Abstract
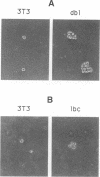
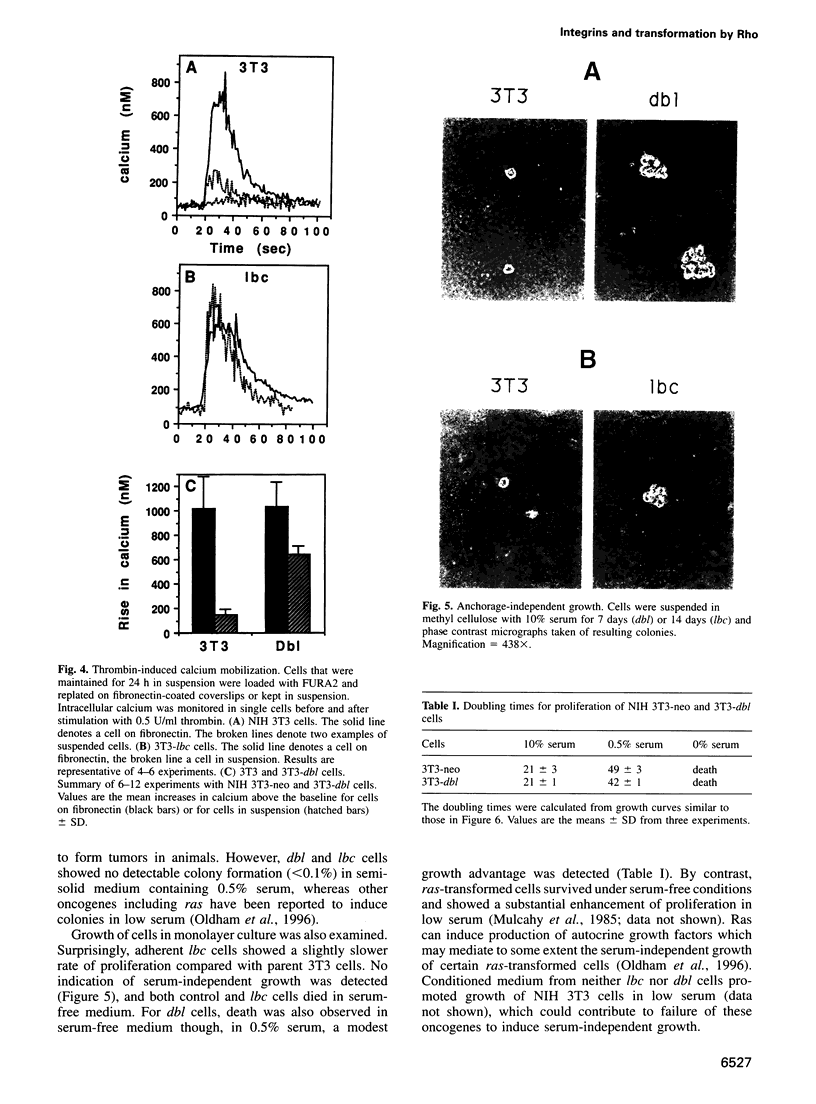
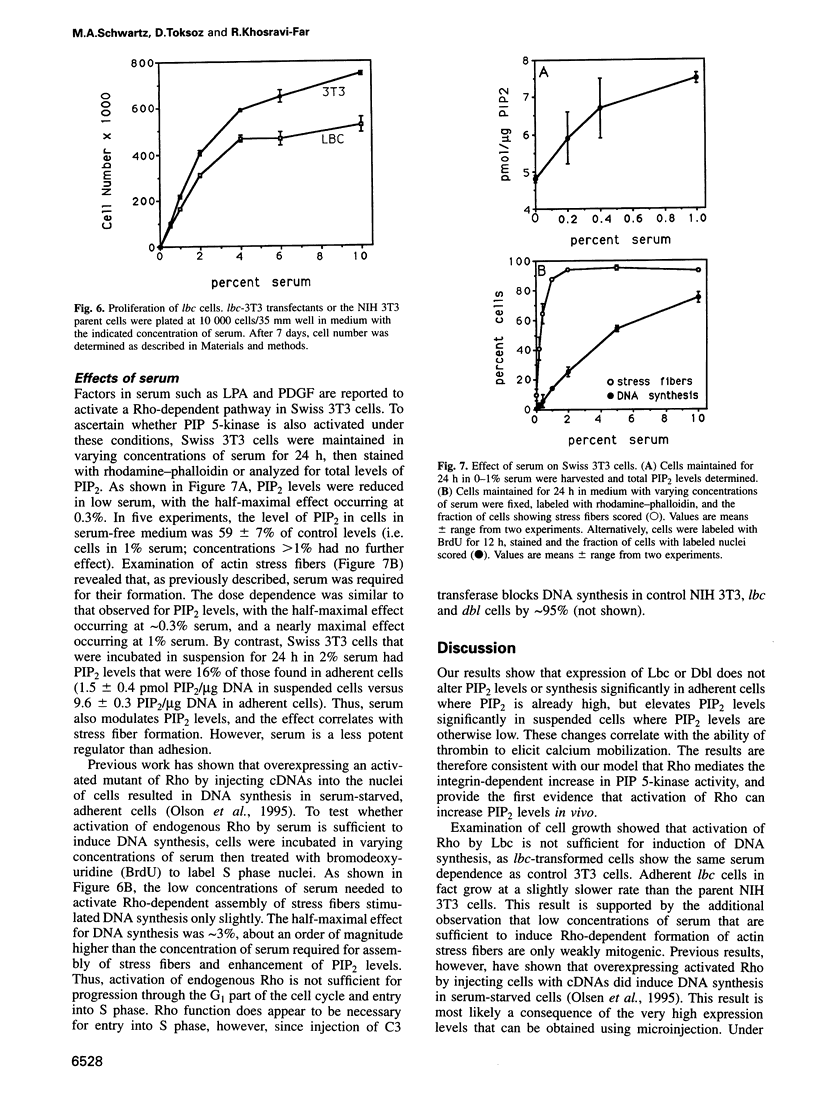
Constitutive activation of growth factor receptor signaling pathways leads to uncontrolled growth, but why tumor cells become anchorage independent is less clear. The fact that integrins transmit signals required for cell growth suggests that constitutive activation of steps downstream from integrins mediates anchorage independence. Since the small GTPase Rho may mediate integrin signal transduction, the effects of serum and the Rho nucleotide exchange factor oncogenes dbl and lbc on cell growth and signaling pathways were examined. Our data show that these oncogenes induce anchorage-independent but serum-dependent growth and stimulation of signaling pathways. These results show, therefore, that anchorage-independent growth results from constitutive activation of integrin-dependent signaling events. They also support the view that Rho is a functionally important mediator of integrin signaling.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano M., Mukai H., Ono Y., Chihara K., Matsui T., Hamajima Y., Okawa K., Iwamatsu A., Kaibuchi K. Identification of a putative target for Rho as the serine-threonine kinase protein kinase N. Science. 1996 Feb 2;271(5249):648–650. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5249.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eva A., Aaronson S. A. Isolation of a new human oncogene from a diffuse B-cell lymphoma. Nature. 1985 Jul 18;316(6025):273–275. doi: 10.1038/316273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman V. H., Shin S. I. Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice: correlation with cell growth in semi-solid medium. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart M. J., Eva A., Zangrilli D., Aaronson S. A., Evans T., Cerione R. A., Zheng Y. Cellular transformation and guanine nucleotide exchange activity are catalyzed by a common domain on the dbl oncogene product. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):62–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotchin N. A., Hall A. The assembly of integrin adhesion complexes requires both extracellular matrix and intracellular rho/rac GTPases. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 2):1857–1865. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamee H. P., Ingber D. E., Schwartz M. A. Adhesion to fibronectin stimulates inositol lipid synthesis and enhances PDGF-induced inositol lipid breakdown. J Cell Biol. 1993 May;121(3):673–678. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldham S. M., Clark G. J., Gangarosa L. M., Coffey R. J., Jr, Der C. J. Activation of the Raf-1/MAP kinase cascade is not sufficient for Ras transformation of RIE-1 epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Jul 9;93(14):6924–6928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.14.6924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson M. F., Ashworth A., Hall A. An essential role for Rho, Rac, and Cdc42 GTPases in cell cycle progression through G1. Science. 