Abstract
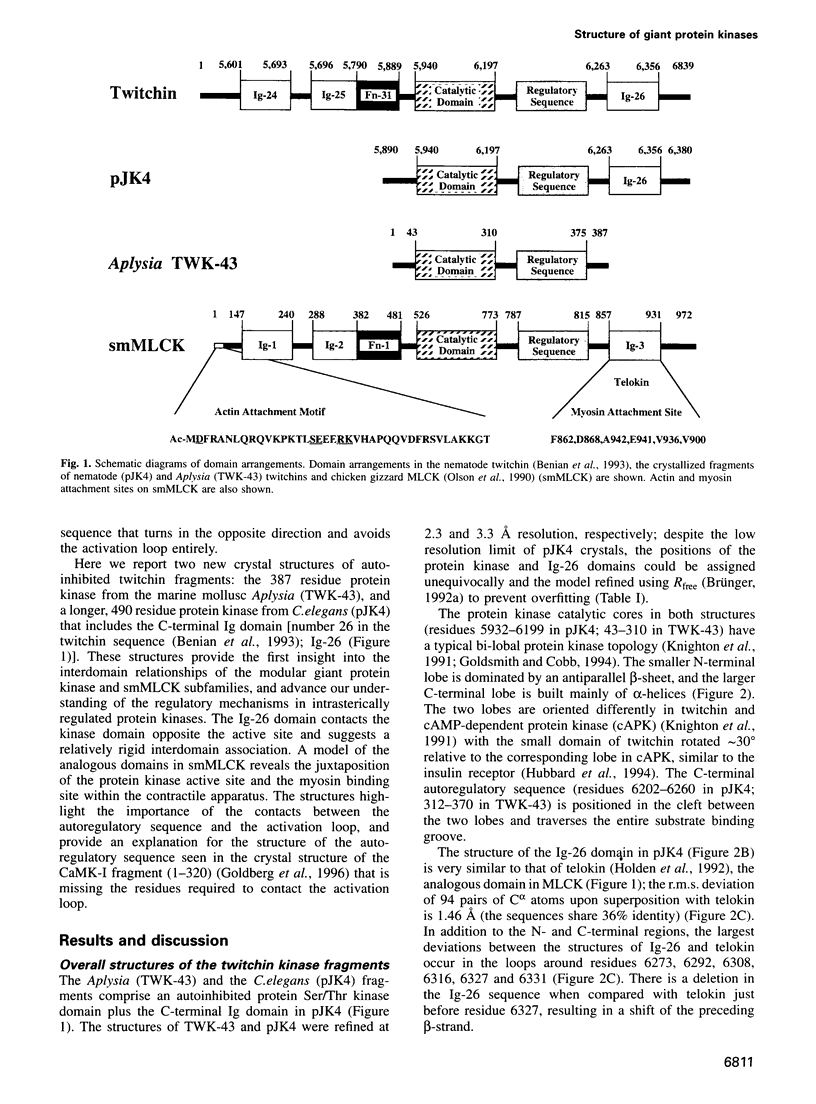
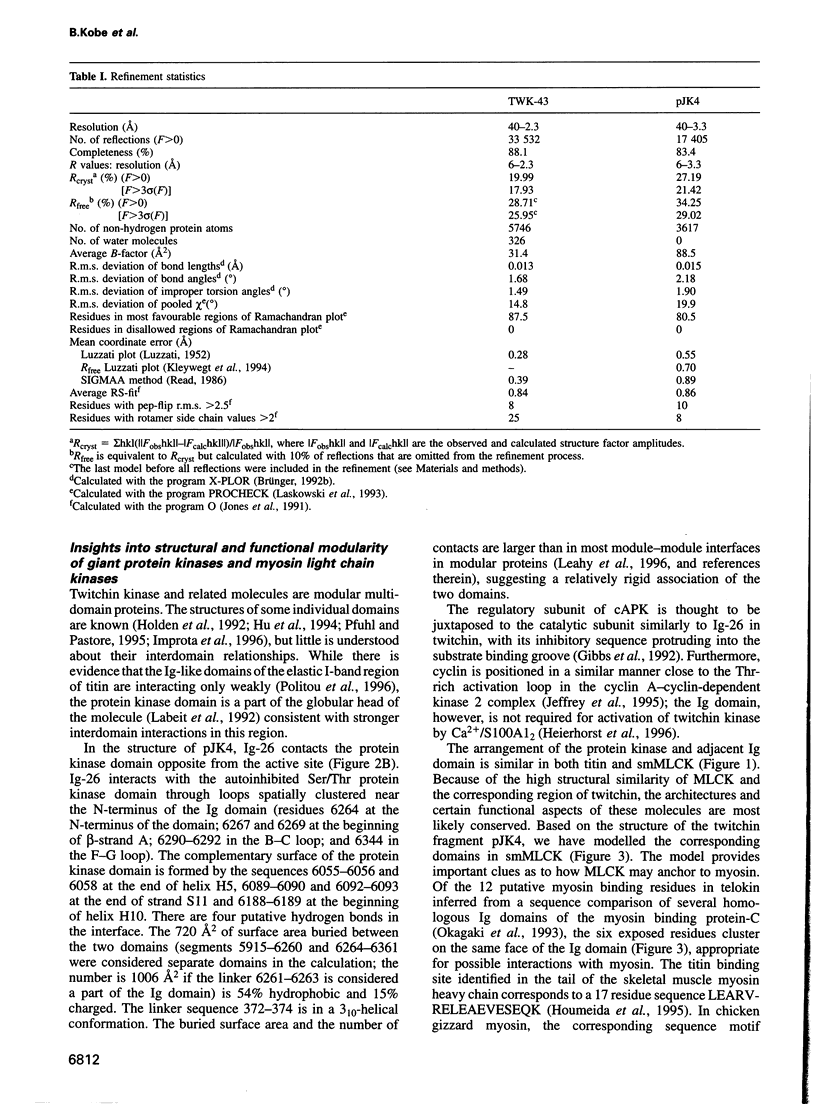
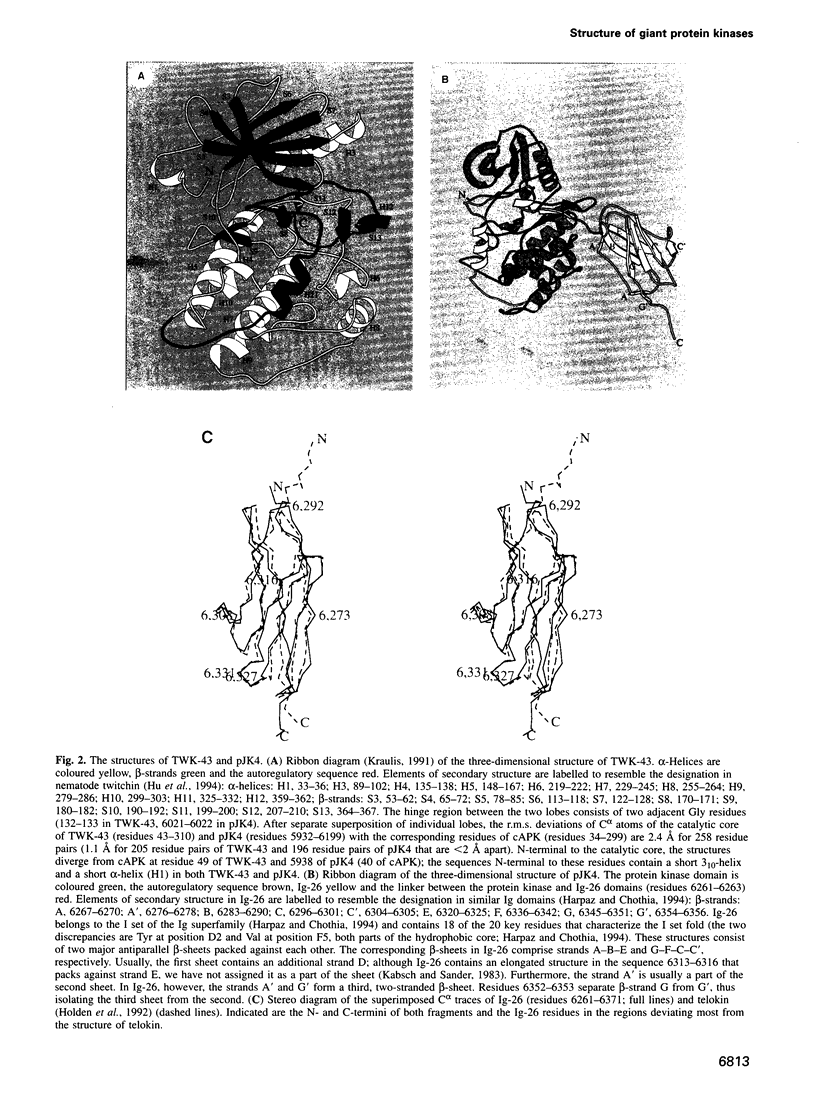
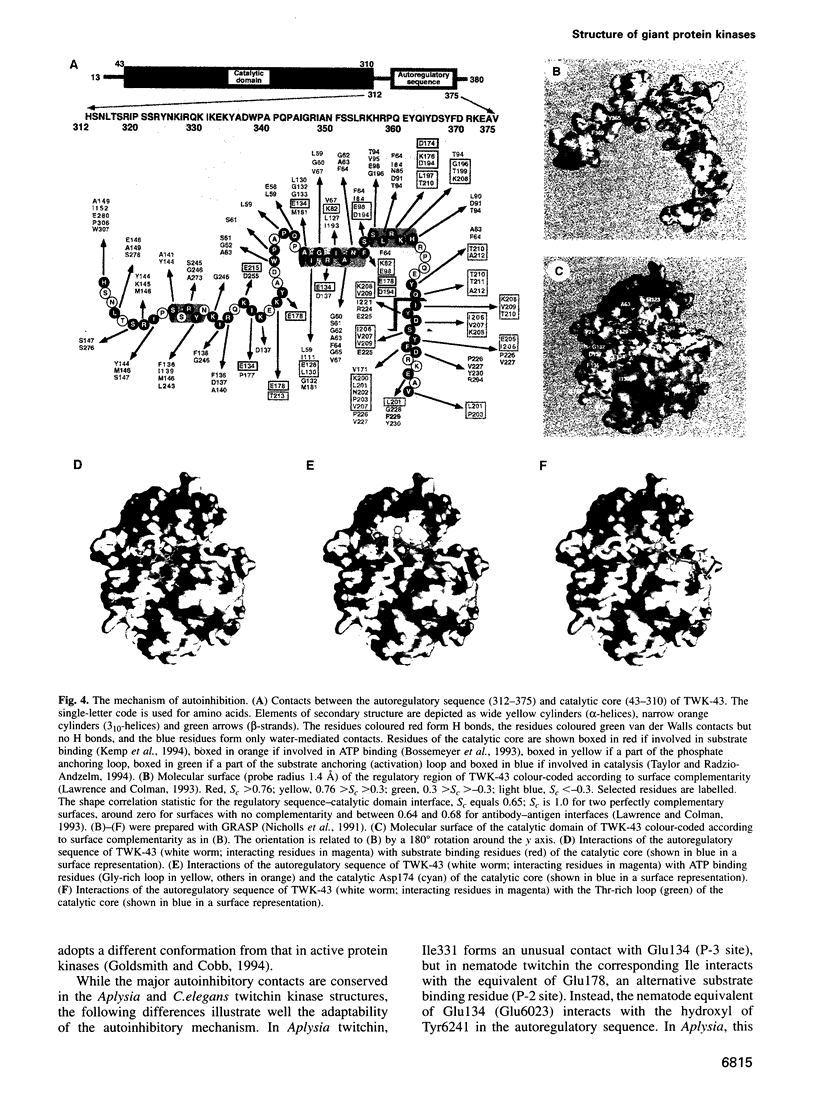
The myosin-associated giant protein kinases twitchin and titin are composed predominantly of fibronectin- and immunoglobulin-like modules. We report the crystal structures of two autoinhibited twitchin kinase fragments, one from Aplysia and a larger fragment from Caenorhabditis elegans containing an additional C-terminal immunoglobulin-like domain. The structure of the longer fragment shows that the immunoglobulin domain contacts the protein kinase domain on the opposite side from the catalytic cleft, laterally exposing potential myosin binding residues. Together, the structures reveal the cooperative interactions between the autoregulatory region and the residues from the catalytic domain involved in protein substrate binding, ATP binding, catalysis and the activation loop, and explain the differences between the observed autoinhibitory mechanism and the one found in the structure of calmodulin-dependent kinase I.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayme-Southgate A., Southgate R., Saide J., Benian G. M., Pardue M. L. Both synchronous and asynchronous muscle isoforms of projectin (the Drosophila bent locus product) contain functional kinase domains. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(3):393–403. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.3.393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babu Y. S., Sack J. S., Greenhough T. J., Bugg C. E., Means A. R., Cook W. J. Three-dimensional structure of calmodulin. Nature. 1985 May 2;315(6014):37–40. doi: 10.1038/315037a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benian G. M., Kiff J. E., Neckelmann N., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):45–50. doi: 10.1038/342045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benian G. M., L'Hernault S. W., Morris M. E. Additional sequence complexity in the muscle gene, unc-22, and its encoded protein, twitchin, of Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics. 1993 Aug;134(4):1097–1104. doi: 10.1093/genetics/134.4.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bossemeyer D., Engh R. A., Kinzel V., Ponstingl H., Huber R. Phosphotransferase and substrate binding mechanism of the cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit from porcine heart as deduced from the 2.0 A structure of the complex with Mn2+ adenylyl imidodiphosphate and inhibitor peptide PKI(5-24). EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):849–859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05725.