Abstract
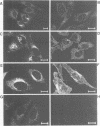
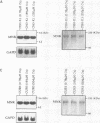
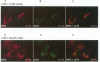
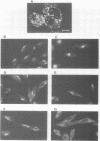
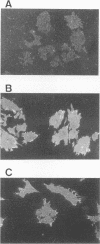
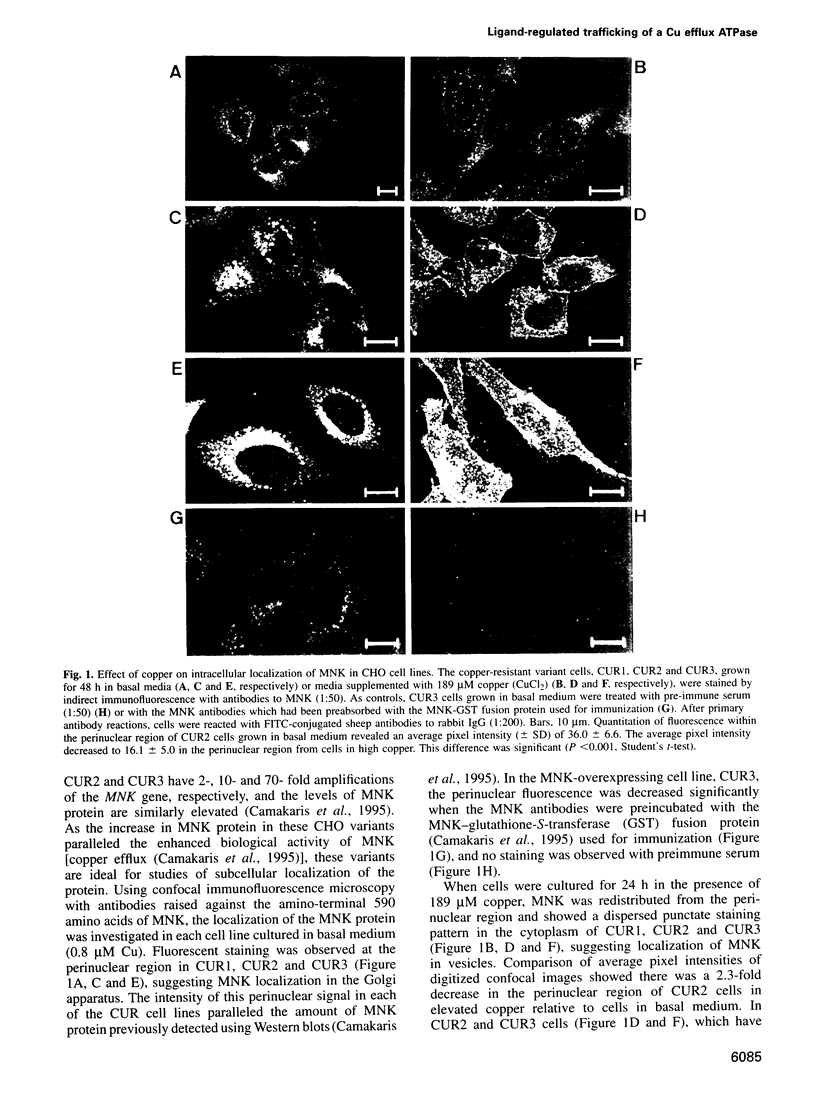
The Menkes P-type ATPase (MNK), encoded by the Menkes gene (MNK; ATP7A), is a transmembrane copper-translocating pump which is defective in the human disorder of copper metabolism, Menkes disease. Recent evidence that the MNK P-type ATPase has a role in copper efflux has come from studies using copper-resistant variants of cultured Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells. These variants have MNK gene amplification and consequently overexpress MNK, the extents of which correlate with the degree of elevated copper efflux. Here, we report on the localization of MNK in these copper-resistant CHO cells when cultured in different levels of copper. Immunofluorescence studies demonstrated that MNK is predominantly localized to the Golgi apparatus of cells in basal medium. In elevated copper conditions there was a rapid trafficking of MNK from the Golgi to the plasma membrane. This shift in steady-state distribution of MNK was reversible and not dependent on new protein synthesis. In media containing basal copper, MNK accumulated in cytoplasmic vesicles after treatment of cells with a variety of agents that inhibit endosomal recycling. We suggest that MNK continuously recycles between the Golgi and the plasma membrane and elevated copper shifts the steady-state distribution from the Golgi to the plasma membrane. These data reveal a novel system of regulated protein trafficking which ultimately leads to the efflux of an essential yet potentially toxic ligand, where the ligand itself appears directly and specifically to stimulate the trafficking of its own transporter.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bos K., Wraight C., Stanley K. K. TGN38 is maintained in the trans-Golgi network by a tyrosine-containing motif in the cytoplasmic domain. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2219–2228. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05870.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull P. C., Thomas G. R., Rommens J. M., Forbes J. R., Cox D. W. The Wilson disease gene is a putative copper transporting P-type ATPase similar to the Menkes gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):327–337. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camakaris J., Danks D. M., Ackland L., Cartwright E., Borger P., Cotton R. G. Altered copper metabolism in cultured cells from human Menkes' syndrome and mottled mouse mutants. Biochem Genet. 1980 Feb;18(1-2):117–131. doi: 10.1007/BF00504364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camakaris J., Petris M. J., Bailey L., Shen P., Lockhart P., Glover T. W., Barcroft C., Patton J., Mercer J. F. Gene amplification of the Menkes (MNK; ATP7A) P-type ATPase gene of CHO cells is associated with copper resistance and enhanced copper efflux. Hum Mol Genet. 1995 Nov;4(11):2117–2123. doi: 10.1093/hmg/4.11.2117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casas-Finet J. R., Hu S., Hamer D., Karpel R. L. Characterization of the copper- and silver-thiolate clusters in N-terminal fragments of the yeast ACE1 transcription factor capable of binding to its specific DNA recognition sequence. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 21;31(28):6617–6626. doi: 10.1021/bi00143a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman R. E., Munro S. Retrieval of TGN proteins from the cell surface requires endosomal acidification. EMBO J. 1994 May 15;13(10):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelly J., Tümer Z., Tønnesen T., Petterson A., Ishikawa-Brush Y., Tommerup N., Horn N., Monaco A. P. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease that encodes a potential heavy metal binding protein. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):14–19. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collawn J. F., Stangel M., Kuhn L. A., Esekogwu V., Jing S. Q., Trowbridge I. S., Tainer J. A. Transferrin receptor internalization sequence YXRF implicates a tight turn as the structural recognition motif for endocytosis. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):1061–1072. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90509-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W., Wardzala L. J. Potential mechanism of insulin action on glucose transport in the isolated rat adipose cell. Apparent translocation of intracellular transport systems to the plasma membrane. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4758–4762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu D., Beeler T. J., Dunn T. M. Sequence, mapping and disruption of CCC2, a gene that cross-complements the Ca(2+)-sensitive phenotype of csg1 mutants and encodes a P-type ATPase belonging to the Cu(2+)-ATPase subfamily. Yeast. 1995 Mar;11(3):283–292. doi: 10.1002/yea.320110310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goka T. J., Stevenson R. E., Hefferan P. M., Howell R. R. Menkes disease: a biochemical abnormality in cultured human fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):604–606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Maxfield F. R. Membrane transport in the endocytic pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;7(4):552–563. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haney P. M., Levy M. A., Strube M. S., Mueckler M. Insulin-sensitive targeting of the GLUT4 glucose transporter in L6 myoblasts is conferred by its COOH-terminal cytoplasmic tail. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):641–658. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. Effects of cytoplasmic acidification on clathrin lattice morphology. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):401–411. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horn N. Copper incorporation studies on cultured cells for prenatal diagnosis of Menkes' disease. Lancet. 1976 May 29;1(7970):1156–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)91543-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey J. S., Peters P. J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S. Localization of TGN38 to the trans-Golgi network: involvement of a cytoplasmic tyrosine-containing sequence. J Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;120(5):1123–1135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.120.5.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Piper R. C., Slot J. W. Targeting of mammalian glucose transporters. J Cell Sci. 1993 Mar;104(Pt 3):607–612. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.3.607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamaru K., Kashiwagi S., Mizuno T. A copper-transporting P-type ATPase found in the thylakoid membrane of the cyanobacterium Synechococcus species PCC7942. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Jul;13(2):369–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooy J., Toh B. H., Pettitt J. M., Erlich R., Gleeson P. A. Human autoantibodies as reagents to conserved Golgi components. Characterization of a peripheral, 230-kDa compartment-specific Golgi protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20255–20263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladinsky M. S., Howell K. E. The trans-Golgi network can be dissected structurally and functionally from the cisternae of the Golgi complex by brefeldin A. Eur J Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;59(1):92–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. C., Moore M. S., Sanan D. A., Anderson R. G. Reconstitution of clathrin-coated pit budding from plasma membranes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(5):881–891. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.5.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Donaldson J. G., Schweizer A., Berger E. G., Hauri H. P., Yuan L. C., Klausner R. D. Microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of proteins into the ER in the presence of brefeldin A suggests an ER recycling pathway. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):821–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90096-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L., Tipper C., Amherdt M., Orci L., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A's effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):601–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90534-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Livingston J., Hall B., Paynter J. A., Begy C., Chandrasekharappa S., Lockhart P., Grimes A., Bhave M., Siemieniak D. Isolation of a partial candidate gene for Menkes disease by positional cloning. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):20–25. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy S. S., Thomas L., VanSlyke J. K., Stenberg P. E., Thomas G. Intracellular trafficking and activation of the furin proprotein convertase: localization to the TGN and recycling from the cell surface. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):18–33. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06231.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Mahaffey D. T., Brodsky F. M., Anderson R. G. Assembly of clathrin-coated pits onto purified plasma membranes. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):558–563. doi: 10.1126/science.2883727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moremen K. W., Touster O., Robbins P. W. Novel purification of the catalytic domain of Golgi alpha-mannosidase II. Characterization and comparison with the intact enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 5;266(25):16876–16885. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murata Y., Yamakawa E., Iizuka T., Kodama H., Abe T., Seki Y., Kodama M. Failure of copper incorporation into ceruloplasmin in the Golgi apparatus of LEC rat hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Apr 6;209(1):349–355. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Navone F., Jahn R., Di Gioia G., Stukenbrok H., Greengard P., De Camilli P. Protein p38: an integral membrane protein specific for small vesicles of neurons and neuroendocrine cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2511–2527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielson K. B., Atkin C. L., Winge D. R. Distinct metal-binding configurations in metallothionein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5342–5350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt A., Solioz M. Two trans-acting metalloregulatory proteins controlling expression of the copper-ATPases of Enterococcus hirae. J Biol Chem. 1995 Mar 3;270(9):4349–4354. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.9.4349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odermatt A., Suter H., Krapf R., Solioz M. Primary structure of two P-type ATPases involved in copper homeostasis in Enterococcus hirae. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12775–12779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
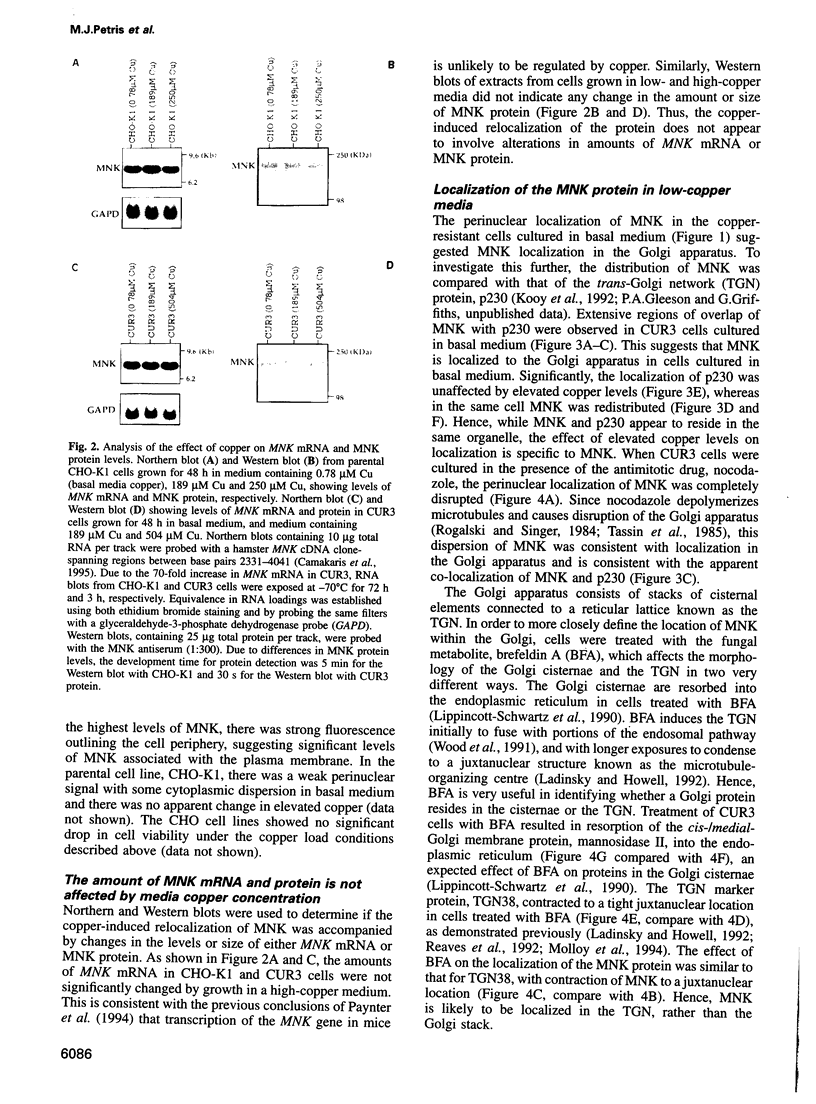
- Paynter J. A., Grimes A., Lockhart P., Mercer J. F. Expression of the Menkes gene homologue in mouse tissues lack of effect of copper on the mRNA levels. FEBS Lett. 1994 Sep 5;351(2):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00868-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Tai C., Kulesza P., Pang S., Warnock D., Baenziger J., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Puri C., James D. E. GLUT-4 NH2 terminus contains a phenylalanine-based targeting motif that regulates intracellular sequestration. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(6):1221–1232. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.6.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Tai C., Slot J. W., Hahn C. S., Rice C. M., Huang H., James D. E. The efficient intracellular sequestration of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT-4) is conferred by the NH2 terminus. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):729–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rad M. R., Kirchrath L., Hollenberg C. P. A putative P-type Cu(2+)-transporting ATPase gene on chromosome II of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1994 Sep;10(9):1217–1225. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Banting G. Perturbation of the morphology of the trans-Golgi network following Brefeldin A treatment: redistribution of a TGN-specific integral membrane protein, TGN38. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(1):85–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Banting G. Vacuolar ATPase inactivation blocks recycling to the trans-Golgi network from the plasma membrane. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 23;345(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00437-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaves B., Wilde A., Banting G. Identification, molecular characterization and immunolocalization of an isoform of the trans-Golgi-network (TGN)-specific integral membrane protein TGN38. Biochem J. 1992 Apr 15;283(Pt 2):313–316. doi: 10.1042/bj2830313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson L. J., Pang S., Harris D. S., Heuser J., James D. E. Translocation of the glucose transporter (GLUT4) to the cell surface in permeabilized 3T3-L1 adipocytes: effects of ATP insulin, and GTP gamma S and localization of GLUT4 to clathrin lattices. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1181–1196. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogalski A. A., Singer S. J. Associations of elements of the Golgi apparatus with microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):1092–1100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royce P. M., Camakaris J., Danks D. M. Reduced lysyl oxidase activity in skin fibroblasts from patients with Menkes' syndrome. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):579–586. doi: 10.1042/bj1920579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer W., Stroh A., Berghöfer S., Seiler J., Vey M., Kruse M. L., Kern H. F., Klenk H. D., Garten W. Two independent targeting signals in the cytoplasmic domain determine trans-Golgi network localization and endosomal trafficking of the proprotein convertase furin. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2424–2435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Kono T. Evidence that insulin causes translocation of glucose transport activity to the plasma membrane from an intracellular storage site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2542–2545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanzi R. E., Petrukhin K., Chernov I., Pellequer J. L., Wasco W., Ross B., Romano D. M., Parano E., Pavone L., Brzustowicz L. M. The Wilson disease gene is a copper transporting ATPase with homology to the Menkes disease gene. Nat Genet. 1993 Dec;5(4):344–350. doi: 10.1038/ng1293-344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tassin A. M., Paintrand M., Berger E. G., Bornens M. The Golgi apparatus remains associated with microtubule organizing centers during myogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):630–638. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terada K., Kawarada Y., Miura N., Yasui O., Koyama K., Sugiyama T. Copper incorporation into ceruloplasmin in rat livers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Jan 25;1270(1):58–62. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(94)00072-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowbridge I. S., Collawn J. F., Hopkins C. R. Signal-dependent membrane protein trafficking in the endocytic pathway. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:129–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voorhees P., Deignan E., van Donselaar E., Humphrey J., Marks M. S., Peters P. J., Bonifacino J. S. An acidic sequence within the cytoplasmic domain of furin functions as a determinant of trans-Golgi network localization and internalization from the cell surface. EMBO J. 1995 Oct 16;14(20):4961–4975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vulpe C., Levinson B., Whitney S., Packman S., Gitschier J. Isolation of a candidate gene for Menkes disease and evidence that it encodes a copper-transporting ATPase. Nat Genet. 1993 Jan;3(1):7–13. doi: 10.1038/ng0193-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox C. A., Redding K., Wright R., Fuller R. S. Mutation of a tyrosine localization signal in the cytosolic tail of yeast Kex2 protease disrupts Golgi retention and results in default transport to the vacuole. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1353–1371. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood S. A., Park J. E., Brown W. J. Brefeldin A causes a microtubule-mediated fusion of the trans-Golgi network and early endosomes. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):591–600. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90533-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi Y., Heiny M. E., Gitlin J. D. Isolation and characterization of a human liver cDNA as a candidate gene for Wilson disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Nov 30;197(1):271–277. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan D. S., Stearman R., Dancis A., Dunn T., Beeler T., Klausner R. D. The Menkes/Wilson disease gene homologue in yeast provides copper to a ceruloplasmin-like oxidase required for iron uptake. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 28;92(7):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Duve C., de Barsy T., Poole B., Trouet A., Tulkens P., Van Hoof F. Commentary. Lysosomotropic agents. Biochem Pharmacol. 1974 Sep 15;23(18):2495–2531. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(74)90174-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]