1995 Sep 1;269(5228):1270–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.7652575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid T., Furuyashiki T., Ishizaki T., Watanabe G., Watanabe N., Fujisawa K., Morii N., Madaule P., Narumiya S. Rhotekin, a new putative target for Rho bearing homology to a serine/threonine kinase, PKN, and rhophilin in the rho-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jun 7;271(23):13556–13560. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.23.13556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren X. D., Bokoch G. M., Traynor-Kaplan A., Jenkins G. H., Anderson R. A., Schwartz M. A. Physical association of the small GTPase Rho with a 68-kDa phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate 5-kinase in Swiss 3T3 cells. Mol Biol Cell. 1996 Mar;7(3):435–442. doi: 10.1091/mbc.7.3.435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):389–399. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90163-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridley A. J., Paterson H. F., Johnston C. L., Diekmann D., Hall A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell. 1992 Aug 7;70(3):401–410. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Denninghoff K. Alpha v integrins mediate the rise in intracellular calcium in endothelial cells on fibronectin even though they play a minor role in adhesion. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11133–11137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M. A., Schaller M. D., Ginsberg M. H. Integrins: emerging paradigms of signal transduction. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:549–599. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.003001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toksoz D., Williams D. A. Novel human oncogene lbc detected by transfection with distinct homology regions to signal transduction products. Oncogene. 1994 Feb;9(2):621–628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker R. W., Butterfield C. E., Folkman J. Interaction of serum and cell spreading affects the growth of neoplastic and non-neoplastic fibroblasts. J Supramol Struct Cell Biochem. 1981;15(1):29–40. doi: 10.1002/jsscb.1981.380150104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe G., Saito Y., Madaule P., Ishizaki T., Fujisawa K., Morii N., Mukai H., Ono Y., Kakizuka A., Narumiya S. Protein kinase N (PKN) and PKN-related protein rhophilin as targets of small GTPase Rho. Science. 1996 Feb 2;271(5249):645–648. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5249.645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng Y., Olson M. F., Hall A., Cerione R. A., Toksoz D. Direct involvement of the small GTP-binding protein Rho in lbc oncogene function. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 21;270(16):9031–9034. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.16.9031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]