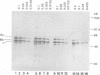
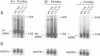Abstract
Blood loss at sites of vascular rupture is controlled by the adhesion and aggregation of platelets and the formation of an insoluble fibrin matrix. Fibrinogen is considered to be critical in these processes by both providing an abundant dimeric ligand for alpha IIb beta 3-mediated platelet aggregation, and serving as the fundamental building block of the fibrin polymer. To establish an in vivo model system to examine in detail the importance of alpha IIb beta 3-fibrinogen interactions in platelet function, hemostasis, response to injury and vasoocclusive disease, and to test the prevailing hypothesis that the C-terminal segment of the fibrinogen gamma chain is essential for alpha IIb beta 3 binding, we have used gene-targeting technology in mice to eliminate the last five residues (QAGDV) from the gamma chain. Mice homozygous for the modified gamma chain gene (gamma delta 5/gamma delta 5) displayed a generally normal hematological profile, including normal platelet count, plasma fibrinogen level, clotting time and fibrin crosslinking. However, both gamma delta 5-fibrinogen binding to alpha IIb beta 3 and platelet aggregation were highly defective. Remarkably, another alpha IIb beta 3-dependent process, clot retraction, was unaffected by the gamma delta 5 mutation. Despite the preservation of clotting function, gamma delta 5/gamma delta 5 mice were unable to control blood loss following a surgical challenge and occasionally developed fatal neonatal bleeding events.
Full text
PDF



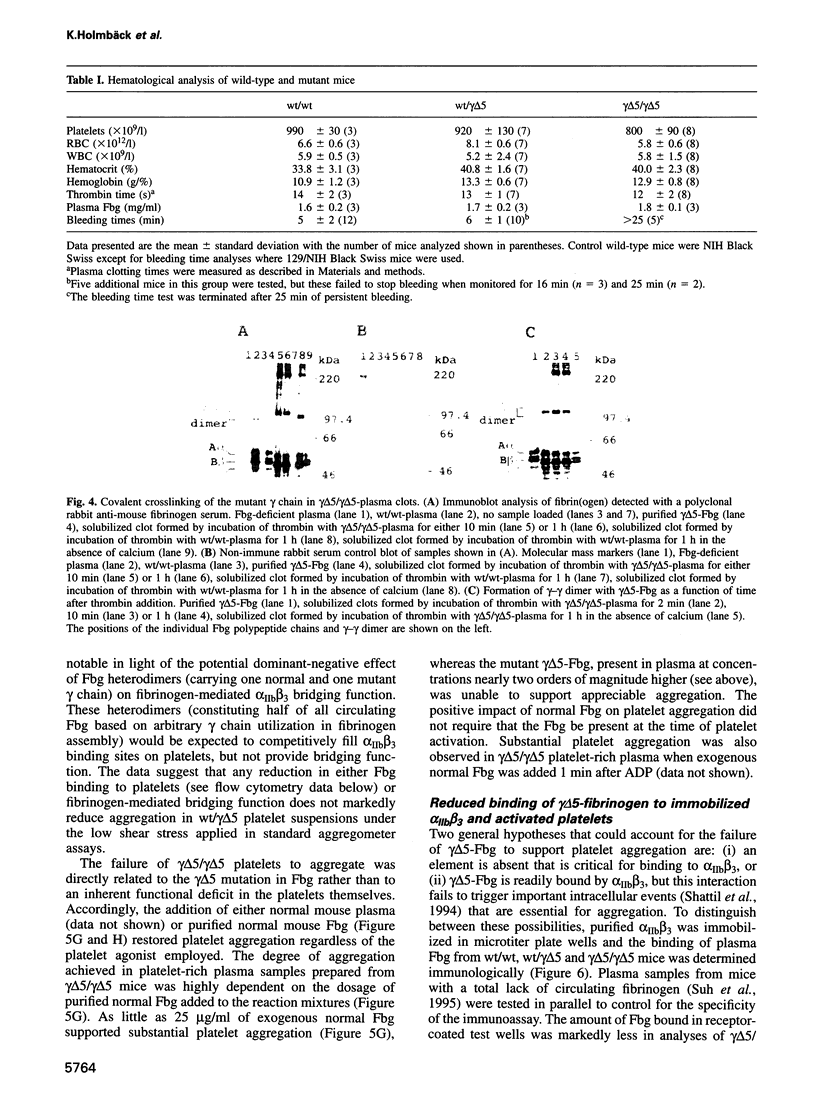
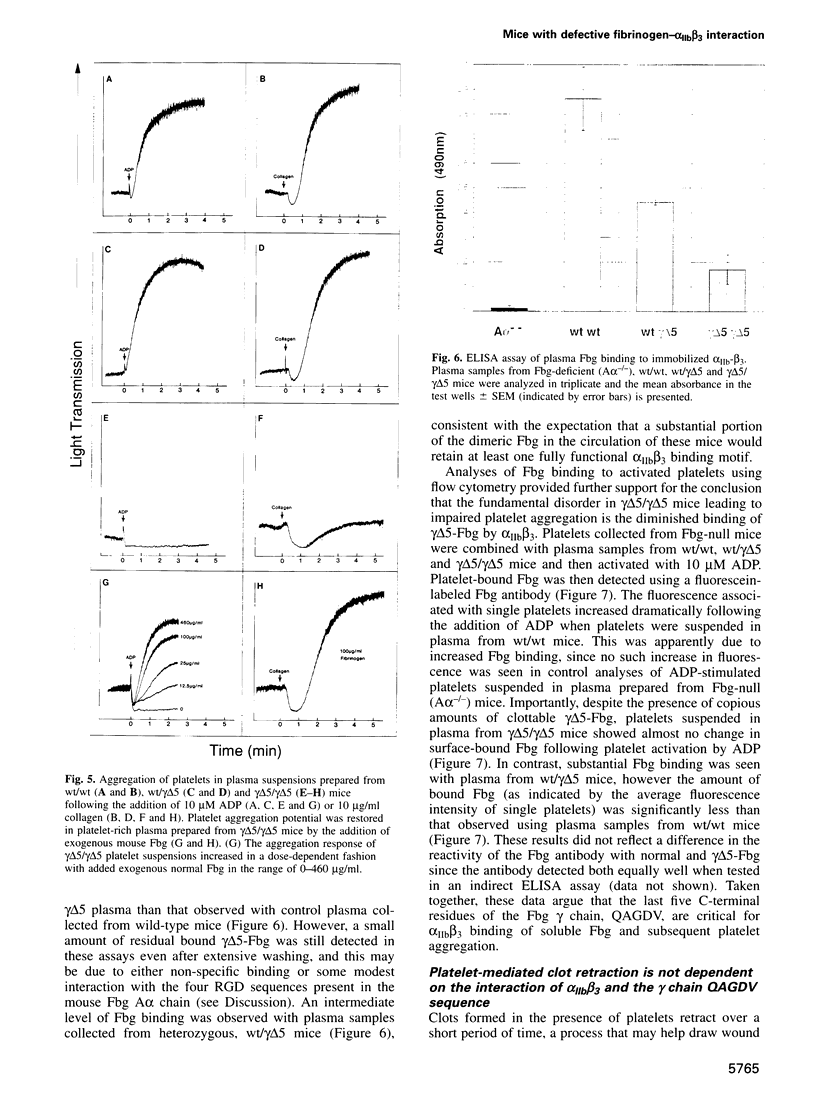
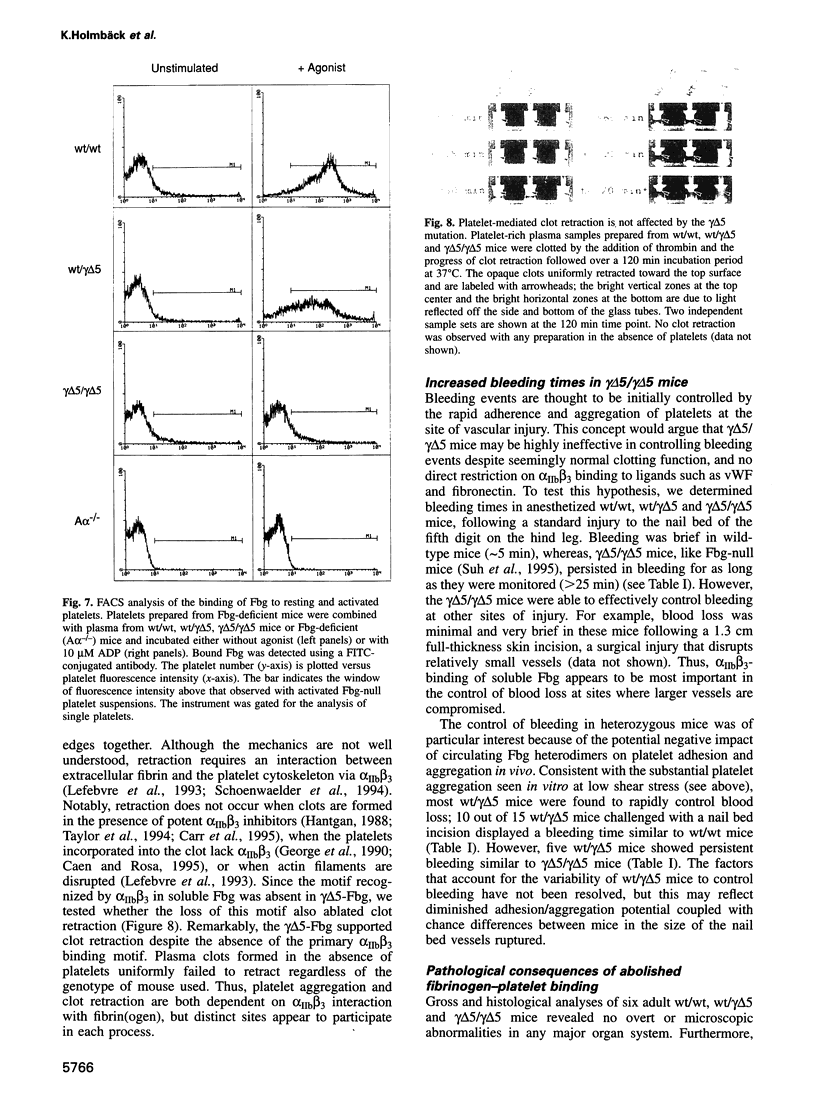





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beacham D. A., Wise R. J., Turci S. M., Handin R. I. Selective inactivation of the Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser (RGDS) binding site in von Willebrand factor by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3409–3415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertagnolli M. E., Beckerle M. C. Evidence for the selective association of a subpopulation of GPIIb-IIIa with the actin cytoskeletons of thrombin-activated platelets. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1329–1342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bi L., Lawler A. M., Antonarakis S. E., High K. A., Gearhart J. D., Kazazian H. H., Jr Targeted disruption of the mouse factor VIII gene produces a model of haemophilia A. Nat Genet. 1995 May;10(1):119–121. doi: 10.1038/ng0595-119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Flick M. J., Daugherty C. C., Degen J. L. Plasminogen deficiency causes severe thrombosis but is compatible with development and reproduction. Genes Dev. 1995 Apr 1;9(7):794–807. