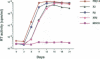Abstract
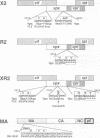
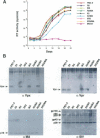
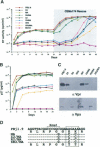
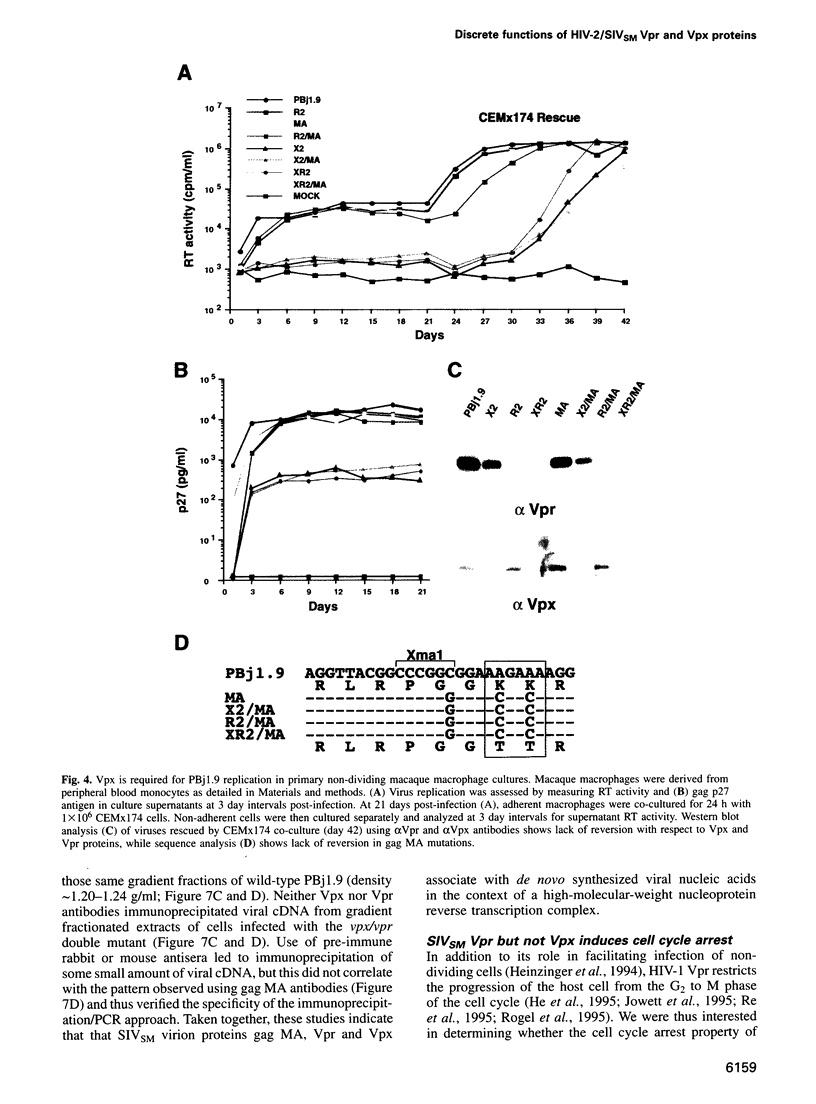
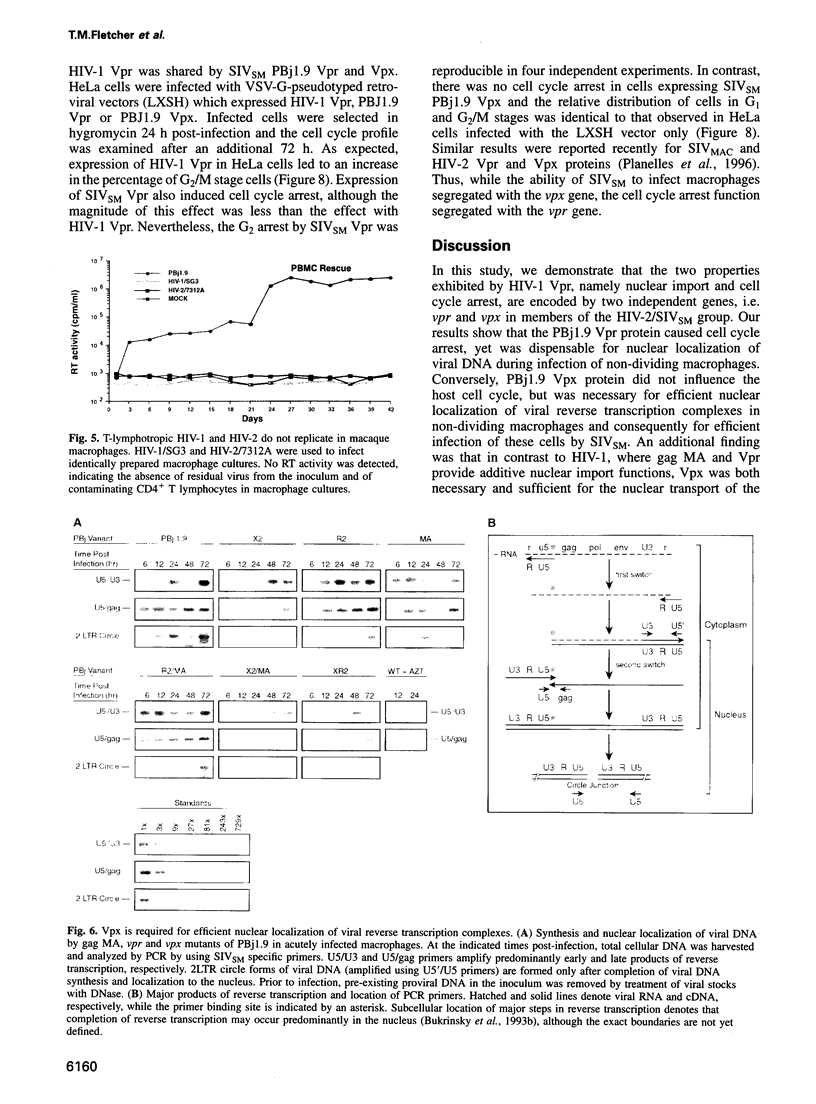
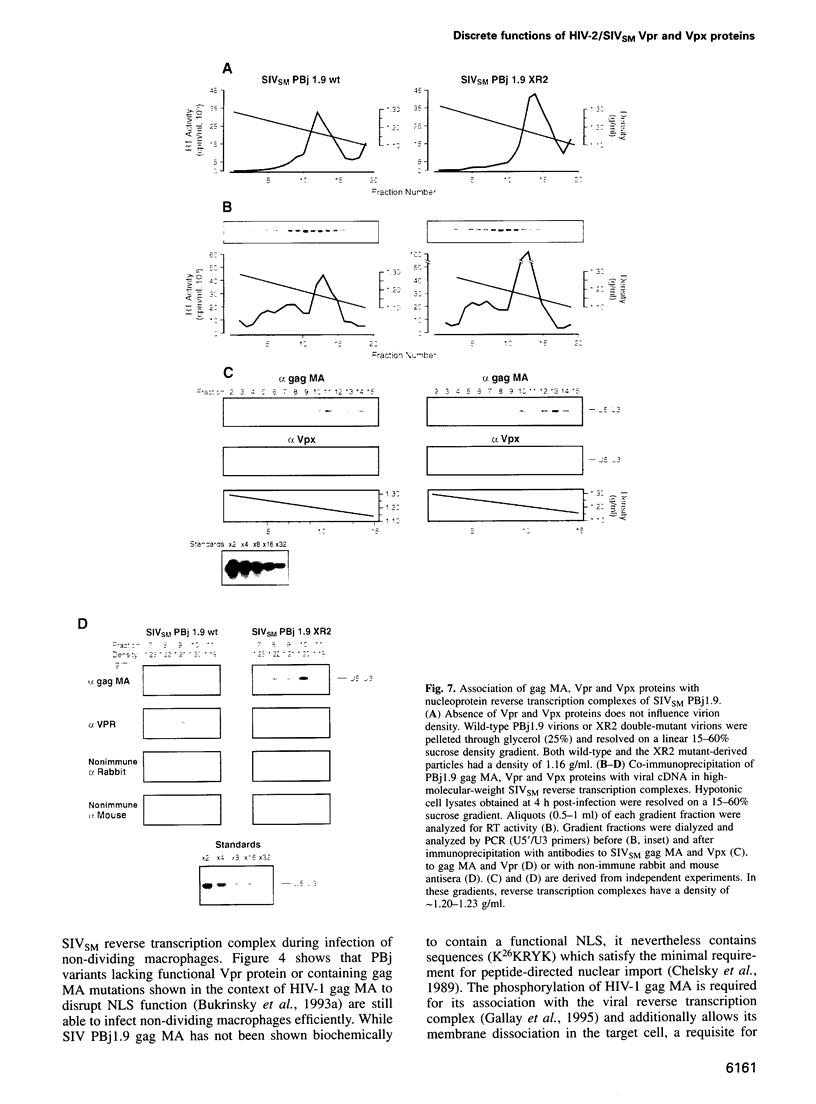
The vpr genes of human and simian immunodeficiency viruses (HIV/SIV) encode proteins which are packaged in the virus particle. HIV-1 Vpr has been shown to mediate the nuclear import of viral reverse transcription complexes in non-dividing target cells (e.g. terminally differentiated macrophages), and to alter the cell cycle and proliferation status of the infected host cell. Members of the HIV-2/SIV(SM) group encode, in addition to Vpr, a related protein called Vpx. Because these two proteins share considerable sequence similarity, it has been assumed that they also exhibit similar functions. Here, we report that the functions of Vpr and Vpx are distinct and non-redundant, although both proteins are components of the HIV-2/SIV(SM) virion and reverse transcription complex. Characterizing SIV(SM) proviruses defective in one or both genes, we found that Vpx is both necessary and sufficient for the nuclear import of the viral reverse transcription complex. In contrast, Vpr, but not Vpx, inhibited the progression of infected host cells from the G2 to the M phase of the cell cycle. Thus, two independent functions of the HIV-1 Vpr protein are encoded by separate genes in HIV-2/SIV(SM). This segregation is consistent with the conservation of these genes in HIV-2/SIV(SM) evolution, and underscores the importance of both nuclear transport and cell cycle arrest functions in primate lentivirus biology.
Full text
PDF

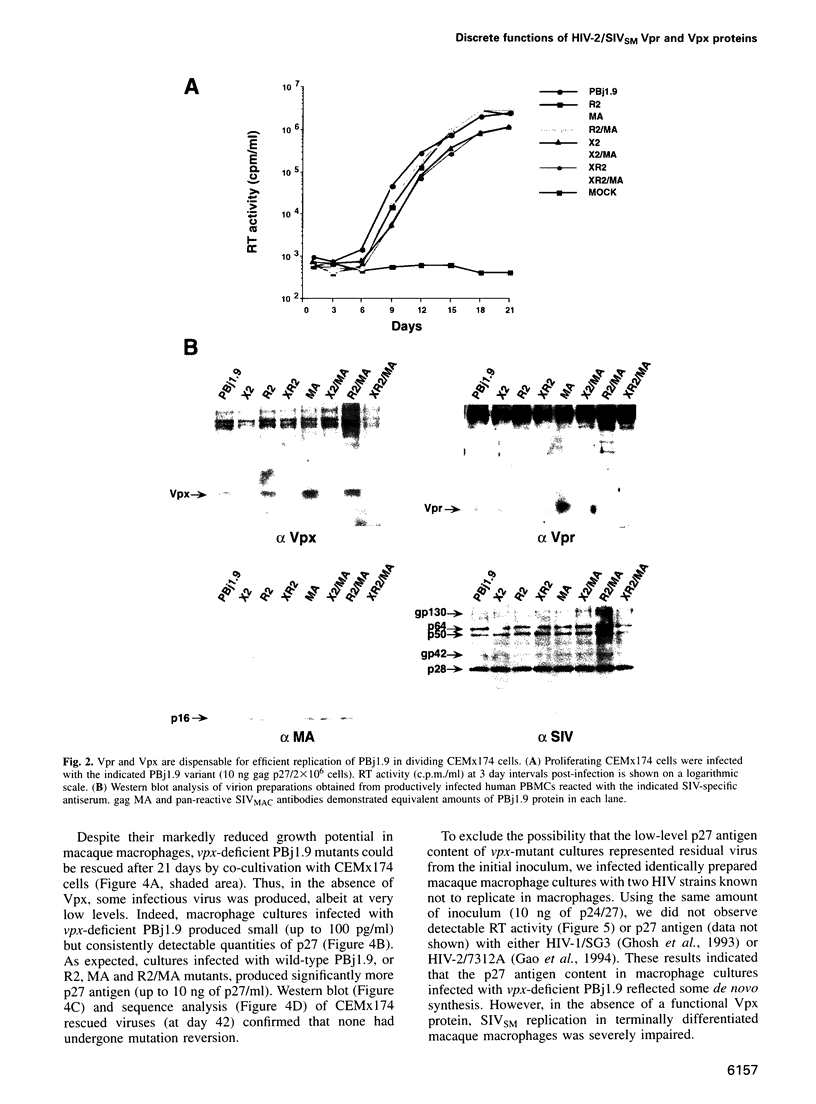





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiken C., Konner J., Landau N. R., Lenburg M. E., Trono D. Nef induces CD4 endocytosis: requirement for a critical dileucine motif in the membrane-proximal CD4 cytoplasmic domain. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):853–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90360-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balliet J. W., Kolson D. L., Eiger G., Kim F. M., McGann K. A., Srinivasan A., Collman R. Distinct effects in primary macrophages and lymphocytes of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 accessory genes vpr, vpu, and nef: mutational analysis of a primary HIV-1 isolate. Virology. 1994 May 1;200(2):623–631. doi: 10.1006/viro.1994.1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banapour B., Marthas M. L., Munn R. J., Luciw P. A. In vitro macrophage tropism of pathogenic and nonpathogenic molecular clones of simian immunodeficiency virus (SIVmac). Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):12–19. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90113-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartz S. R., Rogel M. E., Emerman M. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 cell cycle control: Vpr is cytostatic and mediates G2 accumulation by a mechanism which differs from DNA damage checkpoint control. J Virol. 1996 Apr;70(4):2324–2331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.4.2324-2331.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinskaya A. G., Ghorpade A., Heinzinger N. K., Smithgall T. E., Lewis R. E., Stevenson M. Phosphorylation-dependent human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection and nuclear targeting of viral DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):367–371. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Haggerty S., Dempsey M. P., Sharova N., Adzhubel A., Spitz L., Lewis P., Goldfarb D., Emerman M., Stevenson M. A nuclear localization signal within HIV-1 matrix protein that governs infection of non-dividing cells. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):666–669. doi: 10.1038/365666a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Sharova N., Dempsey M. P., Stanwick T. L., Bukrinskaya A. G., Haggerty S., Stevenson M. Active nuclear import of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 preintegration complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jul 15;89(14):6580–6584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.14.6580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Sharova N., McDonald T. L., Pushkarskaya T., Tarpley W. G., Stevenson M. Association of integrase, matrix, and reverse transcriptase antigens of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 with viral nucleic acids following acute infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 1;90(13):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.13.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chelsky D., Ralph R., Jonak G. Sequence requirements for synthetic peptide-mediated translocation to the nucleus. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2487–2492. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor R. I., Chen B. K., Choe S., Landau N. R. Vpr is required for efficient replication of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 in mononuclear phagocytes. Virology. 1995 Feb 1;206(2):935–944. doi: 10.1006/viro.1995.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Embretson J. E., Anderson D. C., Mullins J. I., Fultz P. N. Sequence analysis and acute pathogenicity of molecularly cloned SIVSMM-PBj14. Nature. 