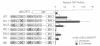Abstract
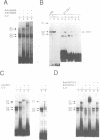
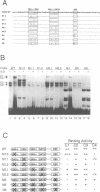
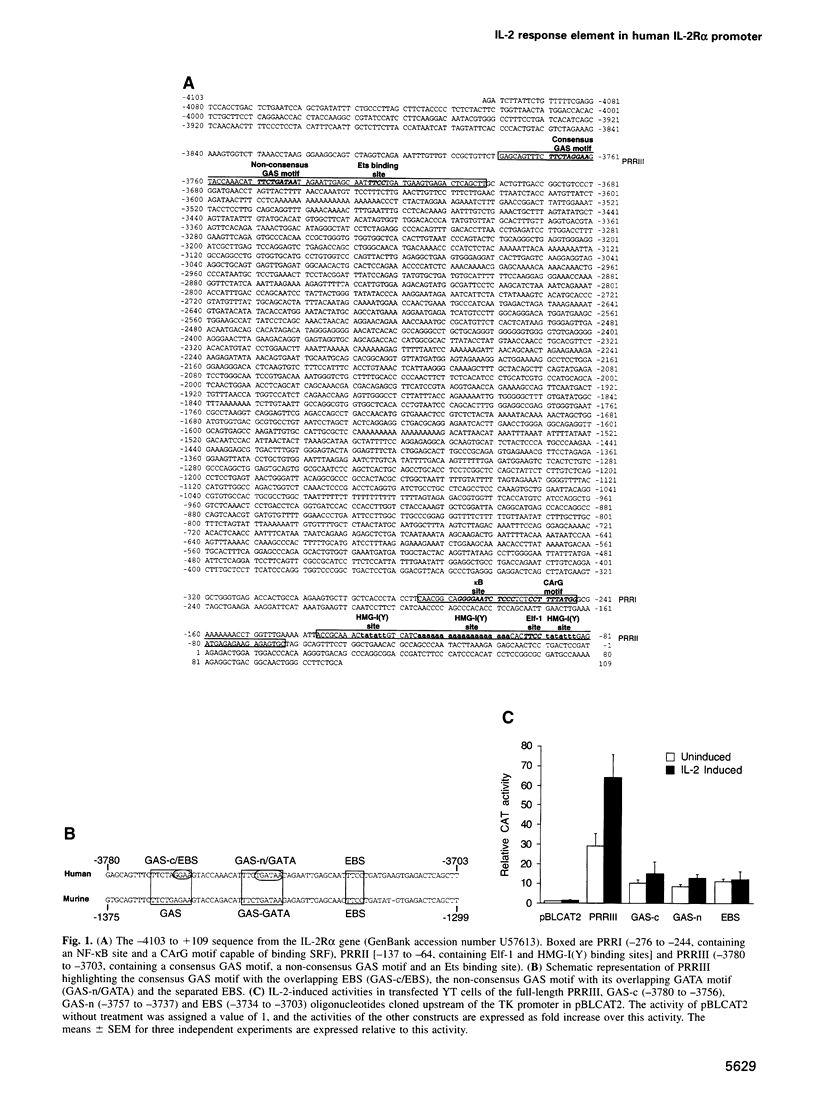
Expression of the human interleukin-2 (IL-2) receptor alpha chain gene is potently upregulated by its own ligand, IL-2. In this study, we characterize an essential upstream IL-2 response element that contains both consensus and non-consensus GAS motifs, two putative Ets binding sites (EBS), one of which overlaps the consensus GAS motif, and a GATA motif, which overlaps the non-consensus GAS motif. We demonstrate that although the individual components of this element do not respond to IL-2, together they form a composite element capable of conferring IL-2 responsiveness to a heterologous promoter. Multiple factors including Stat5, Elf-1, HMG-I(Y) and GATA family proteins bind to the IL-2 response element and mutation of any one of these binding sites diminishes the activity of this element. An unidentified Ets family protein binds to the EBS overlapping the consensus GAS motif and appears to negatively regulate the human IL-2R alpha promoter. Thus, IL-2-induced IL-2R alpha promoter activity requires a complex upstream element, which appears to contain binding sites for both positive and negative regulatory factors.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Algarté M., Lécine P., Costello R., Plet A., Olive D., Imbert J. In vivo regulation of interleukin-2 receptor alpha gene transcription by the coordinated binding of constitutive and inducible factors in human primary T cells. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 16;14(20):5060–5072. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00188.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Hoffman J. A., Bogerd H. P., Dixon E. P., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. Activation of the interleukin-2 receptor alpha gene: regulatory role for DNA-protein interactions flanking the kappa B enhancer. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):83–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhnlein E., Lowenthal J. W., Siekevitz M., Ballard D. W., Franza B. R., Greene W. C. The same inducible nuclear proteins regulates mitogen activation of both the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and type 1 HIV. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):827–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90099-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Feinberg M. B., Wolf J. B., Holbrook N. J., Wong-Staal F., Leonard W. J. Regulation of the human interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain promoter: activation of a nonfunctional promoter by the transactivator gene of HTLV-I. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90754-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Lenardo M. J., Leonard W. J. Functionally distinct NF-kappa B binding sites in the immunoglobulin kappa and IL-2 receptor alpha chain genes. Science. 1989 Apr 28;244(4903):466–469. doi: 10.1126/science.2497520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Drogula C., Krönke M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 (IL-2) augments transcription of the IL-2 receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du W., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Mechanisms of transcriptional synergism between distinct virus-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90468-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvo J. V., Thanos D., Maniatis T. Reversal of intrinsic DNA bends in the IFN beta gene enhancer by transcription factors and the architectural protein HMG I(Y). Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1101–1111. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90137-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujii H., Nakagawa Y., Schindler U., Kawahara A., Mori H., Gouilleux F., Groner B., Ihle J. N., Minami Y., Miyazaki T. Activation of Stat5 by interleukin 2 requires a carboxyl-terminal region of the interleukin 2 receptor beta chain but is not essential for the proliferative signal transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5482–5486. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5482. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaffen S. L., Lai S. Y., Xu W., Gouilleux F., Groner B., Goldsmith M. A., Greene W. C. Signaling through the interleukin 2 receptor beta chain activates a STAT-5-like DNA-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7192–7196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour K. C., Pine R., Reich N. C. Interleukin 2 activates STAT5 transcription factor (mammary gland factor) and specific gene expression in T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Nov 7;92(23):10772–10776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.23.10772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho I. C., Vorhees P., Marin N., Oakley B. K., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H., Leiden J. M. Human GATA-3: a lineage-restricted transcription factor that regulates the expression of the T cell receptor alpha gene. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1187–1192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08059.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou J., Schindler U., Henzel W. J., Wong S. C., McKnight S. L. Identification and purification of human Stat proteins activated in response to interleukin-2. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):321–329. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90140-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue J., Seiki M., Taniguchi T., Tsuru S., Yoshida M. Induction of interleukin 2 receptor gene expression by p40x encoded by human T-cell leukemia virus type 1. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2883–2888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04583.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S., Marais R., Child R., Light Y., Leonard W. J. Importance of low affinity Elf-1 sites in the regulation of lymphoid-specific inducible gene expression. J Exp Med. 1996 Mar 1;183(3):743–750. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.3.743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- John S., Reeves R. B., Lin J. X., Child R., Leiden J. M., Thompson C. B., Leonard W. J. Regulation of cell-type-specific interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression: potential role of physical interactions between Elf-1, HMG-I(Y), and NF-kappa B family proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1786–1796. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Noguchi M., Russell S. M., McBride O. W. The molecular basis of X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency: the role of the interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain as a common gamma chain, gamma c. Immunol Rev. 1994 Apr;138:61–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1994.tb00847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung K., Nabel G. J. HTLV-1 transactivator induces interleukin-2 receptor expression through an NF-kappa B-like factor. Nature. 1988 Jun 23;333(6175):776–778. doi: 10.1038/333776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin B. B., Cross S. L., Halden N. F., Roman D. G., Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Delineation of an enhancerlike positive regulatory element in the interleukin-2 receptor alpha-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):850–853. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Mietz J., Modi W. S., John S., Leonard W. J. Cloning of human Stat5B. Reconstitution of interleukin-2-induced Stat5A and Stat5B DNA binding activity in COS-7 cells. J Biol Chem. 1996 May 3;271(18):10738–10744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. X., Migone T. S., Tsang M., Friedmann M., Weatherbee J. A., Zhou L., Yamauchi A., Bloom E. T., Mietz J., John S. The role of shared receptor motifs and common Stat proteins in the generation of cytokine pleiotropy and redundancy by IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-13, and IL-15. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):331–339. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90141-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenthal J. W., Ballard D. W., Böhnlein E., Greene W. C. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces proteins that bind specifically to kappa B-like enhancer elements and regulate interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2331–2335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magis W., Martin D. I. HMG-I binds to GATA motifs: implications for an HPFH syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Sep 25;214(3):927–933. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama M., Shibuya H., Harada H., Hatakeyama M., Seiki M., Fujita T., Inoue J., Yoshida M., Taniguchi T. Evidence for aberrant activation of the interleukin-2 autocrine loop by HTLV-1-encoded p40x and T3/Ti complex triggering. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90437-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen M., Svejgaard A., Skov S., Odum N. Interleukin-2 induces tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of stat3 in human T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Dec;24(12):3082–3086. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830241225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins C. M., Hsu E., Gillevet P. M. Sequencing homopolymer tracts and repetitive elements. Biotechniques. 1996 May;20(5):862-4, 866-8. doi: 10.2144/96205st06. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman D. G., Toledano M. B., Leonard W. J. Sp1 represses IL-2 receptor alpha chain gene expression. New Biol. 1990 Jul;2(7):642–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Sharon M., Smith P. L., Leonard W. J. The IL-2 receptor beta chain (p70): role in mediating signals for LAK, NK, and proliferative activities. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.3116668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siekevitz M., Feinberg M. B., Holbrook N., Wong-Staal F., Greene W. C. Activation of interleukin 2 and interleukin 2 receptor (Tac) promoter expression by the trans-activator (tat) gene product of human T-cell leukemia virus, type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5389–5393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Danna K. J. Efficient infection of monkey cells with DNA of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7575–7578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperisen P., Wang S. M., Soldaini E., Pla M., Rusterholz C., Bucher P., Corthésy P., Reichenbach P., Nabholz M. Mouse interleukin-2 receptor alpha gene expression. Interleukin-1 and interleukin-2 control transcription via distinct cis-acting elements. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 5;270(18):10743–10753. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.18.10743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugamura K., Asao H., Kondo M., Tanaka N., Ishii N., Nakamura M., Takeshita T. The common gamma-chain for multiple cytokine receptors. Adv Immunol. 1995;59:225–277. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60632-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T. Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):251–255. doi: 10.1126/science.7716517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. The high mobility group protein HMG I(Y) is required for NF-kappa B-dependent virus induction of the human IFN-beta gene. Cell. 1992 Nov 27;71(5):777–789. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90554-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos D., Maniatis T. Virus induction of human IFN beta gene expression requires the assembly of an enhanceosome. Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90136-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Wang C. Y., Ho I. C., Bohjanen P. R., Petryniak B., June C. H., Miesfeldt S., Zhang L., Nabel G. J., Karpinski B. cis-acting sequences required for inducible interleukin-2 enhancer function bind a novel Ets-related protein, Elf-1. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1043–1053. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledano M. B., Roman D. G., Halden N. F., Lin B. B., Leonard W. J. The same target sequences are differentially important for activation of the interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene in two distinct T-cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1830–1834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakao H., Harada N., Kitamura T., Mui A. L., Miyajima A. Interleukin 2 and erythropoietin activate STAT5/MGF via distinct pathways. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2527–2535. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. J., Orkin S. H. GATA transcription factors: key regulators of hematopoiesis. Exp Hematol. 1995 Feb;23(2):99–107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willerford D. M., Chen J., Ferry J. A., Davidson L., Ma A., Alt F. W. Interleukin-2 receptor alpha chain regulates the size and content of the peripheral lymphoid compartment. Immunity. 1995 Oct;3(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]