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.7.794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugge T. H., Xiao Q., Kombrinck K. W., Flick M. J., Holmbäck K., Danton M. J., Colbert M. C., Witte D. P., Fujikawa K., Davie E. W. Fatal embryonic bleeding events in mice lacking tissue factor, the cell-associated initiator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jun 25;93(13):6258–6263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.13.6258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caen J. P., Rosa J. P. Platelet-vessel wall interaction: from the bedside to molecules. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Jul;74(1):18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvete J. J. Clues for understanding the structure and function of a prototypic human integrin: the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. Thromb Haemost. 1994 Jul;72(1):1–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr M. E., Jr, Carr S. L., Hantgan R. R., Braaten J. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade inhibits platelet-mediated force development and reduces gel elastic modulus. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Mar;73(3):499–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheresh D. A., Berliner S. A., Vicente V., Ruggeri Z. M. Recognition of distinct adhesive sites on fibrinogen by related integrins on platelets and endothelial cells. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):945–953. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherny R. C., Honan M. A., Thiagarajan P. Site-directed mutagenesis of the arginine-glycine-aspartic acid in vitronectin abolishes cell adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 5;268(13):9725–9729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Davie E. W. gamma and gamma' chains of human fibrinogen are produced by alternative mRNA processing. Biochemistry. 1984 Aug 28;23(18):4232–4236. doi: 10.1021/bi00313a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Kant J. A. Organization of the rat gamma-fibrinogen gene: alternative mRNA splice patterns produce the gamma A and gamma B (gamma ') chains of fibrinogen. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90415-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell D. H., Thiagarajan P. Binding of recombinant fibrinogen mutants to platelets. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenette P. S., Johnson R. C., Hynes R. O., Wagner D. D. Platelets roll on stimulated endothelium in vivo: an interaction mediated by endothelial P-selectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 1;92(16):7450–7454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.16.7450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Bennett J. S. The tetrapeptide analogue of the cell attachment site of fibronectin inhibits platelet aggregation and fibrinogen binding to activated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11891–11894. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner T. K., Ogilvie M. L. Peptides and monoclonal antibodies which bind to platelet glycoproteins IIb and/or IIIa inhibit clot retraction. Thromb Res. 1988 Jan 1;49(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(88)90358-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George J. N., Caen J. P., Nurden A. T. Glanzmann's thrombasthenia: the spectrum of clinical disease. Blood. 