1990 Jun 14;345(6276):636–640. doi: 10.1038/345636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallay P., Swingler S., Aiken C., Trono D. HIV-1 infection of nondividing cells: C-terminal tyrosine phosphorylation of the viral matrix protein is a key regulator. Cell. 1995 Feb 10;80(3):379–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90488-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F., Yue L., Robertson D. L., Hill S. C., Hui H., Biggar R. J., Neequaye A. E., Whelan T. M., Ho D. D., Shaw G. M. Genetic diversity of human immunodeficiency virus type 2: evidence for distinct sequence subtypes with differences in virus biology. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):7433–7447. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.7433-7447.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia J. V., Miller A. D. Serine phosphorylation-independent downregulation of cell-surface CD4 by nef. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):508–511. doi: 10.1038/350508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S. K., Fultz P. N., Keddie E., Saag M. S., Sharp P. M., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. A molecular clone of HIV-1 tropic and cytopathic for human and chimpanzee lymphocytes. Virology. 1993 Jun;194(2):858–864. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. S., Lackner A. A., Lang S. M., Simon M. A., Sehgal P. K., Daniel M. D., Desrosiers R. C. Progression to AIDS in the absence of a gene for vpr or vpx. J Virol. 1995 Apr;69(4):2378–2383. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.4.2378-2383.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He J., Choe S., Walker R., Di Marzio P., Morgan D. O., Landau N. R. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral protein R (Vpr) arrests cells in the G2 phase of the cell cycle by inhibiting p34cdc2 activity. J Virol. 1995 Nov;69(11):6705–6711. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.11.6705-6711.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzinger N. K., Bukrinsky M. I., Haggerty S. A., Ragland A. M., Kewalramani V., Lee M. A., Gendelman H. E., Ratner L., Stevenson M., Emerman M. The Vpr protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 influences nuclear localization of viral nucleic acids in nondividing host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):7311–7315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzinger N., Baca-Regen L., Stevenson M., Gendelman H. E. Efficient synthesis of viral nucleic acids following monocyte infection by HIV-1. Virology. 1995 Jan 10;206(1):731–735. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(95)80097-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoch J., Lang S. M., Weeger M., Stahl-Hennig C., Coulibaly C., Dittmer U., Hunsmann G., Fuchs D., Müller J., Sopper S. vpr deletion mutant of simian immunodeficiency virus induces AIDS in rhesus monkeys. J Virol. 1995 Aug;69(8):4807–4813. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.8.4807-4813.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoxie J. A., Alpers J. D., Rackowski J. L., Huebner K., Haggarty B. S., Cedarbaum A. J., Reed J. C. Alterations in T4 (CD4) protein and mRNA synthesis in cells infected with HIV. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1123–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.3095925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jowett J. B., Planelles V., Poon B., Shah N. P., Chen M. L., Chen I. S. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpr gene arrests infected T cells in the G2 + M phase of the cell cycle. J Virol. 1995 Oct;69(10):6304–6313. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.10.6304-6313.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappes J. C., Parkin J. S., Conway J. A., Kim J., Brouillette C. G., Shaw G. M., Hahn B. H. Intracellular transport and virion incorporation of vpx requires interaction with other virus type-specific components. Virology. 1993 Mar;193(1):222–233. doi: 10.1006/viro.1993.1118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kent K. A., Gritz L., Stallard G., Cranage M. P., Collignon C., Thiriart C., Corcoran T., Silvera P., Stott E. J. Production and of monoclonal antibodies to simian immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoproteins. AIDS. 1991 Jul;5(7):829–836. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199107000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kewalramani V. N., Emerman M. Vpx association with mature core structures of HIV-2. Virology. 1996 Apr 1;218(1):159–168. doi: 10.1006/viro.1996.0176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. N., Fernandes L. S., Williams W. V., Weiner D. B. Induction of cell differentiation by human immunodeficiency virus 1 vpr. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90073-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Hui H., Burgess C. J., Price R. W., Sharp P. M., Hahn B. H., Shaw G. M. Complete nucleotide sequence, genome organization, and biological properties of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 in vivo: evidence for limited defectiveness and complementation. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6587–6600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6587-6600.