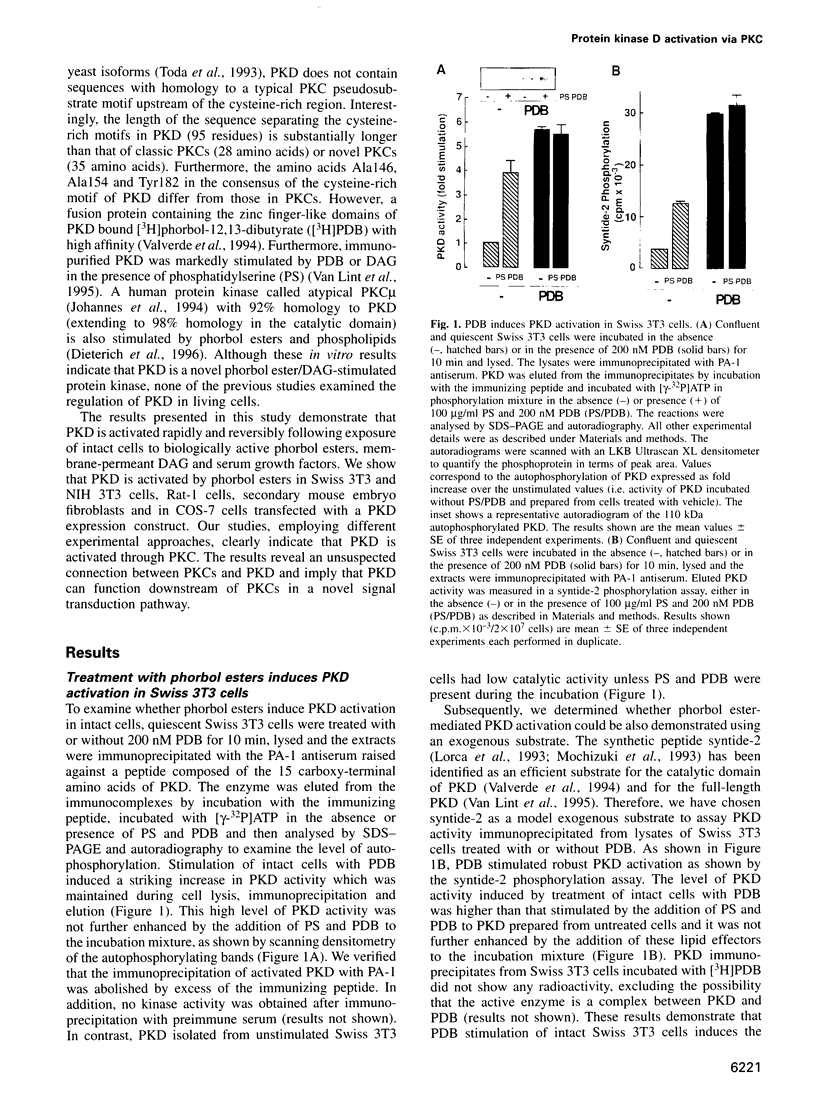
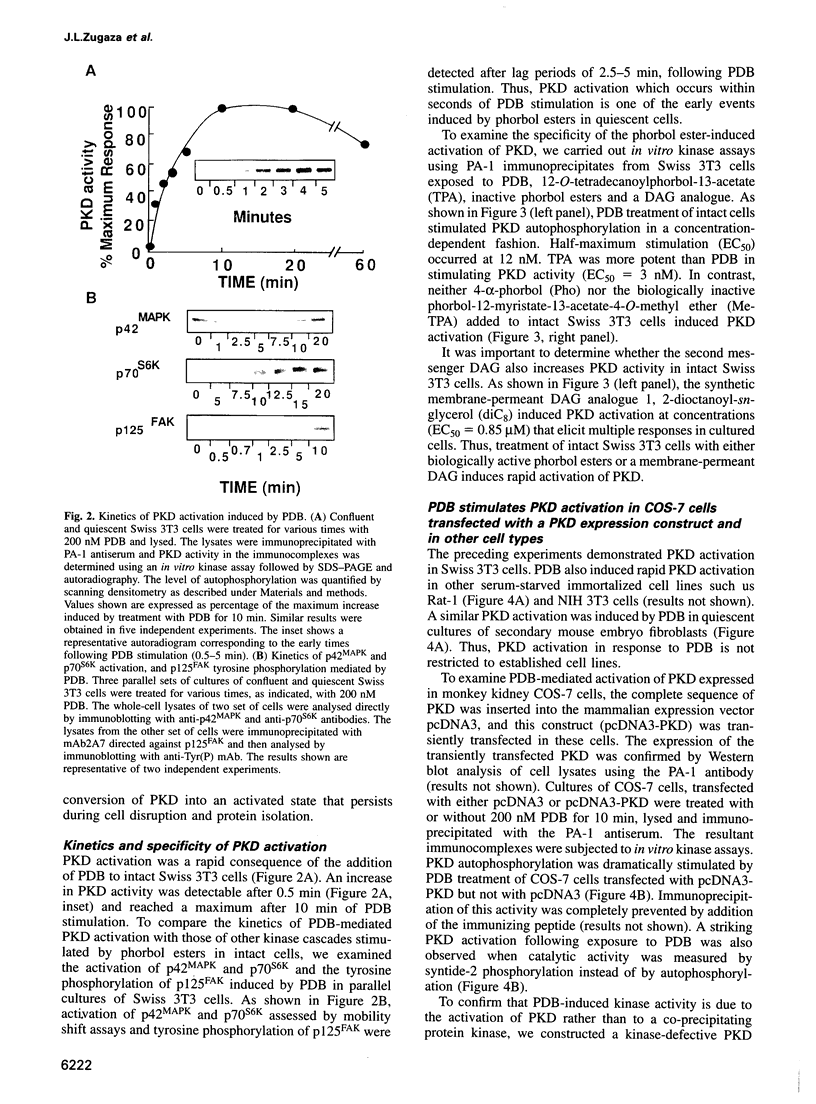
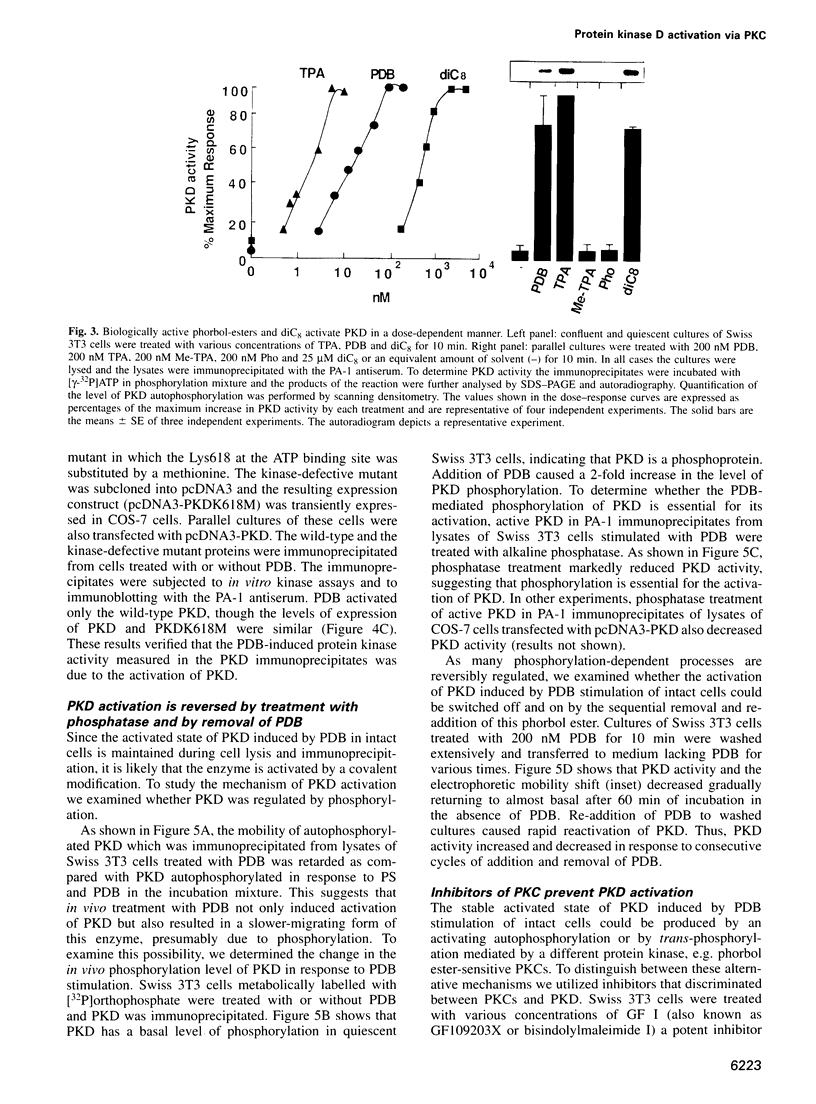
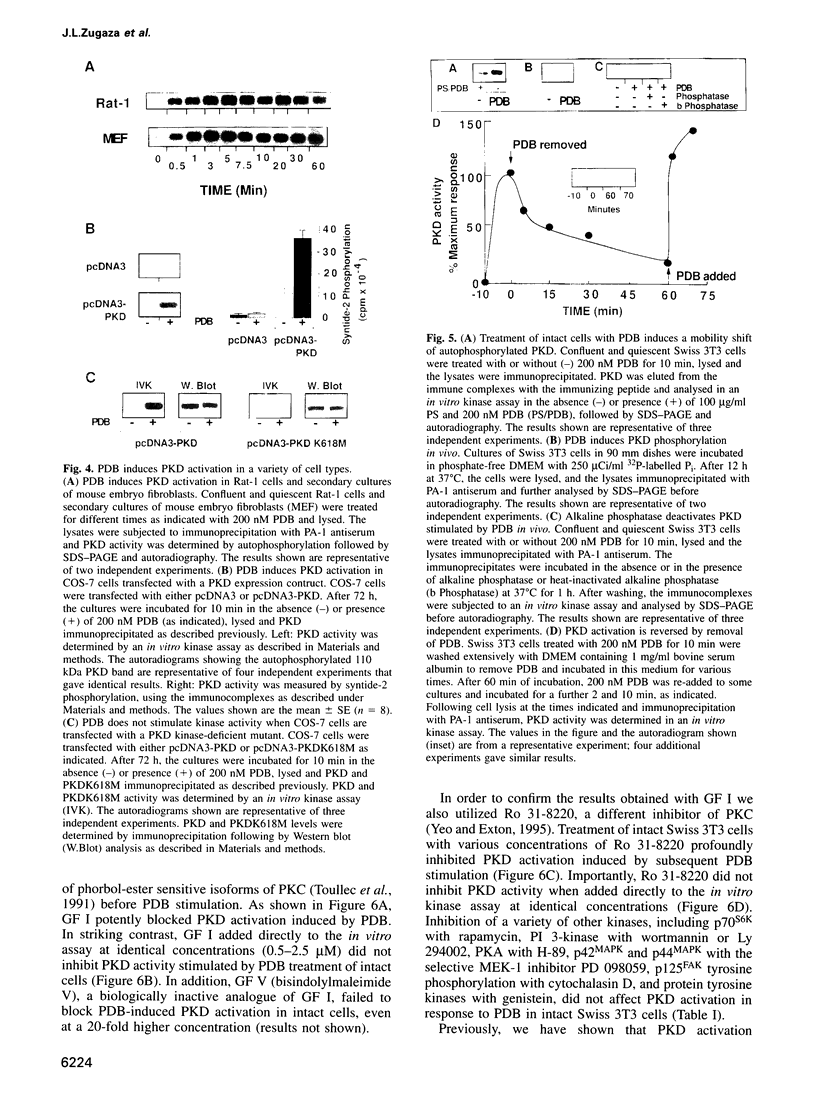
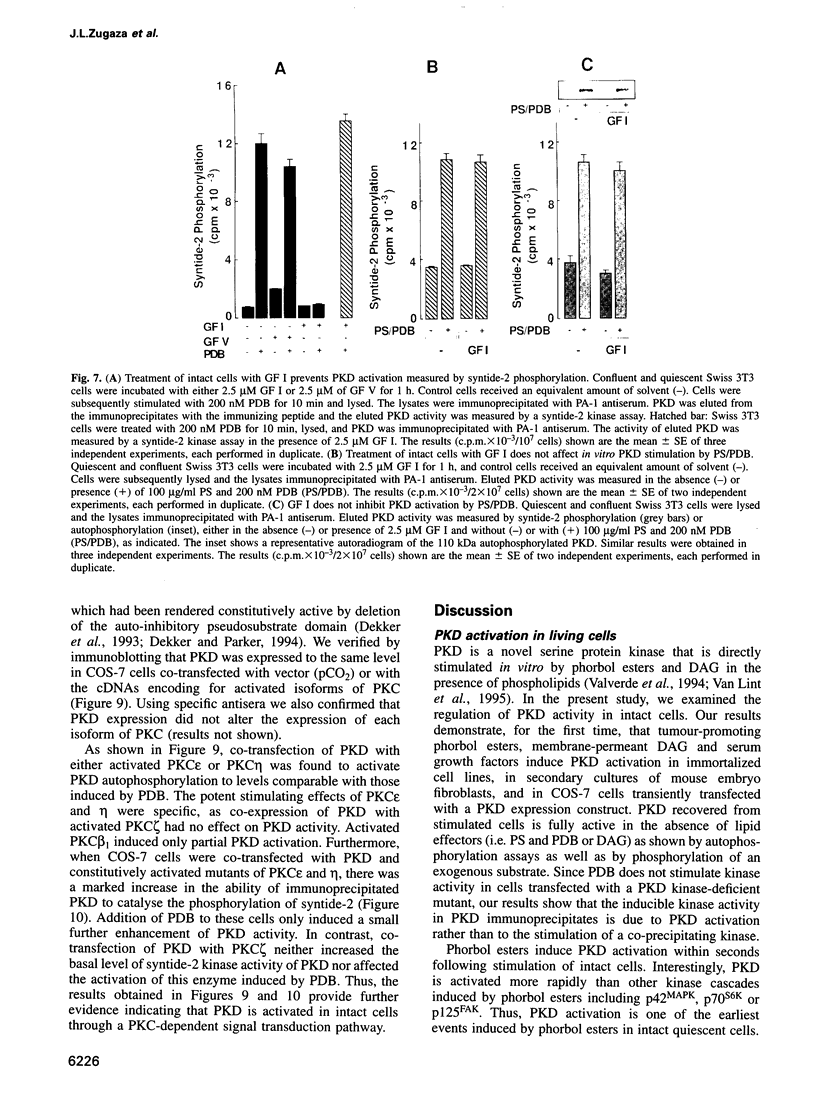
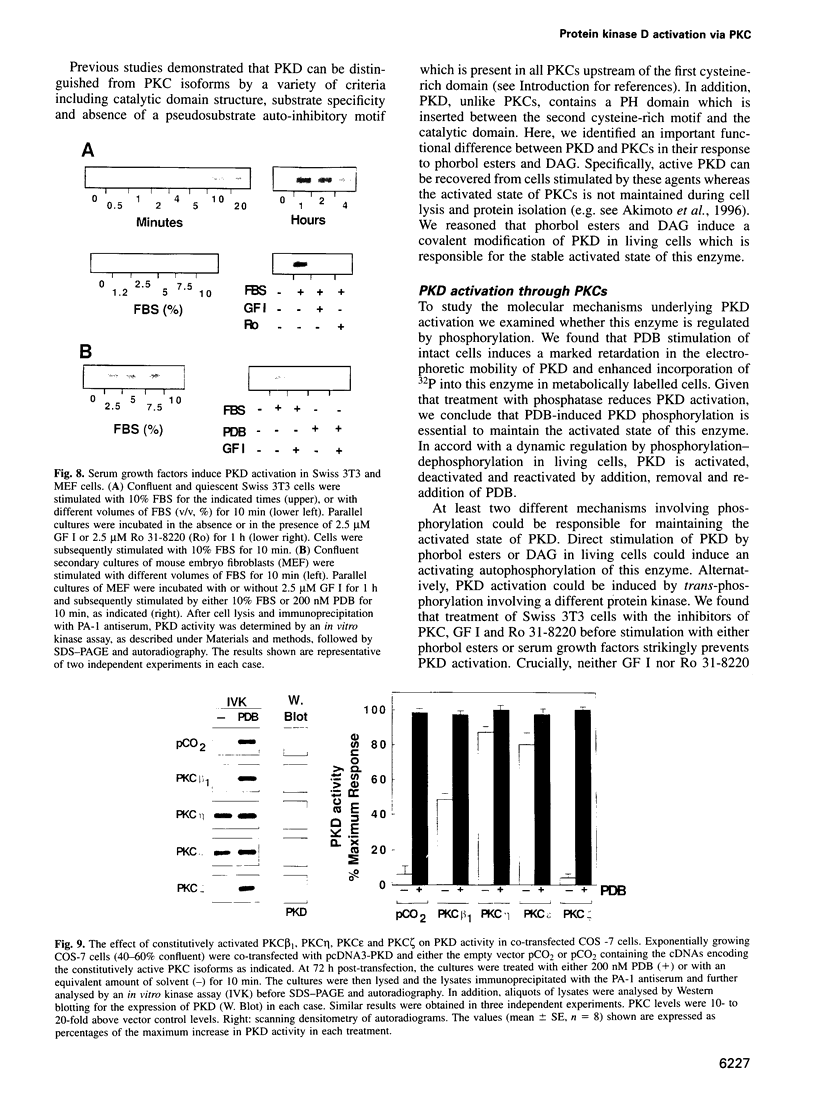
Abstract
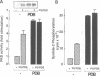
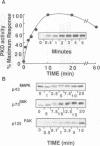
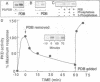
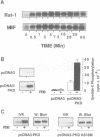
Protein kinase D (PKD) is a serine/threonine protein kinase that is directly stimulated in vitro by phorbol esters and diacylglycerol in the presence of phospholipids. Here, we examine the regulation of PKD in living cells. Our results demonstrate that tumour-promoting phorbol esters, membrane-permeant diacylglycerol and serum growth factors rapidly induced PKD activation in immortalized cell lines (e.g. Swiss 3T3 and Rat-1 cells), in secondary cultures of mouse embryo fibroblasts and in COS-7 cells transiently transfected with a PKD expression construct. PKD activation was maintained during cell disruption and immunopurification and was associated with an electrophoretic mobility shift and enhanced 32P incorporation into the enzyme, but was reversed by treatment with alkaline phosphatase. PKD was activated, deactivated and reactivated in response to consecutive cycles of addition and removal of PDB. PKD activation was completely abrogated by exposure of the cells to the protein kinase C inhibitors GF I and Ro 31-8220. In contrast, these compounds did not inhibit PKD activity when added directly in vitro. Co-transfection of PKD with constitutively activated mutants of PKCs showed that PKCepsilon and eta but not PKCzeta strongly induced PKD activation in COS-7 cells. Thus, our results indicate that PKD is activated in living cells through a PKC-dependent signal transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akimoto K., Takahashi R., Moriya S., Nishioka N., Takayanagi J., Kimura K., Fukui Y., Osada S. i., Mizuno K., Hirai S. i. EGF or PDGF receptors activate atypical PKClambda through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. EMBO J. 1996 Feb 15;15(4):788–798. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Areces L. B., Kazanietz M. G., Blumberg P. M. Close similarity of baculovirus-expressed n-chimaerin and protein kinase C alpha as phorbol ester receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 29;269(30):19553–19558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogoyevitch M. A., Parker P. J., Sugden P. H. Characterization of protein kinase C isotype expression in adult rat heart. Protein kinase C-epsilon is a major isotype present, and it is activated by phorbol esters, epinephrine, and endothelin. Circ Res. 1993 Apr;72(4):757–767. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.4.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns D. J., Bell R. M. Protein kinase C contains two phorbol ester binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):18330–18338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., McIntyre P., Parker P. J. Mutagenesis of the regulatory domain of rat protein kinase C-eta. A molecular basis for restricted histone kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19498–19504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., Parker P. J. Protein kinase C--a question of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterich S., Herget T., Link G., Böttinger H., Pfizenmaier K., Johannes F. J. In vitro activation and substrates of recombinant, baculovirus expressed human protein kinase C mu. FEBS Lett. 1996 Mar 4;381(3):183–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00116-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divecha N., Irvine R. F. Phospholipid signaling. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90409-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genot E. M., Parker P. J., Cantrell D. A. Analysis of the role of protein kinase C-alpha, -epsilon, and -zeta in T cell activation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 28;270(17):9833–9839. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.9833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gulbins E., Coggeshall K. M., Baier G., Telford D., Langlet C., Baier-Bitterlich G., Bonnefoy-Berard N., Burn P., Wittinghofer A., Altman A. Direct stimulation of Vav guanine nucleotide exchange activity for Ras by phorbol esters and diglycerides. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;14(7):4749–4758. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.7.4749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Hunter T. Protein kinases 6. The eukaryotic protein kinase superfamily: kinase (catalytic) domain structure and classification. FASEB J. 1995 May;9(8):576–596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M. Protein kinase catalytic domain sequence database: identification of conserved features of primary structure and classification of family members. Methods Enzymol. 1991;200:38–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)00126-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. R., Bishop W. R., Kirschmeier P., George S. J., Cramer S. P., Hendrickson W. A. Identification and characterization of zinc binding sites in protein kinase C. Science. 1991 Dec 20;254(5039):1776–1779. doi: 10.1126/science.1763327. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hug H., Sarre T. F. Protein kinase C isoenzymes: divergence in signal transduction? Biochem J. 1993 Apr 15;291(Pt 2):329–343. doi: 10.1042/bj2910329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höss M., Dilling A., Currant A., Päbo S. Molecular phylogeny of the extinct ground sloth Mylodon darwinii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jan 9;93(1):181–185. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johannes F. J., Prestle J., Eis S., Oberhagemann P., Pfizenmaier K. PKCu is a novel, atypical member of the protein kinase C family. J Biol Chem. 1994 Feb 25;269(8):6140–6148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazanietz M. G., Wang S., Milne G. W., Lewin N. E., Liu H. L., Blumberg P. M. Residues in the second cysteine-rich region of protein kinase C delta relevant to phorbol ester binding as revealed by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21852–21859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in transmembrane signalling. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:149–178. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.001053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koide H., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Isolation and characterization of the epsilon subspecies of protein kinase C from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1149–1153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama I. N., Brenner S. A phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding protein encoded by the unc-13 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5729–5733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mochizuki H., Ito T., Hidaka H. Purification and characterization of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase V from rat cerebrum. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 25;268(12):9143–9147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi H., Exton J. H. Purification and characterization of the zeta isoform of protein kinase C from bovine kidney. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 15;267(23):16347–16354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Intracellular signaling by hydrolysis of phospholipids and activation of protein kinase C. Science. 1992 Oct 23;258(5082):607–614. doi: 10.1126/science.1411571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and prospectives of the protein kinase c family for cellular regulation. Cancer. 1989 May 15;63(10):1892–1903. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890515)63:10<1892::aid-cncr2820631005>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Ogita K., Kikkawa U., Igarashi K., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C zeta subspecies from rat brain: its structure, expression, and properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3099–3103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proud C. G. p70 S6 kinase: an enigma with variations. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 May;21(5):181–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quest A. F., Bardes E. S., Bell R. M. A phorbol ester binding domain of protein kinase C gamma. High affinity binding to a glutathione-S-transferase/Cys2 fusion protein. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 28;269(4):2953–2960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. G., Choi K. D. Multiple forms of phospholipase C isozymes and their activation mechanisms. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1992;26:35–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E., Sinnett-Smith J., Van Lint J., Valverde A. M. Protein kinase D (PKD): a novel target for diacylglycerol and phorbol esters. Mutat Res. 1995 Dec;333(1-2):153–160. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(95)00141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selbie L. A., Schmitz-Peiffer C., Sheng Y., Biden T. J. Molecular cloning and characterization of PKC iota, an atypical isoform of protein kinase C derived from insulin-secreting cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 15;268(32):24296–24302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Shimanuki M., Yanagida M. Two novel protein kinase C-related genes of fission yeast are essential for cell viability and implicated in cell shape control. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05848.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toker A., Meyer M., Reddy K. K., Falck J. R., Aneja R., Aneja S., Parra A., Burns D. J., Ballas L. M., Cantley L. C. Activation of protein kinase C family members by the novel polyphosphoinositides PtdIns-3,4-P2 and PtdIns-3,4,5-P3. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32358–32367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toullec D., Pianetti P., Coste H., Bellevergue P., Grand-Perret T., Ajakane M., Baudet V., Boissin P., Boursier E., Loriolle F. The bisindolylmaleimide GF 109203X is a potent and selective inhibitor of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 25;266(24):15771–15781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valverde A. M., Sinnett-Smith J., Van Lint J., Rozengurt E. Molecular cloning and characterization of protein kinase D: a target for diacylglycerol and phorbol esters with a distinctive catalytic domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 30;91(18):8572–8576. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.18.8572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Lint J. V., Sinnett-Smith J., Rozengurt E. Expression and characterization of PKD, a phorbol ester and diacylglycerol-stimulated serine protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 20;270(3):1455–1461. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.3.1455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Cooper J. A. Rho family members: activators of MAP kinase cascades. Cell. 1995 Aug 25;82(4):527–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways D. K., Cook P. P., Webster C., Parker P. J. Effect of phorbol esters on protein kinase C-zeta. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4799–4805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein I. B. The origins of human cancer: molecular mechanisms of carcinogenesis and their implications for cancer prevention and treatment--twenty-seventh G.H.A. Clowes memorial award lecture. Cancer Res. 1988 Aug 1;48(15):4135–4143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeo E. J., Exton J. H. Stimulation of phospholipase D by epidermal growth factor requires protein kinase C activation in Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 24;270(8):3980–3988. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.8.3980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachary I., Sinnett-Smith J., Rozengurt E. Bombesin, vasopressin, and endothelin stimulation of tyrosine phosphorylation in Swiss 3T3 cells. Identification of a novel tyrosine kinase as a major substrate. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19031–19034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G., Kazanietz M. G., Blumberg P. M., Hurley J. H. Crystal structure of the cys2 activator-binding domain of protein kinase C delta in complex with phorbol ester. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]