Abstract
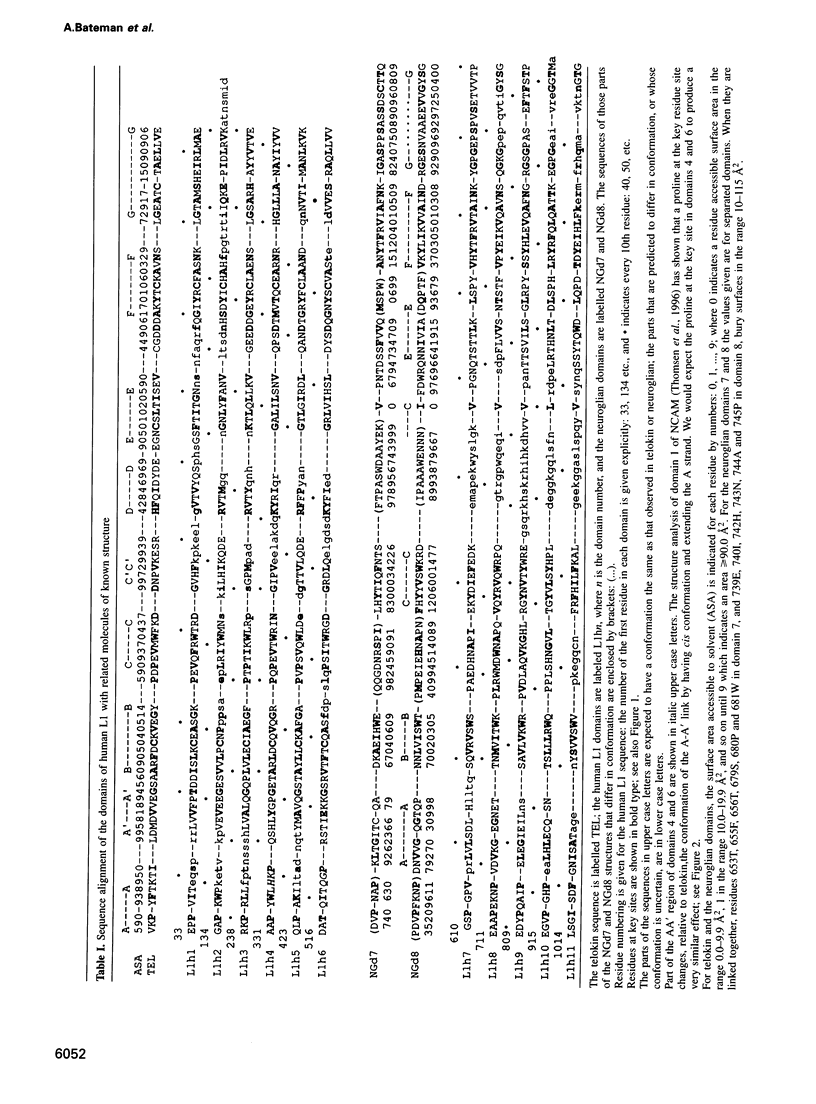
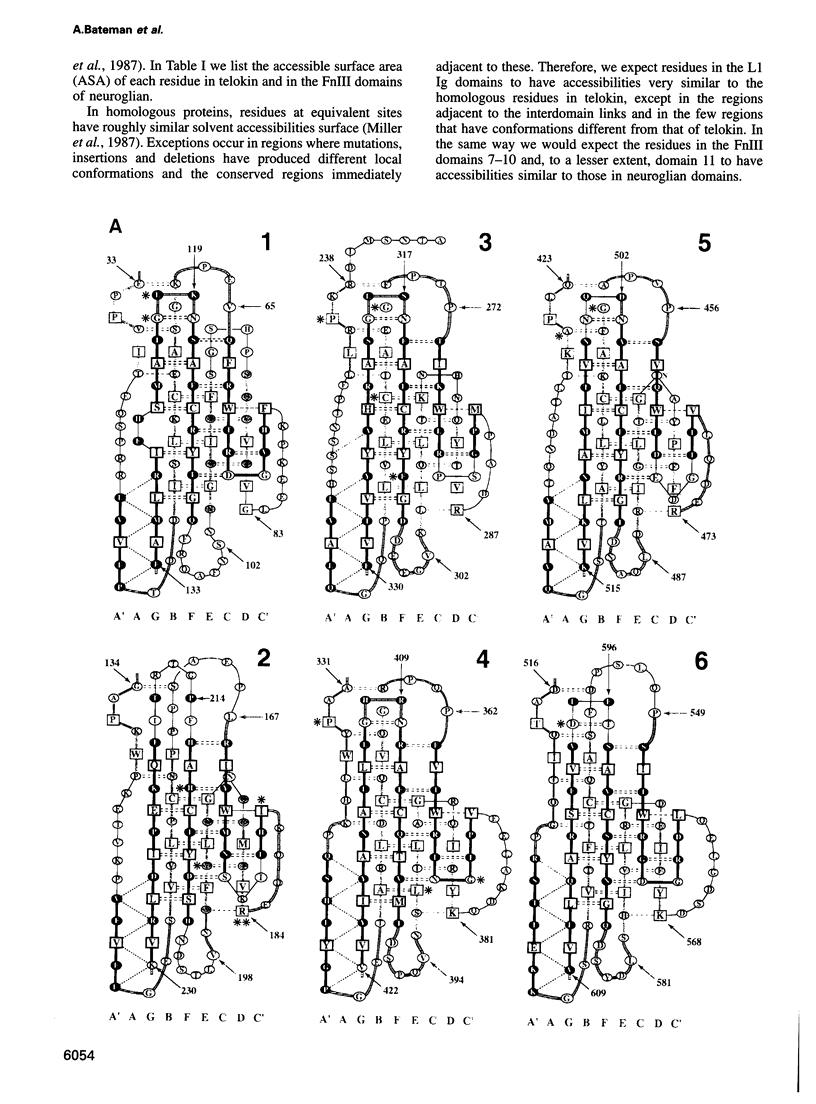
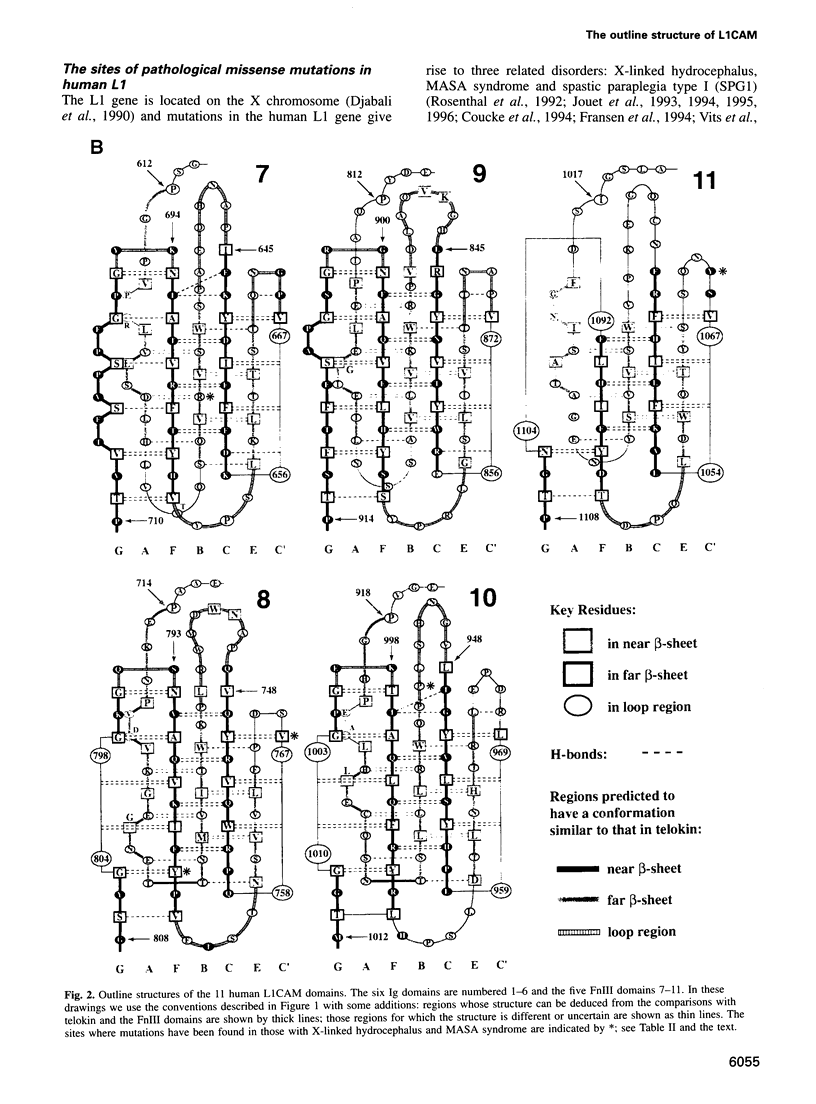
The L1 cell adhesion molecule has six domains homologous to members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and five homologous to fibronectin type III domains. We determined the outline structure of the L1 domains by showing that they have, at the key sites that determine conformation, residues similar to those in proteins of known structure. The outline structure describes the relative positions of residues, the major secondary structures and residue solvent accessibility. We use the outline structure to investigate the likely effects of 22 mutations that cause neurological diseases. The mutations are not randomly distributed but cluster in a few regions of the structure. They can be divided into those that act mainly by changing conformation or denaturing their domain and those that alter its surface properties.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman A., Chothia C. Outline structures for the extracellular domains of the fibroblast growth factor receptors. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Dec;2(12):1068–1074. doi: 10.1038/nsb1295-1068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bateman A., Eddy S. R., Chothia C. Members of the immunoglobulin superfamily in bacteria. Protein Sci. 1996 Sep;5(9):1939–1941. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560050923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bieber A. J., Snow P. M., Hortsch M., Patel N. H., Jacobs J. R., Traquina Z. R., Schilling J., Goodman C. S. Drosophila neuroglian: a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with extensive homology to the vertebrate neural adhesion molecule L1. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):447–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady R. L., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Lange G., Davis S. J., Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. Crystal structure of domains 3 and 4 of rat CD4: relation to the NH2-terminal domains. Science. 1993 May 14;260(5110):979–983. doi: 10.1126/science.8493535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckle A. M., Cramer P., Fersht A. R. Structural and energetic responses to cavity-creating mutations in hydrophobic cores: observation of a buried water molecule and the hydrophilic nature of such hydrophobic cavities. Biochemistry. 