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta M., Honeycutt T., Blumenthal D. K. The gamma-subunit of skeletal muscle phosphorylase kinase contains two noncontiguous domains that act in concert to bind calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17156–17163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibb N. J., Brown D. M., Karn J., Moerman D. G., Bolten S. L., Waterston R. H. Sequence analysis of mutations that affect the synthesis, assembly and enzymatic activity of the unc-54 myosin heavy chain of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., McLachlan A. D. Solvation energy in protein folding and binding. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):199–203. doi: 10.1038/319199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautel M., Castiglione Morelli M. A., Pfuhl M., Motta A., Pastore A. A calmodulin-binding sequence in the C-terminus of human cardiac titin kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Jun 1;230(2):752–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. S., Knighton D. R., Sowadski J. M., Taylor S. S., Zoller M. J. Systematic mutational analysis of cAMP-dependent protein kinase identifies unregulated catalytic subunits and defines regions important for the recognition of the regulatory subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 5;267(7):4806–4814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J., Nairn A. C., Kuriyan J. Structural basis for the autoinhibition of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I. Cell. 1996 Mar 22;84(6):875–887. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81066-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith E. J., Cobb M. H. Protein kinases. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1994 Dec;4(6):833–840. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(94)90264-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haribabu B., Hook S. S., Selbert M. A., Goldstein E. G., Tomhave E. D., Edelman A. M., Snyderman R., Means A. R. Human calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase I: cDNA cloning, domain structure and activation by phosphorylation at threonine-177 by calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase I kinase. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3679–3686. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00037.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harpaz Y., Chothia C. Many of the immunoglobulin superfamily domains in cell adhesion molecules and surface receptors belong to a new structural set which is close to that containing variable domains. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 13;238(4):528–539. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heierhorst J., Kobe B., Feil S. C., Parker M. W., Benian G. M., Weiss K. R., Kemp B. E. Ca2+/S100 regulation of giant protein kinases. Nature. 1996 Apr 18;380(6575):636–639. doi: 10.1038/380636a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heierhorst J., Probst W. C., Kohanski R. A., Buku A., Weiss K. R. Phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light chains by the molluscan twitchin kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Oct 15;233(2):426–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.426_2.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heierhorst J., Probst W. C., Vilim F. S., Buku A., Weiss K. R. Autophosphorylation of molluscan twitchin and interaction of its kinase domain with calcium/calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21086–21093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden H. M., Ito M., Hartshorne D. J., Rayment I. X-ray structure determination of telokin, the C-terminal domain of myosin light chain kinase, at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 5;227(3):840–851. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90226-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houmeida A., Holt J., Tskhovrebova L., Trinick J. Studies of the interaction between titin and myosin. J Cell Biol. 1995 Dec;131(6 Pt 1):1471–1481. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.6.1471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. H., Parker M. W., Lei J. Y., Wilce M. C., Benian G. M., Kemp B. E. Insights into autoregulation from the crystal structure of twitchin kinase. Nature. 1994 Jun 16;369(6481):581–584. doi: 10.1038/369581a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. R., Wei L., Ellis L., Hendrickson W. A. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the human insulin receptor. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):746–754. doi: 10.1038/372746a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikura M., Clore G. M., Gronenborn A. M., Zhu G., Klee C. B., Bax A. Solution structure of a calmodulin-target peptide complex by multidimensional NMR. Science. 1992 May 1;256(5057):632–638. doi: 10.1126/science.1585175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Improta S., Politou A. S., Pastore A. Immunoglobulin-like modules from titin I-band: extensible components of muscle elasticity. Structure. 1996 Mar 15;4(3):323–337. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(96)00036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J. Elusive affinities. Proteins. 1995 Jan;21(1):30–39. doi: 10.1002/prot.340210105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey P. D., Russo A. A., Polyak K., Gibbs E., Hurwitz J., Massagué J., Pavletich N. P. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature. 1995 Jul 27;376(6538):313–320. doi: 10.1038/376313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577–2637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamm K. E., Stull J. T. The function of myosin and myosin light chain kinase phosphorylation in smooth muscle. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1985;25:593–620. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.25.040185.003113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanoh S., Ito M., Niwa E., Kawano Y., Hartshorne D. J. Actin-binding peptide from smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1993 Aug 31;32(34):8902–8907. doi: 10.1021/bi00085a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh T., Fujisawa H. Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Kinetic studies on the interaction with substrates and calmodulin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 31;1091(2):205–212. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(91)90063-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennelly P. J., Colburn J. C., Lorenzen J., Edelman A. M., Stull J. T., Krebs E. G. Activation mechanism of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine as a probe of the MgATP-binding site of the calmodulin-bound and calmodulin-free enzyme. FEBS Lett. 1991 Jul 29;286(1-2):217–220. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80977-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleywegt G. J., Bergfors T., Senn H., Le Motte P., Gsell B., Shudo K., Jones T. A. Crystal structures of cellular retinoic acid binding proteins I and II in complex with all-trans-retinoic acid and a synthetic retinoid. Structure. 1994 Dec 15;2(12):1241–1258. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(94)00125-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleywegt G. J., Jones T. A. Where freedom is given, liberties are taken. Structure. 1995 Jun 15;3(6):535–540. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00187-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knighton D. R., Zheng J. H., Ten Eyck L. F., Ashford V. A., Xuong N. H., Taylor S. S., Sowadski J. M. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1991 Jul 26;253(5018):407–414. doi: 10.1126/science.1862342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. K., Padre R. C., Stull J. T. Intrasteric regulation of myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 14;270(28):16848–16853. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.28.16848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Gautel M., Lakey A., Trinick J. Towards a molecular understanding of titin. EMBO J. 1992 May;11(5):1711–1716. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Kolmerer B. Titins: giant proteins in charge of muscle ultrastructure and elasticity. Science. 1995 Oct 13;270(5234):293–296. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5234.293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence M. C., Colman P. M. Shape complementarity at protein/protein interfaces. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):946–950. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leahy D. J., Aukhil I., Erickson H. P. 2.0 A crystal structure of a four-domain segment of human fibronectin encompassing the RGD loop and synergy region. Cell. 1996 Jan 12;84(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81002-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lei J., Tang X., Chambers T. C., Pohl J., Benian G. M. Protein kinase domain of twitchin has protein kinase activity and an autoinhibitory region. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 19;269(33):21078–21085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüthy R., Bowie J. U., Eisenberg D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature. 1992 Mar 5;356(6364):83–85. doi: 10.1038/356083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador W. E., Means A. R., Quiocho F. A. Modulation of calmodulin plasticity in molecular recognition on the basis of x-ray structures. Science. 1993 Dec 10;262(5140):1718–1721. doi: 10.1126/science.8259515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meador W. E., Means A. R., Quiocho F. A. Target enzyme recognition by calmodulin: 2.4 A structure of a calmodulin-peptide complex. Science. 1992 Aug 28;257(5074):1251–1255. doi: 10.1126/science.1519061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohmstede C. A., Bland M. M., Merrill B. M., Sahyoun N. Relationship of genes encoding Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase Gr and calspermin: a gene within a gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okagaki T., Weber F. E., Fischman D. A., Vaughan K. T., Mikawa T., Reinach F. C. The major myosin-binding domain of skeletal muscle MyBP-C (C protein) resides in the COOH-terminal, immunoglobulin C2 motif. J Cell Biol. 1993 Nov;123(3):619–626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.3.619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. J., Pearson R. B., Needleman D. S., Hurwitz M. Y., Kemp B. E., Means A. R. Regulatory and structural motifs of chicken gizzard myosin light chain kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfuhl M., Pastore A. Tertiary structure of an immunoglobulin-like domain from the giant muscle protein titin: a new member of the I set. Structure. 