Abstract
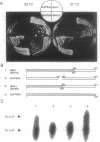
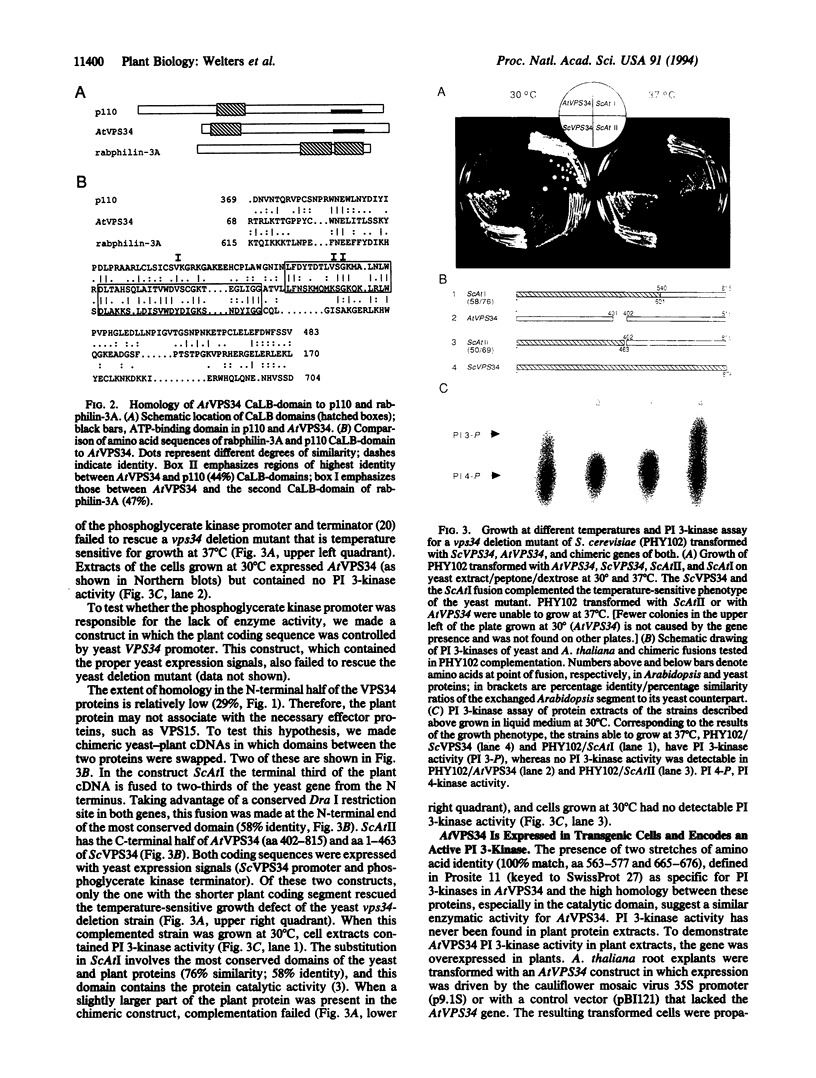
The cDNA encoding phosphatidylinositol (PI) 3-kinase was cloned from Arabidopsis thaliana, and the derived amino acid sequence (AtVPS34) has a significantly higher homology to yeast PI 3-kinase (VPS34) than to the mammalian (p110). The protein has two conserved domains: a catalytic site with the ATP-binding site near the C terminus and a calcium-dependent lipid-binding domain near the N terminus. The plant cDNA does not rescue a yeast vps34 deletion mutant, but a chimeric gene in which the coding sequence for the C-terminal third of VPS34 is replaced by the corresponding sequence from the plant gene does rescue the yeast mutant. PI 3-kinase activity is detectable in extracts from plants that overexpress the plant PI 3-kinase. Expression of antisense constructs gives rise to second-generation transformed plants severely inhibited in growth and development.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Aitken J. R., Cleves A. E., Dowhan W. An essential role for a phospholipid transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):561–562. doi: 10.1038/347561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brearley C. A., Hanke D. E. Pathway of synthesis of 3,4- and 4,5-phosphorylated phosphatidylinositols in the duckweed Spirodela polyrhiza L. Biochem J. 1993 Feb 15;290(Pt 1):145–150. doi: 10.1042/bj2900145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brearley C. A., Hanke D. E. Phosphoinositides in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Aleurone Tissue. Plant Physiol. 1994 Apr;104(4):1381–1384. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.4.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheon C. I., Lee N. G., Siddique A. B., Bal A. K., Verma D. P. Roles of plant homologs of Rab1p and Rab7p in the biogenesis of the peribacteroid membrane, a subcellular compartment formed de novo during root nodule symbiosis. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4125–4135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Vecchio R. L., Pilch P. F. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase is a component of glucose transporter (GLUT 4)-containing vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13278–13283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan C. A., Schnieders E. A., Emerick A. W., Kunisawa R., Admon A., Thorner J. Phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase: gene structure and requirement for yeast cell viability. Science. 1993 Nov 26;262(5138):1444–1448. doi: 10.1126/science.8248783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont P. J., Machesky L. M., Baldassare J. J., Pollard T. D. The actin-binding protein profilin binds to PIP2 and inhibits its hydrolysis by phospholipase C. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1575–1578. doi: 10.1126/science.2157283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J., Picton S., Shabbeer J., Schuch W., Grierson D. Molecular biology of fruit ripening and its manipulation with antisense genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):69–87. doi: 10.1007/BF00015607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi Y., Urade R., Utsumi S., Kito M. Anchoring of peptide elongation factor EF-1 alpha by phosphatidylinositol at the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. J Biochem. 1989 Oct;106(4):560–563. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Henikoff J. G. Automated assembly of protein blocks for database searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6565–6572. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. K., Emr S. D. Characterization of VPS34, a gene required for vacuolar protein sorting and vacuole segregation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6742–6754. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herman P. K., Stack J. H., Emr S. D. A genetic and structural analysis of the yeast Vps15 protein kinase: evidence for a direct role of Vps15p in vacuolar protein delivery. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4049–4060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiles I. D., Otsu M., Volinia S., Fry M. J., Gout I., Dhand R., Panayotou G., Ruiz-Larrea F., Thompson A., Totty N. F. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase: structure and expression of the 110 kd catalytic subunit. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90166-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joly M., Kazlauskas A., Fay F. S., Corvera S. Disruption of PDGF receptor trafficking by mutation of its PI-3 kinase binding sites. Science. 