Abstract
Prospective studies indicate that the risk of microvascular and major thrombosis in untreated thrombocythemia in various myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN-T) is not age dependent and causally related to platelet-mediated thrombosis in early, intermediate and advanced stages of thrombocythemia in MPN-T. If left untreated both microvascular and major thrombosis frequently do occur in MPN-T, but can easily be cured and prevented by low dose aspirin as platelet counts are above 350 × 109/L. The thrombotic risk stratification in the retrospective Bergamo study has been performed in 100 essential thrombocythemia (ET) patients not treated with aspirin thereby overlooking the discovery in 1985 of aspirin responsive platelet-mediated arteriolar and arterial thrombotic tendency in MPN-T disease of ET and polycythemia vera (PV) patients. The Bergamo definition of high thrombotic risk and its persistence in the 2012 International Prognostic Score for ET is based on statistic mystification and not applicable for low and intermediate MPN-T disease burden in ET and PV patients on aspirin. With the advent of molecular screening of MPN patients, MPN-T disease associated with significant leukocytosis, thrombocytosis, constitutional symptoms and/or moderate splenomegaly are candidates for low dose peglyated interferon (PegasysR, 45 μg/mL once per week or every two weeks) as the first line myeloreductive treatment option in JAK2V617F mutated MPN-T disease in ET and PV patients. If non-responsive to or side effects induced by IFN, hydroxyurea is the second line myelosuppressive treatment option in JAK2V617F mutated ET and PV patients with increased MPN-T disease burden.
Keywords: Myeloproliferative neoplasms, Essential thrombocythemia, Polycythemia vera, JAK2V617F mutation, Aspirin, Interferon, Hydroxyurea
Core tip: Spontaneous endogenous erythroid colony formation and low serum erythropoietin (EPO) levels are highly specific for JAK2V617F mutated essential thrombocythemia (ET), prodromal polycythemia vera (PV), masked PV and classical PV. The quantitation of JAK2V617F mutation allele burden plays a key-role in the diagnostic work-up and staging of ET, PV and MF patients. The JAK2V617F mutation allele burden in heterozygous mutated ET is low but high in combined heterozygous - homozygous or homozygous mutated PV. The combined use of JAK2V617F mutation load, spleen size and pretreatment bone marrow biopsy are of major prognostic significance and therapeutic importance in ET and PV patients. Large Prospective Unmet Need studies are warranted to delineate the natural history and outcome of targeted treatment in MPN patients of various molecular etiology during long-term or life long follow-up.
INTRODUCTION CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS IN PV AND ET
The bleeding manifestations in 100 case histories of hemorrhagic thrombocythemia (HT) ranged from gastrointestinal chronic occult blood loss, melena and hematemesis to mucocutaneous bruises, hematomas, ecchymoses, gum bleedings and secondary bleeding[1,2]. HT was usually associated with significant leukocytosis and splenomegaly and the platelet count at time of bleeding in 100 HT cases ranged from 800 to above 4000 × 109/L (Figure 1, left). The manifestation in erythromelalgic thrombotic thrombocythemia (ETT) in 67 ET and 32 PV patients included erythromelalgia, acrocyanosis, digital gangrene, amaurosis fugax, transient ischemic attacks, stroke, angina pectoris and myocardial infarction, superficial thrombophlebitis and deep vein thrombosis[3]. The platelet count at time of ETT in ET and PV patients ranged from 400 to 2000 × 109/L in ET patients and from 350 to 1250 × 109/L in PV patients (Figure 1, left).
Figure 1.
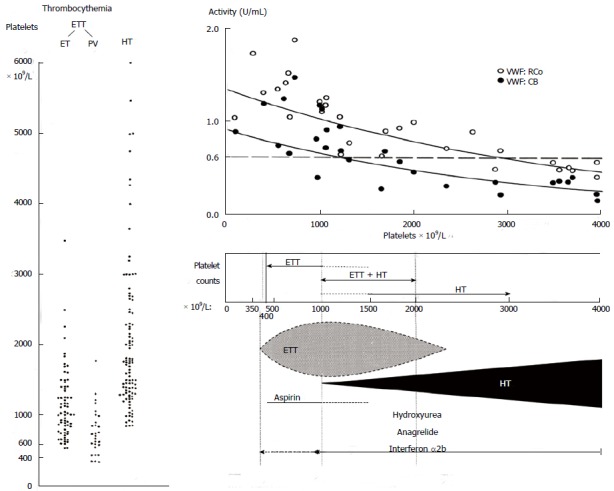
Platelet counts in 100 case histories of hemorrhagic thrombocythemia and 99 cases of erythromelalgic thrombotic thrombocythemia subdivided in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera (left)[1,2]. The relationship between platelet-mediated microvascular thrombosis in ETT at platelet counts between 350 to 1000 × 109/L in ETT and mucocutaneous bleedings at platelet counts between about 1000 to above 2000 x 109/L in HT patients (Table 3)[1-7]. The relationship of increasing platelet counts and decreasing von Willebrand factor (VWF) levels, VWF:ristocetine cofactor activity (VWF:RCo), and VWF collagen binding activity (VWF:CB) as the cause of an acquired Von Willebrand Disease (AVWD) type 2A due to proteolysis of large VWF nultimers in patients with paradoxical occurrence of ETT and HT and in patients with HT[8]. HT: Hemorrhagic thrombocythemia; ETT: Erythromelalgic thrombotic thrombocythemia; ET: Essential thrombocythemia; PV: Polycythemia vera.
