Abstract
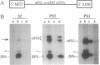
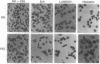
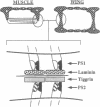
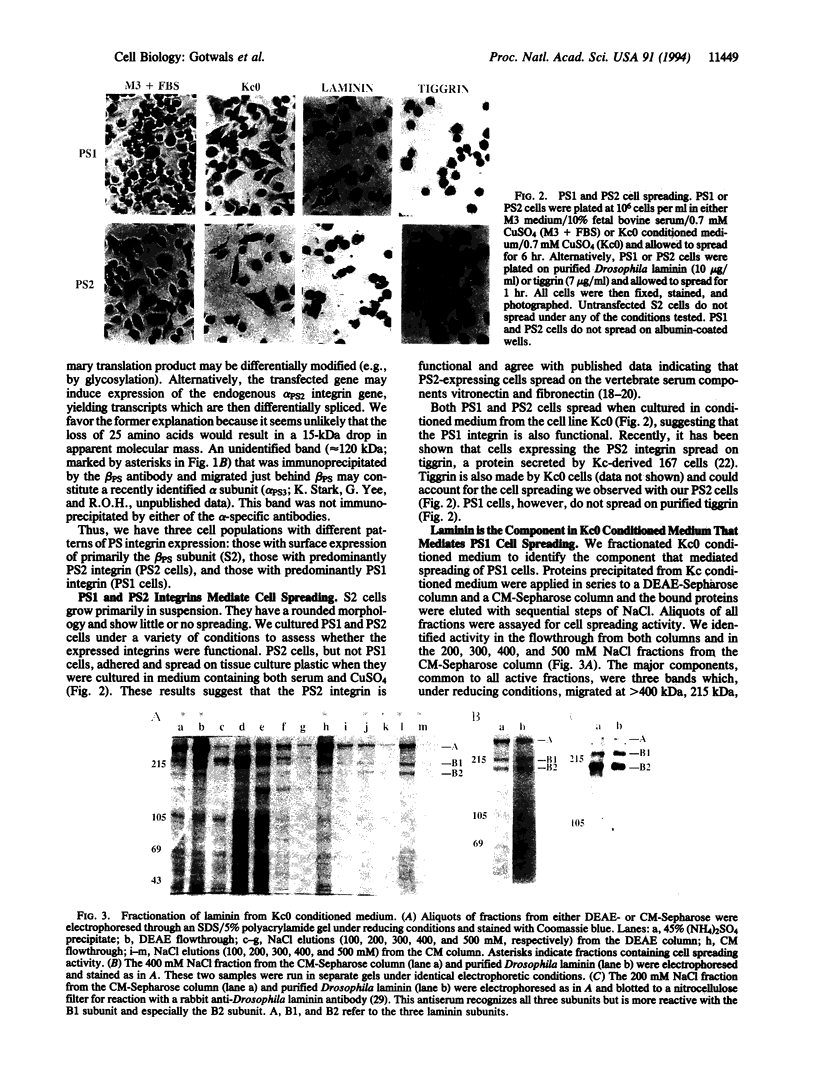
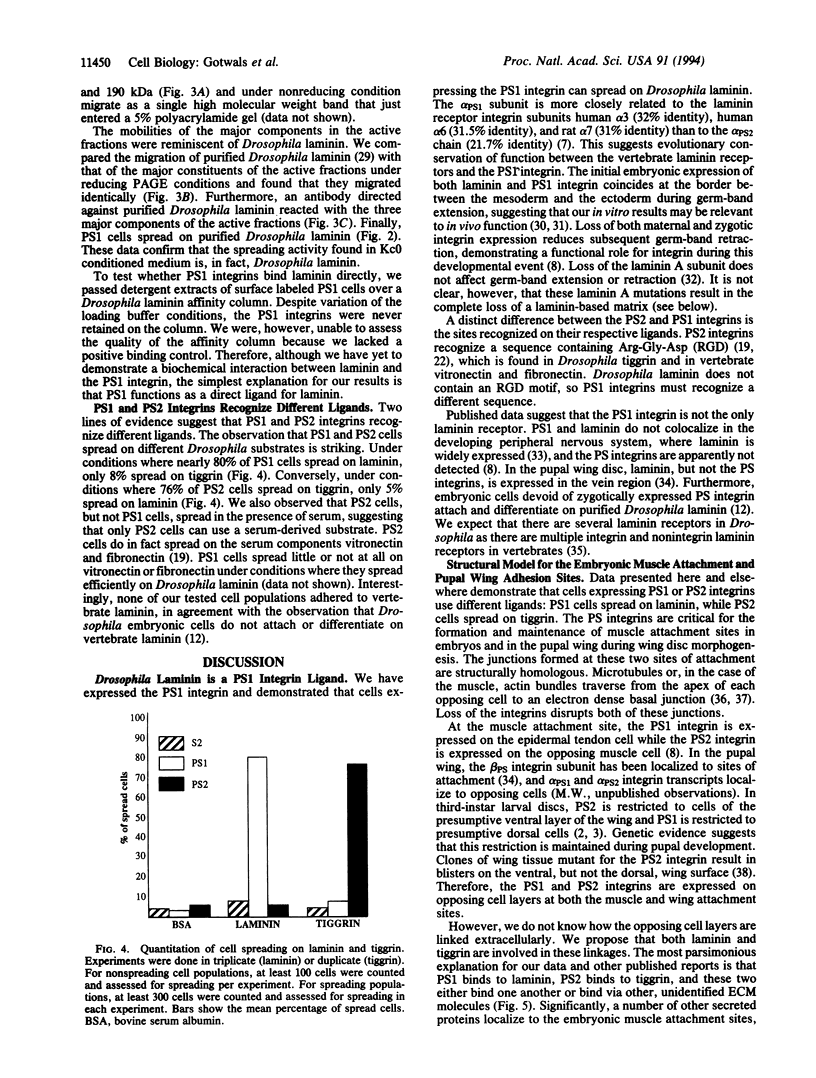
We have expressed Drosophila position-specific (PS) integrins on the surfaces of Schneider S2 cells and tested for adhesion and spreading on various matrix molecules. We report that PS1 integrin is a laminin receptor and that PS1 and PS2 integrins promote cell spreading on two different Drosophila extracellular matrix molecules, laminin and tiggrin, respectively. The differing ligand specificities of these two integrins, combined with data on the in vivo expression patterns of the integrins and their ligands, lead to a model for the structure of integrin-dependent attachments in the pupal wings and embryonic muscles of Drosophila.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bogaert T., Brown N., Wilcox M. The Drosophila PS2 antigen is an invertebrate integrin that, like the fibronectin receptor, becomes localized to muscle attachments. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90580-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brabant M. C., Brower D. L. PS2 integrin requirements in Drosophila embryo and wing morphogenesis. Dev Biol. 1993 May;157(1):49–59. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower D. L., Jaffe S. M. Requirement for integrins during Drosophila wing development. Nature. 1989 Nov 16;342(6247):285–287. doi: 10.1038/342285a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brower D. L., Wilcox M., Piovant M., Smith R. J., Reger L. A. Related cell-surface antigens expressed with positional specificity in Drosophila imaginal discs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7485–7489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H., King D. L., Wilcox M., Kafatos F. C. Developmentally regulated alternative splicing of Drosophila integrin PS2 alpha transcripts. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90880-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown N. H. Null mutations in the alpha PS2 and beta PS integrin subunit genes have distinct phenotypes. Development. 1994 May;120(5):1221–1231. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.5.1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunch T. A., Brower D. L. Drosophila PS2 integrin mediates RGD-dependent cell-matrix interactions. Development. 1992 Sep;116(1):239–247. doi: 10.1242/dev.116.1.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunch T. A., Salatino R., Engelsgjerd M. C., Mukai L., West R. F., Brower D. L. Characterization of mutant alleles of myospheroid, the gene encoding the beta subunit of the Drosophila PS integrins. Genetics. 1992 Oct;132(2):519–528. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler J. H., Fessler L. I. Drosophila extracellular matrix. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:309–339. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fessler L. I., Campbell A. G., Duncan K. G., Fessler J. H. Drosophila laminin: characterization and localization. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2383–2391. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogerty F. J., Fessler L. I., Bunch T. A., Yaron Y., Parker C. G., Nelson R. E., Brower D. L., Gullberg D., Fessler J. H. Tiggrin, a novel Drosophila extracellular matrix protein that functions as a ligand for Drosophila alpha PS2 beta PS integrins. Development. 1994 Jul;120(7):1747–1758. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.7.1747. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fristrom D., Wilcox M., Fristrom J. The distribution of PS integrins, laminin A and F-actin during key stages in Drosophila wing development. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):509–523. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullberg D., Fessler L. I., Fessler J. H. Differentiation, extracellular matrix synthesis, and integrin assembly by Drosophila embryo cells cultured on vitronectin and laminin substrates. Dev Dyn. 1994 Feb;199(2):116–128. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001990205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henchcliffe C., García-Alonso L., Tang J., Goodman C. S. Genetic analysis of laminin A reveals diverse functions during morphogenesis in Drosophila. Development. 1993 Jun;118(2):325–337. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.2.325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Ui K., Miyake T., Uemura T., Takeichi M. Drosophila PS integrins recognize vertebrate vitronectin and function as cell-substratum adhesion receptors in vitro. Development. 1991 Nov;113(3):1007–1016. doi: 10.1242/dev.113.3.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Alteration of cell-surface proteins by viral transformation and by proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Nov;70(11):3170–3174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.11.3170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokerst R. S., Weeks J. R., Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. Analysis of the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):266–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00339727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusche-Gullberg M., Garrison K., MacKrell A. J., Fessler L. I., Fessler J. H. Laminin A chain: expression during Drosophila development and genomic sequence. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4519–4527. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05553.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai-Fook J. The structure of developing muscle insertions in insects. J Morphol. 1967 Dec;123(4):503–527. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051230411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M., Aebersold R., Wilcox M. Drosophila position-specific antigens resemble the vertebrate fibronectin-receptor family. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1037–1043. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04856.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leptin M., Bogaert T., Lehmann R., Wilcox M. The function of PS integrins during Drosophila embryogenesis. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):401–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKrell A. J., Blumberg B., Haynes S. R., Fessler J. H. The lethal myospheroid gene of Drosophila encodes a membrane protein homologous to vertebrate integrin beta subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2633–2637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio E. E., Hynes R. O. Antibodies to the conserved cytoplasmic domain of the integrin beta 1 subunit react with proteins in vertebrates, invertebrates, and fungi. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1765–1772. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mecham R. P. Laminin receptors. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:71–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell D. J., Goodman C. S. Drosophila laminin: sequence of B2 subunit and expression of all three subunits during embryogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2441–2453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. M., Jr, Wright T. R. A histological and ultrastructural analysis of developmental defects produced by the mutation, lethal(1)myospheroid, in Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):393–402. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring J., Paine-Saunders S. E., Hynes R. O., Bernfield M. Drosophila syndecan: conservation of a cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 12;91(8):3334–3338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.8.3334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volk T., Fessler L. I., Fessler J. H. A role for integrin in the formation of sarcomeric cytoarchitecture. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90449-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli M., DiAntonio A., Fearnley I. M., Smith R. J., Wilcox M. Cloning and characterization of alpha PS1, a novel Drosophila melanogaster integrin. Mech Dev. 1993 Sep;43(1):21–36. doi: 10.1016/0925-4773(93)90020-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., Brower D. L., Smith R. J. A position-specific cell surface antigen in the drosophila wing imaginal disc. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M., DiAntonio A., Leptin M. The function of PS integrins in Drosophila wing morphogenesis. Development. 1989 Dec;107(4):891–897. doi: 10.1242/dev.107.4.891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox M. Genetic analysis of the Drosophila PS integrins. Cell Differ Dev. 1990 Dec 2;32(3):391–399. doi: 10.1016/0922-3371(90)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman S., Grinblat Y., Yee G., Kafatos F. C., Hynes R. O. Analyses of PS integrin functions during Drosophila development. Development. 1993 Jul;118(3):737–750. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.3.737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zusman S., Patel-King R. S., Ffrench-Constant C., Hynes R. O. Requirements for integrins during Drosophila development. Development. 1990 Mar;108(3):391–402. doi: 10.1242/dev.108.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]