Abstract
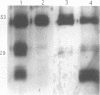
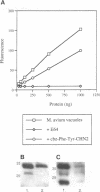
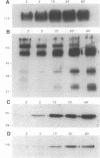
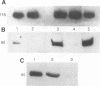
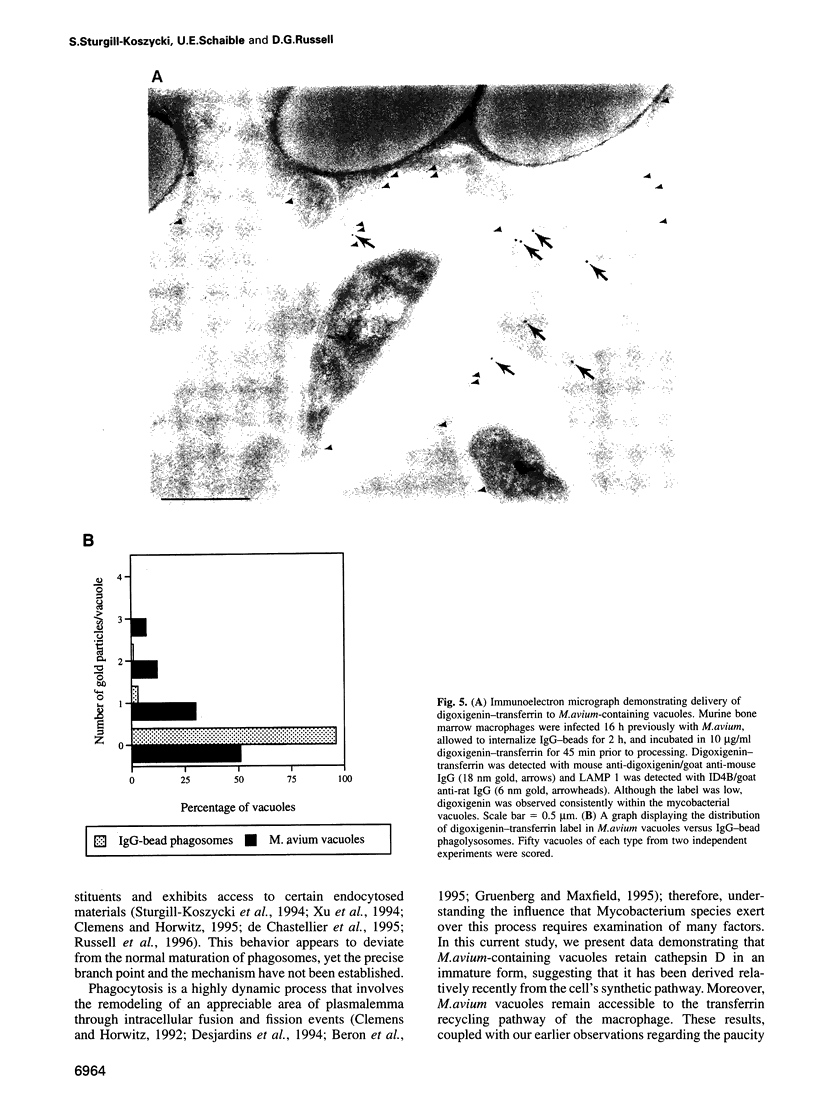
The success of Mycobacterium as a pathogen hinges on its ability to modulate its intracellular environment. Mycobacterium avium reside in vacuoles with limited proteolytic activity, maintain cathepsin D in an immature form and remain accessible to internalized transferrin. Artificial acidification of isolated phagosomes facilitated processing of cathepsin D, demonstrating that pH alone limits proteolysis in these vacuoles. Moreover, analysis of IgG-bead phagosomes at early time points during their formation indicates that these phagosomes also acquire LAMP 1 and cathepsin D prior to the accumulation of proton-ATPases, and are transiently accessible to sorting endosomes. This suggests that the anomolous distribution of endosomal proteins in M. avium-containing vacuoles results from their arrested differentiation in an early transitional stage through which all phagosomes pass.