1990 Apr 1;75(7):1383–1395. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg M. H., Du X., O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C. Platelet integrins. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Jul;74(1):352–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantgan R. R. Localization of the domains of fibrin involved in binding to platelets. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jan 18;968(1):36–44. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90041-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverstick D. M., Cowan J. F., Yamada K. M., Santoro S. A. Inhibition of platelet adhesion to fibronectin, fibrinogen, and von Willebrand factor substrates by a synthetic tetrapeptide derived from the cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):946–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M., Hardy K., Handyside A., Hunter S., Monk M. HPRT-deficient (Lesch-Nyhan) mouse embryos derived from germline colonization by cultured cells. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):292–295. doi: 10.1038/326292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschbaum N. E., Mosesson M. W., Amrani D. L. Characterization of the gamma chain platelet binding site on fibrinogen fragment D. Blood. 1992 May 15;79(10):2643–2648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloczewiak M., Timmons S., Lukas T. J., Hawiger J. Platelet receptor recognition site on human fibrinogen. Synthesis and structure-function relationship of peptides corresponding to the carboxy-terminal segment of the gamma chain. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1767–1774. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuyas C., Haeberli A., Walder P., Straub P. W. Isolation of human fibrinogen and its derivatives by affinity chromatography on Gly-Pro-Arg-Pro-Lys-Fractogel. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Jun 28;63(3):439–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre P., White J. G., Krumwiede M. D., Cohen I. Role of actin in platelet function. Eur J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;62(2):194–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H., Witte D. P., Branford W. W., Aronow B. J., Weinstein M., Kaur S., Wert S., Singh G., Schreiner C. M., Whitsett J. A. Gsh-4 encodes a LIM-type homeodomain, is expressed in the developing central nervous system and is required for early postnatal survival. EMBO J. 1994 Jun 15;13(12):2876–2885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06582.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakawa M., Okamura T., Kamura T., Shibuya T., Harada M., Niho Y. Diversity of primary structures of the carboxy-terminal regions of mammalian fibrinogen A alpha-chains. Characterization of the partial nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences in five mammalian species; rhesus monkey, pig, dog, mouse and Syrian hamster. Thromb Haemost. 