1995 Apr 15;3(4):391–401. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(01)00170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfuhl M., Winder S. J., Castiglione Morelli M. A., Labeit S., Pastore A. Correlation between conformational and binding properties of nebulin repeats. J Mol Biol. 1996 Mar 29;257(2):367–384. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Politou A. S., Gautel M., Improta S., Vangelista L., Pastore A. The elastic I-band region of titin is assembled in a "modular" fashion by weakly interacting Ig-like domains. J Mol Biol. 1996 Feb 2;255(4):604–616. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1996.0050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts B. C., Smith J., Akke M., Macke T. J., Okazaki K., Hidaka H., Case D. A., Chazin W. J. The structure of calcyclin reveals a novel homodimeric fold for S100 Ca(2+)-binding proteins. Nat Struct Biol. 1995 Sep;2(9):790–796. doi: 10.1038/nsb0995-790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice L. M., Brünger A. T. Torsion angle dynamics: reduced variable conformational sampling enhances crystallographic structure refinement. Proteins. 1994 Aug;19(4):277–290. doi: 10.1002/prot.340190403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schäfer B. W., Heizmann C. W. The S100 family of EF-hand calcium-binding proteins: functions and pathology. Trends Biochem Sci. 1996 Apr;21(4):134–140. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(96)80167-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirinsky V. P., Vorotnikov A. V., Birukov K. G., Nanaev A. K., Collinge M., Lukas T. J., Sellers J. R., Watterson D. M. A kinase-related protein stabilizes unphosphorylated smooth muscle myosin minifilaments in the presence of ATP. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16578–16583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J. Titin and nebulin: protein rulers in muscle? Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Oct;19(10):405–409. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R. H., Thomson J. N., Brenner S. Mutants with altered muscle structure of Caenorhabditis elegans. Dev Biol. 1980 Jun 15;77(2):271–302. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90475-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokokura H., Picciotto M. R., Nairn A. C., Hidaka H. The regulatory region of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase I contains closely associated autoinhibitory and calmodulin-binding domains. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23851–23859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]