Abstract
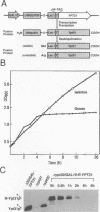
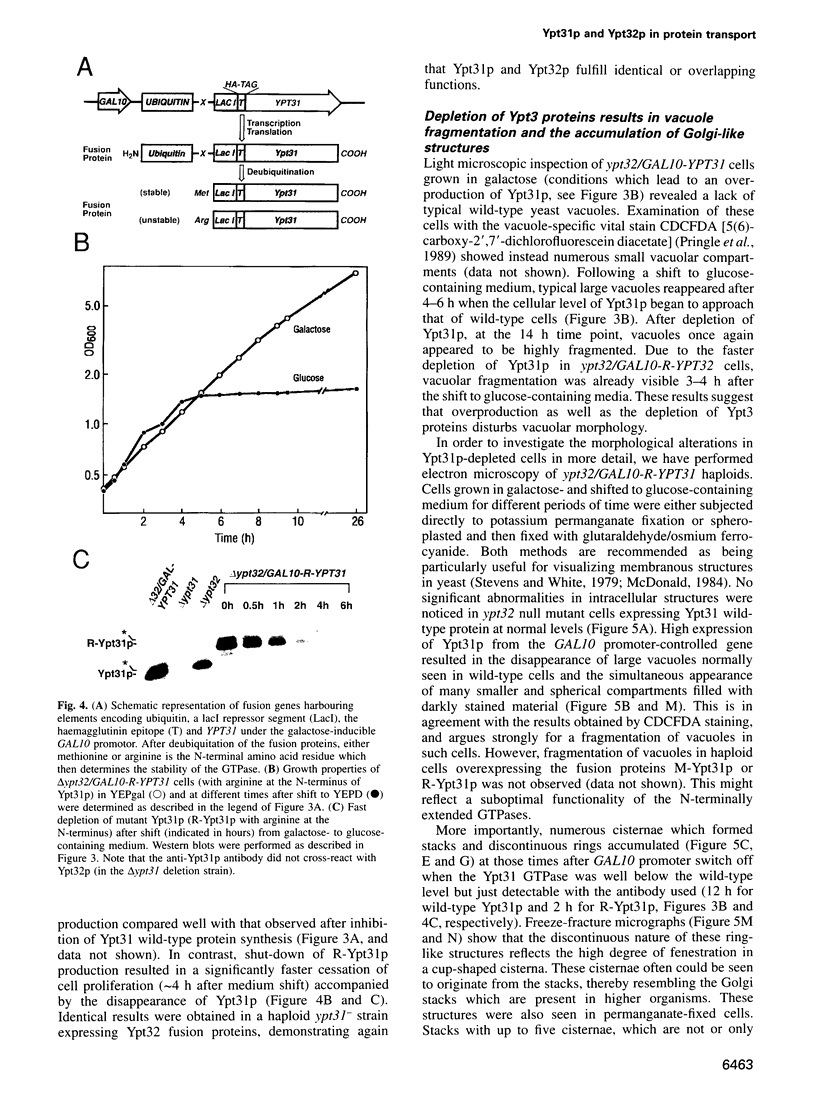
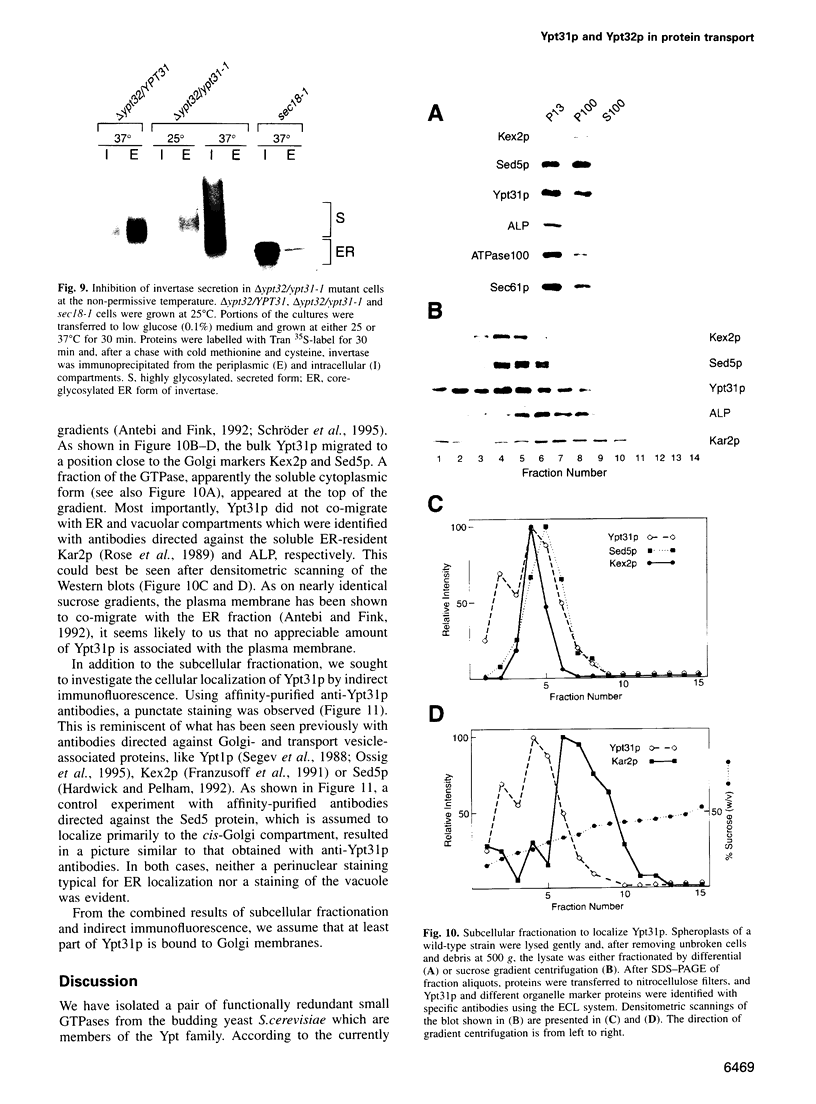
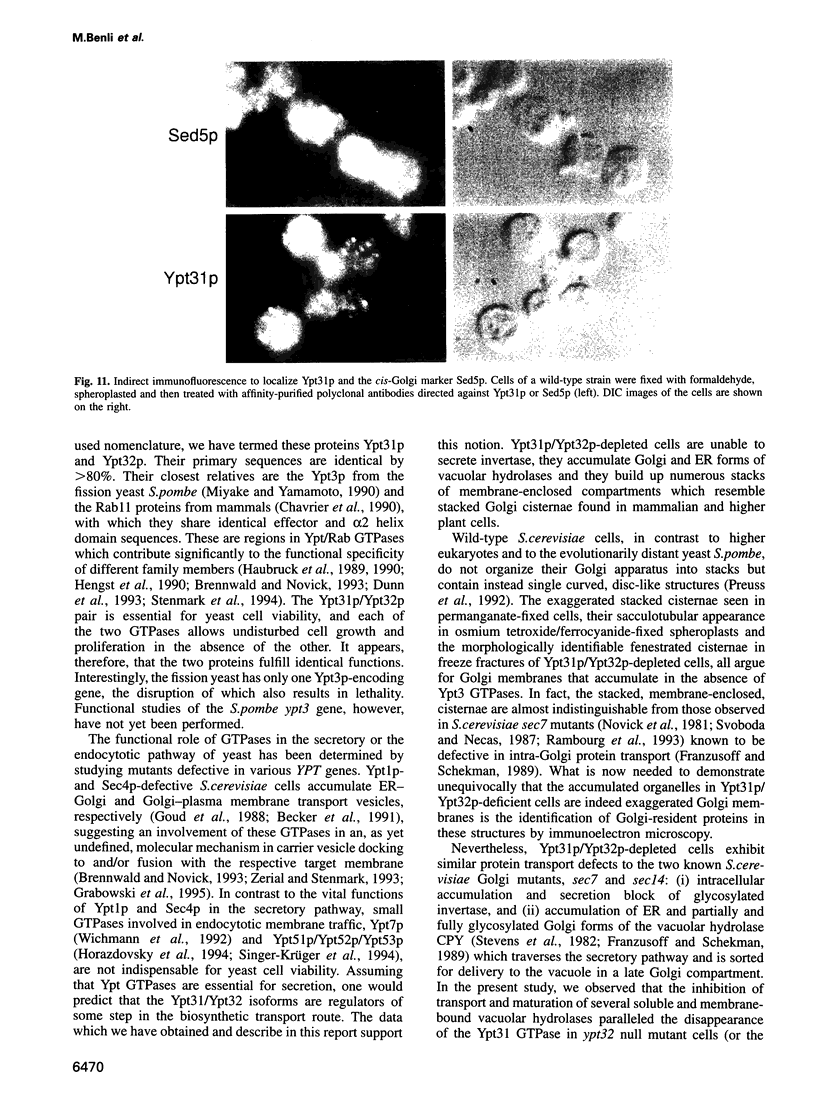
In eukaryotic cells, monomeric GTPases of the Ypt/Rab family function as regulators at defined steps of vesicular transport in exo- and endocytosis. Here we report on the isolation and characterization of two genes (YPT31 and YPT32) of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae which encode members of the Ypt family exhibiting >80% sequence identity. Whereas the disruption of one of the two genes was phenotypically neutral, the disruption of both YPT31 and YPT32 led to lethality. Depletion of wild-type Ypt31p or of a short-lived ubiquitin-Ypt31p in a ypt32 null background led to a massive accumulation of Golgi-like membranes, an inhibition of invertase secretion and defects in vacuolar protein maturation. Similar alterations were observed in a conditional-lethal ypt31-1 mutant at 30 min after shift to the non-permissive temperature. According to subcellular fractionation, a significant part of Ypt31p appeared to be located in Golgi-enriched membrane fractions. In accordance with this, indirect immunofluorescence using affinity-purified anti-Ypt31p antibodies gave a punctate staining similar to that observed with Golgi-located proteins. From the phenotypic alterations observed in ypt31 and ypt32 mutants, it seems likely that the two GTPases are involved in intra-Golgi transport or in the formation of transport vesicles at the most distal Golgi compartment.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aalto M. K., Ronne H., Keränen S. Yeast syntaxins Sso1p and Sso2p belong to a family of related membrane proteins that function in vesicular transport. EMBO J. 1993 Nov;12(11):4095–4104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06093.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antebi A., Fink G. R. The yeast Ca(2+)-ATPase homologue, PMR1, is required for normal Golgi function and localizes in a novel Golgi-like distribution. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jun;3(6):633–654. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.6.633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacon R. A., Salminen A., Ruohola H., Novick P., Ferro-Novick S. The GTP-binding protein Ypt1 is required for transport in vitro: the Golgi apparatus is defective in ypt1 mutants. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1015–1022. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker D., Hicke L., Rexach M., Schleyer M., Schekman R. Reconstitution of SEC gene product-dependent intercompartmental protein transport. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banfield D. K., Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. A SNARE-like protein required for traffic through the Golgi complex. Nature. 1995 Jun 29;375(6534):806–809. doi: 10.1038/375806a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker J., Tan T. J., Trepte H. H., Gallwitz D. Mutational analysis of the putative effector domain of the GTP-binding Ypt1 protein in yeast suggests specific regulation by a novel GAP activity. EMBO J. 1991 Apr;10(4):785–792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08010.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. K., Scheller R. H. A molecular description of synaptic vesicle membrane trafficking. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:63–100. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.000431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennwald P., Novick P. Interactions of three domains distinguishing the Ras-related GTP-binding proteins Ypt1 and Sec4. Nature. 