Abstract
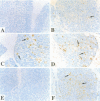
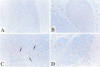
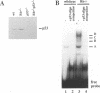
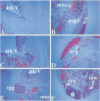
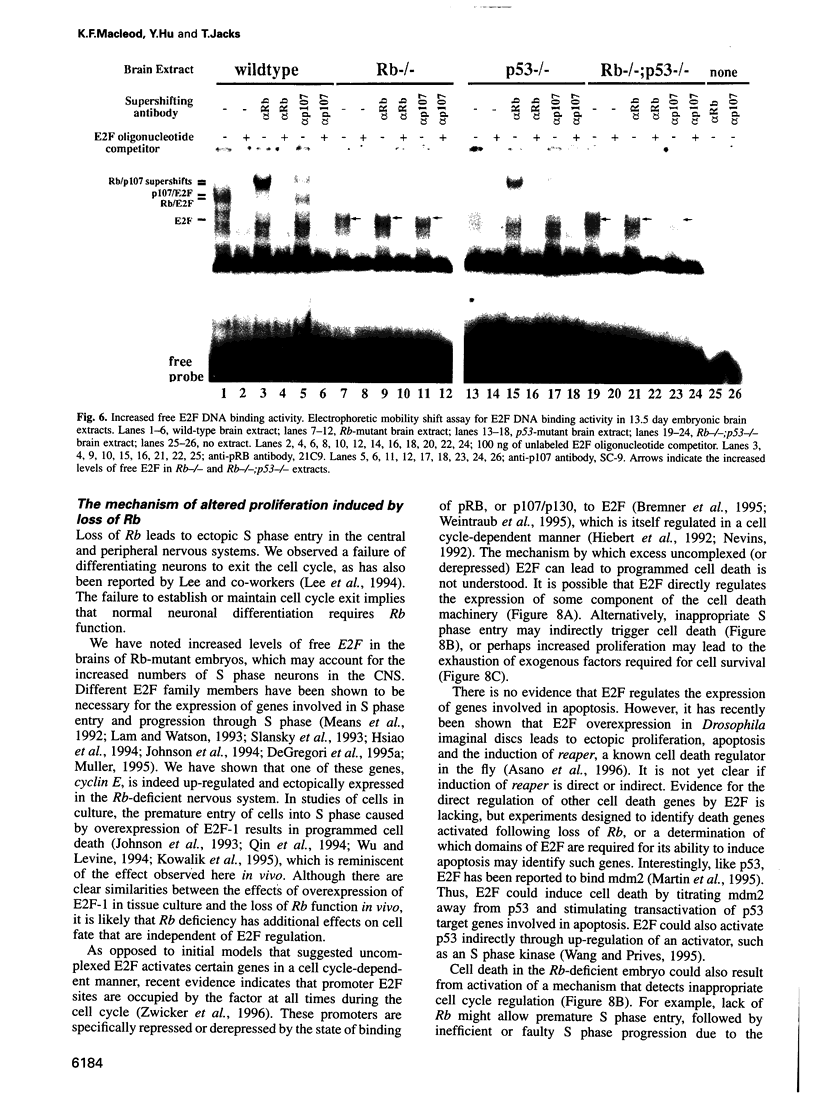
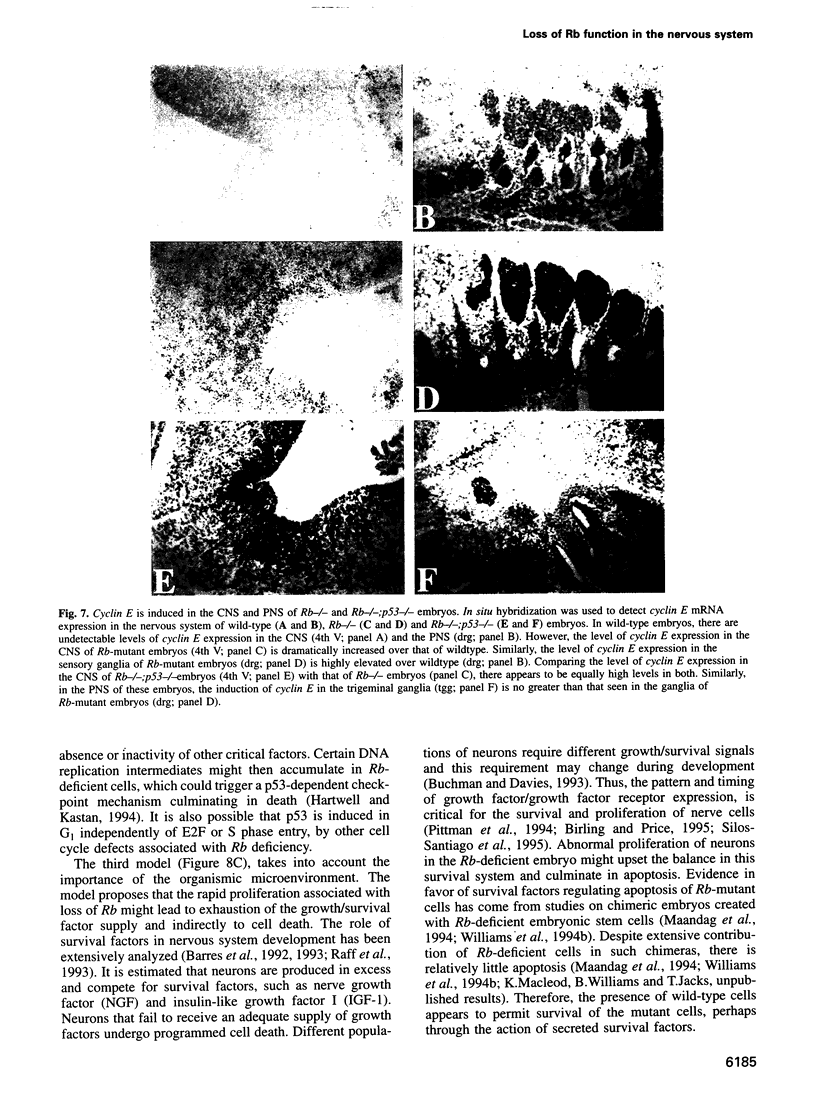
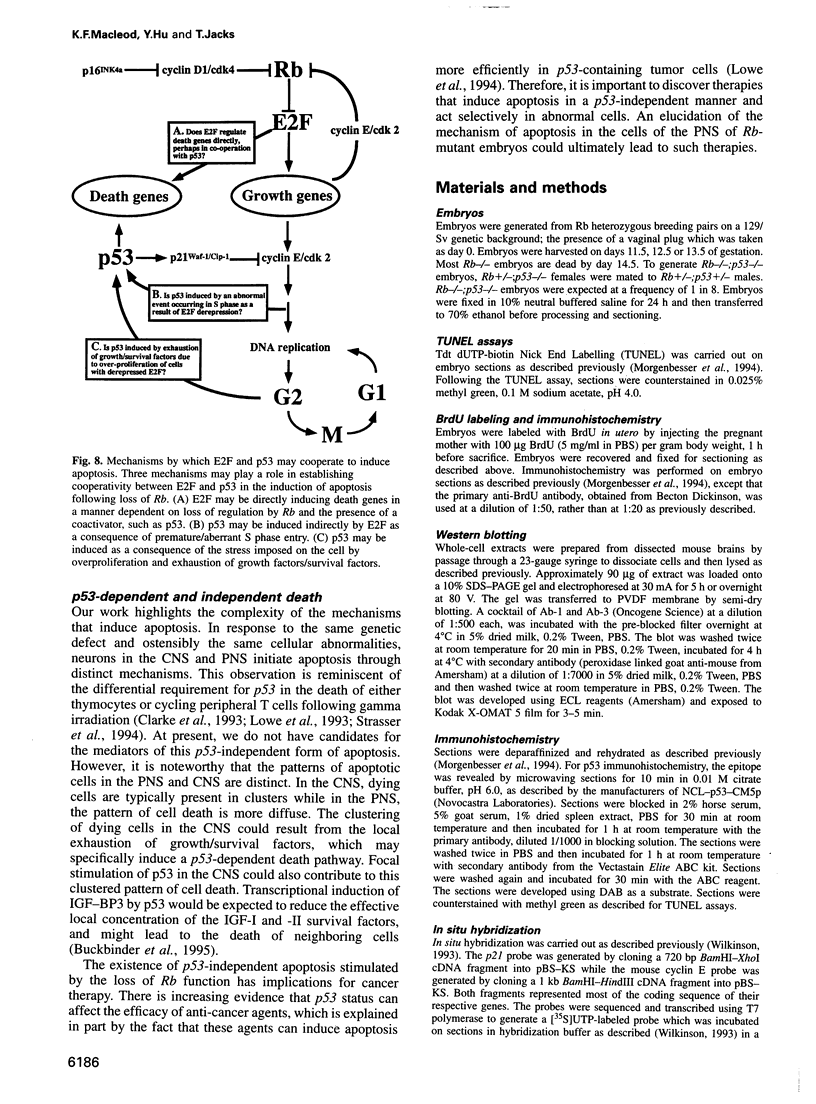
Extensive apoptosis occurs in the nervous system of mouse embryos homozygous mutant for a targeted disruption of the retinoblastoma (Rb) gene. This cell death is present in both the central (CNS) and peripheral nervous systems (PNS) and is associated with abnormal S phase entry of normally post-mitotic neurons. Aberrant proliferation in the CNS correlates with increased free E2F DNA binding activity and increased expression of cyclin E, an E2F target gene and critical cell cycle regulator. Cell death in the CNS is accompanied by increased levels of the p53 tumor suppressor gene product and increased expression of the p53 target gene, p21Waf-1/Cip-1. However, induction of p53 is not observed in the PNS of Rb-mutant embryos, nor does loss of p53 function inhibit cell death in the PNS. Surprisingly, p21Waf-1/Cip-1 is induced in the sensory ganglia of Rb-mutant embryos in a p53-independent manner. Although loss of p53 gene function prevents cell death in the CNS of Rb-mutant embryos, it does not restore normal proliferative control.
Full text
PDF



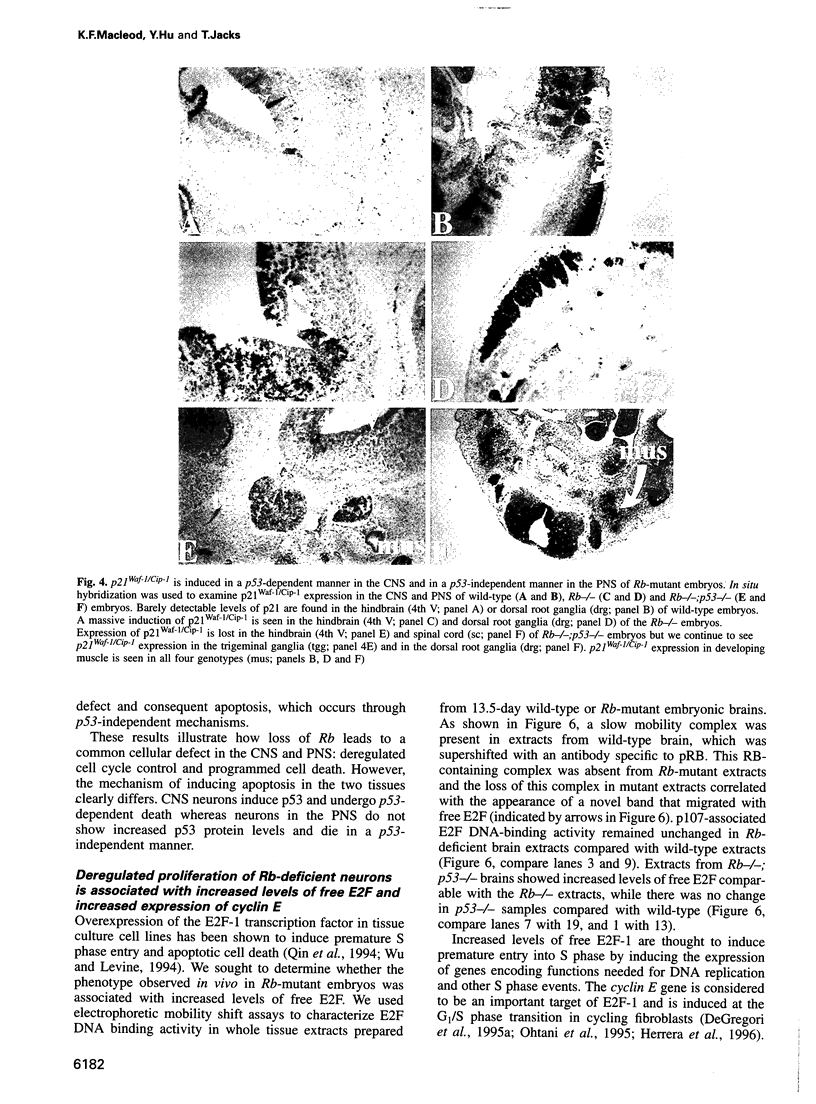



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almasan A., Yin Y., Kelly R. E., Lee E. Y., Bradley A., Li W., Bertino J. R., Wahl G. M. Deficiency of retinoblastoma protein leads to inappropriate S-phase entry, activation of E2F-responsive genes, and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 6;92(12):5436–5440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.12.5436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano M., Nevins J. R., Wharton R. P. Ectopic E2F expression induces S phase and apoptosis in Drosophila imaginal discs. Genes Dev. 1996 Jun 1;10(11):1422–1432. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.11.1422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Attardi L. D., Lowe S. W., Brugarolas J., Jacks T. Transcriptional activation by p53, but not induction of the p21 gene, is essential for oncogene-mediated apoptosis. EMBO J. 1996 Jul 15;15(14):3693–3701. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Hart I. K., Coles H. S., Burne J. F., Voyvodic J. T., Richardson W. D., Raff M. C. Cell death and control of cell survival in the oligodendrocyte lineage. Cell. 1992 Jul 10;70(1):31–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90531-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barres B. A., Schmid R., Sendnter M., Raff M. C. Multiple extracellular signals are required for long-term oligodendrocyte survival. Development. 1993 May;118(1):283–295. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birling M. C., Price J. Influence of growth factors on neuronal differentiation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;7(6):878–884. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bremner R., Cohen B. L., Sopta M., Hamel P. A., Ingles C. J., Gallie B. L., Phillips R. A. Direct transcriptional repression by pRB and its reversal by specific cyclins. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;15(6):3256–3265. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.6.3256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugarolas J., Chandrasekaran C., Gordon J. I., Beach D., Jacks T., Hannon G. J. Radiation-induced cell cycle arrest compromised by p21 deficiency. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):552–557. doi: 10.1038/377552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman V. L., Davies A. M. Different neurotrophins are expressed and act in a developmental sequence to promote the survival of embryonic sensory neurons. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):989–1001. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckbinder L., Talbott R., Velasco-Miguel S., Takenaka I., Faha B., Seizinger B. R., Kley N. Induction of the growth inhibitor IGF-binding protein 3 by p53. Nature. 1995 Oct 19;377(6550):646–649. doi: 10.1038/377646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canman C. E., Gilmer T. M., Coutts S. B., Kastan M. B. Growth factor modulation of p53-mediated growth arrest versus apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1995 Mar 1;9(5):600–611. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.5.600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao L., Faha B., Dembski M., Tsai L. H., Harlow E., Dyson N. Independent binding of the retinoblastoma protein and p107 to the transcription factor E2F. Nature. 1992 Jan 9;355(6356):176–179. doi: 10.1038/355176a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S., Schmidt-Grimminger D. C., Murant T., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Differentiation-dependent up-regulation of the human papillomavirus E7 gene reactivates cellular DNA replication in suprabasal differentiated keratinocytes. Genes Dev. 1995 Oct 1;9(19):2335–2349. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.19.2335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Maandag E. R., van Roon M., van der Lugt N. M., van der Valk M., Hooper M. L., Berns A., te Riele H. Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):328–330. doi: 10.1038/359328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGregori J., Kowalik T., Nevins J. R. Cellular targets for activation by the E2F1 transcription factor include DNA synthesis- and G1/S-regulatory genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;15(8):4215–4224. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.8.4215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGregori J., Leone G., Ohtani K., Miron A., Nevins J. R. E2F-1 accumulation bypasses a G1 arrest resulting from the inhibition of G1 cyclin-dependent kinase activity. Genes Dev. 1995 Dec 1;9(23):2873–2887. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.23.2873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng C., Zhang P., Harper J. W., Elledge S. J., Leder P. Mice lacking p21CIP1/WAF1 undergo normal development, but are defective in G1 checkpoint control. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):675–684. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Leonardo A., Linke S. P., Clarkin K., Wahl G. M. DNA damage triggers a prolonged p53-dependent G1 arrest and long-term induction of Cip1 in normal human fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1994 Nov 1;8(21):2540–2551. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.21.2540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend S. H., Bernards R., Rogelj S., Weinberg R. A., Rapaport J. M., Albert D. M., Dryja T. P. A human DNA segment with properties of the gene that predisposes to retinoblastoma and osteosarcoma. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):643–646. doi: 10.1038/323643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gu W., Schneider J. W., Condorelli G., Kaushal S., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Interaction of myogenic factors and the retinoblastoma protein mediates muscle cell commitment and differentiation. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90110-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris C. C., Hollstein M. Clinical implications of the p53 tumor-suppressor gene. N Engl J Med. 1993 Oct 28;329(18):1318–1327. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199310283291807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H., Kastan M. B. Cell cycle control and cancer. Science. 1994 Dec 16;266(5192):1821–1828. doi: 10.1126/science.7997877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Harlow E., Fattaey A. Inhibition of E2F-1 transactivation by direct binding of the retinoblastoma protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;13(10):6501–6508. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.10.6501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrera R. E., Sah V. P., Williams B. O., Mäkelä T. P., Weinberg R. A., Jacks T. Altered cell cycle kinetics, gene expression, and G1 restriction point regulation in Rb-deficient fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 May;16(5):2402–2407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.5.2402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiebert S. W., Chellappan S. P., Horowitz J. M., Nevins J. R. The interaction of RB with E2F coincides with an inhibition of the transcriptional activity of E2F. Genes Dev. 1992 Feb;6(2):177–185. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao K. M., McMahon S. L., Farnham P. J. Multiple DNA elements are required for the growth regulation of the mouse E2F1 promoter. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 1;8(13):1526–1537. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.13.1526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Fazeli A., Schmitt E. M., Bronson R. T., Goodell M. A., Weinberg R. A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):295–300. doi: 10.1038/359295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Ohtani K., Nevins J. R. Autoregulatory control of E2F1 expression in response to positive and negative regulators of cell cycle progression. Genes Dev. 1994 Jul 1;8(13):1514–1525. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.13.1514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. G., Schwarz J. K., Cress W. D., Nevins J. R. Expression of transcription factor E2F1 induces quiescent cells to enter S phase. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):349–352. doi: 10.1038/365349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Onyekwere O., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Craig R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6304–6311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastan M. B., Zhan Q., el-Deiry W. S., Carrier F., Jacks T., Walsh W. V., Plunkett B. S., Vogelstein B., Fornace A. J., Jr A mammalian cell cycle checkpoint pathway utilizing p53 and GADD45 is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia. Cell. 1992 Nov 13;71(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90593-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokawa H., Richon V. M., Venta-Perez G., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Hexamethylenebisacetamide-induced erythroleukemia cell differentiation involves modulation of events required for cell cycle progression through G1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jul 15;90(14):6746–6750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.14.6746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowalik T. F., DeGregori J., Schwarz J. K., Nevins J. R. E2F1 overexpression in quiescent fibroblasts leads to induction of cellular DNA synthesis and apoptosis. J Virol. 1995 Apr;69(4):2491–2500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.69.4.2491-2500.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kranenburg O., van der Eb A. J., Zantema A. Cyclin D1 is an essential mediator of apoptotic neuronal cell death. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 2;15(1):46–54. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E. W., Watson R. J. An E2F-binding site mediates cell-cycle regulated repression of mouse B-myb transcription. EMBO J. 1993 Jul;12(7):2705–2713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05932.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Skapek S. X., Novitch B. Regulatory mechanisms that coordinate skeletal muscle differentiation and cell cycle withdrawal. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1994 Dec;6(6):788–794. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(94)90046-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Chang C. Y., Hu N., Wang Y. C., Lai C. C., Herrup K., Lee W. H., Bradley A. Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):288–294. doi: 10.1038/359288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Hu N., Yuan S. S., Cox L. A., Bradley A., Lee W. H., Herrup K. Dual roles of the retinoblastoma protein in cell cycle regulation and neuron differentiation. Genes Dev. 1994 Sep 1;8(17):2008–2021. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.17.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Saito M., Vidal M., Valentine M., Look T., Harlow E., Dyson N., Helin K. The retinoblastoma protein binds to a family of E2F transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7813–7825. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Bodis S., McClatchey A., Remington L., Ruley H. E., Fisher D. E., Housman D. E., Jacks T. p53 status and the efficacy of cancer therapy in vivo. Science. 