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lori F., di Marzo Veronese F., de Vico A. L., Lusso P., Reitz M. S., Jr, Gallo R. C. Viral DNA carried by human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5067–5074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5067-5074.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. L., Spearman P., Ratner L. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 viral protein R localization in infected cells and virions. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6542–6550. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6542-6550.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers G., MacInnes K., Korber B. The emergence of simian/human immunodeficiency viruses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1992 Mar;8(3):373–386. doi: 10.1089/aid.1992.8.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman M. A., McPherson S. A., Fletcher T. M., 3rd, Kappes J. C., Hahn B. H. Polyclonal rabbit antisera that detect the Vpr protein of SIVSM and SIVMAC on immunoblots of purified virions. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1995 Mar;11(3):405–408. doi: 10.1089/aid.1995.11.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paxton W., Connor R. I., Landau N. R. Incorporation of Vpr into human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions: requirement for the p6 region of gag and mutational analysis. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7229–7237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7229-7237.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Planelles V., Jowett J. B., Li Q. X., Xie Y., Hahn B., Chen I. S. Vpr-induced cell cycle arrest is conserved among primate lentiviruses. J Virol. 1996 Apr;70(4):2516–2524. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.4.2516-2524.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Re F., Braaten D., Franke E. K., Luban J. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpr arrests the cell cycle in G2 by inhibiting the activation of p34cdc2-cyclin B. J Virol. 1995 Nov;69(11):6859–6864. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.11.6859-6864.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogel M. E., Wu L. I., Emerman M. The human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpr gene prevents cell proliferation during chronic infection. J Virol. 1995 Feb;69(2):882–888. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.2.882-888.