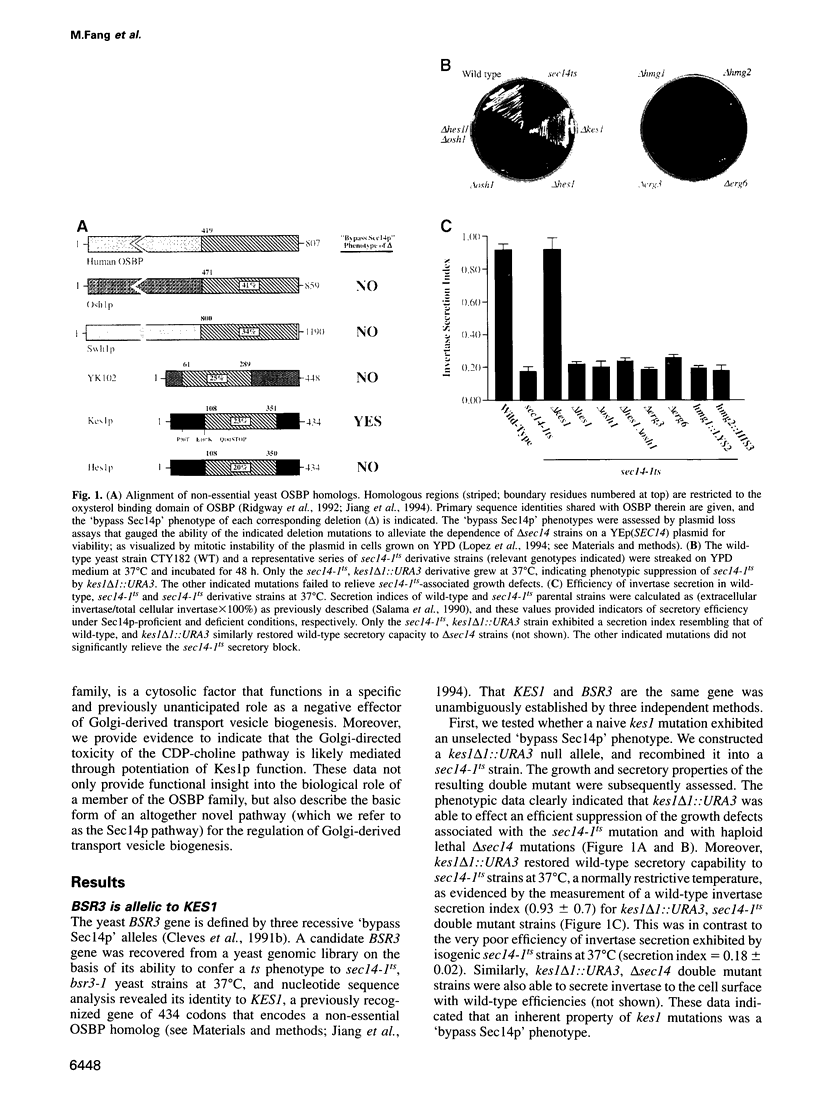
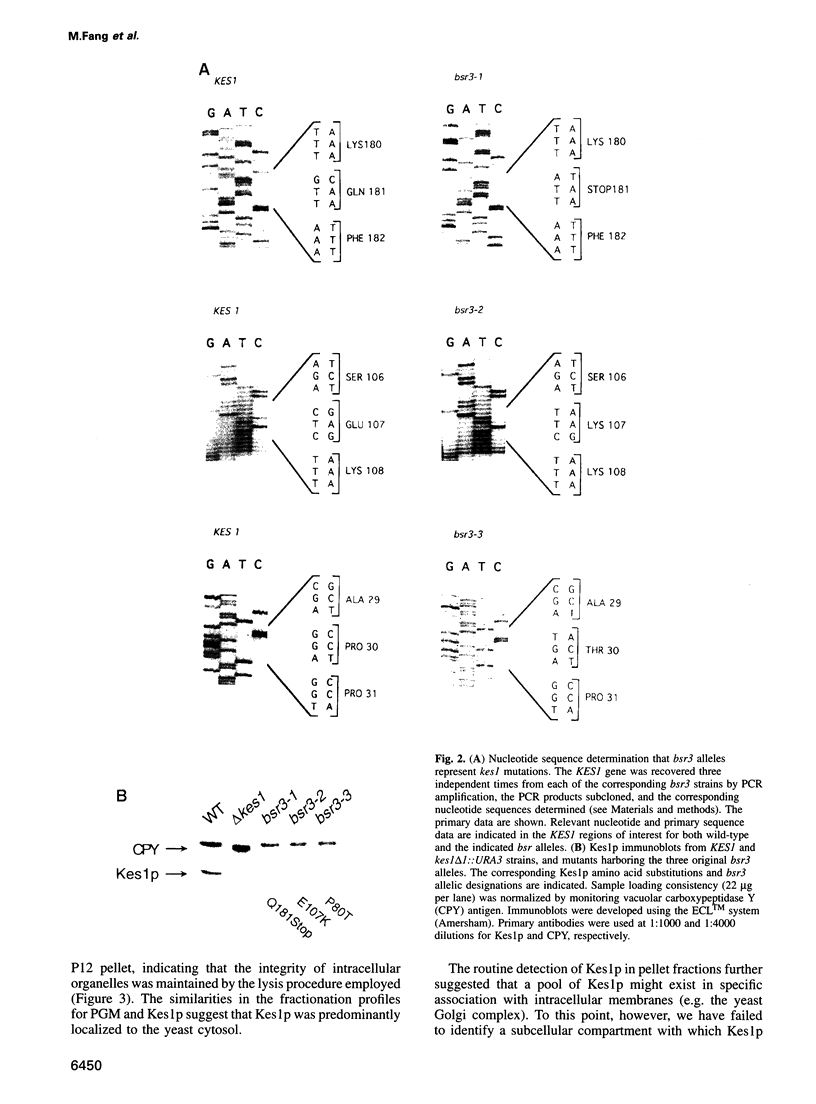
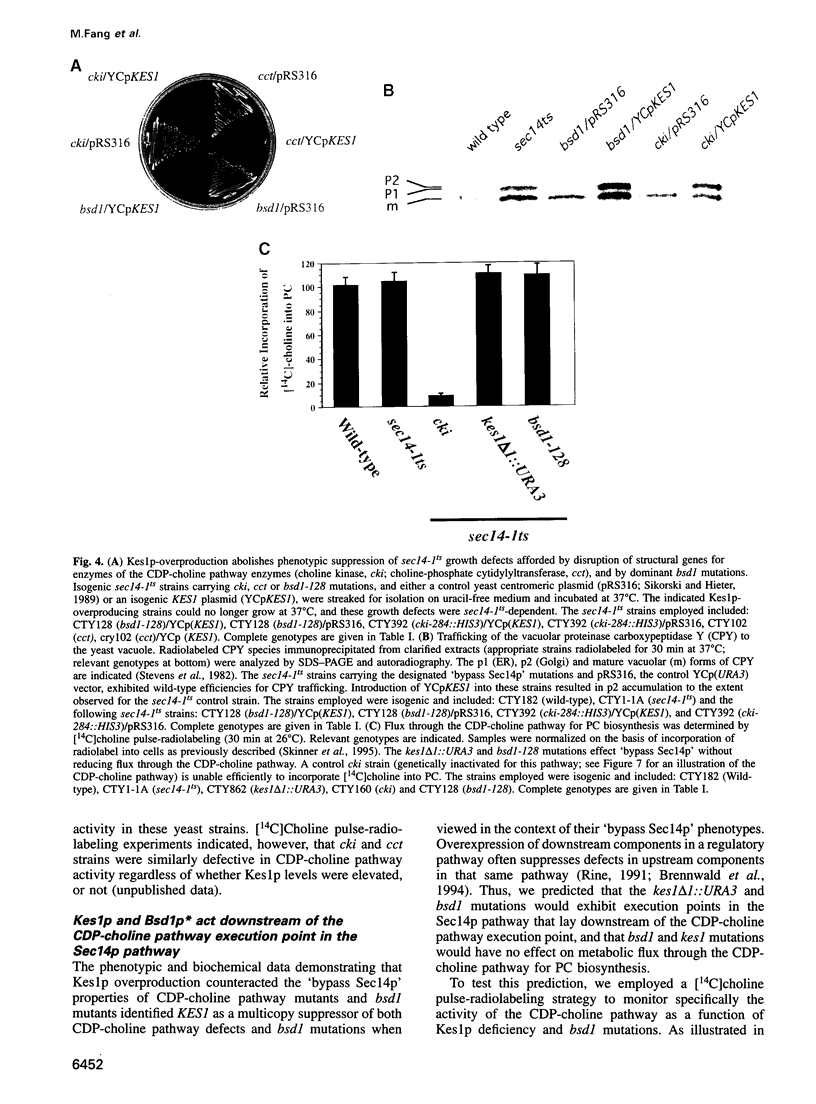
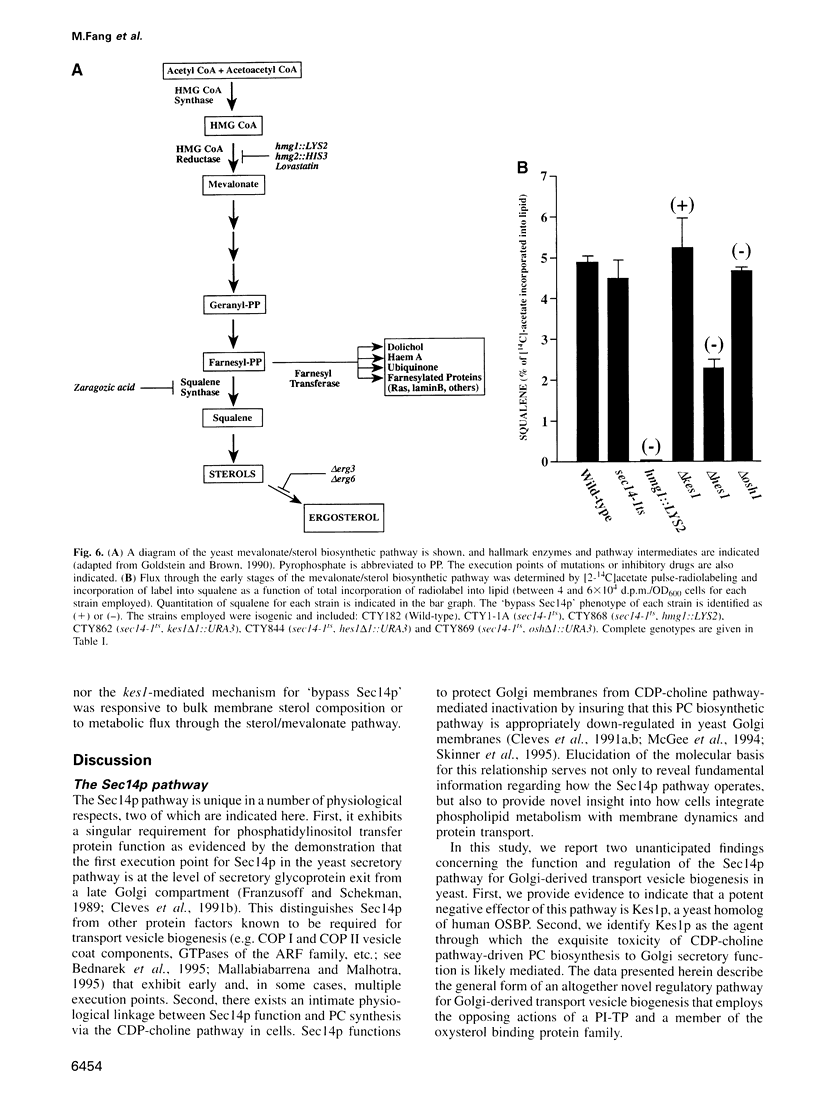
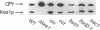Abstract
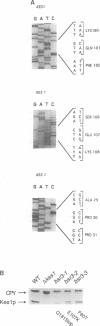
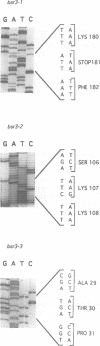
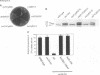
The yeast phosphatidylinositol transfer protein (Sec14p) is required for biogenesis of Golgi-derived transport vesicles and cell viability, and this essential Sec14p requirement is abrogated by inactivation of the CDP-choline pathway for phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. These findings indicate that Sec14p functions to alleviate a CDP-choline pathway-mediated toxicity to yeast Golgi secretory function. We now report that this toxicity is manifested through the action of yeast Kes1p, a polypeptide that shares homology with the ligand-binding domain of human oxysterol binding protein (OSBP). Identification of Kes1p as a negative effector for Golgi function provides the first direct insight into the biological role of any member of the OSBP family, and describes a novel pathway for the regulation of Golgi-derived transport vesicle biogenesis.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberts A. W., Chen J., Kuron G., Hunt V., Huff J., Hoffman C., Rothrock J., Lopez M., Joshua H., Harris E. Mevinolin: a highly potent competitive inhibitor of hydroxymethylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and a cholesterol-lowering agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3957–3961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Aitken J. R., Cleves A. E., Dowhan W. An essential role for a phospholipid transfer protein in yeast Golgi function. Nature. 1990 Oct 11;347(6293):561–562. doi: 10.1038/347561a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Johnson L. M., Emr S. D. Isolation of yeast mutants defective in protein targeting to the vacuole. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9075–9079. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Malehorn D. E., Emr S. D., Greene R. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae SEC14 gene encodes a cytosolic factor that is required for transport of secretory proteins from the yeast Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1271–1281. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basson M. E., Thorsness M., Rine J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains two functional genes encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5563–5567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarek S. Y., Ravazzola M., Hosobuchi M., Amherdt M., Perrelet A., Schekman R., Orci L. COPI- and COPII-coated vesicles bud directly from the endoplasmic reticulum in yeast. Cell. 1995 Dec 29;83(7):1183–1196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90144-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergstrom J. D., Kurtz M. M., Rew D. J., Amend A. M., Karkas J. D., Bostedor R. G., Bansal V. S., Dufresne C., VanMiddlesworth F. L., Hensens O. D. Zaragozic acids: a family of fungal metabolites that are picomolar competitive inhibitors of squalene synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 1;90(1):80–84. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.1.80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser R., Müller H., Govindan B., Novick P. Sec8p and Sec15p are components of a plasma membrane-associated 19.5S particle that may function downstream of Sec4p to control exocytosis. J Cell Biol. 1992 Sep;118(5):1041–1056. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.5.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennwald P., Kearns B., Champion K., Keränen S., Bankaitis V., Novick P. Sec9 is a SNAP-25-like component of a yeast SNARE complex that may be the effector of Sec4 function in exocytosis. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):245–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttke T. M., Pyle A. L. Effects of unsaturated fatty acid deprivation on neutral lipid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Nov;152(2):747–756. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.2.747-756.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleves A. E., McGee T. P., Whitters E. A., Champion K. M., Aitken J. R., Dowhan W., Goebl M., Bankaitis V. A. Mutations in the CDP-choline pathway for phospholipid biosynthesis bypass the requirement for an essential phospholipid transfer protein. Cell. 1991 Feb 22;64(4):789–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90508-v. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleves A. E., Novick P. J., Bankaitis V. A. Mutations in the SAC1 gene suppress defects in yeast Golgi and yeast actin function. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2939–2950. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleves A., McGee T., Bankaitis V. Phospholipid transfer proteins: a biological debut. Trends Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;1(1):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(91)90067-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson P. A., Van der Westhuyzen D. R., Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Purification of oxysterol binding protein from hamster liver cytosol. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):9046–9052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzusoff A., Schekman R. Functional compartments of the yeast Golgi apparatus are defined by the sec7 mutation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2695–2702. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber R. F., Copple D. M., Kennedy B. K., Vidal M., Bard M. The yeast gene ERG6 is required for normal membrane function but is not essential for biosynthesis of the cell-cycle-sparking sterol. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3447–3456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein J. L., Brown M. S. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):425–430. doi: 10.1038/343425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Fisette P. L., Jenkins G. H., Fukami K., Takenawa T., Anderson R. A., Martin T. F. ATP-dependent inositide phosphorylation required for Ca(2+)-activated secretion. Nature. 1995 Mar 9;374(6518):173–177. doi: 10.1038/374173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J. C., Martin T. F. Phosphatidylinositol transfer protein required for ATP-dependent priming of Ca(2+)-activated secretion. Nature. 1993 Dec 9;366(6455):572–575. doi: 10.1038/366572a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horazdovsky B. F., Emr S. D. The VPS16 gene product associates with a sedimentable protein complex and is essential for vacuolar protein sorting in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 5;268(7):4953–4962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang B., Brown J. L., Sheraton J., Fortin N., Bussey H. A new family of yeast genes implicated in ergosterol synthesis is related to the human oxysterol binding protein. Yeast. 1994 Mar;10(3):341–353. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kagiwada S., Kearns B. G., McGee T. P., Fang M., Hosaka K., Bankaitis V. A. The yeast BSD2-1 mutation influences both the requirement for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein function and derepression of phospholipid biosynthetic gene expression in yeast. Genetics. 1996 Jun;143(2):685–697. doi: 10.1093/genetics/143.