Abstract
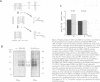
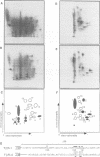
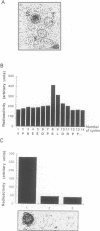
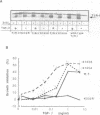
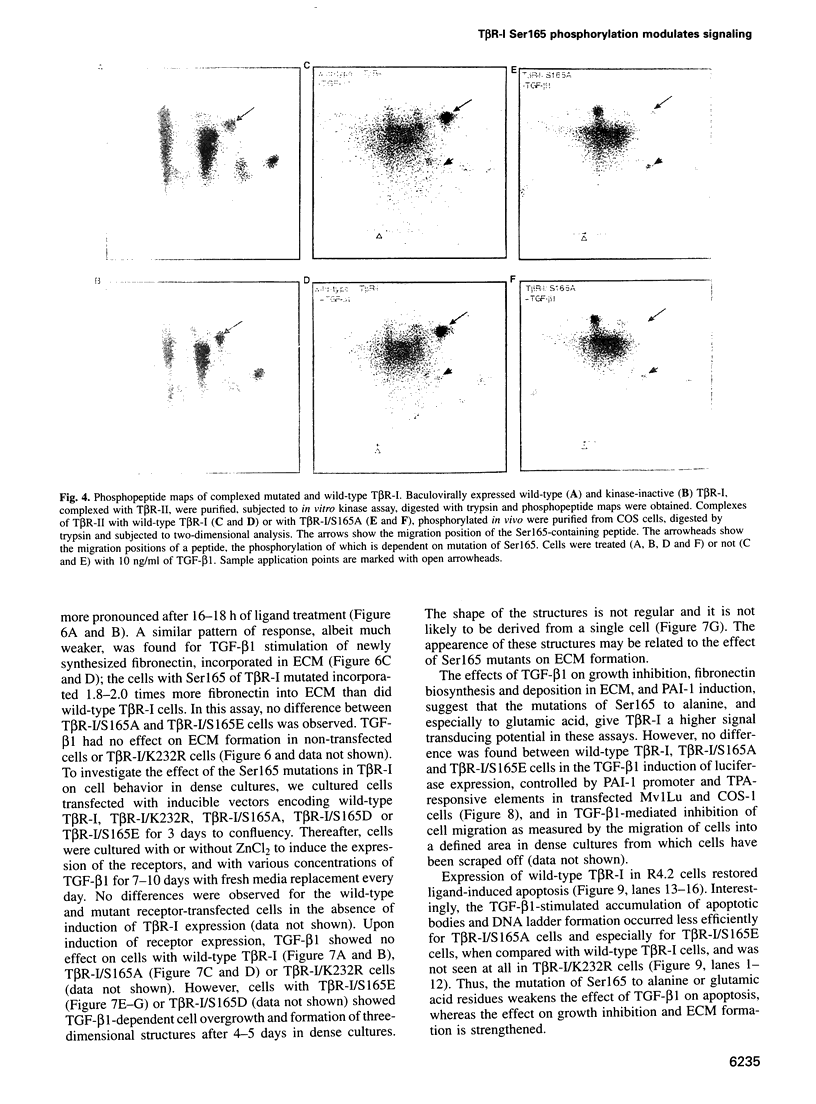
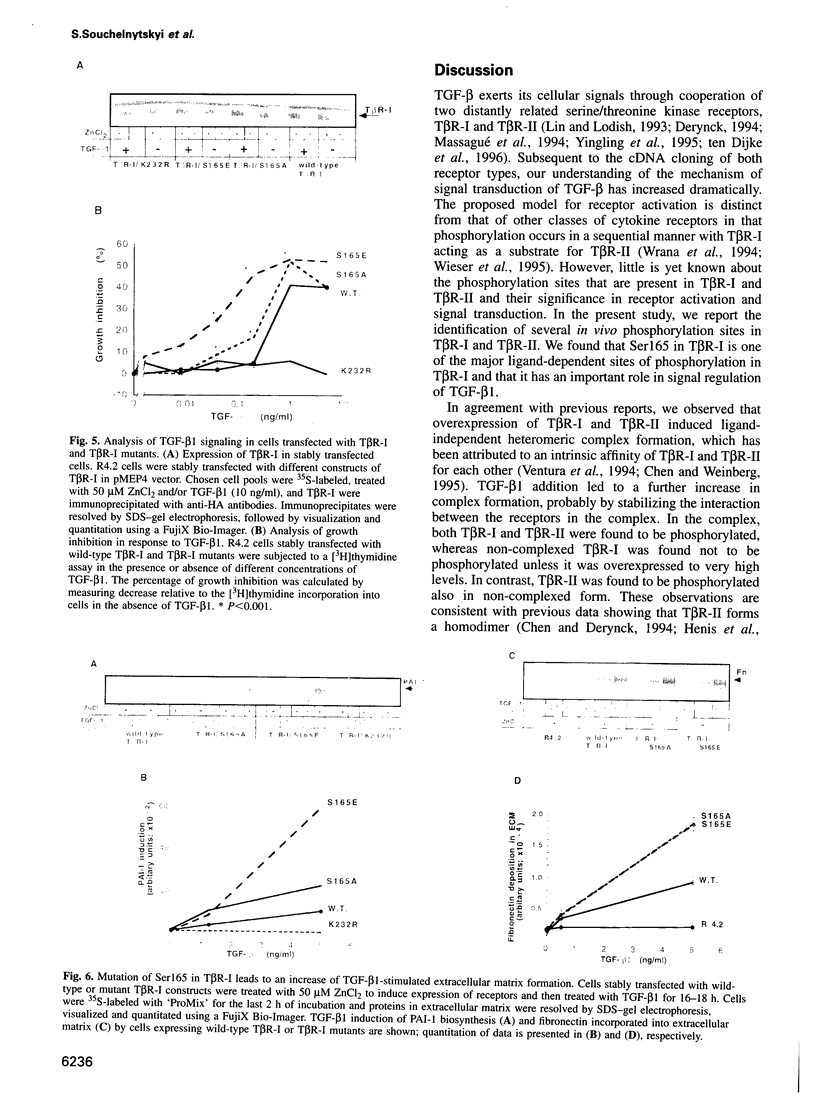
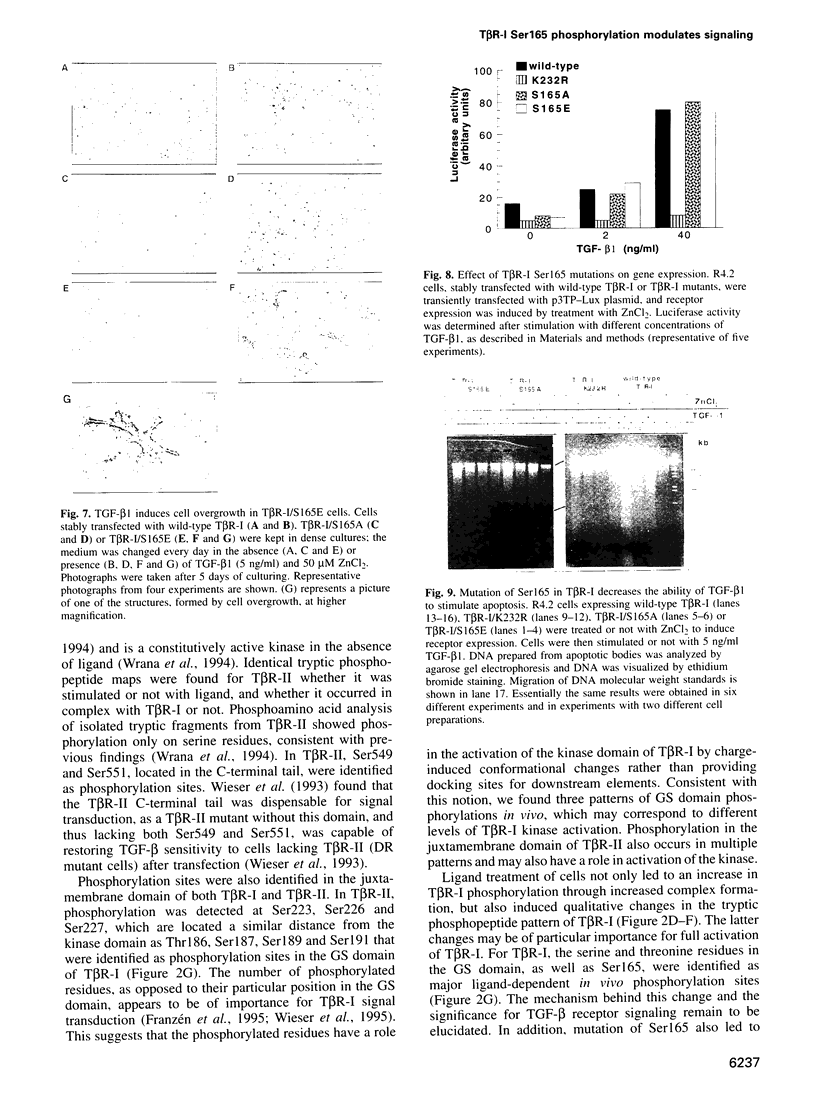
Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signals via an oligomeric complex of two serine/threonine kinase receptors denoted TGF-beta type I receptor (TbetaR-I) and type II receptor (TbetaR-II). We investigated the in vivo phosphorylation sites in TbetaR-I and TbetaR-II after complex formation. Phosphorylation of TbetaR-II was observed at residues in the C-terminus (Ser549 and Ser551) and at residues in the juxtamembrane domain (Ser223, Ser226 and Ser227). TGF-beta1 induced in vivo phosphorylation of serine and threonine residues in the juxtamembrane domain of TbetaR-I in a region rich in glycine, serine and threonine residues (GS domain; Thr185, Thr186, Ser187, Ser189 and Ser191), and more N-terminal of this region (Ser165). Phosphorylation in the GS domain has been shown previously to be involved in activation of the TbetaR-I kinase. We show here that phosphorylation of TbetaR-I at Ser165 is involved in modulation of TGF-beta1 signaling. Mutations of Ser165 in TbetaR-I led to an increase in TGF-beta1-mediated growth inhibition and extracellular matrix formation, but, in contrast, to decreased TGF-beta1-induced apoptosis. A transcriptional activation signal was not affected. Mutations of Ser165 changed the phosphorylation pattern of TbetaR-I. These observations suggest that TGF-beta receptor signaling specificity is modulated by phosphorylation of Ser165 of TbetaR-I.
Full text
PDF
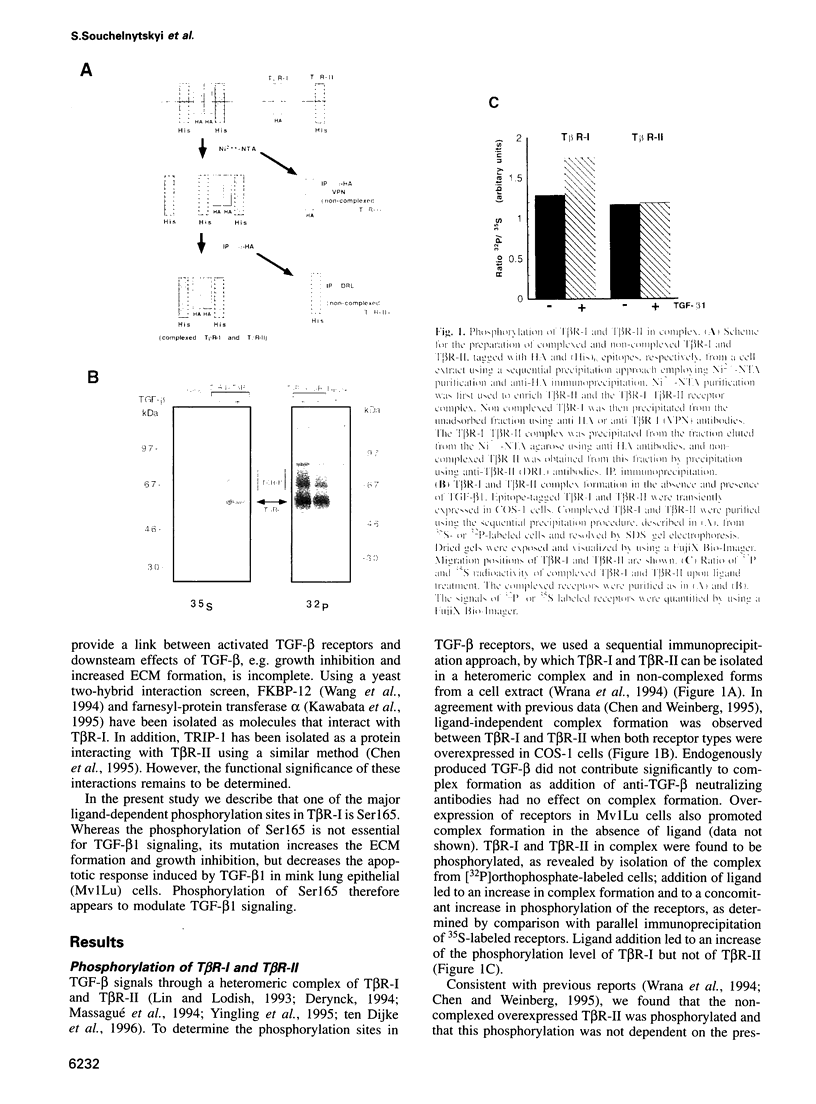

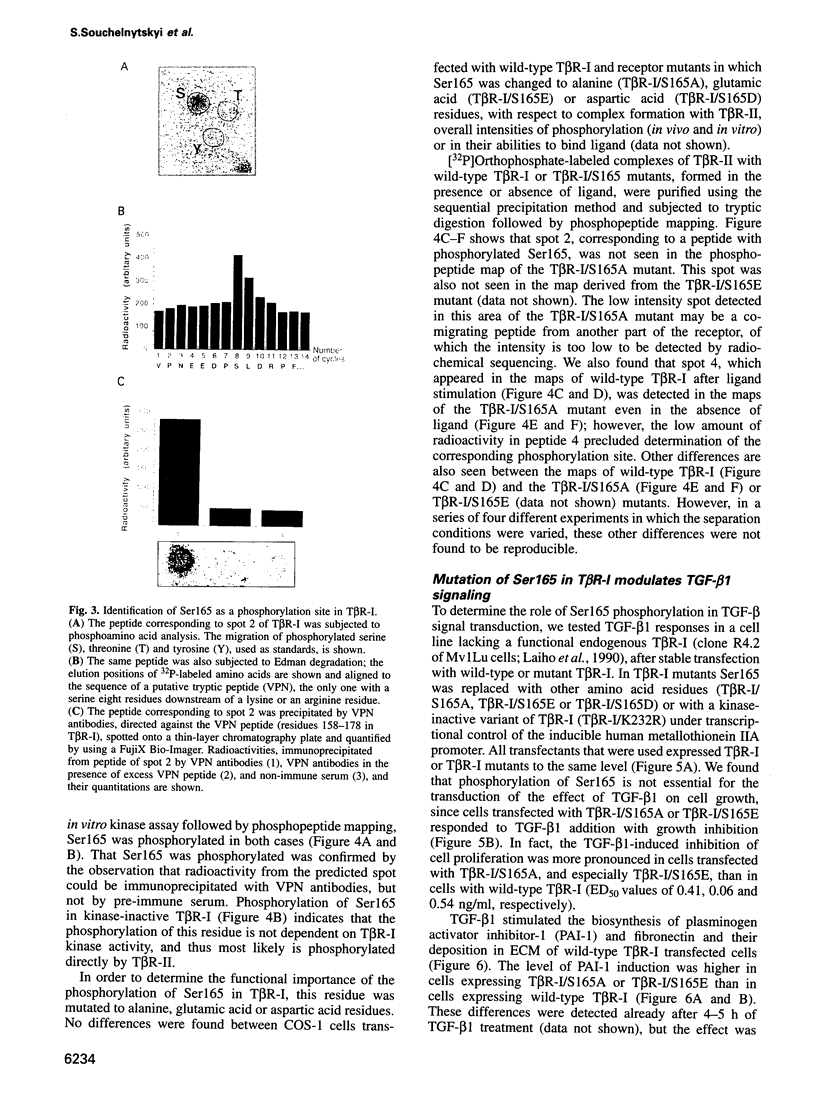



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassing C. H., Yingling J. M., Howe D. J., Wang T., He W. W., Gustafson M. L., Shah P., Donahoe P. K., Wang X. F. A transforming growth factor beta type I receptor that signals to activate gene expression. Science. 