1993 Apr 8;362(6420):560–563. doi: 10.1038/362560a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavrier P., Parton R. G., Hauri H. P., Simons K., Zerial M. Localization of low molecular weight GTP binding proteins to exocytic and endocytic compartments. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):317–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90369-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascher C., Ossig R., Gallwitz D., Schmitt H. D. Identification and structure of four yeast genes (SLY) that are able to suppress the functional loss of YPT1, a member of the RAS superfamily. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):872–885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn B., Stearns T., Botstein D. Specificity domains distinguish the Ras-related GTPases Ypt1 and Sec4. Nature. 1993 Apr 8;362(6420):563–565. doi: 10.1038/362563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon B., Novick P., Schekman R. Compartmentalized assembly of oligosaccharides on exported glycoproteins in yeast. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90063-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzusoff A., Redding K., Crosby J., Fuller R. S., Schekman R. Localization of components involved in protein transport and processing through the yeast Golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;112(1):27–37. doi: 10.1083/jcb.112.1.27. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzusoff A., Schekman R. Functional compartments of the yeast Golgi apparatus are defined by the sec7 mutation. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2695–2702. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08410.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Donath C., Sander C. A yeast gene encoding a protein homologous to the human c-has/bas proto-oncogene product. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):704–707. doi: 10.1038/306704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein A., Lampen J. O. Beta-D-fructofuranoside fructohydrolase from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1975;42:504–511. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(75)42159-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goud B., Salminen A., Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. A GTP-binding protein required for secretion rapidly associates with secretory vesicles and the plasma membrane in yeast. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):753–768. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90093-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham T. R., Seeger M., Payne G. S., MacKay V. L., Emr S. D. Clathrin-dependent localization of alpha 1,3 mannosyltransferase to the Golgi complex of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1994 Nov;127(3):667–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.127.3.667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossmann M. K., Zimmermann F. K. The structural genes of internal invertases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Sep;175(2):223–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00425540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A., Scheglmann D., Lazar T., Gallwitz D., Wickner W. The GTPase Ypt7p of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required on both partner vacuoles for the homotypic fusion step of vacuole inheritance. EMBO J. 1995 Nov 1;14(21):5258–5270. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00210.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardwick K. G., Pelham H. R. SED5 encodes a 39-kD integral membrane protein required for vesicular transport between the ER and the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;119(3):513–521. doi: 10.1083/jcb.119.3.