1994 Feb 4;263(5147):684–687. doi: 10.1126/science.8303278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. I., Gal S., Newman T. C., Raikhel N. V. The Arabidopsis endoplasmic reticulum retention receptor functions in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11433–11437. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minet M., Dufour M. E., Lacroute F. Complementation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae auxotrophic mutants by Arabidopsis thaliana cDNAs. Plant J. 1992 May;2(3):417–422. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1992.00417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. S., Klionsky D. J., Banta L. M., Emr S. D. Protein sorting in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: isolation of mutants defective in the delivery and processing of multiple vacuolar hydrolases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4936–4948. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiestl R. H., Gietz R. D. High efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells using single stranded nucleic acids as a carrier. Curr Genet. 1989 Dec;16(5-6):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00340712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schu P. V., Takegawa K., Fry M. J., Stack J. H., Waterfield M. D., Emr S. D. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase encoded by yeast VPS34 gene essential for protein sorting. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):88–91. doi: 10.1126/science.8385367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. W. A complete, yet flexible, system for DNA/protein sequence analysis using VAX/VMS computers. Comput Appl Biosci. 1988 Mar;4(1):212–212. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/4.1.212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stack J. H., Herman P. K., Schu P. V., Emr S. D. A membrane-associated complex containing the Vps15 protein kinase and the Vps34 PI 3-kinase is essential for protein sorting to the yeast lysosome-like vacuole. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2195–2204. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05867.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens L. R., Jackson T. R., Hawkins P. T. Agonist-stimulated synthesis of phosphatidylinositol(3,4,5)-trisphosphate: a new intracellular signalling system? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 7;1179(1):27–75. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(93)90072-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan Z., Boss W. F. Association of Phosphatidylinositol Kinase, Phosphatidylinositol Monophosphate Kinase, and Diacylglycerol Kinase with the Cytoskeleton and F-Actin Fractions of Carrot (Daucus carota L.) Cells Grown in Suspension Culture : Response to Cell Wall-Degrading Enzymes. Plant Physiol. 1992 Dec;100(4):2116–2120. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.4.2116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trewavas A., Gilroy S. Signal transduction in plant cells. Trends Genet. 1991 Nov-Dec;7(11-12):356–361. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(91)90255-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valvekens D., Van Montagu M., Van Lijsebettens M. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana root explants by using kanamycin selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5536–5540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh J. P., Caldwell K. K., Majerus P. W. Formation of phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate by isomerization from phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9184–9187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu P., Lloyd C. W., Staiger C. J., Drobak B. K. Association of Phosphatidylinositol 4-Kinase with the Plant Cytoskeleton. Plant Cell. 1992 Aug;4(8):941–951. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.8.941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang W., Boss W. F. Regulation of phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase by the protein activator PIK-A49. Activation requires phosphorylation of PIK-A49. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 4;269(5):3852–3857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- d'Enfert C., Gensse M., Gaillardin C. Fission yeast and a plant have functional homologues of the Sar1 and Sec12 proteins involved in ER to Golgi traffic in budding yeast. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):4205–4211. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]