Abstract
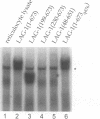
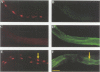
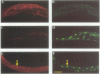
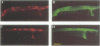
In Caenorhabditis elegans, the GLP-1 receptor acts with a downstream transcriptional regulator, LAG-1, to mediate intercellular signaling. GLP-1 and LAG-1 are homologs of Drosophila Notch and Su(H) respectively. Here, we investigate the functions of two regions of the GLP-1 intracellular domain: the ANK repeat domain, which includes six cdc10/ankyrin repeats plus flanking amino acids, and the RAM domain, which spans approximately 60 amino acids just inside the transmembrane domain. First, we demonstrate that both ANK and RAM domains interact with the LAG-1 transcription factor. The interaction between the ANK domain and LAG-1 is only observed in nematodes by a co-localization assay and, therefore, may be either direct or indirect. By contrast, the interaction between the RAM domain and LAG-1 is likely to be direct, since it is observed by co-precipitation of the proteins in vitro as well as by yeast two-hybrid experiments. Second, we demonstrate that the RAM domain, when expressed in nematodes without a functional ANK repeat domain, does not mimic the unregulated receptor in directing cell fates or interfere with signaling by endogenous components. Finally, we show in yeast that the ANK repeats are strong transcriptional activators. Furthermore, missense mutations that eliminate receptor activity also abolish transcriptional activation by the GLP-1 ANK repeats in yeast. We speculate that one possible function for the ANK repeat domain is to act as a transcriptional co-activator with LAG-1.
Full text
PDF



