Abstract
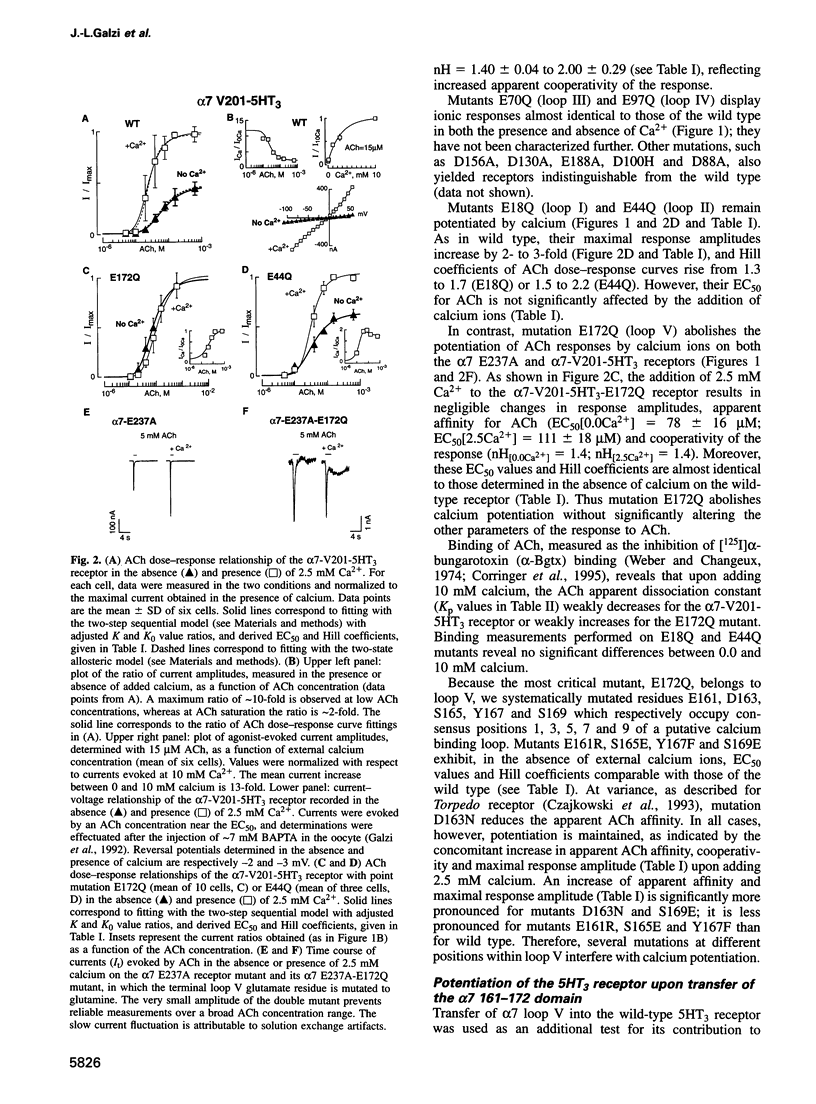
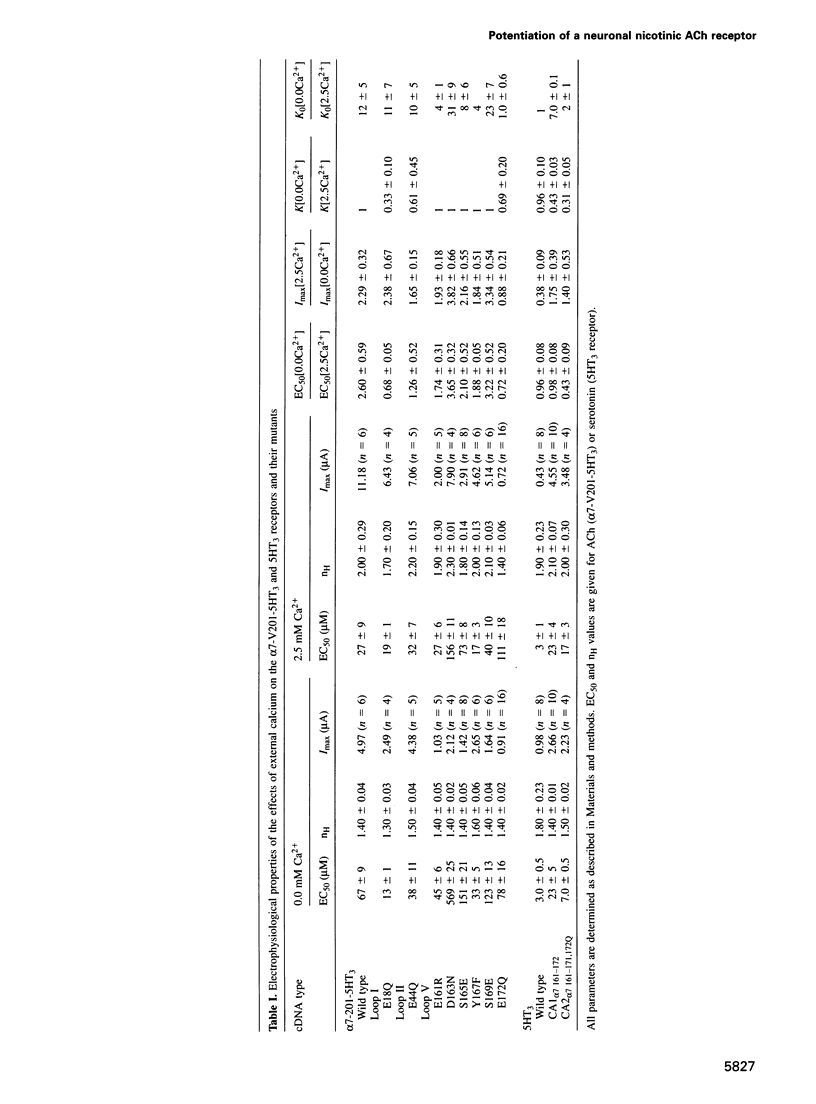
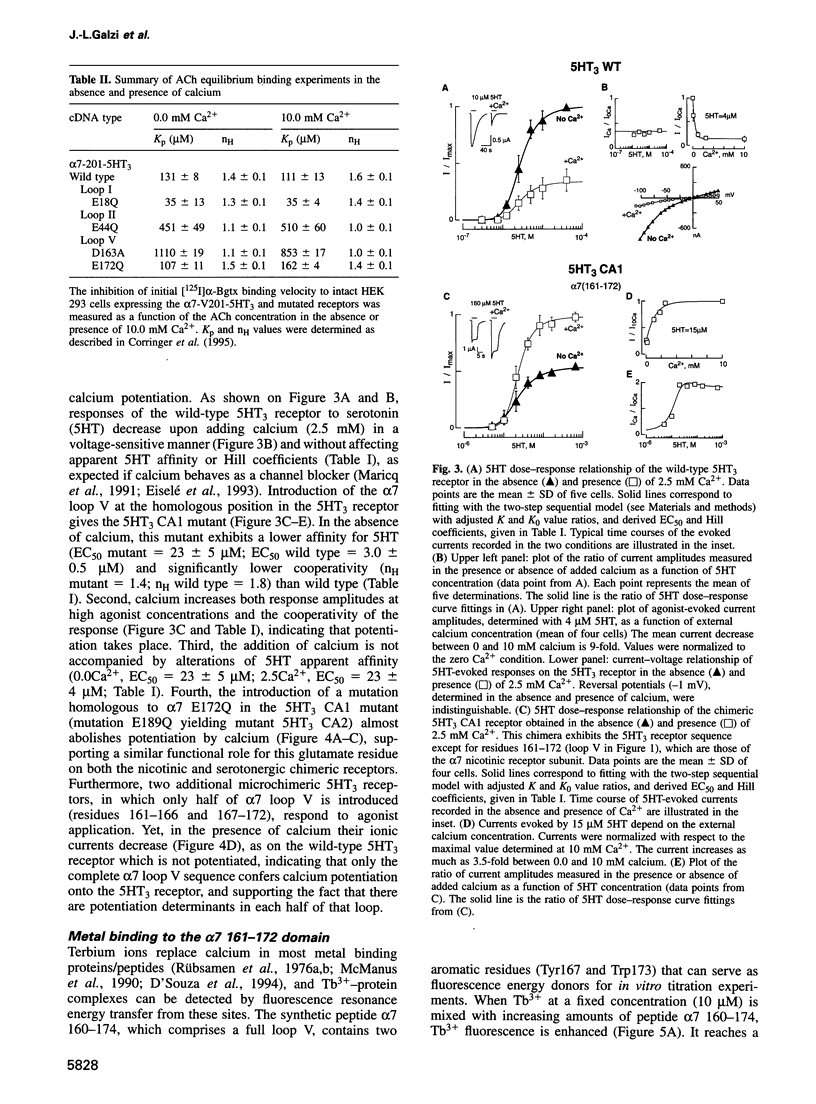
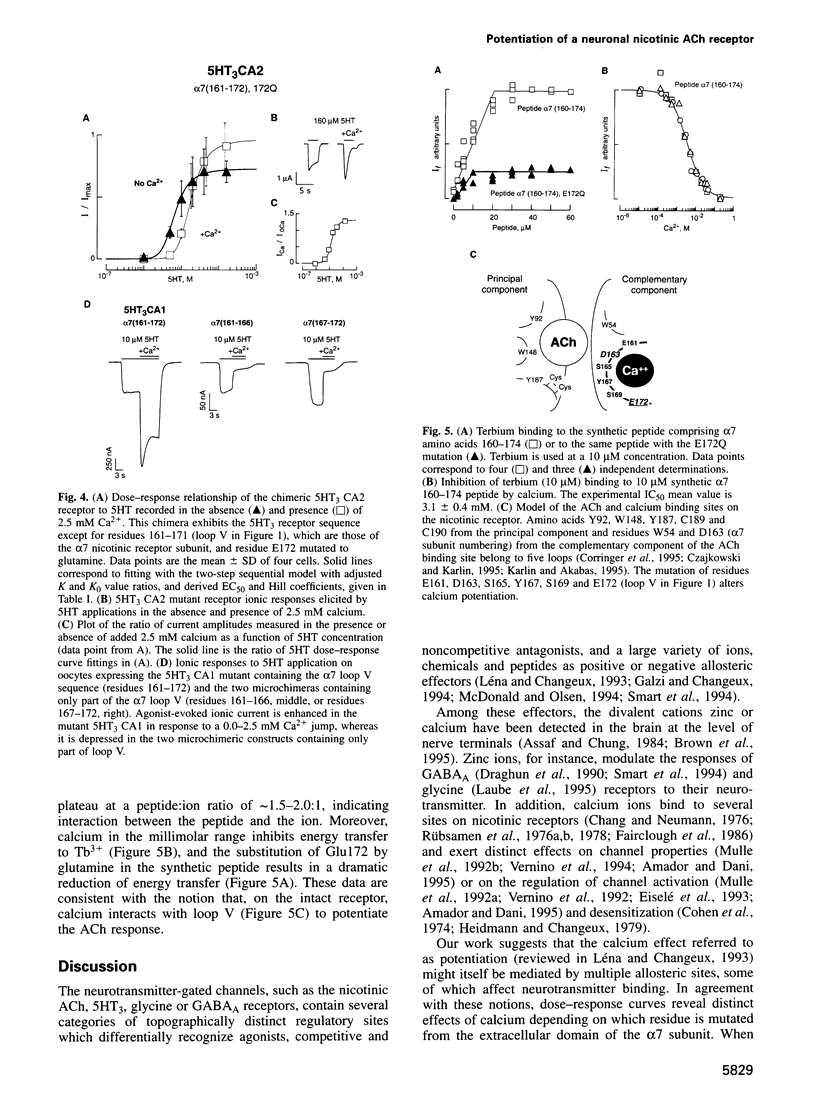
The divalent cation calcium potentiates the physiological response of neuronal nicotinic receptors to agonists by enhancing ionic current amplitudes, apparent agonist affinity and cooperativity. Here we show that mutations in several consensus Ca2+ binding sequences from the N-terminal domain of the neuronal alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alter Ca2+ potentiation of the alpha 7-V201-5HT3 chimera. Mutations E18Q or E44Q abolish calcium-enhanced agonist affinity but preserve the calcium increase of plateau current amplitudes and cooperativity. On the other hand, mutations of amino acids belonging to the 12 amino acid canonical domain (alpha 7 161-172) alter all features of potentiation by enhancing (D163, S169), reducing (E161, S165, Y167) or abolishing (E172) calcium effects on ionic current amplitudes and agonist affinity. Introduction of the alpha 7 161-172 domain in the calcium insensitive 5-hydroxytryptamine (5HT3) serotoninergic receptor results in a receptor activated by 5HT and potentiated by calcium. In vitro terbium fluorescence studies with an alpha 7 160-174 peptide further show that mutation E172Q also alters in vitro calcium binding. Data are consistent with the occurrence of distinct categories of regulatory calcium binding sites, among which the highly conserved (alpha 7 161-172) domain may simultaneously contribute to calcium and agonist binding.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amador M., Dani J. A. Mechanism for modulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors that can influence synaptic transmission. J Neurosci. 1995 Jun;15(6):4525–4532. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-06-04525.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assaf S. Y., Chung S. H. Release of endogenous Zn2+ from brain tissue during activity. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):734–736. doi: 10.1038/308734a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benninger C., Kadis J., Prince D. A. Extracellular calcium and potassium changes in hippocampal slices. Brain Res. 1980 Apr 7;187(1):165–182. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand D., Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Bertrand S., Changeux J. P. Mutations at two distinct sites within the channel domain M2 alter calcium permeability of neuronal alpha 7 nicotinic receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Aug 1;90(15):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.15.