Abstract
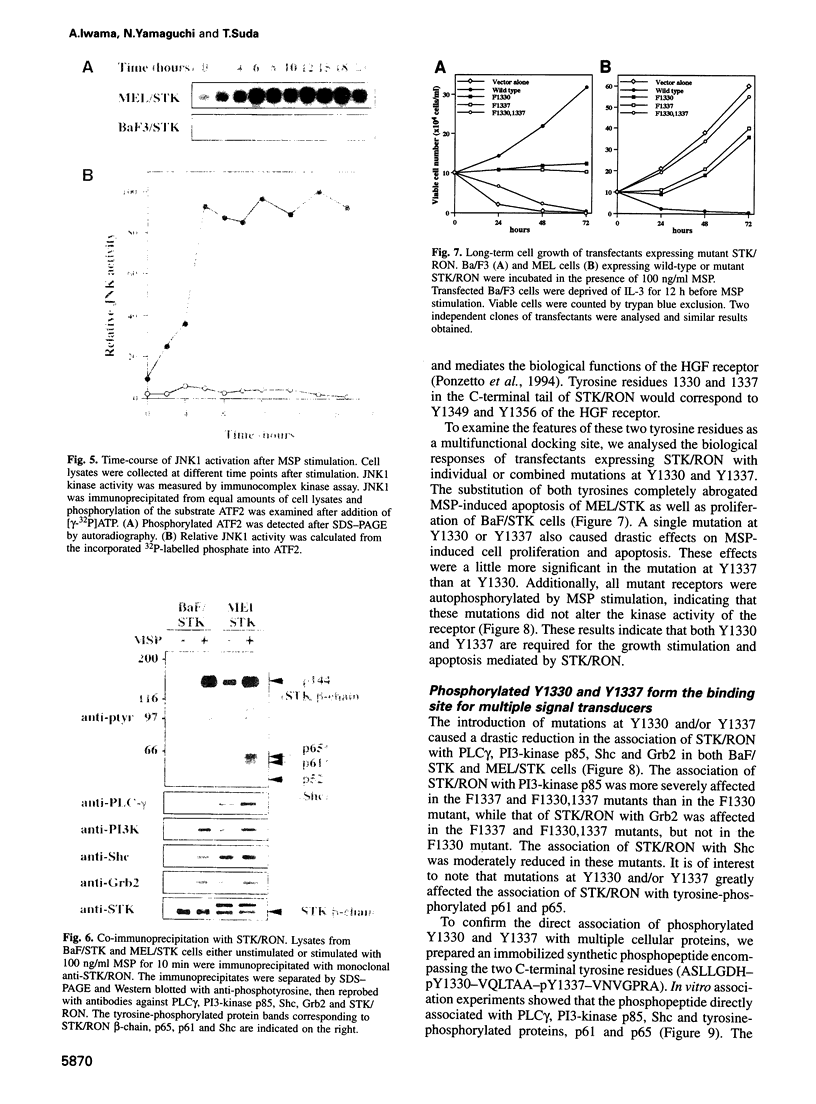
STK/RON tyrosine kinase, a member of the hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) receptor family, is a receptor for macrophage-stimulating protein (MSP). To examine the STK/RON signalling pathway, we generated STK/ RON transfectants showing opposite features in growth. STK/RON-expressing Ba/F3 pro-B cells (BaF/STK) exhibited MSP-dependent growth, whereas STK/ RON-expressing mouse erythroleukaemia cells (MEL/ STK) displayed MSP-induced apoptosis. This apoptosis was accompanied by the prolonged activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), which has recently been implicated in the initiation of apoptosis. Co-immunoprecipitation analyses showed that autophosphorylated STK/RON associated with PLC-gamma, P13-kinase, Shc and Grb2 in both transfectants. However, major tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins, p61 and p65, specifically associated with STK/RON in MEL/STK cells. Mutations at two C-terminal tyrosine residues, Y1330 and Y1337, in the counterpart of the multifunctional docking site of the HGF receptor abolished both MSP-induced growth and apoptosis. Analyses of these mutants and in vitro association revealed that signalling proteins including p61 and p65 directly bound to the phosphotyrosines in the multifunctional docking site. These results demonstrate that positive or negative signals toward cell growth are generated through the multifunctional docking site and suggest the involvement of p61 and p65 as well as JNK in apoptosis. Our findings provide the first evidence for apoptosis via a receptor tyrosine kinase.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardelli A., Ponzetto C., Comoglio P. M. Identification of functional domains in the hepatocyte growth factor and its receptor by molecular engineering. J Biotechnol. 1994 Sep 30;37(2):109–122. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudreau N., Sympson C. J., Werb Z., Bissell M. J. Suppression of ICE and apoptosis in mammary epithelial cells by extracellular matrix. Science. 1995 Feb 10;267(5199):891–893. doi: 10.1126/science.7531366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. R., Meyer C. F., Tan T. H. Persistent activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 (JNK1) in gamma radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):631–634. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. B., Ren R., Baltimore D. Modular binding domains in signal transduction proteins. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):237–248. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Irvine R. F. Phospholipid signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J. Signal transduction. Regulating S6 kinase. Nature. 1994 Sep 29;371(6496):378–379. doi: 10.1038/371378a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Hibi M., Wu I. H., Barrett T., Su B., Deng T., Karin M., Davis R. J. JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1025–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enari M., Hug H., Nagata S. Involvement of an ICE-like protease in Fas-mediated apoptosis. Nature. 1995 May 4;375(6526):78–81. doi: 10.1038/375078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucheu C., Diu A., Chan A. W., Blanchet A. M., Miossec C., Hervé F., Collard-Dutilleul V., Gu Y., Aldape R. A., Lippke J. A. A novel human protease similar to the interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme induces apoptosis in transfected cells. EMBO J. 1995 May 1;14(9):1914–1922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07183.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagliardini V., Fernandez P. A., Lee R. K., Drexler H. C., Rotello R. J., Fishman M. C., Yuan J. Prevention of vertebrate neuronal death by the crmA gene. Science. 1994 Feb 11;263(5148):826–828. doi: 10.1126/science.8303301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galimi F., Bagnara G. P., Bonsi L., Cottone E., Follenzi A., Simeone A., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor induces proliferation and differentiation of multipotent and erythroid hemopoietic progenitors. J Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;127(6 Pt 1):1743–1754. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.6.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudino G., Avantaggiato V., Follenzi A., Acampora D., Simeone A., Comoglio P. M. The proto-oncogene RON is involved in development of epithelial, bone and neuro-endocrine tissues. Oncogene. 1995 Dec 21;11(12):2627–2637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudino G., Follenzi A., Naldini L., Collesi C., Santoro M., Gallo K. A., Godowski P. J., Comoglio P. M. RON is a heterodimeric tyrosine kinase receptor activated by the HGF homologue MSP. EMBO J. 1994 Aug 1;13(15):3524–3532. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta S., Campbell D., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. Transcription factor ATF2 regulation by the JNK signal transduction pathway. Science. 1995 Jan 20;267(5196):389–393. doi: 10.1126/science.7824938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han S., Stuart L. A., Degen S. J. Characterization of the DNF15S2 locus on human chromosome 3: identification of a gene coding for four kringle domains with homology to hepatocyte growth factor. Biochemistry. 1991 Oct 8;30(40):9768–9780. doi: 10.1021/bi00104a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashio K., Shima N., Goto M., Itagaki Y., Nagao M., Yasuda H., Morinaga T. Identity of a tumor cytotoxic factor from human fibroblasts and hepatocyte growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):397–404. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91287-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino M., Nishizawa Y., Tatsumi N., Tojo A., Morii H. Down-modulation of c-kit mRNA and protein expression by erythroid differentiation factor/activin A. FEBS Lett. 1995 Oct 23;374(1):69–71. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)01078-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino M., Tojo A., Misawa Y., Morii H., Takaku F., Shibuya M. Unregulated expression of the erythropoietin receptor gene caused by insertion of spleen focus-forming virus long terminal repeat in a murine erythroleukemia cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5527–5533. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff J. L., Jelinek M. A., Borgman C. A., Lansing T. J., Parsons J. T. The protooncogene c-sea encodes a transmembrane protein-tyrosine kinase related to the Met/hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6140–6144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Yonehara S., Ishii A., Yonehara M., Mizushima S., Sameshima M., Hase A., Seto Y., Nagata S. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama A., Okano K., Sudo T., Matsuda Y., Suda T. Molecular cloning of a novel receptor tyrosine kinase gene, STK, derived from enriched hematopoietic stem cells. Blood. 1994 Jun 1;83(11):3160–3169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwama A., Wang M. H., Yamaguchi N., Ohno N., Okano K., Sudo T., Takeya M., Gervais F., Morissette C., Leonard E. J. Terminal differentiation of murine resident peritoneal macrophages is characterized by expression of the STK protein tyrosine kinase, a receptor for macrophage-stimulating protein. Blood. 1995 Nov 1;86(9):3394–3403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuida K., Lippke J. A., Ku G., Harding M. W., Livingston D. J., Su M. S., Flavell R. A. Altered cytokine export and apoptosis in mice deficient in interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Science. 1995 Mar 31;267(5206):2000–2003. doi: 10.1126/science.7535475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurihara N., Iwama A., Tatsumi J., Ikeda K., Suda T. Macrophage-stimulating protein activates STK receptor tyrosine kinase on osteoclasts and facilitates bone resorption by osteoclast-like cells. Blood. 1996 May 1;87(9):3704–3710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard E. J., Skeel A. A serum protein that stimulates macrophage movement, chemotaxis and spreading. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 15;102(2):434–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Los M., Van de Craen M., Penning L. C., Schenk H., Westendorp M., Baeuerle P. A., Dröge W., Krammer P. H., Fiers W., Schulze-Osthoff K. Requirement of an ICE/CED-3 protease for Fas/APO-1-mediated apoptosis. Nature. 