Abstract
The three ternary complex factors (TCFs), Net (ERP/ SAP-2), ELK-1 and SAP-1, are highly related ets oncogene family members that participate in the response of the cell to Ras and growth signals. Understanding the different roles of these factors will provide insights into how the signals result in coordinate regulation of the cell. We show that Net inhibits transcription under basal conditions, in which SAP-1a is inactive and ELK-1 stimulates. Repression is mediated by the NID, the Net Inhibitory Domain of about 50 amino acids, which autoregulates the Net protein and also inhibits when it is isolated in a heterologous fusion protein. Net is particularly sensitive to Ras activation. Ras activates Net through the C-domain, which is conserved between the three TCFs, and the NID is an efficient inhibitor of Ras activation. The NID, as well as more C-terminal sequences, inhibit DNA binding. Net is more refractory to DNA binding than the other TCFs, possibly due to the presence of multiple inhibitory elements. The NID may adopt a helix-loop-helix (HLH) structure, as evidenced by homology to other HLH motifs, structure predictions, model building and mutagenesis of critical residues. The sequence resemblance with myogenic factors suggested that Net may form complexes with the same partners. Indeed, we found that Net can interact in vivo with the basic HLH factor, E47. We propose that Net is regulated at the level of its latent DNA-binding activity by protein interactions and/or phosphorylation. Net may form complexes with HLH proteins as well as SRF on specific promotor sequences. The identification of the novel inhibitory domain provides a new inroad into exploring the different roles of the ternary complex factors in growth control and transformation.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayer D. E., Lawrence Q. A., Eisenman R. N. Mad-Max transcriptional repression is mediated by ternary complex formation with mammalian homologs of yeast repressor Sin3. Cell. 1995 Mar 10;80(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baichwal V. R., Park A., Tjian R. v-Src and EJ Ras alleviate repression of c-Jun by a cell-specific inhibitor. Nature. 1991 Jul 11;352(6331):165–168. doi: 10.1038/352165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bain G., Gruenwald S., Murre C. E2A and E2-2 are subunits of B-cell-specific E2-box DNA-binding proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3522–3529. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bannister A. J., Brown H. J., Sutherland J. A., Kouzarides T. Phosphorylation of the c-Fos and c-Jun HOB1 motif stimulates its activation capacity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Dec 11;22(24):5173–5176. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.24.5173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bengal E., Ransone L., Scharfmann R., Dwarki V. J., Tapscott S. J., Weintraub H., Verma I. M. Functional antagonism between c-Jun and MyoD proteins: a direct physical association. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):507–519. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90187-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bories J. C., Willerford D. M., Grévin D., Davidson L., Camus A., Martin P., Stéhelin D., Alt F. W. Increased T-cell apoptosis and terminal B-cell differentiation induced by inactivation of the Ets-1 proto-oncogene. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):635–638. doi: 10.1038/377635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown H. J., Sutherland J. A., Cook A., Bannister A. J., Kouzarides T. An inhibitor domain in c-Fos regulates activation domains containing the HOB1 motif. EMBO J. 1995 Jan 3;14(1):124–131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb06982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahill M. A., Ernst W. H., Janknecht R., Nordheim A. Regulatory squelching. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 16;344(2-3):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00320-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campuzano S., Modolell J. Patterning of the Drosophila nervous system: the achaete-scute gene complex. Trends Genet. 1992 Jun;8(6):202–208. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90234-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano E., Mahadevan L. C. Parallel signal processing among mammalian MAPKs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Mar;20(3):117–122. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88978-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatton B., Bahr A., Acker J., Kedinger C. Eukaryotic GST fusion vector for the study of protein-protein associations in vivo: application to interaction of ATFa with Jun and Fos. Biotechniques. 1995 Jan;18(1):142–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary S., Brou C., Valentin M. E., Burton N., Tora L., Chambon P., Davidson I. A cell-specific factor represses stimulation of transcription in vitro by transcriptional enhancer factor 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5290–5299. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary S., Tora L., Davidson I. Characterization of a HeLa cell factor which negatively regulates transcriptional activation in vitro by transcriptional enhancer factor-1 (TEF-1). J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3631–3637. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q., Cheng J. T., Tasi L. H., Schneider N., Buchanan G., Carroll A., Crist W., Ozanne B., Siciliano M. J., Baer R. The tal gene undergoes chromosome translocation in T cell leukemia and potentially encodes a helix-loop-helix protein. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):415–424. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08126.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. P., Roth S. Y., Simpson R. T. The global transcriptional regulators, SSN6 and TUP1, play distinct roles in the establishment of a repressive chromatin structure. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 15;8(12):1400–1410. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.12.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell I. G., Hurst H. C. Transcriptional repression by the human bZIP factor E4BP4: definition of a minimal repression domain. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Jan 11;22(1):59–65. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell I. G. Repression versus activation in the control of gene transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jan;19(1):38–42. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalton S., Treisman R. Characterization of SAP-1, a protein recruited by serum response factor to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):597–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90194-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodou E., Sparrow D. B., Mohun T., Treisman R. MEF2 proteins, including MEF2A, are expressed in both muscle and non-muscle cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995 Nov 11;23(21):4267–4274. doi: 10.1093/nar/23.21.4267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson L. W., Petersen J. M., Graves B. J., McIntosh L. P. Solution structure of the ETS domain from murine Ets-1: a winged helix-turn-helix DNA binding motif. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 2;15(1):125–134. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ernst P., Smale S. T. Combinatorial regulation of transcription II: The immunoglobulin mu heavy chain gene. Immunity. 1995 May;2(5):427–438. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinman R., Qiu W. Q., Pearse R. N., Nikolajczyk B. S., Sen R., Sheffery M., Ravetch J. V. PU.1 and an HLH family member contribute to the myeloid-specific transcription of the Fc gamma RIIIA promoter. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 15;13(16):3852–3860. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkel T., Duc J., Fearon E. R., Dang C. V., Tomaselli G. F. Detection and modulation in vivo of helix-loop-helix protein-protein interactions. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):5–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. J., Fivash M., Casas-Finet J., Erickson J. W., Kondoh A., Bladen S. V., Fisher C., Watson D. K., Papas T. Real-time DNA binding measurements of the ETS1 recombinant oncoproteins reveal significant kinetic differences between the p42 and p51 isoforms. Protein Sci. 1994 Feb;3(2):257–266. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560030210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Sharrocks A. D., Shaw P. E. Phosphorylation of transcription factor p62TCF by MAP kinase stimulates ternary complex formation at c-fos promoter. Nature. 1992 Jul 30;358(6385):414–417. doi: 10.1038/358414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gille H., Strahl T., Shaw P. E. Activation of ternary complex factor Elk-1 by stress-activated protein kinases. Curr Biol. 1995 Oct 1;5(10):1191–1200. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00235-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