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Vassilev P. M., Hebert S. C. Calcium ions as extracellular messengers. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):679–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90180-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. W., Neumann E. Dynamic properties of isolated acetylcholine receptor proteins: release of calcium ions caused by acetylcholine binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3364–3368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corringer P. J., Galzi J. L., Eiselé J. L., Bertrand S., Changeux J. P., Bertrand D. Identification of a new component of the agonist binding site of the nicotinic alpha 7 homooligomeric receptor. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):11749–11752. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.11749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Couturier S., Bertrand D., Matter J. M., Hernandez M. C., Bertrand S., Millar N., Valera S., Barkas T., Ballivet M. A neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit (alpha 7) is developmentally regulated and forms a homo-oligomeric channel blocked by alpha-BTX. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):847–856. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90344-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski C., Karlin A. Agonist binding site of Torpedo electric tissue nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. A negatively charged region of the delta subunit within 0.9 nm of the alpha subunit binding site disulfide. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22603–22612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski C., Karlin A. Structure of the nicotinic receptor acetylcholine-binding site. Identification of acidic residues in the delta subunit within 0.9 nm of the 5 alpha subunit-binding. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3160–3164. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski C., Kaufmann C., Karlin A. Negatively charged amino acid residues in the nicotinic receptor delta subunit that contribute to the binding of acetylcholine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6285–6289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Souza S. E., Haas T. A., Piotrowicz R. S., Byers-Ward V., McGrath D. E., Soule H. R., Cierniewski C., Plow E. F., Smith J. W. Ligand and cation binding are dual functions of a discrete segment of the integrin beta 3 subunit: cation displacement is involved in ligand binding. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90551-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEL CASTILLO L., KATZ B. A study of curare action with an electrical micromethod. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):339–356. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draguhn A., Verdorn T. A., Ewert M., Seeburg P. H., Sakmann B. Functional and molecular distinction between recombinant rat GABAA receptor subtypes by Zn2+. Neuron. 1990 Dec;5(6):781–788. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90337-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiselé J. L., Bertrand S., Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Changeux J. P., Bertrand D. Chimaeric nicotinic-serotonergic receptor combines distinct ligand binding and channel specificities. Nature. 1993 Dec 2;366(6454):479–483. doi: 10.1038/366479a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E. Identification of a calcium-binding subunit of the acetylcholine receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):1020–1027. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90694-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairclough R. H., Miake-Lye R. C., Stroud R. M., Hodgson K. O., Doniach S. Location of terbium binding sites on acetylcholine receptor-enriched membranes. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jun 20;189(4):673–680. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90497-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falke J. J., Drake S. K., Hazard A. L., Peersen O. B. Molecular tuning of ion binding to calcium signaling proteins. Q Rev Biophys. 1994 Aug;27(3):219–290. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galzi J. L., Devillers-Thiéry A., Hussy N., Bertrand S., Changeux J. P., Bertrand D. Mutations in the channel domain of a neuronal nicotinic receptor convert ion selectivity from cationic to anionic. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):500–505. doi: 10.1038/359500a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haiech J., Sallantin J. Computer search of calcium binding sites in a gene data bank: use of learning techniques to build an expert system. Biochimie. 1985 May;67(5):555–560. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80276-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidmann T., Changeux J. P. Fast kinetic studies on the allosteric interactions between acetylcholine receptor and local anesthetic binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 15;94(1):281–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12894.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann U., Stabel J., Rausche G. Activity-dependent ionic changes and neuronal plasticity in rat hippocampus. Prog Brain Res. 1990;83:197–214. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin A., Akabas M. H. Toward a structural basis for the function of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and their cousins. Neuron. 1995 Dec;15(6):1231–1244. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laube B., Kuhse J., Rundström N., Kirsch J., Schmieden V., Betz H. Modulation by zinc ions of native rat and recombinant human inhibitory glycine receptors. J Physiol. 1995 Mar 15;483(Pt 3):613–619. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livsey C. T., Huang B., Xu J., Karwoski C. J. Light-evoked changes in extracellular calcium concentration in frog retina. Vision Res. 1990;30(6):853–861. doi: 10.1016/0042-6989(90)90054-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Léna C., Changeux J. P. Allosteric modulations of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Trends Neurosci. 1993 May;16(5):181–186. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(93)90150-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacManus J. P., Hogue C. W., Marsden B. J., Sikorska M., Szabo A. G. Terbium luminescence in synthetic peptide loops from calcium-binding proteins with different energy donors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10358–10366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maricq A. V., Peterson A. S., Brake A. J., Myers R. M., Julius D. Primary structure and functional expression of the 5HT3 receptor, a serotonin-gated ion channel. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.1718042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Choquet D., Korn H., Changeux J. P. Calcium influx through nicotinic receptor in rat central neurons: its relevance to cellular regulation. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90115-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulle C., Léna C., Changeux J. P. Potentiation of nicotinic receptor response by external calcium in rat central neurons. Neuron. 1992 May;8(5):937–945. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90208-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palma E., Bertrand S., Binzoni T., Bertrand D. Neuronal nicotinic alpha 7 receptor expressed in Xenopus oocytes presents five putative binding sites for methyllycaconitine. J Physiol. 1996 Feb 15;491(Pt 1):151–161. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1996.sp021203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persechini A., Moncrief N. D., Kretsinger R. H. The EF-hand family of calcium-modulated proteins. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Nov;12(11):462–467. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pumain R., Heinemann U. Stimulus- and amino acid-induced calcium and potassium changes in rat neocortex. J Neurophysiol. 1985 Jan;53(1):1–16. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. M., Changeux J. P. On the nature of allosteric transitions: implications of non-exclusive ligand binding. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen H., Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E., Hess G. P. Characterization of calcium-binding sites of the purified acetylcholine receptor and identification of the calcium-binding subunit. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 5;17(18):3818–3825. doi: 10.1021/bi00611a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen H., Hess G. P., Eldefrawi A. T., Eldefrawi M. E. Interaction between calcium and ligand-binding sites of the purified acetylcholine receptor studied by use of a fluorescent lanthanide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 12;68(1):56–63. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sine S. M., Claudio T., Sigworth F. J. Activation of Torpedo acetylcholine receptors expressed in mouse fibroblasts. Single channel current kinetics reveal distinct agonist binding affinities. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Aug;96(2):395–437. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart T. G., Xie X., Krishek B. J. Modulation of inhibitory and excitatory amino acid receptor ion channels by zinc. Prog Neurobiol. 1994 Feb;42(3):393–441. doi: 10.1016/0301-0082(94)90082-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séguéla P., Wadiche J., Dineley-Miller K., Dani J. A., Patrick J. W. Molecular cloning, functional properties, and distribution of rat brain alpha 7: a nicotinic cation channel highly permeable to calcium. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):596–604. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00596.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernino S., Amador M., Luetje C. W., Patrick J., Dani J. A. Calcium modulation and high calcium permeability of neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90114-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernino S., Rogers M., Radcliffe K. A., Dani J. A. Quantitative measurement of calcium flux through muscle and neuronal nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurosci. 1994 Sep;14(9):5514–5524. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-09-05514.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. I. Binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin in the absence of effector. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




