Abstract
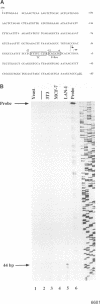
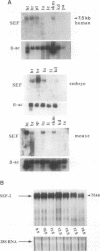
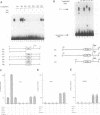
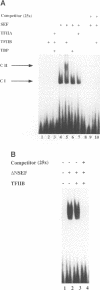
The effects of somatostatin hormones are mediated by a family of five different seven-helix transmembrane spanning receptors (SSTR1-5). The expression of the five different SSTR subtypes displays a complex temporal- and tissue-specific pattern. To investigate the molecular mechanisms controlling the different expression patterns of the SSTRs, we cloned the 5'-flanking region of the human SSTR2 gene. Characterization of the SSTR2 promoter resulted in the identification of a novel initiator element (SSTR2inr). Transcriptional activity of the SSTR2inr is dependent on the presence of a binding site (E-box) for basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors. By screening a mouse brain cDNA expression library we isolated a cDNA coding for the bHLH transcription factor SEF-2. SEF-2 binds to the E-box present in the SSTR2inr, both in vitro and in vivo and activates transcription from the SSTR2inr. A single point mutation within the E-box eliminates binding of SEF-2 and results in a complete loss of transcriptional activity of the SSTR2inr. Furthermore, DNA binding studies demonstrate that the basal transcription factor TFIIB can be tethered to the SSTR2inr through physical interaction with SEF-2. In summary, the SSTR2inr represents a novel type of initiator element that confers gene expression in the absence of a TATA-box or binding sites for other known initiator factors, like YY-1 or USF.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arteaga C. L., Osborne C. K. Growth inhibition of human breast cancer cells in vitro with an antibody against the type I somatomedin receptor. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 15;49(22):6237–6241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell T. K., Kretzner L., Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N., Weintraub H. Sequence-specific DNA binding by the c-Myc protein. Science. 1990 Nov 23;250(4984):1149–1151. doi: 10.1126/science.2251503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brazeau P., Vale W., Burgus R., Ling N., Butcher M., Rivier J., Guillemin R. Hypothalamic polypeptide that inhibits the secretion of immunoreactive pituitary growth hormone. Science. 1973 Jan 5;179(4068):77–79. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4068.77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno J. F., Xu Y., Song J., Berelowitz M. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a brain-specific somatostatin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11151–11155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruno J. F., Xu Y., Song J., Berelowitz M. Pituitary and hypothalamic somatostatin receptor subtype messenger ribonucleic acid expression in the food-deprived and diabetic rat. Endocrinology. 1994 Nov;135(5):1787–1792. doi: 10.1210/endo.135.5.7956902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buettner R., Kannan P., Imhof A., Bauer R., Yim S. O., Glockshuber R., Van Dyke M. W., Tainsky M. A. An alternatively spliced mRNA from the AP-2 gene encodes a negative regulator of transcriptional activation by AP-2. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jul;13(7):4174–4185. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.7.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao D. M., Gadbois E. L., Murray P. J., Anderson S. F., Sonu M. S., Parvin J. D., Young R. A. A mammalian SRB protein associated with an RNA polymerase II holoenzyme. Nature. 1996 Mar 7;380(6569):82–85. doi: 10.1038/380082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corneliussen B., Thornell A., Hallberg B., Grundström T. Helix-loop-helix transcriptional activators bind to a sequence in glucocorticoid response elements of retrovirus enhancers. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):6084–6093. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.6084-6093.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epelbaum J., Dournaud P., Fodor M., Viollet C. The neurobiology of somatostatin. Crit Rev Neurobiol. 1994;8(1-2):25–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood M. T., Panetta R., Robertson L. A., Liu J. L., Patel Y. C. Sequence analysis of the 5'-flanking promoter region of the human somatostatin receptor 5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Dec 30;205(3):1883–1890. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser F., Meyerhof W., Wulfsen I., Schönrock C., Richter D. Sequence analysis of the promoter region of the rat somatostatin receptor subtype 1 gene. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 30;345(2-3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00444-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henthorn P., Kiledjian M., Kadesch T. Two distinct transcription factors that bind the immunoglobulin enhancer microE5/kappa 2 motif. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):467–470. doi: 10.1126/science.2105528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javahery R., Khachi A., Lo K., Zenzie-Gregory B., Smale S. T. DNA sequence requirements for transcriptional initiator activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Jan;14(1):116–127. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann J., Smale S. T. Direct recognition of initiator elements by a component of the transcription factor IID complex. Genes Dev. 1994 Apr 1;8(7):821–829. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.7.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koleske A. J., Young R. A. The RNA polymerase II holoenzyme and its implications for gene regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Mar;20(3):113–116. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88977-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manil L., Perdereau B., Barbaroux C., Brixy F. Strong uptake of 111In-pentetreotide by an MIBG-negative, xenografted neuroblastoma. Int J Cancer. 1994 Apr 15;57(2):245–246. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910570219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maubert E., Slama A., Ciofi P., Viollet C., Tramu G., Dupouy J. P., Epelbaum J. Developmental patterns of somatostatin-receptors and somatostatin-immunoreactivity during early neurogenesis in the rat. Neuroscience. 