1996 Apr 9;35(14):4298–4305. doi: 10.1021/bi9524676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoon M. P., Grumet M., Mauro V., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Structure of the chicken neuron-glia cell adhesion molecule, Ng-CAM: origin of the polypeptides and relation to the Ig superfamily. J Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;112(5):1017–1029. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.5.1017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Boswell D. R., Lesk A. M. The outline structure of the T-cell alpha beta receptor. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3745–3755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chothia C., Lesk A. M., Tramontano A., Levitt M., Smith-Gill S. J., Air G., Sheriff S., Padlan E. A., Davies D., Tulip W. R. Conformations of immunoglobulin hypervariable regions. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):877–883. doi: 10.1038/342877a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coucke P., Vits L., Van Camp G., Serville F., Lyonnet S., Kenwrick S., Rosenthal A., Wehnert M., Munnich A., Willems P. J. Identification of a 5' splice site mutation in intron 4 of the L1CAM gene in an X-linked hydrocephalus family. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Apr;3(4):671–673. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.4.671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson C. D., Veerapandian B., Dai X. P., Hamlin R. C., Xuong N. H., Ruoslahti E., Ely K. R. Crystal structure of the tenth type III cell adhesion module of human fibronectin. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 4;236(4):1079–1092. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Djabali M., Mattei M. G., Nguyen C., Roux D., Demengeot J., Denizot F., Moos M., Schachner M., Goridis C., Jordan B. R. The gene encoding L1, a neural adhesion molecule of the immunoglobulin family, is located on the X chromosome in mouse and man. Genomics. 1990 Aug;7(4):587–593. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(90)90203-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson A. E., Baase W. A., Zhang X. J., Heinz D. W., Blaber M., Baldwin E. P., Matthews B. W. Response of a protein structure to cavity-creating mutations and its relation to the hydrophobic effect. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):178–183. doi: 10.1126/science.1553543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen E., Schrander-Stumpel C., Vits L., Coucke P., Van Camp G., Willems P. J. X-linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome present in one family are due to a single missense mutation in exon 28 of the L1CAM gene. Hum Mol Genet. 