Microvascular ischemic and thrombotic complications such as erythromelalgia, atypical and typical TIAs, ocular transient ischemic events and migraine-like headache dominate the clinical picture at presentation ET and early PV. In contrast to the inefficacy of coumadin, control of platelet function with low dose aspirin and reduction of platelet counts to normal prevented the recurrence of microvascular circulation disturbances in the end-arterial microvasculature of the cerebral, coronary and peripheral circulation[3-10]. Clinicians should be aware that a starting low dose of aspirin, 50 mg daily, in symptomatic ET patients complicated by erythromelalgia induces a slow relief of pain and gradual inhibition of platelet cyclo-oxygenase (COX-1), as it takes 4 to 6 d to completely inhibit platelet COX-1 and to relief erythromelalgia by such a low dose of aspirin. Consequently, symptomatic thrombocythemia vera patients at time of presentation with microvascular circulation disturbances or major thrombosis should be immediately treated with a loading dose of aspirin 300 to 500 mg followed by a low maintenance dose of 50 to 80 mg daily. Our observational studies on a high frequency of microvascular thrombotic complications in particular indicate the existence of platelet thrombophilia in thrombocythemia for which aspirin is a safe and effective antithrombotic agent in ET and PV patients (A1 level of evidence). Low dose aspirin at platelet counts in excess of 1250 ± 250 × 109/L is frequently associated with the paradoxical occurrence of thrombosis and bleeding (ETT + HT, Figure 1). Bleedings spontaneously occur at platelet count in excess of 1250 ± 250 × 109/L due to an acquired von Willebrand Disease (AVWD, type 2A with absence of high and intermediate von Willebrand factor (VWF) multimers increasing in severity at increasing platelet counts to high levels above 1500 × 109/L (Figure 1, upper part)[8]. Correction of the platelet counts to normal (less than 350 × 109/L) is associated with no recurrences of microvascular events after discontinuation of aspirin[2,6,7] together with complete correction of the VWF-multimeric pattern and of all VWF-parameters to normal values[8].
RISK ON MICROVASCULAR AND MAJOR THROMBOSIS IN PV AND ET
The risk stratification for thrombosis by Cortelazzo et al[11] in 1990 in 100 ET patients not treated with aspirin overlooked the 1985 key reference of Michiels et al[3] on the demonstration of aspirin responsive platelet-mediated arteriolar and arterial thrombotic tendency in ET and PV patients. The characteristics of the thrombotic events in the retrospective Bergamo cohort of 100 patients were in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1.
Incidence of thrombotic events related to age in 100 patients with essential thrombocythemia not on aspirin in the 1990 Bergamo study[11]
| Age (yr) | No. of patients | Patient/years | Events number | Events % pt/yr |
| < 40 | 34 | 118 | 2 | 1.70% |
| 40-60 | 37 | 112 | 7 | 6.30% |
| > 60 | 29 | 73 | 11 | 15% |
| Total thrombotic events in 20 of 100 ET patients | ||||
ET: Essential thrombocythemia.
Table 2.
The type and number of microvascular thrombotic events in the 1990 Bergamo study are very characteristic for untreated thrombocythemia[11]
| Cortelazzo et al[11] 1990 | No. of patients | No. of events |
| Total | 20 | 32 |
| Arterial | 17 | 25 |
| Digital ischemia | 7 | |
| Transient ischemic attacks | 15 | |
| Stroke | 0 | |
| Myocardial infarction | 3 | |
| Venous | 3 | 7 |
| Superficial Thrombophlebitis | 3 | |
| Femoral DVT | 1 | |
| Unusual localization DVT | 3 | |
| Bleeding complications | 4 |
DVT: Deep vein thrombosis.
The age distribution of this cohort of ET did not reflect real life experience since the number of young ET patients was artificially manipulated to one third in the young age group to reach statistical significance. The risk for thrombotic complication was low (1.7%) in MPN-T at young age below 40 years, but was high at age of > 60 years (15%), and moderately increased (6.3%) in the age group of 40 to 60 years not on aspirin[11]. In the Dutch prospective ET and PV studies the risk of thrombosis is untreated ET and PV is not age dependent and causally related to platelet-mediated thrombosis in the various stages of ET and PV patients[1-10]. The type and number of 25 arterial and 3 venous thrombotic episodes in 20 out of 100 untreated ET patients in the 1990 Bergamo study were mainly microcirculatory events including digital ischemia, transient ischemic attacks, superficial thrombophlebitis, ususual site of DVT, no stroke, and major thrombosis only in 4, myocardial infarction in 3 and femoral DVT in 1 (Table 2)[11]. If left untreated symptomatic ET patients with microcirculatory disturbances are at very high risk for digital ischemia, TIAs, stroke or acute coronary ischemic syndromes. Based on the results of our prospective studies in Table 3[4,5] we concluded that the stratification in low, intermediate and high thrombotic risk in the 1990 Bergamo study[11] can only be applied to ET patients not on aspirin. This means that the stratification in aspirin responsive low, intermediate and high thrombotic risk in the retrospective Bergamo ET study is based on statistic misinterpretation and mystification leading to authorative overtreatment recommendation with hydroxyurea for ET and PV patients on low dose aspirin. The so-called high thrombotic risk ET as defined by a history or presentation of thrombosis at time of diagnosis or by reaching the age 60 years is not in line with the observed low thrombotic incidence in aspirin treated ET and PV patients[10,12-14]. The 1995 Bergamo prospective randomized clinical trial (RCT) of 114 ET patients comparing hydroxyurea vs placebo in high thrombotic risk ET patients is unbalanced since 69% of the placebo group and 70% of the HU-treated ET patients did not receive aspirin[15]. Two of 56 high thrombotic risk ET patients on hydroxyurea had major thrombotic events (one stroke, one myocardial infarction) and 14 of 58 high thrombotic risk ET patients in the placebo group had microcirculatory disturbances in 12, and major thrombosis in 2. However, 10 of these 14 symptomatic patients in the placebo arm manifested aspirin responsive microvascular disturbances but were not on treatment with aspirin[15]. The conclusion from this RCT is that HU vs low dose aspirin alone in high thrombotic risk ET patients is predicted to be equally effective for the prevention of microvascular circulation disturbances in ET (Figure 1, Table 3)[4,5]. Consequently, the high thrombotic risk in the 2012 IPSET (International Prognostic Score for ET)[14] with the indication of hydroxyurea (HU) simple leads to significant HU overtreatment in ET and PV patients on aspirin with a low or intermediate MPN-T disease burden[12,13].
Table 3.