1994 Sep;62(1):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(94)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerhof W., Wulfsen I., Schönrock C., Fehr S., Richter D. Molecular cloning of a somatostatin-28 receptor and comparison of its expression pattern with that of a somatostatin-14 receptor in rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10267–10271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson-Piercy C., Hammond P. J., Gwilliam M. E., Khandan-Nia N., Myers M. J., Ghatei M. A., Bloom S. R. Effect of a new oral somatostatin analog (SDZ CO 611) on gastric emptying, mouth to cecum transit time, and pancreatic and gut hormone release in normal male subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Feb;78(2):329–336. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.2.7906279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Carroll A. M., Lolait S. J., König M., Mahan L. C. Molecular cloning and expression of a pituitary somatostatin receptor with preferential affinity for somatostatin-28. Mol Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;42(6):939–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Murthy K. K., Escher E. E., Banville D., Spiess J., Srikant C. B. Mechanism of action of somatostatin: an overview of receptor function and studies of the molecular characterization and purification of somatostatin receptor proteins. Metabolism. 1990 Sep;39(9 Suppl 2):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(90)90214-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perlmann T., Rangarajan P. N., Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants for selective RAR and TR recognition of direct repeat HREs. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7B):1411–1422. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7b.1411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzner E., Becker P., Rolke A., Schüle R. Functional antagonism between the retinoic acid receptor and the viral transactivator BZLF1 is mediated by protein-protein interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Dec 19;92(26):12265–12269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.26.12265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rens-Domiano S., Reisine T. Biochemical and functional properties of somatostatin receptors. J Neurochem. 1992 Jun;58(6):1987–1996. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1992.tb10938.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer L., Raulf F., Bruns C., Buettner R., Hofstaedter F., Schüle R. Cloning and characterization of a fourth human somatostatin receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 1;90(9):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.9.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Carruthers C., Gutjahr T., Roeder R. G. Direct role for Myc in transcription initiation mediated by interactions with TFII-I. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):359–361. doi: 10.1038/365359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Malik S., Meisterernst M., Roeder R. G. An alternative pathway for transcription initiation involving TFII-I. Nature. 1993 Sep 23;365(6444):355–359. doi: 10.1038/365355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy A. L., Meisterernst M., Pognonec P., Roeder R. G. Cooperative interaction of an initiator-binding transcription initiation factor and the helix-loop-helix activator USF. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):245–248. doi: 10.1038/354245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seto E., Shi Y., Shenk T. YY1 is an initiator sequence-binding protein that directs and activates transcription in vitro. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):241–245. doi: 10.1038/354241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smale S. T., Baltimore D. The "initiator" as a transcription control element. Cell. 1989 Apr 7;57(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90176-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. B., Johnson K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene. 1988 Jul 15;67(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90005-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Chromatin structure and RNA polymerase II connection: implications for transcription. Cell. 1996 Jan 26;84(2):179–182. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80970-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Maniatis T. Transcriptional activation: a complex puzzle with few easy pieces. Cell. 1994 Apr 8;77(1):5–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90227-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usheva A., Shenk T. TATA-binding protein-independent initiation: YY1, TFIIB, and RNA polymerase II direct basal transcription on supercoiled template DNA. Cell. 1994 Mar 25;76(6):1115–1121. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90387-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrijzer C. P., Chen J. L., Yokomori K., Tjian R. Binding of TAFs to core elements directs promoter selectivity by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1115–1125. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80016-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Y., Bruno J. F., Berelowitz M. Characterization of the proximal promoter region of the rat somatostatin receptor gene, SSTR4. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Jan 26;206(3):935–941. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.1132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Post S. R., Wang K., Tager H. S., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and functional characterization of a family of human and mouse somatostatin receptors expressed in brain, gastrointestinal tract, and kidney. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):251–255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasuda K., Rens-Domiano S., Breder C. D., Law S. F., Saper C. B., Reisine T., Bell G. I. Cloning of a novel somatostatin receptor, SSTR3, coupled to adenylylcyclase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20422–20428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]