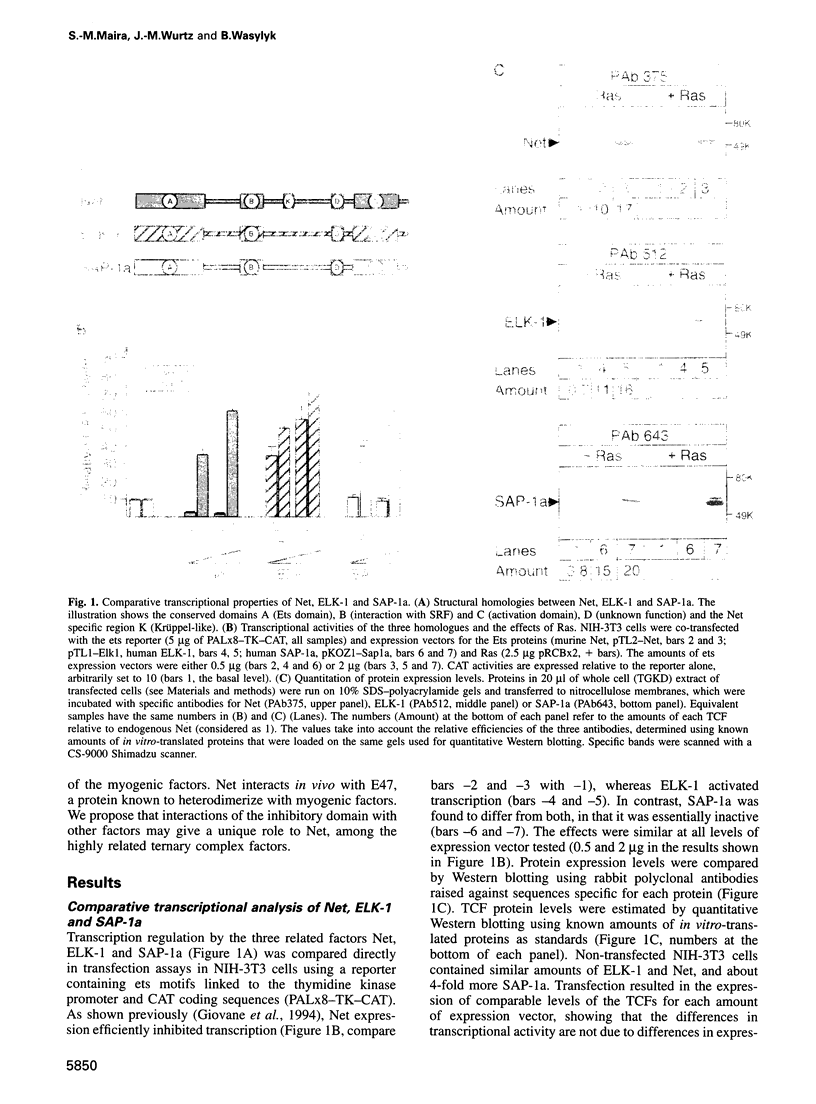
- Giovane A., Pintzas A., Maira S. M., Sobieszczuk P., Wasylyk B. Net, a new ets transcription factor that is activated by Ras. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 1;8(13):1502–1513. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.13.1502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovane A., Sobieszczuk P., Mignon C., Mattei M. G., Wasylyk B. Locations of the ets subfamily members net, elk1, and sap1 (ELK3, ELK1, and ELK4) on three homologous regions of the mouse and human genomes. Genomics. 1995 Oct 10;29(3):769–772. doi: 10.1006/geno.1995.9938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman R., Masutani H., Leibovitch M. P., Robin P., Soudant I., Trouche D., Harel-Bellan A. Physical interaction between the mitogen-responsive serum response factor and myogenic basic-helix-loop-helix proteins. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 1;271(9):5258–5264. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.5258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutman A., Wasylyk C., Wasylyk B. Cell-specific regulation of oncogene-responsive sequences of the c-fos promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5381–5387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
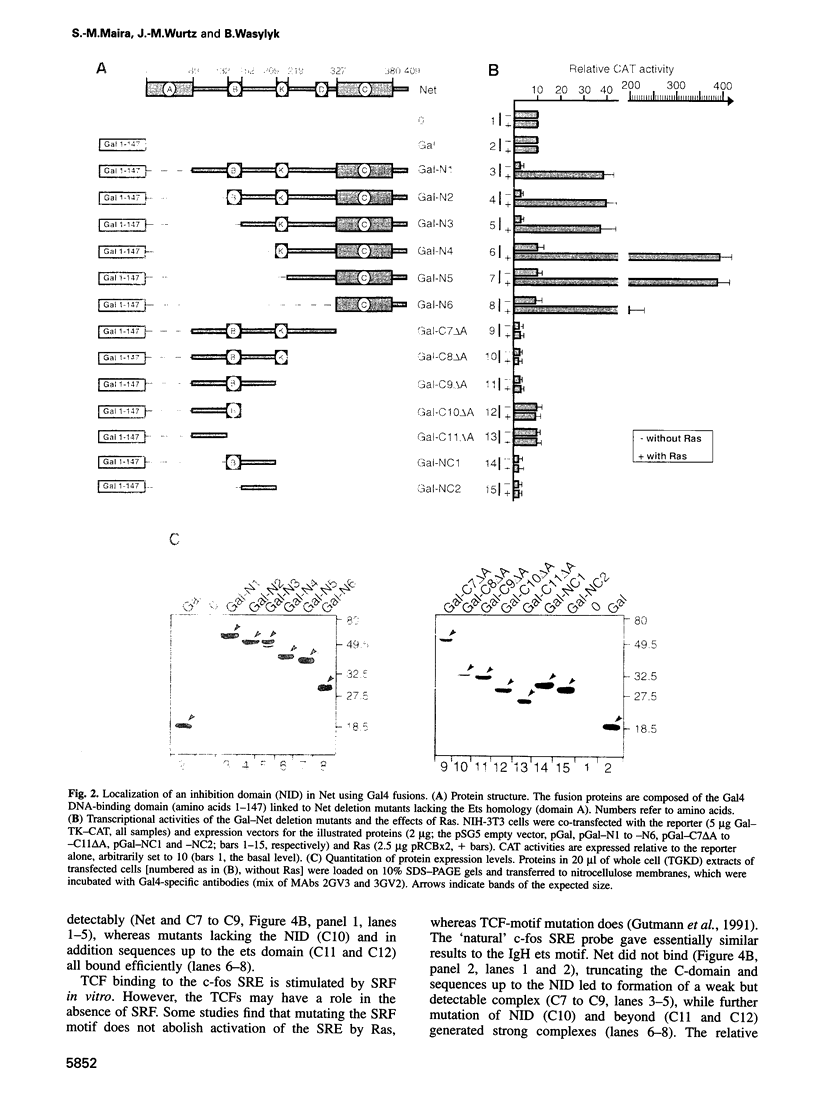
- Hagman J., Grosschedl R. An inhibitory carboxyl-terminal domain in Ets-1 and Ets-2 mediates differential binding of ETS family factors to promoter sequences of the mb-1 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8889–8893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S. L., Wasylyk B. The oncoprotein v-Ets is less selective in DNA binding than c-Ets-1 due to the C-terminal sequence change. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2499–2512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression by the Drosophila even-skipped protein: definition of a minimal repression domain. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):491–503. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanna-Rose W., Hansen U. Active repression mechanisms of eukaryotic transcription repressors. Trends Genet. 1996 Jun;12(6):229–234. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(96)10022-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Marais R., John S., Wynne J., Dalton S., Treisman R. Functional analysis of a growth factor-responsive transcription factor complex. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):395–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90238-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. S., Wynne J., Treisman R. The Rho family GTPases RhoA, Rac1, and CDC42Hs regulate transcriptional activation by SRF. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1159–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Büscher D., Nordheim A., Baccarini M. Ras/MAP kinase-dependent and -independent signaling pathways target distinct ternary complex factors. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1803–1816. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm L., Sander C. Fast and simple Monte Carlo algorithm for side chain optimization in proteins: application to model building by homology. Proteins. 1992 Oct;14(2):213–223. doi: 10.1002/prot.340140208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. L., Wadman I., Baer R. Formation of in vivo complexes between the TAL1 and E2A polypeptides of leukemic T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3181–3185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hupp T. R., Sparks A., Lane D. P. Small peptides activate the latent sequence-specific DNA binding function of p53. Cell. 1995 Oct 20;83(2):237–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurlin P. J., Quéva C., Koskinen P. J., Steingrímsson E., Ayer D. E., Copeland N. G., Jenkins N. A., Eisenman R. N. Mad3 and Mad4: novel Max-interacting transcriptional repressors that suppress c-myc dependent transformation and are expressed during neural and epidermal differentiation. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 15;14(22):5646–5659. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iavarone A., Garg P., Lasorella A., Hsu J., Israel M. A. The helix-loop-helix protein Id-2 enhances cell proliferation and binds to the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 1;8(11):1270–1284. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.11.1270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Ernst W. H., Nordheim A. SAP1a is a nuclear target of signaling cascades involving ERKs. Oncogene. 1995 Mar 16;10(6):1209–1216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Ernst W. H., Pingoud V., Nordheim A. Activation of ternary complex factor Elk-1 by MAP kinases. EMBO J. 1993 Dec 15;12(13):5097–5104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06204.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Nordheim A. Gene regulation by Ets proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 23;1155(3):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janknecht R., Zinck R., Ernst W. H., Nordheim A. Functional dissection of the transcription factor Elk-1. Oncogene. 1994 Apr;9(4):1273–1278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D. The price of repression. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):655–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90524-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D., Lorch Y. Interplay between chromatin structure and transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;7(3):371–375. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kortenjann M., Thomae O., Shaw P. E. Inhibition of v-raf-dependent c-fos expression and transformation by a kinase-defective mutant of the mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk2. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4815–4824. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leprince D., Crepieux P., Stehelin D. c-ets-1 DNA binding to the PEA3 motif is differentially inhibited by all the mutations found in v-ets. Oncogene. 1992 Jan;7(1):9–17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libermann T. A., Baltimore D. Pi, a pre-B-cell-specific enhancer element in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):5957–5969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.5957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht J. D., Hanna-Rose W., Reddy J. C., English M. A., Ro M., Grossel M., Shaknovich R., Hansen U. Mapping and mutagenesis of the amino-terminal transcriptional repression domain of the Drosophila Krüppel protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;14(6):4057–4066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.6.4057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim F., Kraut N., Framptom J., Graf T. DNA binding by c-Ets-1, but not v-Ets, is repressed by an intramolecular mechanism. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):643–652. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez M., Oettgen P., Akbarali Y., Dendorfer U., Libermann T. A. ERP, a new member of the ets transcription factor/oncoprotein family: cloning, characterization, and differential expression during B-lymphocyte development. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 May;14(5):3292–3309. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.5.3292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma P. C., Rould M. A., Weintraub H., Pabo C. O. Crystal structure of MyoD bHLH domain-DNA complex: perspectives on DNA recognition and implications for transcriptional activation. Cell. 1994 May 6;77(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod K., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The ets gene family. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jul;17(7):251–256. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90404-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marais R., Wynne J., Treisman R. The SRF accessory protein Elk-1 contains a growth factor-regulated transcriptional activation domain. Cell. 1993 Apr 23;73(2):381–393. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90237-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolin J. F., Friedman J. R., Meyer W. K., Vissing H., Thiesen H. J., Rauscher F. J., 3rd Krüppel-associated boxes are potent transcriptional repression domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellentin J. D., Smith S. D., Cleary M. L. lyl-1, a novel gene altered by chromosomal translocation in T cell leukemia, codes for a protein with a helix-loop-helix DNA binding motif. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):77–83. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90404-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreau-Gachelin F. Spi-1/PU.1: an oncogene of the Ets family. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Dec 30;1198(2-3):149–163. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(94)90011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., Bain G., van Dijk M. A., Engel I., Furnari B. A., Massari M. E., Matthews J. R., Quong M. W., Rivera R. R., Stuiver M. H. Structure and function of helix-loop-helix proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jun 21;1218(2):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(94)90001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muthusamy N., Barton K., Leiden J. M. Defective activation and survival of T cells lacking the Ets-1 transcription factor. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):639–642. doi: 10.1038/377639a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Vennström B. The sound of silence. Nature. 1995 Oct 5;377(6548):387–388. doi: 10.1038/377387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petersen J. M., Skalicky J. J., Donaldson L. W., McIntosh L. P., Alber T., Graves B. J. Modulation of transcription factor Ets-1 DNA binding: DNA-induced unfolding of an alpha helix. Science. 1995 Sep 29;269(5232):1866–1869. doi: 10.1126/science.7569926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. E. Built by association: structure and function of helix-loop-helix DNA-binding proteins. Structure. 1994 Jan 15;2(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price M. A., Rogers A. E., Treisman R. Comparative analysis of the ternary complex factors Elk-1, SAP-1a and SAP-2 (ERP/NET). EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2589–2601. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabault B., Ghysdael J. Calcium-induced phosphorylation of ETS1 inhibits its specific DNA binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 11;269(45):28143–28151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Huebner K., Isobe M., ar-Rushdi A., Croce C. M., Reddy E. S. elk, tissue-specific ets-related genes on chromosomes X and 14 near translocation breakpoints. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):66–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2539641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao V. N., Reddy E. S. elk-1 domains responsible for autonomous DNA binding, SRE:SRF interaction and negative regulation of DNA binding. Oncogene. 1992 Nov;7(11):2335–2340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivera R. R., Stuiver M. H., Steenbergen R., Murre C. Ets proteins: new factors that regulate immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;13(11):7163–7169. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.11.7163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rushlow C. A., Hogan A., Pinchin S. M., Howe K. M., Lardelli M., Ish-Horowicz D. The Drosophila hairy protein acts in both segmentation and bristle patterning and shows homology to N-myc. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3095–3103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08461.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlissel M., Voronova A., Baltimore D. Helix-loop-helix transcription factor E47 activates germ-line immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene transcription and rearrangement in a pre-T-cell line. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1367–1376. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seger R., Krebs E. G. The MAPK signaling cascade. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):726–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Ascione R., Fisher R. J., Mavrothalassitis G. J., Bhat N. K., Papas T. S. The ets gene family. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 May;3(5):327–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seth A., Robinson L., Thompson D. M., Watson D. K., Papas T. S. Transactivation of GATA-1 promoter with ETS1, ETS2 and ERGB/Hu-FLI-1 proteins: stabilization of the ETS1 protein binding on GATA-1 promoter sequences by monoclonal antibody. Oncogene. 1993 Jul;8(7):1783–1790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sgouras D. N., Athanasiou M. A., Beal G. J., Jr, Fisher R. J., Blair D. G., Mavrothalassitis G. J. ERF: an ETS domain protein with strong transcriptional repressor activity, can suppress ets-associated tumorigenesis and is regulated by phosphorylation during cell cycle and mitogenic stimulation. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 2;14(19):4781–4793. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore P., Sharrocks A. D. The MADS-box family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Apr 1;229(1):1–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thisse B., Stoetzel C., Gorostiza-Thisse C., Perrin-Schmitt F. Sequence of the twist gene and nuclear localization of its protein in endomesodermal cells of early Drosophila embryos. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2175–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. D., Higgins D. G., Gibson T. J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Nov 11;22(22):4673–4680. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.22.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Marais R., Wynne J. Spatial flexibility in ternary complexes between SRF and its accessory proteins. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4631–4640. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Ternary complex factors: growth factor regulated transcriptional activators. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1994 Feb;4(1):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(94)90097-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. The serum response element. Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Oct;17(10):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90013-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trouche D., Grigoriev M., Lenormand J. L., Robin P., Leibovitch S. A., Sassone-Corsi P., Harel-Bellan A. Repression of c-fos promoter by MyoD on muscle cell differentiation. Nature. 1993 May 6;363(6424):79–82. doi: 10.1038/363079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronova A., Baltimore D. Mutations that disrupt DNA binding and dimer formation in the E47 helix-loop-helix protein map to distinct domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4722–4726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Hahn S. L., Giovane A. The Ets family of transcription factors. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Jan 15;211(1-2):7–18. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-78757-7_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B., Wasylyk C., Flores P., Begue A., Leprince D., Stehelin D. The c-ets proto-oncogenes encode transcription factors that cooperate with c-Fos and c-Jun for transcriptional activation. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):191–193. doi: 10.1038/346191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Kerckaert J. P., Wasylyk B. A novel modulator domain of Ets transcription factors. Genes Dev. 1992 Jun;6(6):965–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.6.965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk C., Maira S. M., Sobieszczuk P., Wasylyk B. Reversion of Ras transformed cells by Ets transdominant mutants. Oncogene. 1994 Dec;9(12):3665–3673. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N., Jin J. R., Green S., Hollis M., Chambon P. The yeast UASG is a transcriptional enhancer in human HeLa cells in the presence of the GAL4 trans-activator. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J., Brou C., Wu J., Lutz Y., Moncollin V., Chambon P. The acidic transcriptional activator GAL-VP16 acts on preformed template-committed complexes. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2229–2240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05282.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitmarsh A. J., Shore P., Sharrocks A. D., Davis R. J. Integration of MAP kinase signal transduction pathways at the serum response element. Science. 1995 Jul 21;269(5222):403–407. doi: 10.1126/science.7618106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witzgall R., O'Leary E., Leaf A., Onaldi D., Bonventre J. V. The Krüppel-associated box-A (KRAB-A) domain of zinc finger proteins mediates transcriptional repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 10;91(10):4514–4518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.10.4514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Soriano P., Weintraub H. The helix-loop-helix gene E2A is required for B cell formation. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):875–884. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]