Incidence of thrombotic and bleeding complications in the prospective 1975-1996 Rotterdam study of 68 ET patients during a median follow-up of 6.7 years according to treatment strategy (Van Genderen et al[4,5] 1997)
| Treatment strategy | Duration of follow-up person (yr) |
Thrombotic events |
Bleeding events |
||
| Events (n) | Events/100 person (yr) | Events (n) | Events/100 person (yr) | ||
| Asymptomatic 14 patients | |||||
| Watchful waiting | 127 | 271 | 33.3 | 2 | 1.6 |
| Symptomatic 54 patients | |||||
| Low-dose aspirin | 139 | 5 | 3.6 | 103 | 7.2 |
| Platelet reduction | 113 | 102 | 8.9 | 2 | 1.8 |
| Low-dose aspirin + platelet reduction | 40 | 0 | - | 4 | 10 |
| Total | 419 | 42 | 18 | ||
Mean platelet count 610, range 410-831 × 109/L at time of thrombotic event;
Platelet count 624 ± 255 × 109/L at time of thrombotic event;
Platelet count 1737, range 661-3460 × 109/L at time of bleeding event. These observations by Van Genderen et al[4,5] confirm the concept in Figure 1 on the relationship between platelet-mediated microvascular thrombosis in thrombocythemia at platelet counts between 350 to 1000 × 109/L in ETT and mucocutaneous bleedings at platelet counts of 1000 to above 2000 × 109/L in HT patients.
With the advent of molecular screening of MPN-T patients, it should be realized that WHO-ET patients with less than 50% JAK2V617F mutation load are usually heterozygous, and WHO-PV patients with less than 50% JAK2V617F mutation load are frequently combined heterozygous homozygous positive for the JAK2V617F mutation[16-18]. In the study of Vannucchi et al[19], the JAK2V617F allele burden in 173 PV ranged from 1%-25% in 33%, from 25%-50% in 29%, from 50% to 75% in 20% and from 75% to 10% in 18%. Treatment consisted of phlebotomy in 49% and cytoreductive therapy (mainly hydroxyurea) in 51%. The JAK2V617F allele mutation burden correlated with MPN disease activity in terms of stimulated erythropoiesis by higher hematocrit and erythrocytes, lower MCV, serum EPO and ferritine, and stimulated myelopiesis by higher leukocytes, serum LDH and LAP score[19]. Comparing PV patients with low (1% to 50%) vs high (50%-100%) JAK2V617F allele burden, the relative risks for MPN disease burden increased from 1 to 4 for pruritis, from 1 to 4 for palpable splenomegaly and from 1 to 4 for spleen sizes above 15 cm length diameter on scan. In a subsequent elegant study Vannucchi et al[20] assessed the incidence of thrombosis related to the JAK2 allele burden in a large retrospective study of 962 MPN-T patients subdivided in 323 PV and 639 ET patients[20]. Aspirin responsive platelet thrombophilia or microvascular symptoms due to microvessel disorder including migraine-like headache, acral paresthesia, erythromelalgia, transient neurological and visual disturbances were excluded by definition and not considered in this retrospective analysis[20]. Only major thrombotic events ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attacks, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, deep vein thrombosis abdominal vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism were assessed. The incidence of major thrombotic events in 188 JAK2V617F homozygous MPN patients (JAK2V617F mutation above 50% in 104 PV and 14 ET) and in 587 heterozygous (JAK2V617F mutation less than 50% in 219 PV and 257 ET) and 257 wild type ET patients was assessed and calculated in Table 4 and Figure 2. Anno 2014, JAK2 wild ET are predicted to carry one of the CALR positive in 80%[21]. Homozygous JAK2V617F positive patients with JAK2V617F mutation above 50% in ET and PV are truly homozygous. Homozygous JAK2V617F mutated MPN patients with a mutation allele load above 50% were older, had higher leukocyte counts, hematocrits and larger spleen volumes indicating advanced MPN disease. One hundred seventy-six patients (18.3%) had a major thrombotic event at diagnosis with a similar frequency in PV (19.2%) and ET (17.8%)[20]. A similar incidence was found in our analysis of the literature in 1241 ET patients not on aspirin from 14 retrospective studies[22]. In the Italian study, major thrombosis (usually not on aspirin) occurred in 122 patients (12.7%), corresponding to 14.9% in PV and 11.6% in ET patients and hemorrhages at diagnosis manifested in 55 (5.7%) patients, 5.3% in PV and 6.0% in ET[20]. The overall incidence of major thrombotic events during 10 years follow-up usually not on aspirin was about 20% in ET heterozygous for the JAK2V617F mutation and in about 10% for JAK2 wild type ET[20]. Hemorrhages during follow-up was recorded in 45 (4.7%) ET/PV patients. A similar incidence of hemorrhages was found in our analysis of the literature in 1241 ET patients from 14 retrospective studies[22]. The frequency of bleeding was higher in JAK2V617F homozygous (21.4%) than in wild type or heterozygous ET patients, 3.1% and 3.8% respectively. The higher bleeding tendency in homozygous JAK2V617F MPN-T patients is predicted to be related to higher erythrocyte counts at increased platelet and leukocyte counts and its pathophysiology of the underlying mechanisms is currently under our investigation[10].
Table 4.
Major cardiovascular and venous thrombotic events at diagnosis or during long-term follow-up in 323 polycythemia vera and 639 essential thrombocthemia patients according to the JAK2V617F mutation status in the retrospective study of Vannucchi (only major thrombotic events were retrospectively recorded excluding the erythromelalgic and migraine like cerebral ischemic events[20])
| Patients | PV n = 323 | ET n = 625 | ||
| JAK2V617 mutation status | Hetero homozygous hetero wild type | |||
| No. of patients | 219 | 104 | 368 | 237 |
| At diagnosis | ||||
| Major arterial events | 21% | 15.4% | 21.7% | 10.5% |
| Venous events | 2.9% | 2.9% | 7.9% | 4.7% |
| During 10 yr follow-up (not on aspirin) | ||||
| Major arterial events | 10.1% | 12.5% | 6.3% | 5.8% |
| Venous events | 4.1% | 7.7% | 6.3% | 2.7% |
| Total during life time follow-up | ||||
| Major arterial | 31.1% | 27.9% | 28% | 16.3% |
| Venous | 10.5% | 10.6% | 14.2% | 7.4% |
In 14 homozygous ET patients total major arterial and venous events had occurred in 78.6% and 57.1% respectively. PV: Polycythemia vera; ET: Essential thrombocthemia.