1993 Apr 1;69(4):351–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole T. E., Loftus J. C., Du X. P., Glass A. A., Ruggeri Z. M., Shattil S. J., Plow E. F., Ginsberg M. H. Affinity modulation of the alpha IIb beta 3 integrin (platelet GPIIb-IIIa) is an intrinsic property of the receptor. Cell Regul. 1990 Nov;1(12):883–893. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.12.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., McEver R. P., Coller B. S., Woods V. L., Jr, Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. Related binding mechanisms for fibrinogen, fibronectin, von Willebrand factor, and thrombospondin on thrombin-stimulated human platelets. Blood. 1985 Sep;66(3):724–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G. A., Ginsberg M. H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8057–8061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E., Marguerie G., Ginsberg M. H. Arginyl-glycyl-aspartic acid sequences and fibrinogen binding to platelets. Blood. 1987 Jul;70(1):110–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F., Ruoslahti E. Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb/IIIa: member of a family of Arg-Gly-Asp--specific adhesion receptors. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1559–1562. doi: 10.1126/science.2420006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney M. M., Parise L. V., Lord S. T. Dissecting clot retraction and platelet aggregation. Clot retraction does not require an intact fibrinogen gamma chain C terminus. J Biol Chem. 1996 Apr 12;271(15):8553–8555. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.15.8553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M., De Marco L., Gatti L., Bader R., Montgomery R. R. Platelets have more than one binding site for von Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jul;72(1):1–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI110946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggeri Z. M. The role of von Willebrand factor and fibrinogen in the initiation of platelet adhesion to thrombogenic surfaces. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Jul;74(1):460–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage B., Ruggeri Z. M. Selective recognition of adhesive sites in surface-bound fibrinogen by glycoprotein IIb-IIIa on nonactivated platelets. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 15;266(17):11227–11233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage B., Saldívar E., Ruggeri Z. M. Initiation of platelet adhesion by arrest onto fibrinogen or translocation on von Willebrand factor. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):289–297. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80983-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenwaelder S. M., Jackson S. P., Yuan Y., Teasdale M. S., Salem H. H., Mitchell C. A. Tyrosine kinases regulate the cytoskeletal attachment of integrin alpha IIb beta 3 (platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa) and the cellular retraction of fibrin polymers. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32479–32487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shattil S. J., Ginsberg M. H., Brugge J. S. Adhesive signaling in platelets. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;6(5):695–704. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90096-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivdasani R. A., Rosenblatt M. F., Zucker-Franklin D., Jackson C. W., Hunt P., Saris C. J., Orkin S. H. Transcription factor NF-E2 is required for platelet formation independent of the actions of thrombopoietin/MGDF in megakaryocyte development. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):695–704. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90531-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P. J., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F., Shattil S. J. Effect of platelet activation on the conformation of the plasma membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7345–7352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sixma J. J., van Zanten G. H., Saelman E. U., Verkleij M., Lankhof H., Nieuwenhuis H. K., de Groot P. G. Platelet adhesion to collagen. Thromb Haemost. 1995 Jul;74(1):454–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong D. D., Moore M., Cottrell B. A., Bohonus V. L., Pontes M., Evans B., Riley M., Doolittle R. F. Lamprey fibrinogen gamma chain: cloning, cDNA sequencing, and general characterization. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 1;24(1):92–101. doi: 10.1021/bi00322a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suh T. T., Holmbäck K., Jensen N. J., Daugherty C. C., Small K., Simon D. I., Potter S., Degen J. L. Resolution of spontaneous bleeding events but failure of pregnancy in fibrinogen-deficient mice. Genes Dev. 1995 Aug 15;9(16):2020–2033. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.16.2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ugarova T. P., Budzynski A. Z., Shattil S. J., Ruggeri Z. M., Ginsberg M. H., Plow E. F. Conformational changes in fibrinogen elicited by its interaction with platelet membrane glycoprotein GPIIb-IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 5;268(28):21080–21087. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witke W., Sharpe A. H., Hartwig J. H., Azuma T., Stossel T. P., Kwiatkowski D. J. Hemostatic, inflammatory, and fibroblast responses are blunted in mice lacking gelsolin. Cell. 1995 Apr 7;81(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90369-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Lugt N., Maandag E. R., te Riele H., Laird P. W., Berns A. A pgk::hprt fusion as a selectable marker for targeting of genes in mouse embryonic stem cells: disruption of the T-cell receptor delta-chain-encoding gene. Gene. 1991 Sep 15;105(2):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]