1994 Nov 4;266(5186):807–810. doi: 10.1126/science.7973635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe S. W., Schmitt E. M., Smith S. W., Osborne B. A., Jacks T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apoptosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):847–849. doi: 10.1038/362847a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maandag E. C., van der Valk M., Vlaar M., Feltkamp C., O'Brien J., van Roon M., van der Lugt N., Berns A., te Riele H. Developmental rescue of an embryonic-lethal mutation in the retinoblastoma gene in chimeric mice. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4260–4268. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06746.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D. p53 and the Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1993 Apr;66(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(93)90233-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K., Trouche D., Hagemeier C., Sørensen T. S., La Thangue N. B., Kouzarides T. Stimulation of E2F1/DP1 transcriptional activity by MDM2 oncoprotein. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):691–694. doi: 10.1038/375691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Means A. L., Slansky J. E., McMahon S. L., Knuth M. W., Farnham P. J. The HIP1 binding site is required for growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Mar;12(3):1054–1063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.3.1054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley C. A., Owens B., Briscoe C. V., Thomas D. B., Lane D. P., Hall P. A. Coupling between gamma irradiation, p53 induction and the apoptotic response depends upon cell type in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1995 May;108(Pt 5):1843–1848. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.5.1843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R. Transcriptional regulation during the mammalian cell cycle. Trends Genet. 1995 May;11(5):173–178. doi: 10.1016/S0168-9525(00)89039-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins. Science. 1992 Oct 16;258(5081):424–429. doi: 10.1126/science.1411535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtani K., DeGregori J., Nevins J. R. Regulation of the cyclin E gene by transcription factor E2F1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 19;92(26):12146–12150. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan H., Griep A. E. Altered cell cycle regulation in the lens of HPV-16 E6 or E7 transgenic mice: implications for tumor suppressor gene function in development. Genes Dev. 1994 Jun 1;8(11):1285–1299. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.11.1285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pan H., Griep A. E. Temporally distinct patterns of p53-dependent and p53-independent apoptosis during mouse lens development. Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 1;9(17):2157–2169. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.17.2157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavletich N. P., Chambers K. A., Pabo C. O. The DNA-binding domain of p53 contains the four conserved regions and the major mutation hot spots. Genes Dev. 1993 Dec;7(12B):2556–2564. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.12b.2556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pittman R. N., Mills J. C., DiBenedetto A. J., Hynicka W. P., Wang S. Neuronal cell death: searching for the smoking gun. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1994 Feb;4(1):87–94. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(94)90036-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin X. Q., Livingston D. M., Kaelin W. G., Jr, Adams P. D. Deregulated transcription factor E2F-1 expression leads to S-phase entry and p53-mediated apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Nov 8;91(23):10918–10922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.23.10918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Barres B. A., Burne J. F., Coles H. S., Ishizaki Y., Jacobson M. D. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):695–700. doi: 10.1126/science.8235590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richon V. M., Rifkind R. A., Marks P. A. Expression and phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein during induced differentiation of murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1992 Jul;3(7):413–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabbatini P., Lin J., Levine A. J., White E. Essential role for p53-mediated transcription in E1A-induced apoptosis. Genes Dev. 1995 Sep 1;9(17):2184–2192. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.17.2184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J. W., Gu W., Zhu L., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Reversal of terminal differentiation mediated by p107 in Rb-/- muscle cells. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1467–1471. doi: 10.1126/science.8197461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silos-Santiago I., Greenlund L. J., Johnson E. M., Jr, Snider W. D. Molecular genetics of neuronal survival. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995 Feb;5(1):42–49. doi: 10.1016/0959-4388(95)80085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh P., Wong S. H., Hong W. Overexpression of E2F-1 in rat embryo fibroblasts leads to neoplastic transformation. EMBO J. 1994 Jul 15;13(14):3329–3338. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06635.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack R. S., Skerjanc I. S., Lach B., Craig J., Jardine K., McBurney M. W. Cells differentiating into neuroectoderm undergo apoptosis in the absence of functional retinoblastoma family proteins. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):779–788. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slansky J. E., Li Y., Kaelin W. G., Farnham P. J. A protein synthesis-dependent increase in E2F1 mRNA correlates with growth regulation of the dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1610–1618. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slebos R. J., Lee M. H., Plunkett B. S., Kessis T. D., Williams B. O., Jacks T., Hedrick L., Kastan M. B., Cho K. R. p53-dependent G1 arrest involves pRB-related proteins and is disrupted by the human papillomavirus 16 E7 oncoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5320–5324. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A., Harris A. W., Jacks T., Cory S. DNA damage can induce apoptosis in proliferating lymphoid cells via p53-independent mechanisms inhibitable by Bcl-2. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):329–339. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Symonds H., Krall L., Remington L., Saenz-Robles M., Lowe S., Jacks T., Van Dyke T. p53-dependent apoptosis suppresses tumor growth and progression in vivo. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90534-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vousden K. Interactions of human papillomavirus transforming proteins with the products of tumor suppressor genes. FASEB J. 1993 Jul;7(10):872–879. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.10.8393818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Prives C. Increased and altered DNA binding of human p53 by S and G2/M but not G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):88–91. doi: 10.1038/376088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub S. J., Chow K. N., Luo R. X., Zhang S. H., He S., Dean D. C. Mechanism of active transcriptional repression by the retinoblastoma protein. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):812–815. doi: 10.1038/375812a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. O., Remington L., Albert D. M., Mukai S., Bronson R. T., Jacks T. Cooperative tumorigenic effects of germline mutations in Rb and p53. Nat Genet. 1994 Aug;7(4):480–484. doi: 10.1038/ng0894-480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams B. O., Schmitt E. M., Remington L., Bronson R. T., Albert D. M., Weinberg R. A., Jacks T. Extensive contribution of Rb-deficient cells to adult chimeric mice with limited histopathological consequences. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 15;13(18):4251–4259. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu G., Livingston D. M., Krek W. Multiple members of the E2F transcription factor family are the products of oncogenes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1357–1361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker J., Liu N., Engeland K., Lucibello F. C., Müller R. Cell cycle regulation of E2F site occupation in vivo. Science. 1996 Mar 15;271(5255):1595–1597. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5255.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Harper J. W., O'Connor P. M., Velculescu V. E., Canman C. E., Jackman J., Pietenpol J. A., Burrell M., Hill D. E., Wang Y. WAF1/CIP1 is induced in p53-mediated G1 arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 1994 Mar 1;54(5):1169–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Deiry W. S., Tokino T., Velculescu V. E., Levy D. B., Parsons R., Trent J. M., Lin D., Mercer W. E., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):817–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90500-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]