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubruck H., Engelke U., Mertins P., Gallwitz D. Structural and functional analysis of ypt2, an essential ras-related gene in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe encoding a Sec4 protein homologue. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1957–1962. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08323.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haubruck H., Prange R., Vorgias C., Gallwitz D. The ras-related mouse ypt1 protein can functionally replace the YPT1 gene product in yeast. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1427–1432. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengst L., Lehmeier T., Gallwitz D. The ryh1 gene in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe encoding a GTP-binding protein related to ras, rho and ypt: structure, expression and identification of its human homologue. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1949–1955. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08322.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horazdovsky B. F., Busch G. R., Emr S. D. VPS21 encodes a rab5-like GTP binding protein that is required for the sorting of yeast vacuolar proteins. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1297–1309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jedd G., Richardson C., Litt R., Segev N. The Ypt1 GTPase is essential for the first two steps of the yeast secretory pathway. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(3):583–590. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.3.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. M., Bankaitis V. A., Emr S. D. Distinct sequence determinants direct intracellular sorting and modification of a yeast vacuolar protease. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):875–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser C. A., Schekman R. Distinct sets of SEC genes govern transport vesicle formation and fusion early in the secretory pathway. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):723–733. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90483-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyono K., Miura K., Kushima Y., Hikiji T., Fukushima M., Shibuya I., Ohta A. Primary structure and product characterization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CHO1 gene that encodes phosphatidylserine synthase. J Biochem. 1987 Nov;102(5):1089–1100. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerner T. J., Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A. High-expression vectors with multiple cloning sites for construction of trpE fusion genes: pATH vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:477–490. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94036-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krawetz S. A., Pon R. T., Dixon G. H. Increased efficiency of the Taq polymerase catalyzed polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):819–819. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. H., Bard M., Kirsch D. R. Identification of a gene encoding a new Ypt/Rab-like monomeric G-protein in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast. 1994 Mar;10(3):399–402. doi: 10.1002/yea.320100313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis M. J., Pelham H. R. SNARE-mediated retrograde traffic from the Golgi complex to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1996 Apr 19;85(2):205–215. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald K. Osmium ferricyanide fixation improves microfilament preservation and membrane visualization in a variety of animal cell types. J Ultrastruct Res. 1984 Feb;86(2):107–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(84)80051-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyake S., Yamamoto M. Identification of ras-related, YPT family genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1417–1422. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08257.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Brennwald P. Friends and family: the role of the Rab GTPases in vesicular traffic. Cell. 1993 Nov 19;75(4):597–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90478-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Ferro S., Schekman R. Order of events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90064-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Field C., Schekman R. Identification of 23 complementation groups required for post-translational events in the yeast secretory pathway. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):205–215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90128-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuoffer C., Balch W. E. GTPases: multifunctional molecular switches regulating vesicular traffic. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:949–990. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuoffer C., Davidson H. W., Matteson J., Meinkoth J., Balch W. E. A GDP-bound of rab1 inhibits protein export from the endoplasmic reticulum and transport between Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):225–237. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossig R., Dascher C., Trepte H. H., Schmitt H. D., Gallwitz D. The yeast SLY gene products, suppressors of defects in the essential GTP-binding Ypt1 protein, may act in endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi transport. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):2980–2993. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossig R., Laufer W., Schmitt H. D., Gallwitz D. Functionality and specific membrane localization of transport GTPases carrying C-terminal membrane anchors of synaptobrevin-like proteins. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3645–3653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00034.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park E. C., Finley D., Szostak J. W. A strategy for the generation of conditional mutations by protein destabilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 15;89(4):1249–1252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.4.1249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plutner H., Cox A. D., Pind S., Khosravi-Far R., Bourne J. R., Schwaninger R., Der C. J., Balch W. E. Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(1):31–43. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preuss D., Mulholland J., Franzusoff A., Segev N., Botstein D. Characterization of the Saccharomyces Golgi complex through the cell cycle by immunoelectron microscopy. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Jul;3(7):789–803. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.7.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. R., Preston R. A., Adams A. E., Stearns T., Drubin D. G., Haarer B. K., Jones E. W. Fluorescence microscopy methods for yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;31:357–435. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61620-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Protopopov V., Govindan B., Novick P., Gerst J. E. Homologs of the synaptobrevin/VAMP family of synaptic vesicle proteins function on the late secretory pathway in S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1993 Sep 10;74(5):855–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90465-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rambourg A., Clermont Y., Képès F. Modulation of the Golgi apparatus in Saccharomyces cerevisiae sec7 mutants as seen by three-dimensional electron microscopy. Anat Rec. 1993 Dec;237(4):441–452. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092370402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond C. K., Howald-Stevenson I., Vater C. A., Stevens T. H. Morphological classification of the yeast vacuolar protein sorting mutants: evidence for a prevacuolar compartment in class E vps mutants. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Dec;3(12):1389–1402. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.12.1389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redding K., Holcomb C., Fuller R. S. Immunolocalization of Kex2 protease identifies a putative late Golgi compartment in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):527–538. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid G. A. Pulse labeling of yeast cells and spheroplasts. Methods Enzymol. 1983;97:324–329. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)97144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rexach M. F., Schekman R. W. Distinct biochemical requirements for the budding, targeting, and fusion of ER-derived transport vesicles. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;114(2):219–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.2.219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder S. E., Banta L. M., Köhrer K., McCaffery J. M., Emr S. D. Multilamellar endosome-like compartment accumulates in the yeast vps28 vacuolar protein sorting mutant. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Jun;7(6):985–999. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.6.985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts C. J., Raymond C. K., Yamashiro C. T., Stevens T. H. Methods for studying the yeast vacuole. Methods Enzymol. 1991;194:644–661. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)94047-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Mechanisms of intracellular protein transport. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):55–63. doi: 10.1038/372055a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Solomon F., Botstein D. Isolation and characterization of conditional-lethal mutations in the TUB1 alpha-tubulin gene of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1988 Nov;120(3):681–695. doi: 10.1093/genetics/120.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer I., Emr S., Gross C., Schekman R. Invertase signal and mature sequence substitutions that delay intercompartmental transport of active enzyme. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1664–1675. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimmöller F., Riezman H. Involvement of Ypt7p, a small GTPase, in traffic from late endosome to the vacuole in yeast. J Cell Sci. 1993 Nov;106(Pt 3):823–830. doi: 10.1242/jcs.106.3.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Puzicha M., Gallwitz D. Study of a temperature-sensitive mutant of the ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast suggests a role in the regulation of intracellular calcium. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):635–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90579-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröder S., Schimmöller F., Singer-Krüger B., Riezman H. The Golgi-localization of yeast Emp47p depends on its di-lysine motif but is not affected by the ret1-1 mutation in alpha-COP. J Cell Biol. 1995 Nov;131(4):895–912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.4.895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N. Mediation of the attachment or fusion step in vesicular transport by the GTP-binding Ypt1 protein. Science. 