1994 Dec;3(12):2255–2256. doi: 10.1093/hmg/3.12.2255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grumet M., Mauro V., Burgoon M. P., Edelman G. M., Cunningham B. A. Structure of a new nervous system glycoprotein, Nr-CAM, and its relationship to subgroups of neural cell adhesion molecules. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1399–1412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu S. M., Orth U., Veske A., Enders H., Klunder K., Schlosser M., Engel W., Schwinger E., Gal A. Five novel mutations in the L1CAM gene in families with X linked hydrocephalus. J Med Genet. 1996 Feb;33(2):103–106. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpaz Y., Chothia C. Many of the immunoglobulin superfamily domains in cell adhesion molecules and surface receptors belong to a new structural set which is close to that containing variable domains. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 13;238(4):528–539. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hlavin M. L., Lemmon V. Molecular structure and functional testing of human L1CAM: an interspecies comparison. Genomics. 1991 Oct;11(2):416–423. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90150-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
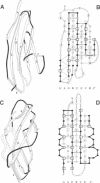
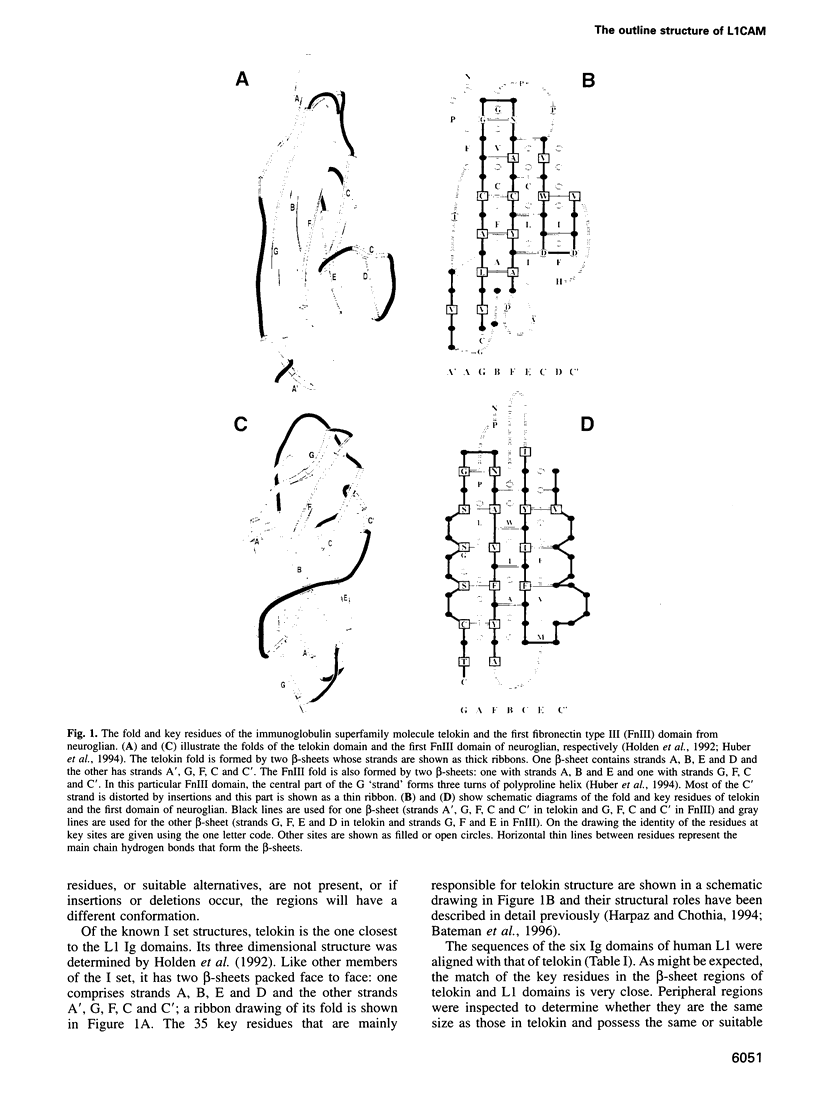
- Holden H. M., Ito M., Hartshorne D. J., Rayment I. X-ray structure determination of telokin, the C-terminal domain of myosin light chain kinase, at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):840–851. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90226-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber A. H., Wang Y. M., Bieber A. J., Bjorkman P. J. Crystal structure of tandem type III fibronectin domains from Drosophila neuroglian at 2.0 A. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):717–731. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Improta S., Politou A. S., Pastore A. Immunoglobulin-like modules from titin I-band: extensible components of muscle elasticity. Structure. 1996 Mar 15;4(3):323–337. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones E. Y., Harlos K., Bottomley M. J., Robinson R. C., Driscoll P. C., Edwards R. M., Clements J. M., Dudgeon T. J., Stuart D. I. Crystal structure of an integrin-binding fragment of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 at 1.8 A resolution. Nature. 1995 Feb 9;373(6514):539–544. doi: 10.1038/373539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Kenwrick S. Gene analysis of L1 neural cell adhesion molecule in prenatal diagnosis of hydrocephalus. Lancet. 1995 Jan 21;345(8943):161–162. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(95)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Moncla A., Paterson J., McKeown C., Fryer A., Carpenter N., Holmberg E., Wadelius C., Kenwrick S. New domains of neural cell-adhesion molecule L1 implicated in X-linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1995 Jun;56(6):1304–1314. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., Armstrong G., MacFarlane J., Stevenson R., Paterson J., Metzenberg A., Ionasescu V., Temple K., Kenwrick S. X-linked spastic paraplegia (SPG1), MASA syndrome and X-linked hydrocephalus result from mutations in the L1 gene. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):402–407. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Rosenthal A., MacFarlane J., Kenwrick S., Donnai D. A missense mutation confirms the L1 defect in X-linked hydrocephalus (HSAS) Nat Genet. 1993 Aug;4(4):331–331. doi: 10.1038/ng0893-331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jouet M., Strain L., Bonthron D., Kenwrick S. Discordant segregation of Xq28 markers and a mutation in the L1 gene in a family with X linked hydrocephalus. J Med Genet. 1996 Mar;33(3):248–250. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.3.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenwrick S., Jouet M., Donnai D. X linked hydrocephalus and MASA syndrome. J Med Genet. 1996 Jan;33(1):59–65. doi: 10.1136/jmg.33.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy D. J., Hendrickson W. A., Aukhil I., Erickson H. P. Structure of a fibronectin type III domain from tenascin phased by MAD analysis of the selenomethionyl protein. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):987–991. doi: 10.1126/science.1279805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Chothia C. Evolution of proteins formed by beta-sheets. II. The core of the immunoglobulin domains. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):325–342. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90179-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main A. L., Harvey T. S., Baron M., Boyd J., Campbell I. D. The three-dimensional structure of the tenth type III module of fibronectin: an insight into RGD-mediated interactions. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):671–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90600-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S., Janin J., Lesk A. M., Chothia C. Interior and surface of monomeric proteins. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):641–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90038-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Kobayashi M., Asou H., Uyemura K. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding the rat neural cell adhesion molecule L1. Two L1 isoforms in the cytoplasmic region are produced by differential splicing. FEBS Lett. 1991 Sep 2;289(1):91–95. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80915-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moos M., Tacke R., Scherer H., Teplow D., Früh K., Schachner M. Neural adhesion molecule L1 as a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily with binding domains similar to fibronectin. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):701–703. doi: 10.1038/334701a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfuhl M., Pastore A. Tertiary structure of an immunoglobulin-like domain from the giant muscle protein titin: a new member of the I set. Structure. 1995 Apr 15;3(4):391–401. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politou A. S., Gautel M., Pfuhl M., Labeit S., Pastore A. Immunoglobulin-type domains of titin: same fold, different stability? Biochemistry. 1994 Apr 19;33(15):4730–4737. doi: 10.1021/bi00181a604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathjen F. G., Schachner M. Immunocytological and biochemical characterization of a new neuronal cell surface component (L1 antigen) which is involved in cell adhesion. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid R. A., Hemperly J. J. Variants of human L1 cell adhesion molecule arise through alternate splicing of RNA. J Mol Neurosci. 1992;3(3):127–135. doi: 10.1007/BF02919404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Jouet M., Kenwrick S. Aberrant splicing of neural cell adhesion molecule L1 mRNA in a family with X-linked hydrocephalus. Nat Genet. 1992 Oct;2(2):107–112. doi: 10.1038/ng1092-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz J. C., Cuppens H., Legius E., Fryns J. P., Glover T., Marynen P., Cassiman J. J. Mutations in L1-CAM in two families with X linked complicated spastic paraplegia, MASA syndrome, and HSAS. J Med Genet. 1995 Jul;32(7):549–552. doi: 10.1136/jmg.32.7.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryu S. E., Kwong P. D., Truneh A., Porter T. G., Arthos J., Rosenberg M., Dai X. P., Xuong N. H., Axel R., Sweet R. W. Crystal structure of an HIV-binding recombinant fragment of human CD4. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):419–426. doi: 10.1038/348419a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonderegger P., Rathjen F. G. Regulation of axonal growth in the vertebrate nervous system by interactions between glycoproteins belonging to two subgroups of the immunoglobulin superfamily. J Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;119(6):1387–1394. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.6.1387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takechi T., Tohyama J., Kurashige T., Maruta K., Uyemura K., Ohi T., Matsukura S., Sakuragawa N. A deletion of five nucleotides in the L1CAM gene in a Japanese family with X-linked hydrocephalus. Hum Genet. 1996 Mar;97(3):353–356. doi: 10.1007/BF02185770. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen N. K., Soroka V., Jensen P. H., Berezin V., Kiselyov V. V., Bock E., Poulsen F. M. The three-dimensional structure of the first domain of neural cell adhesion molecule. Nat Struct Biol. 1996 Jul;3(7):581–585. doi: 10.1038/nsb0796-581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tongiorgi E., Bernhardt R. R., Schachner M. Zebrafish neurons express two L1-related molecules during early axonogenesis. J Neurosci Res. 1995 Nov 1;42(4):547–561. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490420413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vits L., Van Camp G., Coucke P., Fransen E., De Boulle K., Reyniers E., Korn B., Poustka A., Wilson G., Schrander-Stumpel C. MASA syndrome is due to mutations in the neural cell adhesion gene L1CAM. Nat Genet. 1994 Jul;7(3):408–413. doi: 10.1038/ng0794-408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. H., Yan Y. W., Garrett T. P., Liu J. H., Rodgers D. W., Garlick R. L., Tarr G. E., Husain Y., Reinherz E. L., Harrison S. C. Atomic structure of a fragment of human CD4 containing two immunoglobulin-like domains. Nature. 1990 Nov 29;348(6300):411–418. doi: 10.1038/348411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie A. O., Morriss-Kay G. M., Jones E. Y., Heath J. K. Functions of fibroblast growth factors and their receptors. Curr Biol. 1995 May 1;5(5):500–507. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00102-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. F., Barclay A. N. The immunoglobulin superfamily--domains for cell surface recognition. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:381–405. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X., Siu C. H. Differential effects of two hydrocephalus/MASA syndrome-related mutations on the homophilic binding and neuritogenic activities of the cell adhesion molecule L1. J Biol Chem. 1996 Mar 22;271(12):6563–6566. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.12.6563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vos A. M., Ultsch M., Kossiakoff A. A. Human growth hormone and extracellular domain of its receptor: crystal structure of the complex. Science. 1992 Jan 17;255(5042):306–312. doi: 10.1126/science.1549776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]