1994 Jan 7;263(5143):87–89. doi: 10.1126/science.8272871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., van der Geer P., Hunter T. Phosphopeptide mapping and phosphoamino acid analysis by two-dimensional separation on thin-layer cellulose plates. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:110–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01013-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen F., Weinberg R. A. Biochemical evidence for the autophosphorylation and transphosphorylation of transforming growth factor beta receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1565–1569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Derynck R. Homomeric interactions between type II transforming growth factor-beta receptors. J Biol Chem. 1994 Sep 9;269(36):22868–22874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen R. H., Miettinen P. J., Maruoka E. M., Choy L., Derynck R. A WD-domain protein that is associated with and phosphorylated by the type II TGF-beta receptor. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):548–552. doi: 10.1038/377548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cárcamo J., Zentella A., Massagué J. Disruption of transforming growth factor beta signaling by a mutation that prevents transphosphorylation within the receptor complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;15(3):1573–1581. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.3.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derynck R. TGF-beta-receptor-mediated signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Dec;19(12):548–553. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90059-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén P., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. The GS domain of the transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor is important in signal transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Feb 15;207(2):682–689. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzén P., ten Dijke P., Ichijo H., Yamashita H., Schulz P., Heldin C. H., Miyazono K. Cloning of a TGF beta type I receptor that forms a heteromeric complex with the TGF beta type II receptor. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):681–692. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90489-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henis Y. I., Moustakas A., Lin H. Y., Lodish H. F. The types II and III transforming growth factor-beta receptors form homo-oligomers. J Cell Biol. 1994 Jul;126(1):139–154. doi: 10.1083/jcb.126.1.139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata M., Imamura T., Miyazono K., Engel M. E., Moses H. L. Interaction of the transforming growth factor-beta type I receptor with farnesyl-protein transferase-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 15;270(50):29628–29631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.50.29628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Rönnstrand L., Heino J., Decaprio J. A., Ludlow J. W., Livingston D. M., Massagué J. Control of junB and extracellular matrix protein expression by transforming growth factor-beta 1 is independent of simian virus 40 T antigen-sensitive growth-sensitive growth-inhibitory events. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):972–978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laiho M., Weis M. B., Massagué J. Concomitant loss of transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta receptor types I and II in TGF-beta-resistant cell mutants implicates both receptor types in signal transduction. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18518–18524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Lodish H. F. Receptors for the TGF-beta superfamily: multiple polypeptides and serine/threonine kinases. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Jan;3(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. Y., Wang X. F., Ng-Eaton E., Weinberg R. A., Lodish H. F. Expression cloning of the TGF-beta type II receptor, a functional transmembrane serine/threonine kinase. Cell. 1992 Feb 21;68(4):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Attisano L., Wrana J. L. The TGF-beta family and its composite receptors. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 May;4(5):172–178. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Boyd F. T., Andres J. L. TGF-beta receptors and TGF-beta binding proteoglycans: recent progress in identifying their functional properties. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;593:59–72. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb16100.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses H. L., Yang E. Y., Pietenpol J. A. TGF-beta stimulation and inhibition of cell proliferation: new mechanistic insights. Cell. 1990 Oct 19;63(2):245–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90155-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts A. B., Anzano M. A., Lamb L. C., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B. New class of transforming growth factors potentiated by epidermal growth factor: isolation from non-neoplastic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5339–5343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh M., Nishitoh H., Amagasa T., Miyazono K., Takagi M., Ichijo H. Identification of important regions in the cytoplasmic juxtamembrane domain of type I receptor that separate signaling pathways of transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 2;271(5):2769–2775. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.5.2769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventura F., Doody J., Liu F., Wrana J. L., Massagué J. Reconstitution and transphosphorylation of TGF-beta receptor complexes. EMBO J. 1994 Dec 1;13(23):5581–5589. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06895.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T., Donahoe P. K., Zervos A. S. Specific interaction of type I receptors of the TGF-beta family with the immunophilin FKBP-12. Science. 1994 Jul 29;265(5172):674–676. doi: 10.1126/science.7518616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis-Garcia F., Massagué J. Complementation between kinase-defective and activation-defective TGF-beta receptors reveals a novel form of receptor cooperativity essential for signaling. EMBO J. 1996 Jan 15;15(2):276–289. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieser R., Attisano L., Wrana J. L., Massagué J. Signaling activity of transforming growth factor beta type II receptors lacking specific domains in the cytoplasmic region. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;13(12):7239–7247. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.12.7239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieser R., Wrana J. L., Massagué J. GS domain mutations that constitutively activate T beta R-I, the downstream signaling component in the TGF-beta receptor complex. EMBO J. 1995 May 15;14(10):2199–2208. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrana J. L., Attisano L., Cárcamo J., Zentella A., Doody J., Laiho M., Wang X. F., Massagué J. TGF beta signals through a heteromeric protein kinase receptor complex. Cell. 1992 Dec 11;71(6):1003–1014. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90395-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrana J. L., Attisano L., Wieser R., Ventura F., Massagué J. Mechanism of activation of the TGF-beta receptor. Nature. 1994 Aug 4;370(6488):341–347. doi: 10.1038/370341a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., Ichijo H., Grimsby S., Morén A., ten Dijke P., Miyazono K. Endoglin forms a heteromeric complex with the signaling receptors for transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1995–2001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita H., ten Dijke P., Franzén P., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Formation of hetero-oligomeric complexes of type I and type II receptors for transforming growth factor-beta. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):20172–20178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yingling J. M., Wang X. F., Bassing C. H. Signaling by the transforming growth factor-beta receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Dec 18;1242(2):115–136. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(95)00007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ten Dijke P., Miyazono K., Heldin C. H. Signaling via hetero-oligomeric complexes of type I and type II serine/threonine kinase receptors. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1996 Apr;8(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(96)80058-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]