1995 May 4;375(6526):81–83. doi: 10.1038/375081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall C. J. Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90401-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Zhu H., Rotello R., Hartwieg E. A., Yuan J. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by IL-1 beta-converting enzyme, a mammalian homolog of the C. elegans cell death gene ced-3. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):653–660. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90486-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Steinmetz M. Il-3-dependent mouse clones that express B-220 surface antigen, contain Ig genes in germ-line configuration, and generate B lymphocytes in vivo. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):727–734. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80053-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Bardelli A., Maina F., Longati P., Panayotou G., Dhand R., Waterfield M. D., Comoglio P. M. A novel recognition motif for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase binding mediates its association with the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;13(8):4600–4608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.8.4600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Bardelli A., Zhen Z., Maina F., dalla Zonca P., Giordano S., Graziani A., Panayotou G., Comoglio P. M. A multifunctional docking site mediates signaling and transformation by the hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor receptor family. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):261–271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90318-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quantin B., Schuhbaur B., Gesnel M. C., Doll'e P., Breathnach R. Restricted expression of the ron gene encoding the macrophage stimulating protein receptor during mouse development. Dev Dyn. 1995 Dec;204(4):383–390. doi: 10.1002/aja.1002040405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raingeaud J., Gupta S., Rogers J. S., Dickens M., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 31;270(13):7420–7426. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.13.7420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C. Bcl-2 and the regulation of programmed cell death. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;124(1-2):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ronsin C., Muscatelli F., Mattei M. G., Breathnach R. A novel putative receptor protein tyrosine kinase of the met family. Oncogene. 1993 May;8(5):1195–1202. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Osthoff K., Walczak H., Dröge W., Krammer P. H. Cell nucleus and DNA fragmentation are not required for apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Oct;127(1):15–20. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., Osborne B. A. Programmed cell death, apoptosis and killer genes. Immunol Today. 1993 Dec;14(12):582–590. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90197-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiota G., Rhoads D. B., Wang T. C., Nakamura T., Schmidt E. V. Hepatocyte growth factor inhibits growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):373–377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiozaki M., Sakai R., Tabuchi M., Nakamura T., Sugino K., Sugino H., Eto Y. Evidence for the participation of endogenous activin A/erythroid differentiation factor in the regulation of erythropoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1553–1556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skeel A., Yoshimura T., Showalter S. D., Tanaka S., Appella E., Leonard E. J. Macrophage stimulating protein: purification, partial amino acid sequence, and cellular activity. J Exp Med. 1991 May 1;173(5):1227–1234. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.5.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sluss H. K., Barrett T., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor mediated by JNK protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;14(12):8376–8384. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.12.8376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Vogt P. K., Hayman M. J. The v-sea oncogene of avian erythroblastosis retrovirus S13: another member of the protein-tyrosine kinase gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5291–5295. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., Chaudhuri M., Gish G., Pawson T., Haser W. G., King F., Roberts T., Ratnofsky S., Lechleider R. J. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell. 1993 Mar 12;72(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90404-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Songyang Z., Shoelson S. E., McGlade J., Olivier P., Pawson T., Bustelo X. R., Barbacid M., Sabe H., Hanafusa H., Yi T. Specific motifs recognized by the SH2 domains of Csk, 3BP2, fps/fes, GRB-2, HCP, SHC, Syk, and Vav. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;14(4):2777–2785. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.4.2777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steller H. Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1445–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.7878463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari M., Quan L. T., O'Rourke K., Desnoyers S., Zeng Z., Beidler D. R., Poirier G. G., Salvesen G. S., Dixit V. M. Yama/CPP32 beta, a mammalian homolog of CED-3, is a CrmA-inhibitable protease that cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):801–809. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90541-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science. 1995 Mar 10;267(5203):1456–1462. doi: 10.1126/science.7878464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij M., Bose R., Lin X. H., Yao B., Jarvis W. D., Grant S., Birrer M. J., Szabo E., Zon L. I., Kyriakis J. M. Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1996 Mar 7;380(6569):75–79. doi: 10.1038/380075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L., Miura M., Bergeron L., Zhu H., Yuan J. Ich-1, an Ice/ced-3-related gene, encodes both positive and negative regulators of programmed cell death. Cell. 1994 Sep 9;78(5):739–750. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(94)90422-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Cox G. W., Yoshimura T., Sheffler L. A., Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Macrophage-stimulating protein inhibits induction of nitric oxide production by endotoxin- or cytokine-stimulated mouse macrophages. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 13;269(19):14027–14031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Iwama A., Skeel A., Suda T., Leonard E. J. The murine stk gene product, a transmembrane protein tyrosine kinase, is a receptor for macrophage-stimulating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 25;92(9):3933–3937. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.9.3933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. H., Ronsin C., Gesnel M. C., Coupey L., Skeel A., Leonard E. J., Breathnach R. Identification of the ron gene product as the receptor for the human macrophage stimulating protein. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):117–119. doi: 10.1126/science.7939629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia Z., Dickens M., Raingeaud J., Davis R. J., Greenberg M. E. Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science. 1995 Nov 24;270(5240):1326–1331. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5240.1326. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura T., Yuhki N., Wang M. H., Skeel A., Leonard E. J. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of human macrophage stimulating protein (MSP, MST1) confirms MSP as a member of the family of kringle proteins and locates the MSP gene on chromosome 3. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15461–15468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K. The many faces of hepatocyte growth factor: from hepatopoiesis to hematopoiesis. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(5):1177–1180. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