Figure 2.
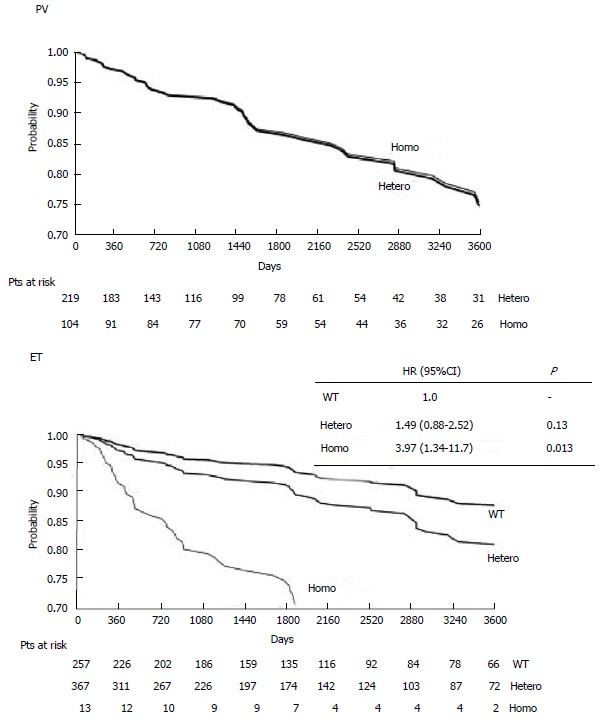
Retrospective study on the probability of cardiovascular thrombotic event-free survival (days up to 3600 d = 10 years) according to the JAK2V617F mutational state in 323 polycythemia vera and 639 essential thrombocythemia patients (Vannucchi et al[20]). Only major thrombotic events were retrospectively recorded and the erythromelalgic peripheral, ocular and cerebral ischemic events were excluded from evaluation. The overall incidence of major thrombotic events in JAK2V617F mutated PV patients during 10 years follow-up is about 25% in the Italian study[20]. A similar incidence of thrombotic events was found in our literature analysis of 1241 ET patients not on aspirin from 14 retrospective studies[22]. Source Vannucchi et al[20] Blood 2007. ET: Essential thrombocythemia; PV: Polycythemia vera.
CLINICAL SYMPTOMS AND DIAGNOSIS IN 497 DUTCH MPN PATIENTS
The results from the 2008 MPN Questioaires of the Dutch MPN Patient Foundation are the reflection of ECMP criteria for the diagnosis, classification and staging of MPN and treatment recommendations of ET and PV patients in The Netherlands between 2000 and 2008[13,23,24]. Low dose aspirin in ET and phlebotomy on top of aspirin is effective in the majority of ET and in two third of PV patients with low or mild MPN disease burden. Low dose pegylated interferon is recommended in PV with mild to moderately increased MPN disease like leukocytosis, itching and mild to moderate splenomegaly to postpone hydroxyurea. The collected Dutch MPN data were published in PUR SANG in 2010 based on 497 filled forms by MPN patients: 271 females (54%) and 212 males (43%), mean age at diagnosis 57 years (range 20 to 84 years)[23]. The diagnoses of 497 MPN patients were ET in 181 (36%), PV in 244 (50% of whom 18 as ET/PV), MF in 67 (13%), and MPN unclassifiable in 5 (1%). The detection of MPN disease 115 Dutch and Belgian hospitals was related to MPN specific complaints in 55%, coincidental (e.g., routine laboratory investigation for other reasons) in 30% and after significant delay of disease specific complications 15%. Diagnosis of MPN was confirmed by bone marrow investigations in 475 (96%) of 497 MPN patients[23]. Red cell mass (RCM) measurement to diagnose PV and to distinguish ET from PV was performed in 31%. PCR test for the JAK2V617 mutation anno 2008 was performed in 230 (46%) MPN patients and found positive in 74% (ET n = 52, PV n = 103, MF n = 14) and negative in 26%. Sixty percent of ET, 91% of PV and 52% of MF patients were JAK2V617F positive, thereby confirming the data in the literature. After primary diagnosis 144 (25%) MPN patients (ET n = 38, PV n = 49, MF n = 27) were referred for a second opinion. The second expert evaluation led to a change in diagnosis in 8% and a change in treatment in 28% (n = 29). The second treatment option in 29 (28%) proved to be superior to the initial treatment. A change of diagnosis during follow-up occurred in 60 MPN patients, from ET into PV in 16 (9% of PV), from PV into MF in 15 (6% of PV), and from ET into MF in 10 (6% of ET)[23].
MPN RELATED SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS IN 497 DUTCH ET, PV AND MF PATIENTS
Based on the Dutch MPN questionaire including 36 questions the top 20 complaints at time of diagnosis in 399 out of 497 (81%) MPN patients is shown in Table 5[23]. The most frequent complaint is fatigue (81%) equally high in ET, PV and MF patients. Apart from variable severity of fatigue a specific pattern of signs and symptoms could be retrieved. The signs and symptoms in ET are mainly featured by aspirin responsive tingling and prickling sensations in footsoles, hand palms, toes and fingers (erythromelalgia), and aspirin responsive cognitive concentration and visual disturbances (Table 5). PV patients presented with similar signs and symptoms but on top of that both aspirin resistent itching (PV 58% vs ET 30%) and fatigue were much more prominent in PV. A second most frequent complaint were various degrees of night sweats related to splenomegaly in about half of the MPN patients. About one third of MPN patients suffered from bone pain (Table 5). MF patients suffered more frequently from constitutional symptoms of prominent fatigue and night sweats related to pronounced splenomegaly. Before the MPN diagnosis was made the complaints were ascribed by doctors in 173 (35%) patients to other causes including stress, burned out or overstrained in 41 (24%), to depression or hystery in 14 (8%), migraine of unknown origin (and therefore not treated with aspirin) in 13 (8%) and to rheuma, hypertension or fibromyalgia in a few[23].