1991 Jun 14;252(5012):1553–1556. doi: 10.1126/science.1904626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Mulholland J., Botstein D. The yeast GTP-binding YPT1 protein and a mammalian counterpart are associated with the secretion machinery. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):915–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90433-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Krüger B., Stenmark H., Düsterhöft A., Philippsen P., Yoo J. S., Gallwitz D., Zerial M. Role of three rab5-like GTPases, Ypt51p, Ypt52p, and Ypt53p, in the endocytic and vacuolar protein sorting pathways of yeast. J Cell Biol. 1994 Apr;125(2):283–298. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.2.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer-Krüger B., Stenmark H., Zerial M. Yeast Ypt51p and mammalian Rab5: counterparts with similar function in the early endocytic pathway. J Cell Sci. 1995 Nov;108(Pt 11):3509–3521. doi: 10.1242/jcs.108.11.3509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenmark H., Parton R. G., Steele-Mortimer O., Lütcke A., Gruenberg J., Zerial M. Inhibition of rab5 GTPase activity stimulates membrane fusion in endocytosis. EMBO J. 1994 Mar 15;13(6):1287–1296. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens B. J., White J. G. Computer reconstruction of mitochondria from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1979;56:718–728. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)56064-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens T., Esmon B., Schekman R. Early stages in the yeast secretory pathway are required for transport of carboxypeptidase Y to the vacuole. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svoboda A., Necas O. Ultrastructure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells accumulating Golgi organelles. J Basic Microbiol. 1987;27(10):603–612. doi: 10.1002/jobm.3620271008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Søgaard M., Tani K., Ye R. R., Geromanos S., Tempst P., Kirchhausen T., Rothman J. E., Söllner T. A rab protein is required for the assembly of SNARE complexes in the docking of transport vesicles. Cell. 1994 Sep 23;78(6):937–948. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valencia A., Chardin P., Wittinghofer A., Sander C. The ras protein family: evolutionary tree and role of conserved amino acids. Biochemistry. 1991 May 14;30(19):4637–4648. doi: 10.1021/bi00233a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P., Hengst L., Gallwitz D. Ypt proteins in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:369–387. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wichmann H., Hengst L., Gallwitz D. Endocytosis in yeast: evidence for the involvement of a small GTP-binding protein (Ypt7p). Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1131–1142. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuestehube L. J., Schekman R. W. Reconstitution of transport from endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi complex using endoplasmic reticulum-enriched membrane fraction from yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1992;219:124–136. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(92)19015-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zerial M., Stenmark H. Rab GTPases in vesicular transport. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):613–620. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90130-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]