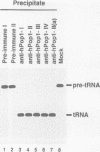
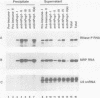
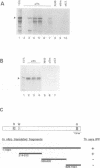
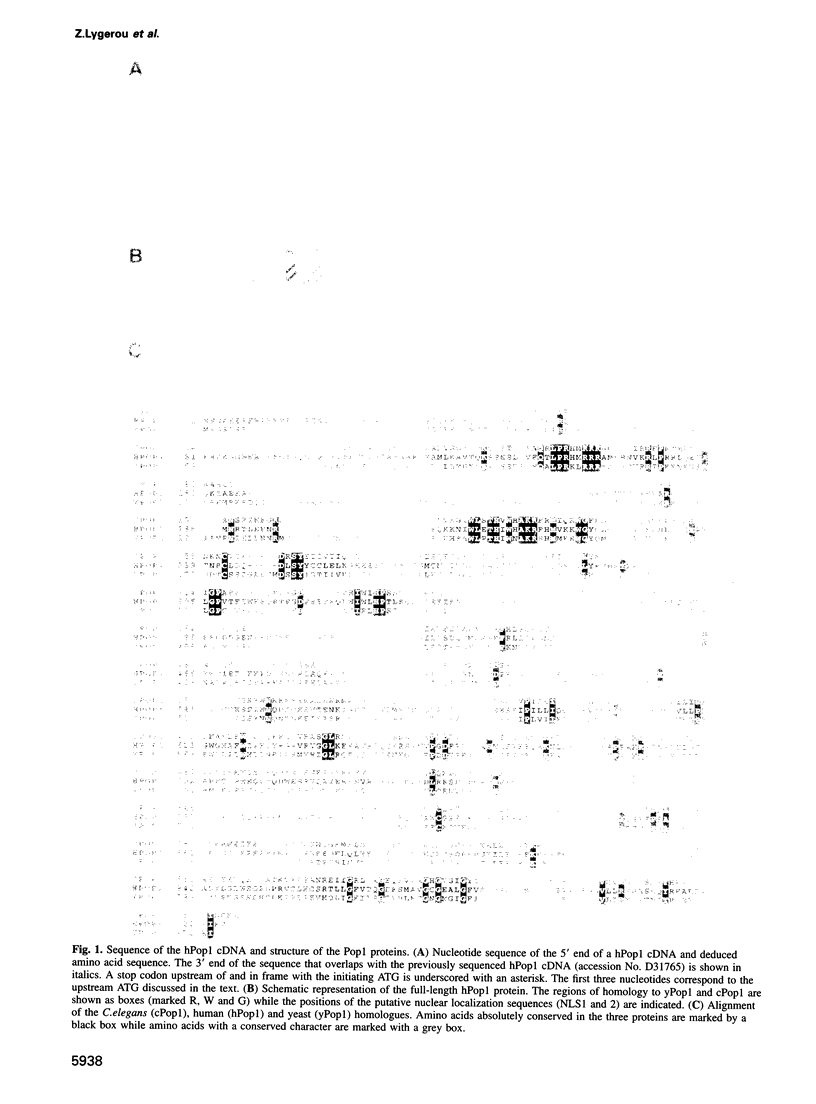
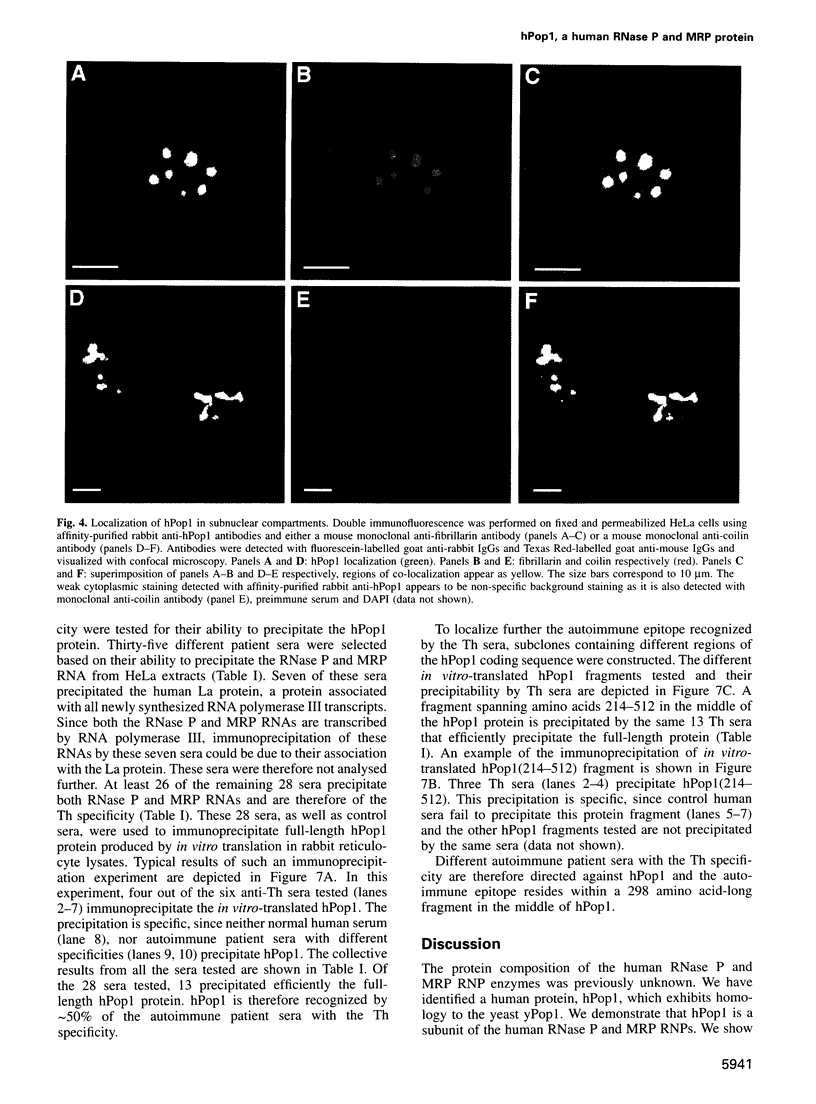
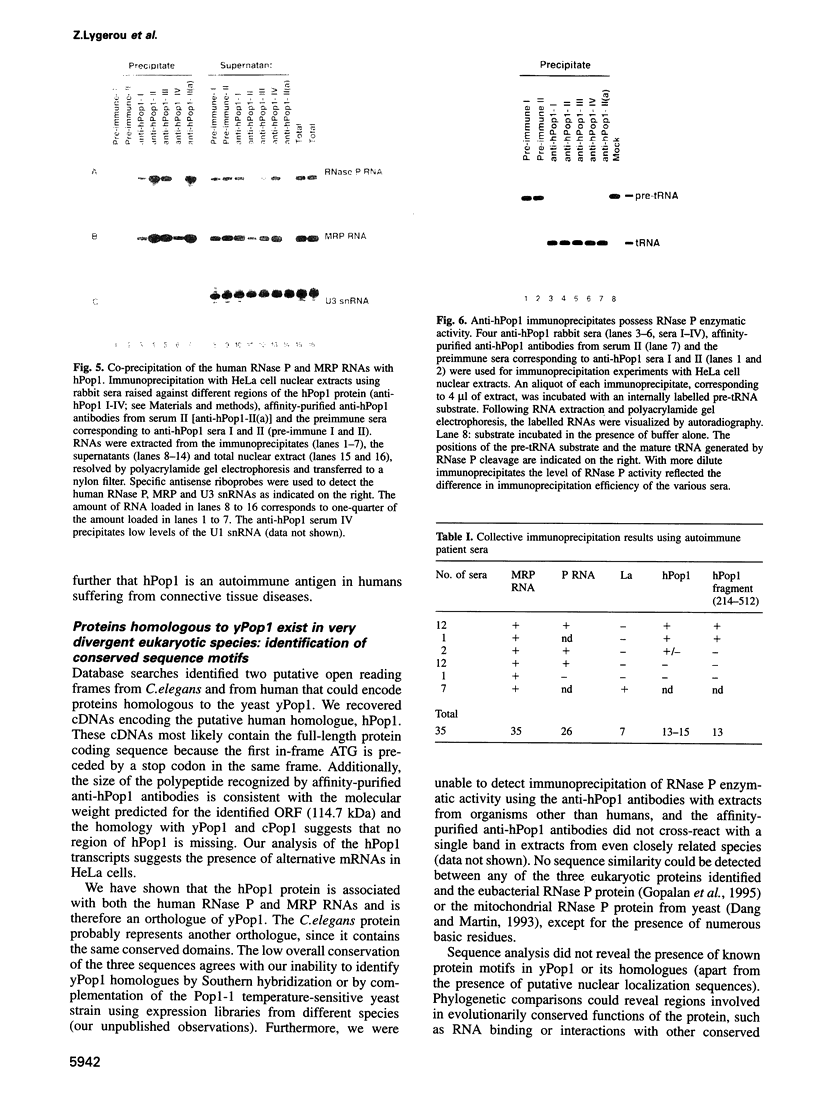
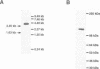Abstract
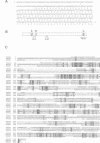
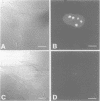
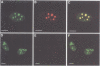
The eukaryotic endonucleases RNase P and RNase MRP require both RNA and protein subunits for function. Even though the human RNase P and MRP RNAs were previously characterized, the protein composition of the particles remains unknown. We have identified a human a Caenorhabditis elegans sequence showing homology to yPop1, a protein subunit of the yeast RNase P and MRP particles. A cDNA containing the complete coding sequence for the human protein, hPop1, was cloned. Sequence analysis identifies three novel sequence motifs, conserved between the human, C. elegans and yeast proteins. Affinity-purified anti-hPop1 antibodies recognize a single 115 kDa protein in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. Immunoprecipitations with different anti-hPop1 antibodies demonstrate an association of hPop1 with the vast majority of the RNase P and MRP RNAs in HeLa cell nuclear extracts. Additionally, anti-hPop1 immunoprecipitates possess RNase P enzymatic activity. These results establish hPop1 as the first identified RNase P and MRP protein subunit from humans. Anti-hPop1 antibodies generate a strong nucleolar and a weaker homogeneous nuclear staining in HeLa cells. A certain class of autoimmune patient serum precipitates in vitro-translated hPop1. hPop1 is therefore an autoantigen in patients suffering from connective tissue diseases.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altman S., Kirsebom L., Talbot S. Recent studies of ribonuclease P. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):7–14. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7916700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altman S., Wesolowski D., Puranam R. S. Nucleotide sequences of the RNA subunit of RNase P from several mammals. Genomics. 1993 Nov;18(2):418–422. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aris J. P., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a yeast nucleolar protein that is similar to a rat liver nucleolar protein. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;107(1):17–31. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartkiewicz M., Gold H., Altman S. Identification and characterization of an RNA molecule that copurifies with RNase P activity from HeLa cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):488–499. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.488. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett J. L., Jeong-Yu S., Clayton D. A. Characterization of a Xenopus laevis ribonucleoprotein endoribonuclease. Isolation of the RNA component and its expression during development. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21765–21772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmo-Fonseca M., Pepperkok R., Carvalho M. T., Lamond A. I. Transcription-dependent colocalization of the U1, U2, U4/U6, and U5 snRNPs in coiled bodies. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):1–14. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. A mammalian mitochondrial RNA processing activity contains nucleus-encoded RNA. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1178–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.2434997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. A novel endoribonuclease cleaves at a priming site of mouse mitochondrial DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):409–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang D. D., Clayton D. A. Mouse RNAase MRP RNA is encoded by a nuclear gene and contains a decamer sequence complementary to a conserved region of mitochondrial RNA substrate. Cell. 1989 Jan 13;56(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90991-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Spliceosome assembly in yeast. Genes Dev. 1987 Nov;1(9):1014–1027. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.9.1014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu S., Archer R. H., Zengel J. M., Lindahl L. The RNA of RNase MRP is required for normal processing of ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 18;91(2):659–663. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clayton D. A. A nuclear function for RNase MRP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4615–4617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dairaghi D. J., Clayton D. A. Bovine RNase MRP cleaves the divergent bovine mitochondrial RNA sequence at the displacement-loop region. J Mol Evol. 1993 Oct;37(4):338–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00178864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang Y. L., Martin N. C. Yeast mitochondrial RNase P. Sequence of the RPM2 gene and demonstration that its product is a protein subunit of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19791–19796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doria M., Carrara G., Calandra P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. An RNA molecule copurifies with RNase P activity from Xenopus laevis oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2315–2320. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forster A. C., Altman S. Similar cage-shaped structures for the RNA components of all ribonuclease P and ribonuclease MRP enzymes. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):407–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90003-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. A., Craft J., Hardin J. A., Bartkiewicz M., Altman S. Antibodies in human serum that precipitate ribonuclease P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5483–5487. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold H. A., Topper J. N., Clayton D. A., Craft J. The RNA processing enzyme RNase MRP is identical to the Th RNP and related to RNase P. Science. 1989 Sep 22;245(4924):1377–1380. doi: 10.1126/science.2476849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrier-Takada C., Gardiner K., Marsh T., Pace N., Altman S. The RNA moiety of ribonuclease P is the catalytic subunit of the enzyme. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habets W., Hoet M., Bringmann P., Lührmann R., van Venrooij W. Autoantibodies to ribonucleoprotein particles containing U2 small nuclear RNA. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1545–1550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. Sequential association of nucleolar 7-2 RNA with two different autoantigens. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1379–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. R., Cao L. G., Wang Y. L., Pederson T. Dynamic localization of RNase MRP RNA in the nucleolus observed by fluorescent RNA cytochemistry in living cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1649–1658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwan R., Bennett J. L., Clayton D. A. Nuclear RNase MRP processes RNA at multiple discrete sites: interaction with an upstream G box is required for subsequent downstream cleavages. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1264–1276. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karwan R. RNase MRP/RNase P: a structure-function relation conserved in evolution? FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 15;319(1-2):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80025-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kipnis R. J., Craft J., Hardin J. A. The analysis of antinuclear and antinucleolar autoantibodies of scleroderma by radioimmunoprecipitation assays. Arthritis Rheum. 1990 Sep;33(9):1431–1437. doi: 10.1002/art.1780330917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Bortolin M. L., Filipowicz W. Characterization of the intron-encoded U19 RNA, a new mammalian small nucleolar RNA that is not associated with fibrillarin. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;16(4):1391–1400. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.4.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Filipowicz W. Evidence against a mitochondrial location of the 7-2/MRP RNA in mammalian cells. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):11–16. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90528-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiss T., Marshallsay C., Filipowicz W. 7-2/MRP RNAs in plant and mammalian cells: association with higher order structures in the nucleolus. EMBO J. 1992 Oct;11(10):3737–3746. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05459.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp G., Cherayil B., Frendewey D., Nishikawa S., Söll D. Two RNA species co-purify with RNase P from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1697–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamond A. I., Carmo-Fonseca M. The coiled body. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;3(6):198–204. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90214-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Engelke D. R. Partial characterization of an RNA component that copurifies with Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNase P. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2536–2543. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. Y., Rohlman C. E., Molony L. A., Engelke D. R. Characterization of RPR1, an essential gene encoding the RNA component of Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear RNase P. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):721–730. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li K., Smagula C. S., Parsons W. J., Richardson J. A., Gonzalez M., Hagler H. K., Williams R. S. Subcellular partitioning of MRP RNA assessed by ultrastructural and biochemical analysis. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(6):871–882. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.6.871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Archer R. H., Zengel J. M. A new rRNA processing mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):295–301. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu M. H., Yuan Y., Reddy R. Human RNaseP RNA and nucleolar 7-2 RNA share conserved 'To' antigen-binding domains. Mol Cell Biochem. 1994 Jan 12;130(1):75–82. doi: 10.1007/BF01084270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lygerou Z., Allmang C., Tollervey D., Séraphin B. Accurate processing of a eukaryotic precursor ribosomal RNA by ribonuclease MRP in vitro. Science. 1996 Apr 12;272(5259):268–270. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5259.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lygerou Z., Mitchell P., Petfalski E., Séraphin B., Tollervey D. The POP1 gene encodes a protein component common to the RNase MRP and RNase P ribonucleoproteins. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 15;8(12):1423–1433. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.12.1423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mamula M. J., Baer M., Craft J., Altman S. An immunological determinant of RNase P protein is conserved between Escherichia coli and humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8717–8721. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matera A. G., Frey M. R., Margelot K., Wolin S. L. A perinucleolar compartment contains several RNA polymerase III transcripts as well as the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein, hnRNP I. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(5):1181–1193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.5.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Tollervey D., Séraphin B. Small nuclear RNAs in messenger RNA and ribosomal RNA processing. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):47–53. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.8422974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. P., Tollervey D. Birth of the snoRNPs: the evolution of RNase MRP and the eukaryotic pre-rRNA-processing system. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Feb;20(2):78–82. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88962-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols M., Söll D., Willis I. Yeast RNase P: catalytic activity and substrate binding are separate functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1379–1383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Brown J. W. Evolutionary perspective on the structure and function of ribonuclease P, a ribozyme. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(8):1919–1928. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.8.1919-1928.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paluh J. L., Clayton D. A. Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNase MRP RNA is homologous to metazoan RNase MRP RNAs and may provide clues to interrelationships between RNase MRP and RNase P. Yeast. 1995 Oct;11(13):1249–1264. doi: 10.1002/yea.320111305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potuschak T., Rossmanith W., Karwan R. RNase MRP and RNase P share a common substrate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 11;21(14):3239–3243. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.14.3239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raska I., Andrade L. E., Ochs R. L., Chan E. K., Chang C. M., Roos G., Tan E. M. Immunological and ultrastructural studies of the nuclear coiled body with autoimmune antibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1991 Jul;195(1):27–37. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(91)90496-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy R., Tan E. M., Henning D., Nohga K., Busch H. Detection of a nucleolar 7-2 ribonucleoprotein and a cytoplasmic 8-2 ribonucleoprotein with autoantibodies from patients with scleroderma. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1383–1386. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimer G., Pollard K. M., Penning C. A., Ochs R. L., Lischwe M. A., Busch H., Tan E. M. Monoclonal autoantibody from a (New Zealand black x New Zealand white)F1 mouse and some human scleroderma sera target an Mr 34,000 nucleolar protein of the U3 RNP particle. Arthritis Rheum. 1987 Jul;30(7):793–800. doi: 10.1002/art.1780300709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokeach L. A., Hoch S. O. B-cell epitopes of Sm autoantigens. Mol Biol Rep. 1992 Jun;16(3):165–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00464704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossmanith W., Karwan R. Definition of the Th/To ribonucleoprotein by RNase P and RNase MRP. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Jun;18(1):29–35. doi: 10.1007/BF01006892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherly D., Boelens W., van Venrooij W. J., Dathan N. A., Hamm J., Mattaj I. W. Identification of the RNA binding segment of human U1 A protein and definition of its binding site on U1 snRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4163–4170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Bennett J. L., Dairaghi D. J., Clayton D. A. Secondary structure of RNase MRP RNA as predicted by phylogenetic comparison. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):208–213. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7678563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Clayton D. A. Characterization of a unique protein component of yeast RNase MRP: an RNA-binding protein with a zinc-cluster domain. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2617–2628. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt M. E., Clayton D. A. Yeast site-specific ribonucleoprotein endoribonuclease MRP contains an RNA component homologous to mammalian RNase MRP RNA and essential for cell viability. Genes Dev. 1992 Oct;6(10):1975–1985. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.10.1975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan E. M. Antinuclear antibodies: diagnostic markers for autoimmune diseases and probes for cell biology. Adv Immunol. 1989;44:93–151. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60641-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollervey D., Mattaj I. W. Fungal small nuclear ribonucleoproteins share properties with plant and vertebrate U-snRNPs. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):469–476. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04777.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper J. N., Bennett J. L., Clayton D. A. A role for RNAase MRP in mitochondrial RNA processing. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90529-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topper J. N., Clayton D. A. Characterization of human MRP/Th RNA and its nuclear gene: full length MRP/Th RNA is an active endoribonuclease when assembled as an RNP. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):793–799. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tranguch A. J., Engelke D. R. Comparative structural analysis of nuclear RNase P RNAs from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):14045–14055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R., Ainscough R., Anderson K., Baynes C., Berks M., Bonfield J., Burton J., Connell M., Copsey T., Cooper J. 2.2 Mb of contiguous nucleotide sequence from chromosome III of C. elegans. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):32–38. doi: 10.1038/368032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Y., Tan E., Reddy R. The 40-kilodalton to autoantigen associates with nucleotides 21 to 64 of human mitochondrial RNA processing/7-2 RNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5266–5274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerly S., Drainas D., Sylvers L. A., Söll D. Identification of a 100-kDa protein associated with nuclear ribonuclease P activity in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Oct 15;217(2):501–507. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18270.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerly S., Gamulin V., Burkard U., Söll D. The RNA component of RNase P in Schizosaccharomyces species. FEBS Lett. 1990 Oct 1;271(1-2):189–193. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Venrooij W. J., Slobbe R. L., Pruijn G. J. Structure and function of La and Ro RNPs. Mol Biol Rep. 1993 Aug;18(2):113–119. doi: 10.1007/BF00986765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]