Table 5.
Top 20 clinical manifestations in patients with who defined myeloproliferative neoplasm essential thrombocythemia, polycythemia vera and myelofibrosis based on the Dutch myeloproliferative neoplasm Questionaire 2009-2010[23]
| Symptom | Top 20 MPN complaints |
All MPN |
MPN |
ET |
PV |
MF |
| n = 497 | % | % | % | % | ||
| 1 | Fatigue, listless | 399 | 81 | 80 | 81 | 85 |
| 2 | Microvascular acra37 | 278 | 57 | 61 | 56 | 46 |
| 3 | Cognitive disturbances37 | 262 | 53 | 52 | 56 | 45 |
| 4 | Visual disturbances37 | 249 | 51 | 50 | 52 | 46 |
| 5 | Night sweats | 236 | 48 | 44 | 50 | 52 |
| 6 | Itching | 220 | 45 | 30 | 58 | 36 |
| 7 | Dizziness | 218 | 44 | 44 | 46 | 39 |
| 8 | Bruises, bleedings | 211 | 43 | 40 | 45 | 43 |
| 9 | Splenomegaly constitutional symptoms | 198 | 40 | 22 | 43 | 78 |
| 10 | Tinnitus | 188 | 38 | 38 | 39 | 37 |
| 11 | Migraine headache without visual symptoms | 184 | 37 | 46 | 35 | 22 |
| 12 | Bone pain | 172 | 35 | 33 | 36 | 34 |
| 13 | Heart arrythmias | 154 | 31 | 34 | 31 | 24 |
| 14 | Dysarthria, dyslexia | 151 | 31 | 31 | 31 | 30 |
| 15 | Hypersensitive to sounds and noices | 149 | 30 | 29 | 32 | 28 |
| 16 | Paleness | 145 | 29 | 30 | 26 | 40 |
| 17 | Claudicatio intermittens | 140 | 28 | 28 | 30 | 24 |
| 18 | Hypersensitive to lights | 136 | 28 | 25 | 32 | 16 |
| 19 | Visual disturbances without headache | 18 | 33 | 54 | 3 | 90 |
| 20 | Headache without visual symptoms | 24 | 43 | 43 | 4 | 90 |
Microvascular acra: Tingling, prickeling sensations, redness,swelling and/or bluish discolouration of footsoles, handpalms, toes and/or fingers37. Cognitive disturbances of concentration and memory and sudden attacks of unconscienceness. Visual disturbances of scintillating scotomas, light flashes, blurred vision, transient monocular blindness, rapid spreading of visual figure disturbances37. Attacks of migraine-like headaches followed by nausea or vomiting or loss of consciencenous or transient paresis of one extermity37. MPN: Myeloproliferative neoplasm; ET: Essential thrombocythemia; PV: Polycythemia vera; MF: Myelofibrosis.
TREATMENT AND ADVERSE EVENTS IN DUTCH MPN PATIENTS 2003-2008
Treatment in 497 MPN patients was started with low dose aspirin or calcium carbasalate (Ascal) in 70% and phlebotomy in 42% (mainly PV 91%), hydroxyurea in 29%, and pegylated interferon-alpha2a in 7%, wait and see in 8% (n = 42 of whom 26 with MF) of MPN patients at time of diagnosis (Figure 3)[23]. The treatment changed during follow-up in 294 (60%) of MPN patients: ET in 64% (n = 115), PV in 59% (n = 143) and MF in 49% (n = 33). Out of 459 evaluable adverse drug reactions or side effects were recorded in one third (N = 168 = 35%) of MPN patients. Out of the 168 recorded side effects were related to HU in 41% (n = 69) and to IFN in 28% (n = 47) of all side effects. Most frequent side effects of HU were skin and mucocutaneous complaints including dry skin, skin lesions, skin ulcers, itching, skin carcinoma, brittle nails, aphtous ulcers and hair loss, and most frequent side effects of IFN were flue-like symptoms, fatigue and mood disturbances[23]. Low dose aspirin or Ascal induced gastritic complaints in 11% for which treatment with metronidazol was usually indicated[23].
Figure 3.
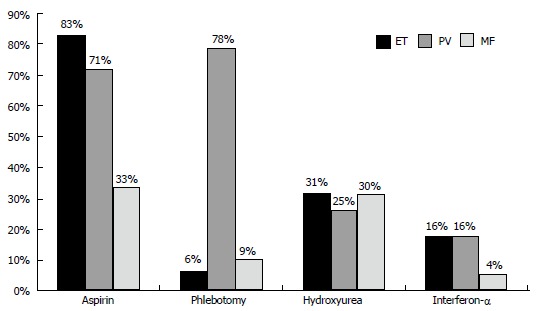
Mode of treatment in the Dutch 2008 survey of 363 myeloproliferative neoplasm (123 essential thrombocythemia, 190 polycythemia vera and 50 myelofibrosis) patients: 93% of polycythemia vera, 71% of essential thrombocythemia and 37% of myelofibrosis were on aspirin; 6% of essential thrombocythemia, 78% of polycythemia vera and 9% of myelofibrosis were treated with phlebotomy[23]. Because of symptomatic MNP disease burden 31% of ET, 29% of PV and 30% of MF were on treatment with hydroxyurea and 16% of ET, 16% of PV and 4% of MF were on treatment with pegylated interferon (PegasysR)[23]. ET: Essential thrombocythemia; PV: Polycythemia vera; MF: Myelofibrosis; MNP: Myeloproliferative neoplasm.