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Meier C., Mann A. M., Chapman N., Wasiak A. Envelope glycoprotein of HIV induces interference and cytolysis resistance in CD4+ cells: mechanism for persistence in AIDS. Cell. 1988 May 6;53(3):483–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90168-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strebel K., Klimkait T., Maldarelli F., Martin M. A. Molecular and biochemical analyses of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 vpu protein. J Virol. 1989 Sep;63(9):3784–3791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.9.3784-3791.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbramanian R. A., Cohen E. A. Molecular biology of the human immunodeficiency virus accessory proteins. J Virol. 1994 Nov;68(11):6831–6835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.11.6831-6835.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tristem M., Marshall C., Karpas A., Hill F. Evolution of the primate lentiviruses: evidence from vpx and vpr. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3405–3412. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05419.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tristem M., Marshall C., Karpas A., Petrik J., Hill F. Origin of vpx in lentiviruses. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):341–342. doi: 10.1038/347341b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D. HIV accessory proteins: leading roles for the supporting cast. Cell. 1995 Jul 28;82(2):189–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trono D. Partial reverse transcripts in virions from human immunodeficiency and murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4893–4900. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4893-4900.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willey R. L., Maldarelli F., Martin M. A., Strebel K. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 Vpu protein regulates the formation of intracellular gp160-CD4 complexes. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):226–234. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.226-234.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu X., Conway J. A., Kim J., Kappes J. C. Localization of the Vpx packaging signal within the C terminus of the human immunodeficiency virus type 2 Gag precursor protein. J Virol. 1994 Oct;68(10):6161–6169. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.10.6161-6169.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Schwedler U., Kornbluth R. S., Trono D. The nuclear localization signal of the matrix protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 allows the establishment of infection in macrophages and quiescent T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jul 19;91(15):6992–6996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.6992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]