Full text
PDF
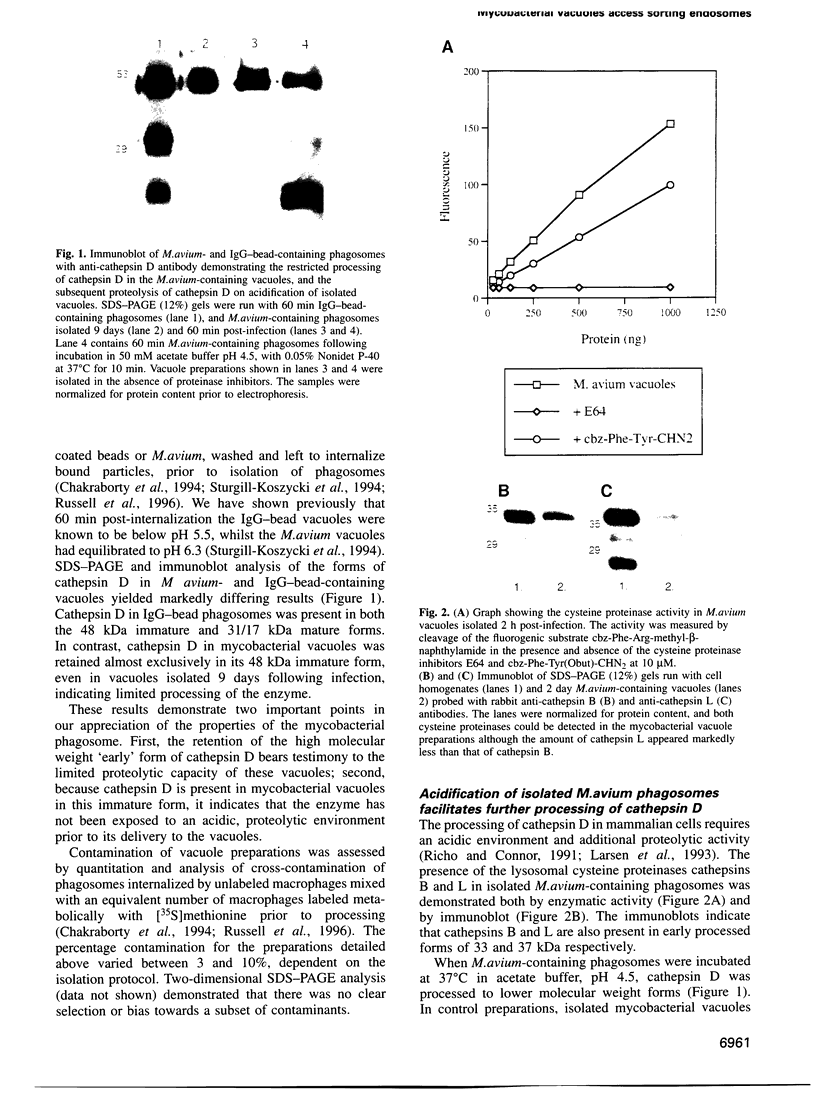
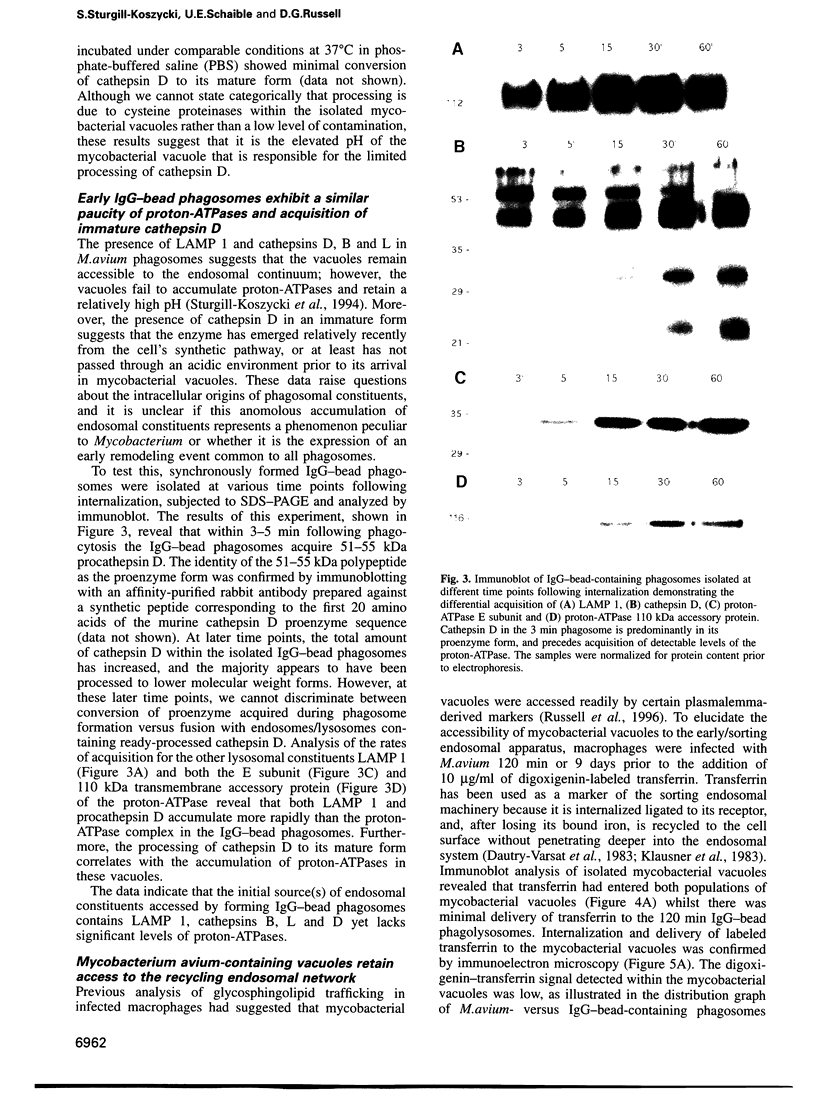





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berón W., Alvarez-Dominguez C., Mayorga L., Stahl P. D. Membrane trafficking along the phagocytic pathway. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Mar;5(3):100–104. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88958-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty P., Sturgill-Koszycki S., Russell D. G. Isolation and characterization of pathogen-containing phagosomes. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;45:261–276. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61856-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. W., Cha Y., Yuksel K. U., Gracy R. W., August J. T. Isolation and sequencing of a cDNA clone encoding lysosomal membrane glycoprotein mouse LAMP-1. Sequence similarity to proteins bearing onco-differentiation antigens. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8754–8758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clague M. J., Urbé S., Aniento F., Gruenberg J. Vacuolar ATPase activity is required for endosomal carrier vesicle formation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):21–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens D. L., Horwitz M. A. Characterization of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis phagosome and evidence that phagosomal maturation is inhibited. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):257–270. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens D. L., Horwitz M. A. Membrane sorting during phagocytosis: selective exclusion of major histocompatibility complex molecules but not complement receptor CR3 during conventional and coiling phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1992 May 1;175(5):1317–1326. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.5.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dautry-Varsat A., Ciechanover A., Lodish H. F. pH and the recycling of transferrin during receptor-mediated endocytosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2258–2262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delbrück R., Desel C., von Figura K., Hille-Rehfeld A. Proteolytic processing of cathepsin D in prelysosomal organelles. Eur J Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;64(1):7–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins M. Biogenesis of phagolysosomes: the 'kiss and run' hypothesis. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 May;5(5):183–186. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88989-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins M., Huber L. A., Parton R. G., Griffiths G. Biogenesis of phagolysosomes proceeds through a sequential series of interactions with the endocytic apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;124(5):677–688. doi: 10.1083/jcb.124.5.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diedrich J. F., Staskus K. A., Retzel E. F., Haase A. T. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding mouse cathepsin D. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7184–7184. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R., Ellinger A., Pavelka M., Mellman I., Klapper H. Rat liver endocytic coated vesicles do not exhibit ATP-dependent acidification in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4811–4815. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh R. N., Maxfield F. R. Evidence for nonvectorial, retrograde transferrin trafficking in the early endosomes of HEp2 cells. J Cell Biol. 1995 Feb;128(4):549–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.128.4.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorvel J. P., Chavrier P., Zerial M., Gruenberg J. rab5 controls early endosome fusion in vitro. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90316-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Nanda A., Lukacs G., Rotstein O. V-ATPases in phagocytic cells. J Exp Biol. 1992 Nov;172:179–192. doi: 10.1242/jeb.172.1.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J., Maxfield F. R. Membrane transport in the endocytic pathway. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;7(4):552–563. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grusby M. J., Mitchell S. C., Glimcher L. H. Molecular cloning of mouse cathepsin D. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):4008–4008. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.4008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Armstrong J. A., Brown C. A., Draper P. Ultrastructural study of the behavior of macrophages toward parasitic mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.803-807.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Armstrong J. A. Strain virulence and the lysosomal response in macrophages infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1974 Oct;10(4):742–746. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.4.742-746.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R. Ammonium chloride, an inhibitor of phagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages, concurrently induces phagosome-endosome fusion, and opens a novel pathway: studies of a pathogenic mycobacterium and a nonpathogenic yeast. J Exp Med. 1991 Oct 1;174(4):881–889. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R., Gordon A. H., Sullivan K. H. Inhibition of phagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages by certain mycobacteria can be explained by inhibition of lysosomal movements observed after phagocytosis. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):933–946. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.933. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R. Manipulations of the phagosome-lysosome fusion response in cultured macrophages. Enhancement of fusion by chloroquine and other amines. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Jul;114(2):486–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90516-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. S., Dunn K. W., Pytowski B., McGraw T. E. Endosome acidification and receptor trafficking: bafilomycin A1 slows receptor externalization by a mechanism involving the receptor's internalization motif. Mol Biol Cell. 1993 Dec;4(12):1251–1266. doi: 10.1091/mbc.4.12.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausner R. D., Ashwell G., van Renswoude J., Harford J. B., Bridges K. R. Binding of apotransferrin to K562 cells: explanation of the transferrin cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2263–2266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen L. B., Boisen A., Petersen T. E. Procathepsin D cannot autoactivate to cathepsin D at acid pH. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 15;319(1-2):54–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80036-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig T., Griffiths G., Hoflack B. Distribution of newly synthesized lysosomal enzymes in the endocytic pathway of normal rat kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1991 Dec;115(6):1561–1572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.6.1561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayorga L. S., Bertini F., Stahl P. D. Fusion of newly formed phagosomes with endosomes in intact cells and in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6511–6517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough K. A., Kress Y. Cytotoxicity for lung epithelial cells is a virulence-associated phenotype of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Infect Immun. 1995 Dec;63(12):4802–4811. doi: 10.1128/iai.63.12.4802-4811.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellman I. The importance of being acid: the role of acidification in intracellular membrane traffic. J Exp Biol. 1992 Nov;172:39–45. doi: 10.1242/jeb.172.1.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanda A., Gukovskaya A., Tseng J., Grinstein S. Activation of vacuolar-type proton pumps by protein kinase C. Role in neutrophil pH regulation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 15;267(32):22740–22746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan C. F., Hibbs J. B., Jr Role of nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):65–70. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90079-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh Y. K., Straubinger R. M. Intracellular fate of Mycobacterium avium: use of dual-label spectrofluorometry to investigate the influence of bacterial viability and opsonization on phagosomal pH and phagosome-lysosome interaction. Infect Immun. 1996 Jan;64(1):319–325. doi: 10.1128/iai.64.1.319-325.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orme I. M., Furney S. K., Skinner P. S., Roberts A. D., Brennan P. J., Russell D. G., Shiratsuchi H., Ellner J. J., Weiser W. Y. Inhibition of growth of Mycobacterium avium in murine and human mononuclear phagocytes by migration inhibitory factor. Infect Immun. 1993 Jan;61(1):338–342. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.1.338-342.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- Pitt A., Mayorga L. S., Stahl P. D., Schwartz A. L. Alterations in the protein composition of maturing phagosomes. J Clin Invest. 1992 Nov;90(5):1978–1983. doi: 10.1172/JCI116077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijnboutt S., Stoorvogel W., Geuze H. J., Strous G. J. Identification of subcellular compartments involved in biosynthetic processing of cathepsin D. J Biol Chem. 1992 Aug 5;267(22):15665–15672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrer J., Schweizer A., Russell D., Kornfeld S. The targeting of Lamp1 to lysosomes is dependent on the spacing of its cytoplasmic tail tyrosine sorting motif relative to the membrane. J Cell Biol. 1996 Feb;132(4):565–576. doi: 10.1083/jcb.132.4.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Dant J., Sturgill-Koszycki S. Mycobacterium avium- and Mycobacterium tuberculosis-containing vacuoles are dynamic, fusion-competent vesicles that are accessible to glycosphingolipids from the host cell plasmalemma. J Immunol. 