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez M. C., Nicaud J. M., Skinner H. B., Vergnolle C., Kader J. C., Bankaitis V. A., Gaillardin C. A phosphatidylinositol/phosphatidylcholine transfer protein is required for differentiation of the dimorphic yeast Yarrowia lipolytica from the yeast to the mycelial form. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(1):113–127. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mallabiabarrena A., Malhotra V. Vesicle biogenesis: the coat connection. Cell. 1995 Dec 1;83(5):667–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90177-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGee T. P., Skinner H. B., Whitters E. A., Henry S. A., Bankaitis V. A. A phosphatidylinositol transfer protein controls the phosphatidylcholine content of yeast Golgi membranes. J Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;124(3):273–287. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.3.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Szczesna-Skorupa E., Kemper B. Single-stranded DNA 'blue' T7 promoter plasmids: a versatile tandem promoter system for cloning and protein engineering. Protein Eng. 1986 Oct-Nov;1(1):67–74. doi: 10.1093/protein/1.1.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi M., Jan de Vries K., Frank R., Snoek G., Bankaitis V., Wirtz K., Huttner W. B. A role for phosphatidylinositol transfer protein in secretory vesicle formation. Nature. 1995 Oct 12;377(6549):544–547. doi: 10.1038/377544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway N. D., Dawson P. A., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Translocation of oxysterol binding protein to Golgi apparatus triggered by ligand binding. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jan;116(2):307–319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.2.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway N. D., Lagace T. A. Brefeldin A renders Chinese hamster ovary cells insensitive to transcriptional suppression by 25-hydroxycholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 7;270(14):8023–8031. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.14.8023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rine J. Gene overexpression in studies of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:239–251. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Novick P., Thomas J. H., Botstein D., Fink G. R. A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene. 1987;60(2-3):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90232-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. H., Stevens T. H. Protein sorting in yeast: mutants defective in vacuole biogenesis mislocalize vacuolar proteins into the late secretory pathway. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):1041–1051. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90819-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salama S. R., Cleves A. E., Malehorn D. E., Whitters E. A., Bankaitis V. A. Cloning and characterization of Kluyveromyces lactis SEC14, a gene whose product stimulates Golgi secretory function in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4510–4521. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4510-4521.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner H. B., Alb J. G., Jr, Whitters E. A., Helmkamp G. M., Jr, Bankaitis V. A. Phospholipid transfer activity is relevant to but not sufficient for the essential function of the yeast SEC14 gene product. EMBO J. 1993 Dec;12(12):4775–4784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06166.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner H. B., McGee T. P., McMaster C. R., Fry M. R., Bell R. M., Bankaitis V. A. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae phosphatidylinositol-transfer protein effects a ligand-dependent inhibition of choline-phosphate cytidylyltransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jan 3;92(1):112–116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.1.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. J., Parks L. W. The ERG3 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for the utilization of respiratory substrates and in heme-deficient cells. Yeast. 1993 Nov;9(11):1177–1187. doi: 10.1002/yea.320091104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T., Esmon B., Schekman R. Early stages in the yeast secretory pathway are required for transport of carboxypeptidase Y to the vacuole. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitters E. A., Cleves A. E., McGee T. P., Skinner H. B., Bankaitis V. A. SAC1p is an integral membrane protein that influences the cellular requirement for phospholipid transfer protein function and inositol in yeast. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;122(1):79–94. doi: 10.1083/jcb.122.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz K. W. Phospholipid transfer proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:73–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]