F., Holmes K. C. Atomic structure of the actin:DNase I complex. Nature. 1990 Sep 6;347(6288):37–44. doi: 10.1038/347037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Taylor S. S., Sefton B. M. Direct evidence that oncogenic tyrosine kinases and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase have homologous ATP-binding sites. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):589–592. doi: 10.1038/310589a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambright D. G., Sondek J., Bohm A., Skiba N. P., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. The 2.0 A crystal structure of a heterotrimeric G protein. Nature. 1996 Jan 25;379(6563):311–319. doi: 10.1038/379311a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maru Y., Witte O. N. The BCR gene encodes a novel serine/threonine kinase activity within a single exon. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):459–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90521-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Isenberg G. Ca2+-dependent actin-binding phosphoprotein in Physarum polycephalum. II. Ca2+-dependent f-actin-capping activity of subunit a and its regulation by phosphorylation of subunit b. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10151–10158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Isenberg G. Ca2+-dependent actin-binding phosphoprotein in Physarum polycephalum. Subunit b is a DNase I-binding and F-actin capping protein. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5208–5213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruta H., Isenberg G., Schreckenbach T., Hallmann R., Risse G., Shibayama T., Hesse J. Ca2+-dependent actin-binding phosphoprotein in Physarum polycephalum. I. Ca2+/actin-dependent inhibition of its phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10144–10150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. T., Burgess D. R. SDS microslab linear gradient polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jul 1;87(2):386–396. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90688-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens N., Remaut E., Fiers W. Tight transcriptional control mechanism ensures stable high-level expression from T7 promoter-based expression plasmids. Biotechnology (N Y) 1995 Feb;13(2):175–179. doi: 10.1038/nbt0295-175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murzin A. G. Structural principles for the propeller assembly of beta-sheets: the preference for seven-fold symmetry. Proteins. 1992 Oct;14(2):191–201. doi: 10.1002/prot.340140206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Smith T. F. G protein heterodimers: new structures propel new questions. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80969-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. A., Baxter-Gabbard K. L., Levine A. S. Avian reticuloendotheliosis virus (strain T): V. DNA polymerase. Virology. 1972 Jan;47(1):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90259-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi F., Labourier E., Forné T., Divita G., Derancourt J., Riou J. F., Antoine E., Cathala G., Brunel C., Tazi J. Specific phosphorylation of SR proteins by mammalian DNA topoisomerase I. Nature. 1996 May 2;381(6577):80–82. doi: 10.1038/381080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saraste M., Sibbald P. R., Wittinghofer A. The P-loop--a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Nov;15(11):430–434. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90281-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schutt C. E., Myslik J. C., Rozycki M. D., Goonesekere N. C., Lindberg U. The structure of crystalline profilin-beta-actin. Nature. 1993 Oct 28;365(6449):810–816. doi: 10.1038/365810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweiger A., Mihalache O., Ecke M., Gerisch G. Stage-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of actin in Dictyostelium discoideum cells. J Cell Sci. 1992 Jul;102(Pt 3):601–609. doi: 10.1242/jcs.102.3.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondek J., Bohm A., Lambright D. G., Hamm H. E., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure of a G-protein beta gamma dimer at 2.1A resolution. Nature. 1996 Jan 25;379(6563):369–374. doi: 10.1038/379369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. S., Knighton D. R., Zheng J., Ten Eyck L. F., Sowadski J. M. Structural framework for the protein kinase family. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:429–462. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.002241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varghese J. N., Laver W. G., Colman P. M. Structure of the influenza virus glycoprotein antigen neuraminidase at 2.9 A resolution. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):35–40. doi: 10.1038/303035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varkey J. P., Muhlrad P. J., Minniti A. N., Do B., Ward S. The Caenorhabditis elegans spe-26 gene is necessary to form spermatids and encodes a protein similar to the actin-associated proteins kelch and scruin. Genes Dev. 1995 May 1;9(9):1074–1086. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.9.1074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waelkens E., Gettemans J., De Corte V., De Ville Y., Goris J., Vandekerckhove J., Merlevede W. Microfilament dynamics: regulation of actin polymerization by actin-fragmin kinase and phosphatases. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1995;35:199–227. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(94)00013-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall M. A., Coleman D. E., Lee E., Iñiguez-Lluhi J. A., Posner B. A., Gilman A. G., Sprang S. R. The structure of the G protein heterotrimer Gi alpha 1 beta 1 gamma 2. Cell. 1995 Dec 15;83(6):1047–1058. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Sanders M., Chafel M., Tu Y. H., Knight A., Matsudaira P. beta-Scruin, a homologue of the actin crosslinking protein scruin, is localized to the acrosomal vesicle of Limulus sperm. J Cell Sci. 1995 Oct;108(Pt 10):3155–3162. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.10.3155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Way M., Sanders M., Garcia C., Sakai J., Matsudaira P. Sequence and domain organization of scruin, an actin-cross-linking protein in the acrosomal process of Limulus sperm. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;128(1-2):51–60. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. C., LaMarco K., Peterson M. G., Herr W. The VP16 accessory protein HCF is a family of polypeptides processed from a large precursor protein. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Hofmann A., Köppel B., Schleicher M., Noegel A. A. The Ca(2+)-binding domains in non-muscle type alpha-actinin: biochemical and genetic analysis. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):599–606. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Sharpe A. H., Hartwig J. H., Azuma T., Stossel T. P., Kwiatkowski D. J. Hemostatic, inflammatory, and fibroblast responses are blunted in mice lacking gelsolin. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xue F., Cooley L. kelch encodes a component of intercellular bridges in Drosophila egg chambers. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):681–693. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90397-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Nelson N. C., Taylor S. S. Affinity labeling of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine. Covalent modification of lysine 71. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10837–10842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Delft S., Verkleij A. J., Boonstra J., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M. Epidermal growth factor induces serine phosphorylation of actin. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 9;357(3):251–254. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01359-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]