1996 Jun 15;156(12):4764–4773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G. Immunoelectron microscopy of endosomal trafficking in macrophages infected with microbial pathogens. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;45:277–288. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61857-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell D. G., Xu S., Chakraborty P. Intracellular trafficking and the parasitophorous vacuole of Leishmania mexicana-infected macrophages. J Cell Sci. 1992 Dec;103(Pt 4):1193–1210. doi: 10.1242/jcs.103.4.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S., Fuchs R., Kielian M., Helenius A., Mellman I. Acidification of endosome subpopulations in wild-type Chinese hamster ovary cells and temperature-sensitive acidification-defective mutants. J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;108(4):1291–1300. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.4.1291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley L. D., Franzblau S. G., Krahenbuhl J. L. Intracellular fate of Mycobacterium leprae in normal and activated mouse macrophages. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):680–685. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.680-685.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill-Koszycki S., Schlesinger P. H., Chakraborty P., Haddix P. L., Collins H. L., Fok A. K., Allen R. D., Gluck S. L., Heuser J., Russell D. G. Lack of acidification in Mycobacterium phagosomes produced by exclusion of the vesicular proton-ATPase. Science. 1994 Feb 4;263(5147):678–681. doi: 10.1126/science.8303277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie X. S., Crider B. P., Ma Y. M., Stone D. K. Role of a 50-57-kDa polypeptide heterodimer in the function of the clathrin-coated vesicle proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1994 Oct 14;269(41):25809–25815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S., Cooper A., Sturgill-Koszycki S., van Heyningen T., Chatterjee D., Orme I., Allen P., Russell D. G. Intracellular trafficking in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and Mycobacterium avium-infected macrophages. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2568–2578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chastellier C., Fréhel C., Offredo C., Skamene E. Implication of phagosome-lysosome fusion in restriction of Mycobacterium avium growth in bone marrow macrophages from genetically resistant mice. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3775–3784. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3775-3784.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Chastellier C., Lang T., Thilo L. Phagocytic processing of the macrophage endoparasite, Mycobacterium avium, in comparison to phagosomes which contain Bacillus subtilis or latex beads. Eur J Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;68(2):167–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Weert A. W., Dunn K. W., Geuze H. J., Maxfield F. R., Stoorvogel W. Transport from late endosomes to lysosomes, but not sorting of integral membrane proteins in endosomes, depends on the vacuolar proton pump. J Cell Biol. 1995 Aug;130(4):821–834. doi: 10.1083/jcb.130.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]