DISCUSSION
In the Dutch 2008 survey of 363 MPN (123 ET, 190 PV and 50 MF) patients 93% of PV, 71% of ET and 37% of MF were on aspirin mainly because of microvascular symptoms including migraine-like headache, acral paresthesia, erythromelalgia, transient neurological and visual disturbances. Phlebotomy became the first line treatment in 6% of ET, 78% of PV and 9% of MF[23]. Because of advanced or symptomatic MPN disease 31% of ET, 29% of PV and 30% of MF were on treatment with hydroxyurea and 16% of ET and PV and 4% of MF were on treatment with pegylated interferon (PegasysR). In the study of Vannucchi et al[20], a total of 214 patients were treated with phlebotomy, 58% of 219 PV and 4% of 257 ET patients. Myelosuppressive chemotherapy was administered to 497 patients (52%) including 59% of 219 PV and 48% of 257 ET patients. The 20% difference of HU use (50% of Italian MPN-T patients vs 30% of Dutch MPN-T patients) can readily be ascribed to significant differences in the Italian vs the Dutch guidelines for MPN-T disease in ET and PV patients. MPN-T patients in the Netherlands were treated according to the 2000 guidelines for ET and PV[13]. Low risk MPN-T disease in ET and PV patients at ages 18 to 80 years is defined by platelet count < 1500 × 109/L, absence of vascular risk factors like hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes atherosclrosis and absence of bleeding complications. First line treatment option in MPN-T disease in ET and PV patients followed the published Dutch guidelines since 2000[6-10]. If asymptomatic, no microvascular symptoms and no major thrombosis like minor stroke of myocardial infarction low dose aspirin 40 mg a day is given in JAK2V617F mutated MPN-T. Symptomatic MPN-T patients including migraine atypical TIAs, minor TIAs, low back pain, painfull toes or fingers, and major thrombosis were treated low dose aspirin. When MPN-T is associated with leukocytosis, moderate splenomegaly or platelet count above 1000 × 109/L low dose Pegasys 45 μg/mL will become the treatment of choice in JAK2V617F mutated ET and PV. At age above 70 freedom to choose hydroxyurea or low dose pegasys must prevail. Please note that these are general Dutch MPN-T treatment guidelines, which has to be discussed with the local hematologist or internist for approval[22-26].
The 2013 WHO-ECMP criteria clearly define and stage the JAK2V617F defined MPN entity of prodromal PV, prefibrotic PV, early fibrotic PV, PV complicated by myelofibrosis (post-PV MF), significant myeloid metaplasia of the spleen with splenomegaly and related constitutional symptoms (Table 6)[13]. Within the JAK2V617F MPN phenotypes, the JAK2V617F mutated hypercellular ET is associated with clustered pleiomorphic megakaryopoiesis, increased granulopoiesis and relative decrease of erythropoiesis without a documented history of ET or PV. The integrated WHO-CMP criteria surely will have important implications in choosing proper targeted treatment options for the prevention of thrombotic and bleeding complications in prodromal PV and PV and for the management of serious complications of progressive MPN disease burden requiring myeloreductive treatment with pegylated interferon (PegasysR) and if non-responsive or side effects low dose hydroxyurea to correct increased blood cell counts in overt and advanced PV patients (Table 6)[10,13]. Venesection aiming at a hematocrit below 0.45 in males and below 0.42 in females is the first line treatment option in PV patients[24-29]. Phlebotomy aiming more strictly at a hemotocrit of less than 0.40 and a MCV of less than 70 fl in males and females on top of well controlled low dose aspirin in PV patients will significantly reduce the cumulative incidence of major thrombosis, but the microvascular syndrome of associated thrombocythemia persist when not on aspirin[13]. According to current insights, low dose interferon is the treatment of choice in intermediate stage PV patients (Figure 1, Table 6)[13,30-33]. If not responsive to IFN or side effects induced by IFN, hydroxyurea is the second line myelosupressive treatment option in JAK2V617F mutated ET and PV patients (Table 6). Hydroxyurea is not an innocent drug and should be used with caution (Table 6). The final analysis of the 1980 French PVSG study of HU as upfront therapy at time of diagnosis in 136 evaluable PV patients younger than 65 years is published in 2011[32]. The cumulative incidence (probability) of myelofibrosis (MF) at 10, 15 and 20 years was 15%, 24% and 32% in the HU arm and the cumulative incidence of AML/MDS at 10, 15 and 20 years was 7.3%, 10.7% and 16.6% for HU treated PV patients. Proper staging of PV in terms of JAK2V617F mutation load, and MPN disease burden by measuring the degree of splenomegaly and severity of constitutional symptoms including itching on top of bone marrow histology and grading of fibrosis is of huge importance since it has significant implications for a non-leukemogenic or the least potential leukemogenic treatment options in low, intermediate and high risk PV patients (Figure 1, Table 6)[10,34-37]. As shown in Table 6, high risk PV and MF patients with advanced MPN-T disease in terms of high JAK2V617F allele burden, progressive MPN disease with splenomegaly and constitutional symptoms are candidates for myelosuppressive (hydroxyurea) or myeloreductive (JAK2 inhibitors) treatment[10,34-37].
Table 6.
