Abstract
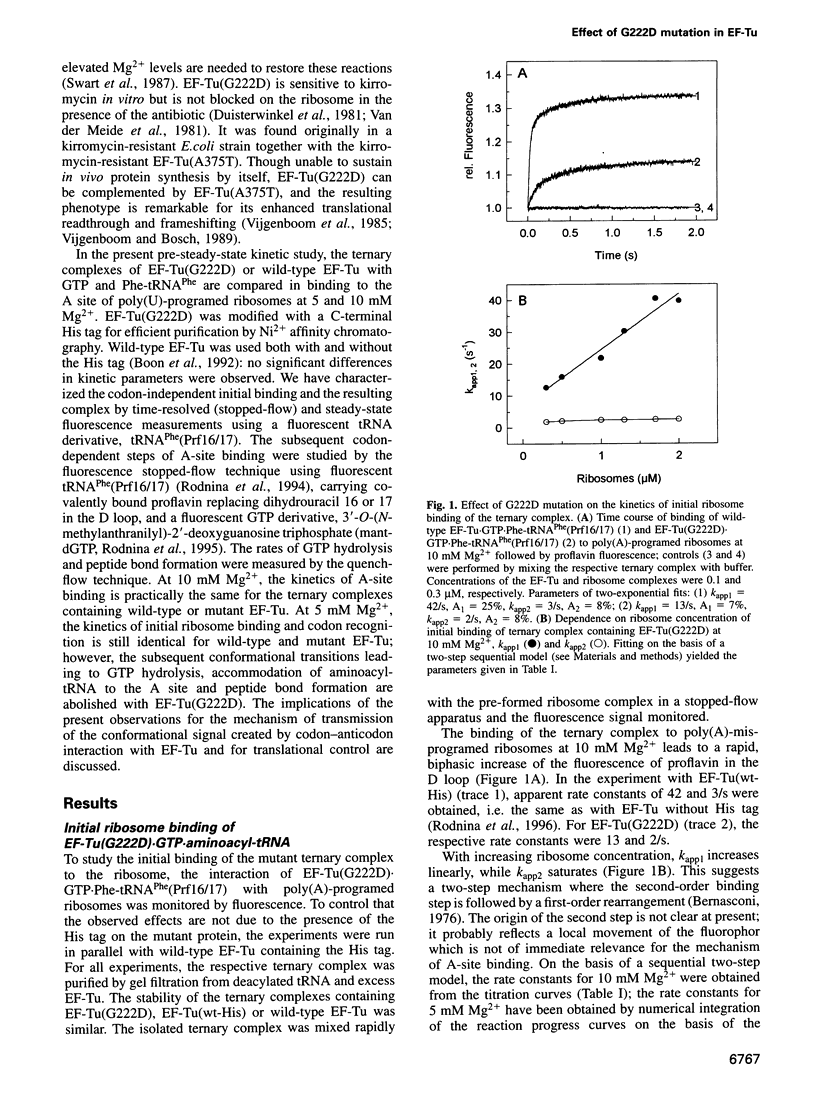
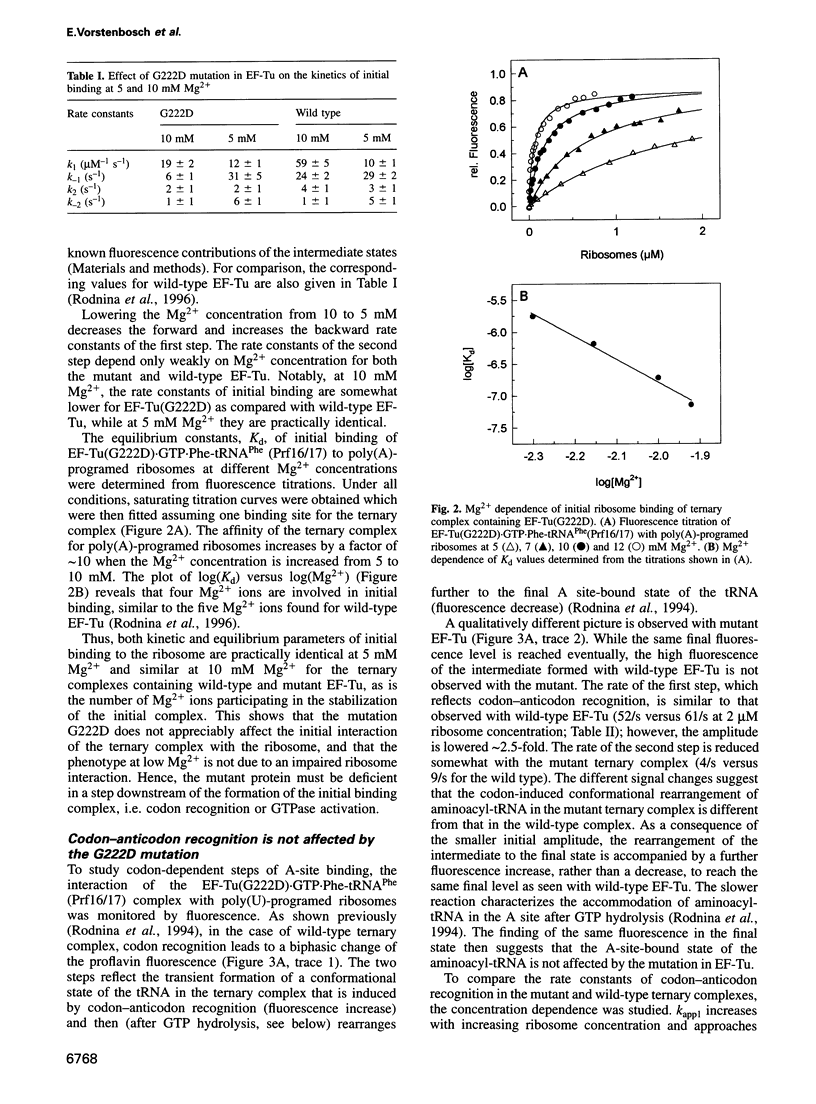
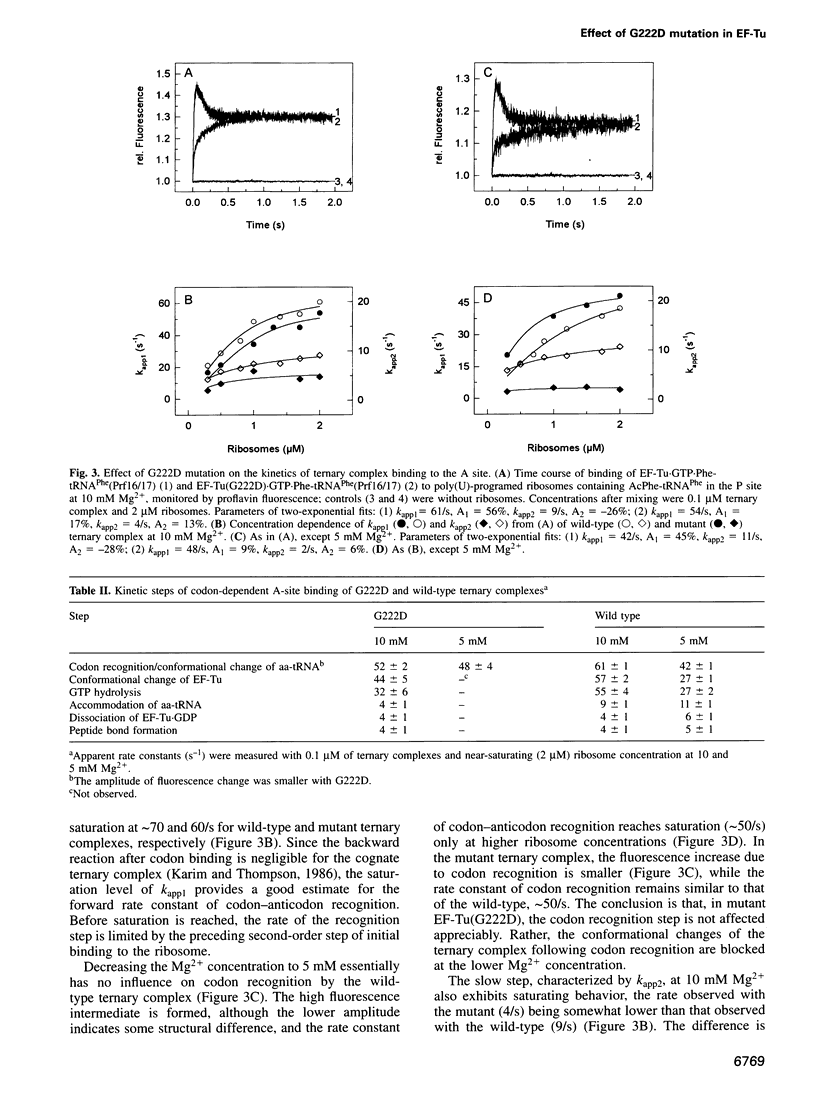
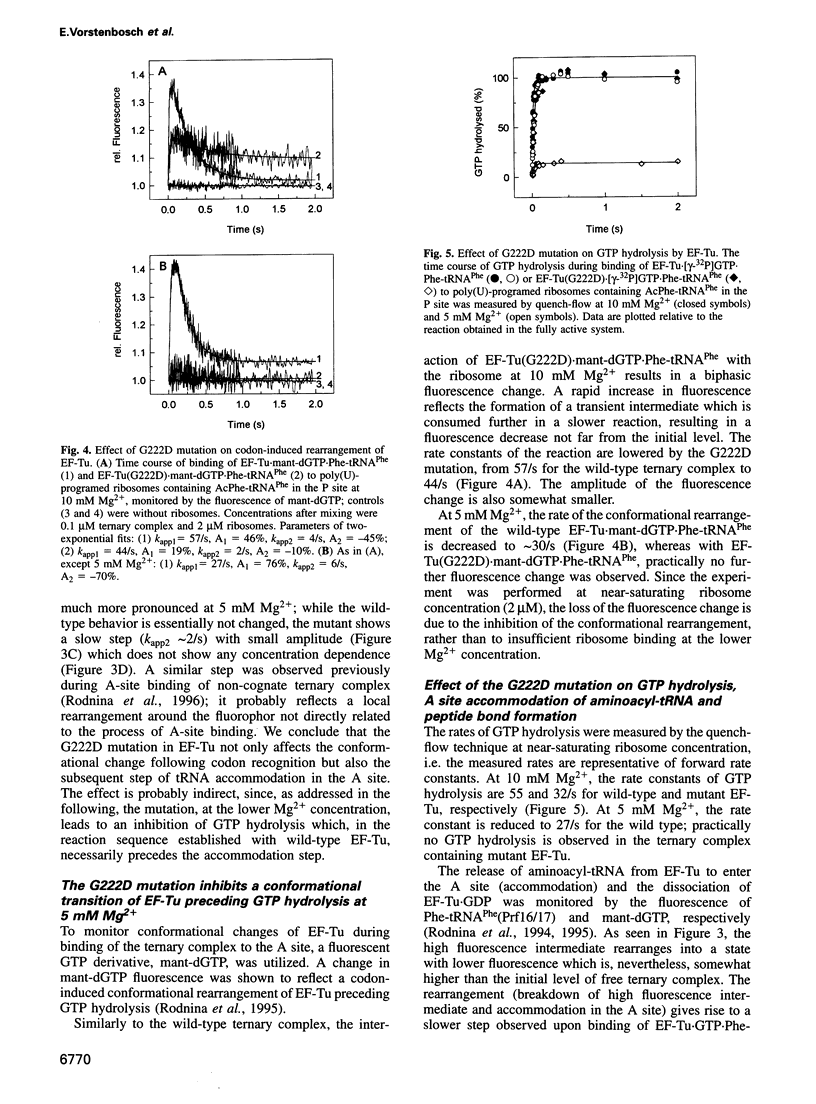
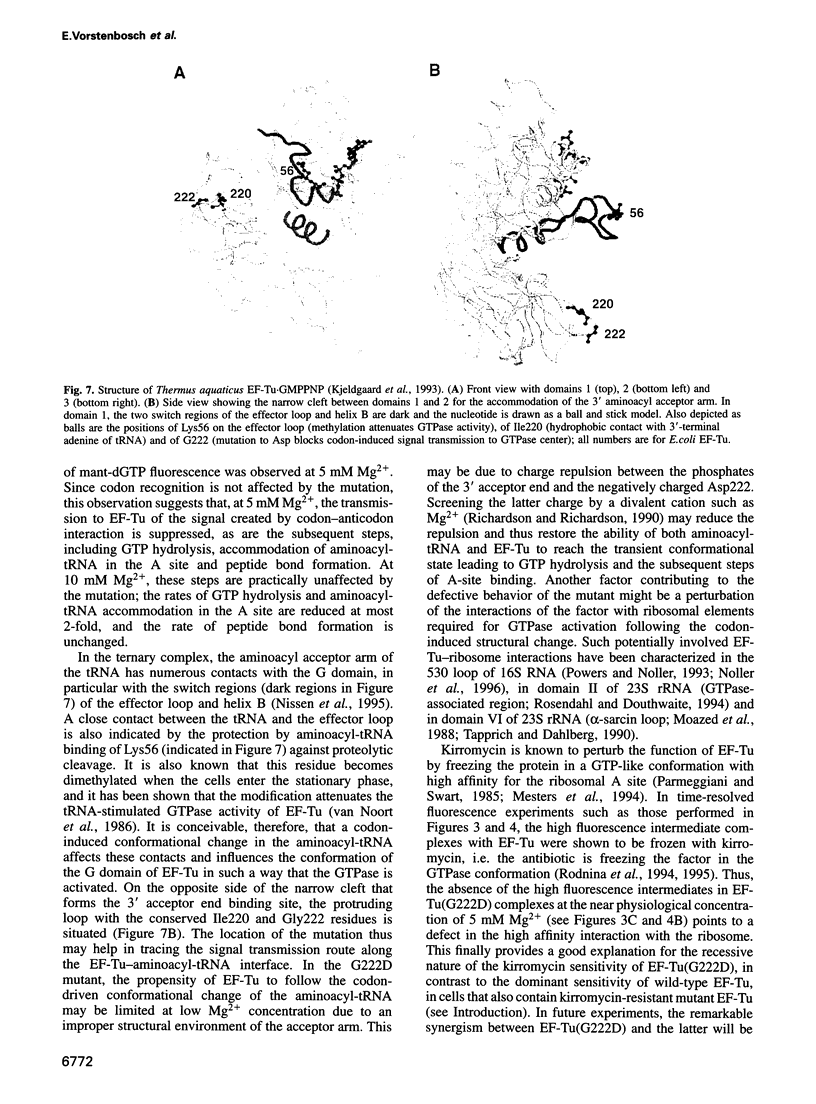
Elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) from Escherichia coli carrying the mutation G222D is unable to hydrolyze GTP on the ribosome and to sustain polypeptide synthesis at near physiological Mg2+ concentration, although the interactions with guanine nucleotides and aminoacyl-tRNA are not changed significantly. GTPase and polypeptide synthesis activities are restored by increasing the Mg2+ concentration. Here we report a pre-steady-state kinetic study of the binding of the ternary complexes of wild-type and mutant EF-Tu with Phe-tRNA(Phe) and GTP to the A site of poly(U)-programed ribosomes. The kinetic parameters of initial binding to the ribosome and subsequent codon-anticodon interaction are similar for mutant and wild-type EF-Tu, independent of the Mg2+ concentration, suggesting that the initial interaction with the ribosome is not affected by the mutation. Codon recognition following initial binding is also not affected by the mutation. The main effect of the G222D mutation is the inhibition, at low Mg2+ concentration, of codon-induced structural transitions of the tRNA and, in particular, their transmission to EF-Tu that precedes GTP hydrolysis and the subsequent steps of A-site binding. Increasing the Mg2+ concentration to 10 mM restores the complete reaction sequence of A-site binding at close to wild-type rates. The inhibition of the structural transitions is probably due to the interference of the negative charge introduced by the mutation with negative charges either of the 3' terminus of the tRNA, bound in the vicinity of the mutated amino acid in domain 2 of EF-Tu, or of the ribosome. Increasing the Mg2+ concentration appears to overcome the inhibition by screening the negative charges.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abrahams J. P., Acampo J. J., Ott G., Sprinzl M., de Graaf J. M., Talens A., Kraal B. The interaction between aminoacyl-tRNA and the mutant elongation factors Tu AR and B0. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):226–229. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90171-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberty R. A. Standard Gibbs free energy, enthalpy, and entropy changes as a function of pH and pMg for several reactions involving adenosine phosphates. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jun 25;244(12):3290–3302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berchtold H., Reshetnikova L., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Sprinzl M., Hilgenfeld R. Crystal structure of active elongation factor Tu reveals major domain rearrangements. Nature. 1993 Sep 9;365(6442):126–132. doi: 10.1038/365126a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon K., Krab I., Parmeggiani A., Bosch L., Kraal B. Substitution of Arg230 and Arg233 in Escherichia coli elongation factor Tu strongly enhances its pulvomycin resistance. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Feb 1;227(3):816–822. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boon K., Vijgenboom E., Madsen L. V., Talens A., Kraal B., Bosch L. Isolation and functional analysis of histidine-tagged elongation factor Tu. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Nov 15;210(1):177–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. F., Kjeldgaard M., la Cour T. F., Thirup S., Nyborg J. Structural determination of the functional sites of E. coli elongation factor Tu. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90167-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duisterwinkel F. J., De Graaf J. M., Schretlen P. J., Kraal B., Bosch L. A mutant elongation factor Tu which does not immobilize the ribosome upon binding of kirromycin. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):7–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duisterwinkel F. J., Kraal B., De Graaf J. M., Talens A., Bosch L., Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A., La Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Clark B. F. Specific alterations of the EF-Tu polypeptide chain considered in the light of its three-dimensional structure. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):113–120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karim A. M., Thompson R. C. Guanosine 5'-O-(3-thiotriphosphate) as an analog of GTP in protein biosynthesis. The effects of temperature and polycations on the accuracy of initial recognition of aminoacyl-tRNA ternary complexes by ribosomes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3238–3243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nissen P., Thirup S., Nyborg J. The crystal structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Thermus aquaticus in the GTP conformation. Structure. 1993 Sep 15;1(1):35–50. doi: 10.1016/0969-2126(93)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesters J. R., Zeef L. A., Hilgenfeld R., de Graaf J. M., Kraal B., Bosch L. The structural and functional basis for the kirromycin resistance of mutant EF-Tu species in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1994 Oct 17;13(20):4877–4885. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06815.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Robertson J. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):362–364. doi: 10.1038/334362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nissen P., Kjeldgaard M., Thirup S., Polekhina G., Reshetnikova L., Clark B. F., Nyborg J. Crystal structure of the ternary complex of Phe-tRNAPhe, EF-Tu, and a GTP analog. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1464–1472. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai E. F., Krengel U., Petsko G. A., Goody R. S., Kabsch W., Wittinghofer A. Refined crystal structure of the triphosphate conformation of H-ras p21 at 1.35 A resolution: implications for the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2351–2359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07409.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Sander G. Properties and regulation of the GTPase activities of elongation factors Tu and G, and of initiation factor 2. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Mar 27;35(3):129–158. doi: 10.1007/BF02357085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Swart G. W. Mechanism of action of kirromycin-like antibiotics. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1985;39:557–577. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.39.100185.003013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M. E., Schirmer N. K., Reiser C. O., Sprinzl M. Mapping the effector region in Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2876–2884. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Noller H. F. Evidence for functional interaction between elongation factor Tu and 16S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1364–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Fricke R., Kuhn L., Wintermeyer W. Codon-dependent conformational change of elongation factor Tu preceding GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome. EMBO J. 1995 Jun 1;14(11):2613–2619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07259.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Fricke R., Wintermeyer W. Transient conformational states of aminoacyl-tRNA during ribosome binding catalyzed by elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1994 Oct 11;33(40):12267–12275. doi: 10.1021/bi00206a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Pape T., Fricke R., Kuhn L., Wintermeyer W. Initial binding of the elongation factor Tu.GTP.aminoacyl-tRNA complex preceding codon recognition on the ribosome. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 12;271(2):646–652. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.2.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Wintermeyer W. GTP consumption of elongation factor Tu during translation of heteropolymeric mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):1945–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.1945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodnina M. V., Wintermeyer W. Two tRNA-binding sites in addition to A and P sites on eukaryotic ribosomes. J Mol Biol. 1992 Nov 20;228(2):450–459. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90834-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendahl G., Douthwaite S. The antibiotics micrococcin and thiostrepton interact directly with 23S rRNA nucleotides 1067A and 1095A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Feb 11;22(3):357–363. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.3.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A., Kraal B., Bosch L. Effects of the mutation glycine-222----aspartic acid on the functions of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):2047–2054. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapprich W. E., Dahlberg A. E. A single base mutation at position 2661 in E. coli 23S ribosomal RNA affects the binding of ternary complex to the ribosome. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2649–2655. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubulekas I., Hughes D. A single amino acid substitution in elongation factor Tu disrupts interaction between the ternary complex and the ribosome. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jan;175(1):240–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.1.240-250.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Noort J. M., Kraal B., Sinjorgo K. M., Persoon N. L., Johanns E. S., Bosch L. Methylation in vivo of elongation factor EF-Tu at lysine-56 decreases the rate of tRNA-dependent GTP hydrolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 3;160(3):557–561. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meide P. H., Duisterwinkel F. J., De Graaf J. M., Kraal B., Bosch L., Douglass J., Blumenthal T. Molecular properties of two mutant species of the elongation factor Tu. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jun;117(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. Translational frameshifts induced by mutant species of the polypeptide chain elongation factor Tu of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13012–13017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Vink T., Kraal B., Bosch L. Mutants of the elongation factor EF-Tu, a new class of nonsense suppressors. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):1049–1052. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03737.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintermeyer W., Zachau H. G. Fluorescent derivatives of yeast tRNAPhe. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13207.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]