Staging of JAK2V617F positive prodromal polycythemia vera, erythrocythemic polycythemia vera, and five stages of PV according to WHO-ECMP criteria related to therapy anno 2014[10,13,34-37]
| PV: WHO-ECMP stage | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
| WHO-ECMP clinical diagnosis | Prodromal PV | Erythrocy-themic PV | Early PV | Overt PV Classical PV | PV PMF Masked PV | Post-PV MF Spent PV | Leukemic PV MDS/AL |
| LAP-score | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑/↑↑ | Variable | Variable |
| Red cell mass | N | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | Variable | N/↓ |
| Serum EPO | N/↓ | N/↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | Variable | N/↓ |
| Erythrocytes × 1012/L | < 5.8 | > 5.8 | > 5.8 | > 5.8 | < 5.8 | Variable | N/↓ |
| Leukocytes × 109/L | < 12 | < 12 | < or > 12 | < or- > 15 | > 15 | > 20 | > 20 |
| Platelets × 109/L | > 400 | 400 | < or > 400 | > 400 | < or > 1000 | Variable | Variable |
| WHO-ECMP bone marrow | Early PV | Early PV | Early PV | Trilinear PV | Trilinear PV | Myelofibrosis | Leukemic |
| Bone marrow cellularity (%) | 50-80 | 50-80 | 60-100 | 80-100 | 80-100 | Decreased | Increased |
| Grading reticulin fibrosis: RF | RF 0-1 | RF 0-1 | RF 0-1 | RF 0/1, | RCF 2/3 | RCF 3/4 | |
| Grading myelofibrosis: MF57 | MF 0 | MF 0 | MF 0 | MF 0 | MF 1/2 | MF 2/3 | |
| Splenomegaly on palpation | No/+ | No | No/+ | + | ++/+++ | /Large | Large |
| Spleen size, echogram cm | < 12-15 | < 13 | 12-15 | 12-18 | 18 - > 20 | > 20 | > 20 |
| Spleen size on palpation cm | 0-3 | NP | 0-3 | 4-6 | > 6 | > 8 | > 8 |
| JAK2V617F in Granulocytes % | low | low | Moderate < 50 | High > 50 | High > 50 | High > 50 | No or ++ |
| JAK2V617F in BFU-e (exon 12) | +(++) | +(++) | +(++) | ++ | ++ | ++ | |
| Therapeutic implications | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Intermediate risk PV | High risk PV-MF | Post-PV MF Spent phase PV | Leukemia |
| Anno 2014 | |||||||
| First line aspirin/Phlebotomy Second line IFN vs HU Third line JAK2 inhibitor | Aspirin Phlebotomy | Aspirin Phlebotomy | Phlebotomy Aspirin Low dose IFN → responsive | Phlebotomy1 Aspirin IFN à resistant → HU | If IFN resistant → HU or JAK2 inhibitor | JAK2 Inhibitor → Bone marrow transplantation | Chemotherapy Bone marrow transplantation? Supportive |
↑: Increased; ↓: Decreased; N: Normal; +: Present or heterozygous; ++: Homozygous; HU: Hydroxyurea; PV: Polycythemia vera; MF: Myelofibrosis; WHO-ECMP: World Health Organization and European Cliical Molecular and Pathological; LAP: Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase; EPO: Erythropoietin.
Footnotes
Conflict-of-interest statement: The author declares no confict of interest.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Peer-review started: March 4, 2015
First decision: April 10, 2015
Article in press: July 14, 2015
P- Reviewer: Boucek C, Kriebardis AG S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Wu HL
References
- 1.Michiels JJ. Erythromelalgia and thrombocythemia: Thesis Rotterdam. Rotterdam: Erasmus University Rotterdam; 1981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.van Genderen PJ, Michiels JJ. Erythromelalgic, thrombotic and haemorrhagic manifestations of thrombocythaemia. Presse Med. 1994;23:73–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Michiels JJ, Abels J, Steketee J, van Vliet HH, Vuzevski VD. Erythromelalgia caused by platelet-mediated arteriolar inflammation and thrombosis in thrombocythemia. Ann Intern Med. 1985;102:466–471. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-102-4-466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Van Genderen PJ, Michiels JJ. Hydroxyurea in essential thrombocytosis. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:802–803. doi: 10.1056/nejm199509213331216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van Genderen PJ, Mulder PG, Waleboer M, van de Moesdijk D, Michiels JJ. Prevention and treatment of thrombotic complications in essential thrombocythaemia: efficacy and safety of aspirin. Br J Haematol. 1997;97:179–184. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.d01-2127.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Michiels JJ. Aspirin and platelet-lowering agents for the prevention of vascular complications in essential thrombocythemia. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 1999;5:247–251. doi: 10.1177/107602969900500408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Michiels JJ. Normal life expectancy and thrombosis-free survival in aspirin treated essential thrombocythemia. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 1999;5:30–36. doi: 10.1177/107602969900500107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.van Genderen PJ, Michiels JJ, van der Poel-van de Luytgaarde SC, van Vliet HH. Acquired von Willebrand disease as a cause of recurrent mucocutaneous bleeding in primary thrombocythemia: relationship with platelet count. Ann Hematol. 1994;69:81–84. doi: 10.1007/BF01698487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Michiels JJ. Erythromelalgia and vascular complications in polycythemia vera. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1997;23:441–454. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-996121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Michiels JJ, Ten Kate FWJ, Koudstaal PJ, Van Genderen PJJ. Aspirin responsive platelet thrombophilia in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. World J Hematol. 2013;2:20–43. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cortelazzo S, Viero P, Finazzi G, D’Emilio A, Rodeghiero F, Barbui T. Incidence and risk factors for thrombotic complications in a historical cohort of 100 patients with essential thrombocythemia. J Clin Oncol. 1990;8:556–562. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.3.556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Michiels JJ, van Genderen PJ, Lindemans J, van Vliet HH. Erythromelalgic, thrombotic and hemorrhagic manifestations in 50 cases of thrombocythemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 1996;22 Suppl 1:47–56. doi: 10.3109/10428199609074360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Michiels JJ, Berneman Z, Schroyens W, Hebeda K, Bot F, Lam KH, De Raeve H. PVSG and the WHO versus the European Clinical, Molecular and Pathological (ECMP) criteria for the diagnosis, classification and staging of the myeloproliferative neoplasms. World J Hematol. 2013;2:71–90. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Passamonti F, Thiele J, Girodon F, Rumi E, Carobbio A, Gisslinger H, Kvasnicka HM, Ruggeri M, Randi ML, Gangat N, et al. A prognostic model to predict survival in 867 World Health Organization-defined essential thrombocythemia at diagnosis: a study by the International Working Group on Myelofibrosis Research and Treatment. Blood. 2012;120:1197–1201. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-01-403279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Cortelazzo S, Finazzi G, Ruggeri M, Vestri O, Galli M, Rodeghiero F, Barbui T. Hydroxyurea for patients with essential thrombocythemia and a high risk of thrombosis. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1132–1136. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199504273321704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scott LM, Scott MA, Campbell PJ, Green AR. Progenitors homozygous for the V617F mutation occur in most patients with polycythemia vera, but not essential thrombocythemia. Blood. 2006;108:2435–2437. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-04-018259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moliterno AR, Williams DM, Rogers O, Isaacs MA, Spivak JL. Phenotypic variability within the JAK2 V617F-positive MPD: roles of progenitor cell and neutrophil allele burdens. Exp Hematol. 2008;36:1480–1486. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2008.05.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Godfrey AL, Chen E, Pagano F, Ortmann CA, Silber Y, Bellosillo B, Guglielmelli P, Harrison CN, Reilly JT, Stegelmann F, et al. JAK2V617F homozygosity arises commonly and recurrently in PV and ET, but PV is characterized by expansion of a dominant homozygous subclone. Blood. 2012;120:2704–2707. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-431791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vannucchi AM, Antonioli E, Guglielmelli P, Longo G, Pancrazzi A, Ponziani V, Bogani C, Ferrini PR, Rambaldi A, Guerini V, et al. Prospective identification of high-risk polycythemia vera patients based on JAK2(V617F) allele burden. Leukemia. 2007;21:1952–1959. doi: 10.1038/sj.leu.2404854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Vannucchi AM, Antonioli E, Guglielmelli P, Rambaldi A, Barosi G, Marchioli R, Marfisi RM, Finazzi G, Guerini V, Fabris F, et al. Clinical profile of homozygous JAK2 617V& gt; F mutation in patients with polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia. Blood. 2007;110:840–846. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-12-064287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rumi E, Pietra D, Ferretti V, Klampfl T, Harutyunyan AS, Milosevic JD, Them NC, Berg T, Elena C, Casetti IC, et al. JAK2 or CALR mutation status defines subtypes of essential thrombocythemia with substantially different clinical course and outcomes. Blood. 2014;123:1544–1551. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-539098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Griesshammer M, Bangerter M, van Vliet HH, Michiels JJ. Aspirin in essential thrombocythemia: status quo and quo vadis. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1997;23:371–377. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-996111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Commandeur S. 500 MPD-ers onder de loep. Resultaten MPD enquete. Pur Sang. 2010;7:12–15. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Michiels JJ, Barbui T, Finazzi G, Fuchtman SM, Kutti J, Rain JD, Silver RT, Tefferi A, Thiele J. Diagnosis and treatment of polycythemia vera and possible future study designs of the PVSG. Leuk Lymphoma. 2000;36:239–253. doi: 10.3109/10428190009148845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Michiels JJ, Schouten HC. Artsenbrochure Myeloproliferative Disorders (MPD) Essentiaelel. Thrombocythemia, Polycythemia Vera Chronische Idiopathische Myelofibrose. Nederlandse MPD Stichting. Rotterdam: Erasmus University Rotterdam; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Commendeur S, Michiels JJ, te Boekhorst PAW, Schouten HC, Zweegman S. Quality of life, social activity and work participation of MPD patients in The Netherlands: a survey of 363 MPD patients. Dutch: The Dutch MPD Foundation; 2008. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Pearson TC, Wetherley-Mein G. Vascular occlusive episodes and venous haematocrit in primary proliferative polycythaemia. Lancet. 1978;2:1219–1222. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pearson TC. Diagnosis and classification of erythrocytoses and thrombocythoses. Bailliere’s Clin Haematol. 1998;11:695–720. doi: 10.1016/s0950-3536(98)80035-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Messinezy M, Westwood NB, El-Hemaidi I, Marsden JT, Sherwood RS, Pearson TC. Serum erythropoietin values in erythrocytoses and in primary thrombocythaemia. Br J Haematol. 2002;117:47–53. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2141.2002.03386.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Najean Y, Rain JD. Treatment of polycythemia vera: the use of hydroxyurea and pipobroman in 292 patients under the age of 65 years. Blood. 1997;90:3370–3377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kiladjian JJ, Chevret S, Dosquet C, Chomienne C, Rain JD. Treatment of polycythemia vera with hydroxyurea and pipobroman: final results of a randomized trial initiated in 1980. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:3907–3913. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2011.36.0792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kiladjian JJ, Cassinat B, Turlure P, Cambier N, Roussel M, Bellucci S, Menot ML, Massonnet G, Dutel JL, Ghomari K, et al. High molecular response rate of polycythemia vera patients treated with pegylated interferon alpha-2a. Blood. 2006;108:2037–2040. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-03-009860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mullally A, Bruedigam C, Poveromo L, Heidel FH, Purdon A, Vu T, Austin R, Heckl D, Breyfogle LJ, Kuhn CP, et al. Depletion of Jak2V617F myeloproliferative neoplasm-propagating stem cells by interferon-α in a murine model of polycythemia vera. Blood. 2013;121:3692–3702. doi: 10.1182/blood-2012-05-432989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Verstovsek S, Mesa RA, Gotlib J, Levy RS, Gupta V, DiPersio JF, Catalano JV, Deininger M, Miller C, Silver RT, et al. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of ruxolitinib for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:799–807. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Harrison C, Kiladjian JJ, Al-Ali HK, Gisslinger H, Waltzman R, Stalbovskaya V, McQuitty M, Hunter DS, Levy R, Knoops L, et al. JAK inhibition with ruxolitinib versus best available therapy for myelofibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:787–798. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1110556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vannucchi AM, Kiladjian JJ, Griesshammer M, Masszi T, Durrant S, Passamonti F, Harrison CN, Pane F, Zachee P, Mesa R, et al. Ruxolitinib versus standard therapy for the treatment of polycythemia vera. N Engl J Med. 2015;372:426–435. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1409002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Michiels JJ, Berneman Z, Schroyens W, De Raeve H. Changing concepts of diagnostic criteria of myeloproliferative disorders and the molecular etiology and classification of myeloproliferative neoplasms: from Dameshek 1950 to Vainchenker 2005 and beyond. Acta Haematol. 2015;133:36–51. doi: 10.1159/000358580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