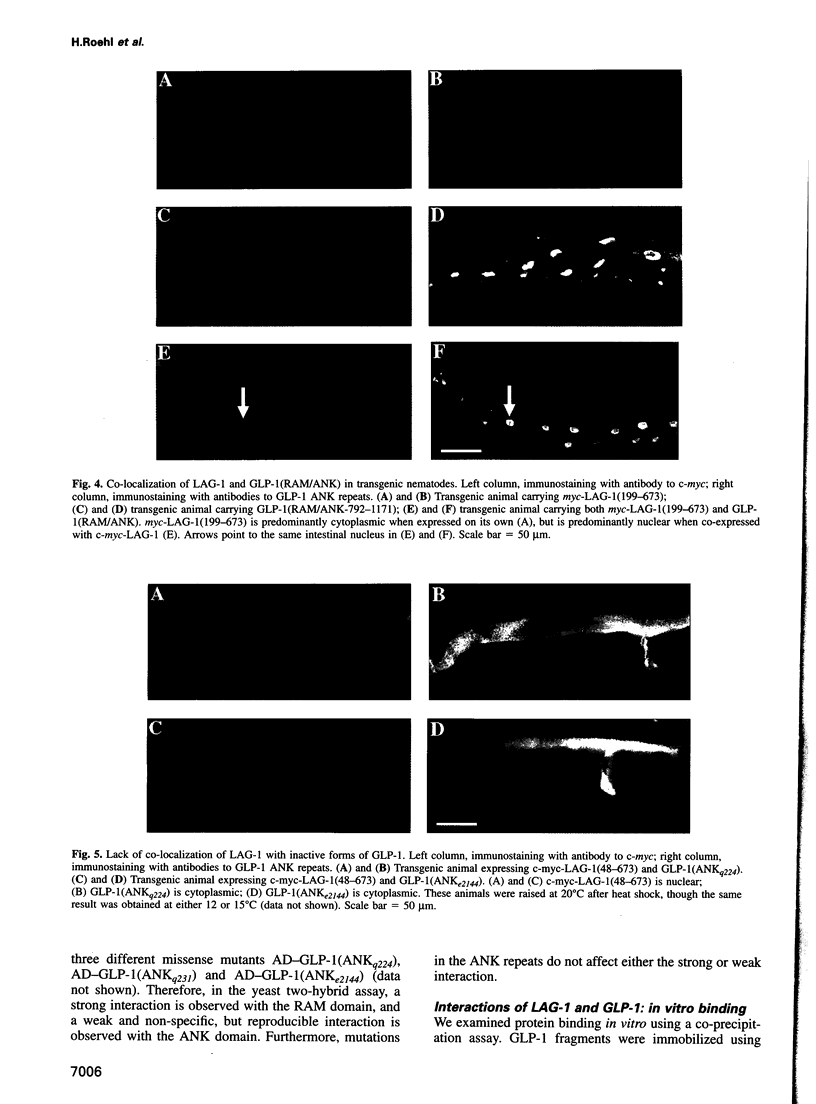

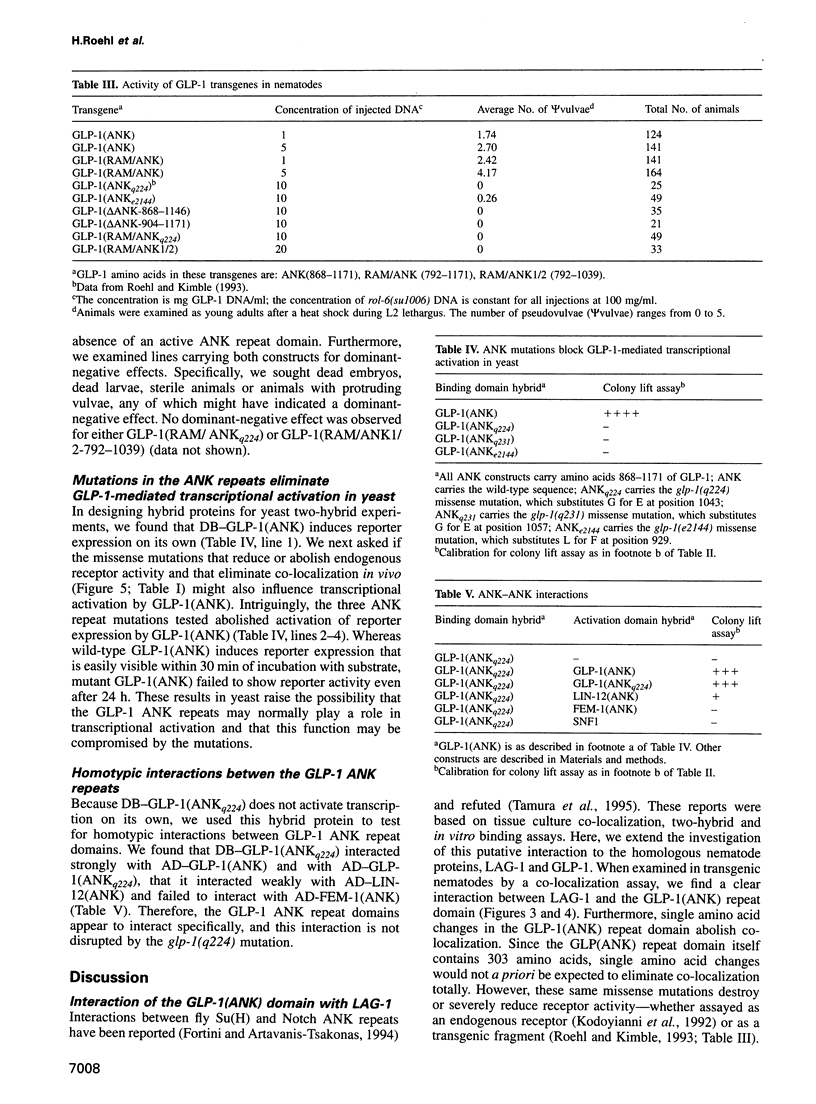




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artavanis-Tsakonas S., Matsuno K., Fortini M. E. Notch signaling. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):225–232. doi: 10.1126/science.7716513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aster J., Pear W., Hasserjian R., Erba H., Davi F., Luo B., Scott M., Baltimore D., Sklar J. Functional analysis of the TAN-1 gene, a human homolog of Drosophila notch. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1994;59:125–136. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1994.059.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Austin J., Kimble J. glp-1 is required in the germ line for regulation of the decision between mitosis and meiosis in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):589–599. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90128-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. M., Posakony J. W. Suppressor of hairless directly activates transcription of enhancer of split complex genes in response to Notch receptor activity. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 1;9(21):2609–2622. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen S., Kodoyianni V., Bosenberg M., Friedman L., Kimble J. lag-1, a gene required for lin-12 and glp-1 signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans, is homologous to human CBF1 and Drosophila Su(H). Development. 1996 May;122(5):1373–1383. doi: 10.1242/dev.122.5.1373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung C. N., Hamaguchi Y., Honjo T., Kawaichi M. Site-directed mutagenesis study on DNA binding regions of the mouse homologue of Suppressor of Hairless, RBP-J kappa. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Aug 11;22(15):2938–2944. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.15.2938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crittenden S. L., Troemel E. R., Evans T. C., Kimble J. GLP-1 is localized to the mitotic region of the C. elegans germ line. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2901–2911. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diederich R. J., Matsuno K., Hing H., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Cytosolic interaction between deltex and Notch ankyrin repeats implicates deltex in the Notch signaling pathway. Development. 1994 Mar;120(3):473–481. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.3.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfee T., Becherer K., Chen P. L., Yeh S. H., Yang Y., Kilburn A. E., Lee W. H., Elledge S. J. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):555–569. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Song O. A novel genetic system to detect protein-protein interactions. Nature. 1989 Jul 20;340(6230):245–246. doi: 10.1038/340245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney M., Ruvkun G. The unc-86 gene product couples cell lineage and cell identity in C. elegans. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):895–905. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The suppressor of hairless protein participates in notch receptor signaling. Cell. 1994 Oct 21;79(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90196-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fortini M. E., Rebay I., Caron L. A., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. An activated Notch receptor blocks cell-fate commitment in the developing Drosophila eye. Nature. 1993 Oct 7;365(6446):555–557. doi: 10.1038/365555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gietz D., St Jean A., Woods R. A., Schiestl R. H. Improved method for high efficiency transformation of intact yeast cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1425–1425. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I. S., Sternberg P. W., Horvitz H. R. The lin-12 locus specifies cell fates in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman S. R., Johannsen E., Tong X., Yalamanchili R., Kieff E. The Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen 2 transactivator is directed to response elements by the J kappa recombination signal binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7568–7572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson S. T., Gao D., Lambie E. J., Kimble J. lag-2 may encode a signaling ligand for the GLP-1 and LIN-12 receptors of C. elegans. Development. 1994 Oct;120(10):2913–2924. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.10.2913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henkel T., Ling P. D., Hayward S. D., Peterson M. G. Mediation of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2 transactivation by recombination signal-binding protein J kappa. Science. 1994 Jul 1;265(5168):92–95. doi: 10.1126/science.8016657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh J. J., Henkel T., Salmon P., Robey E., Peterson M. G., Hayward S. D. Truncated mammalian Notch1 activates CBF1/RBPJk-repressed genes by a mechanism resembling that of Epstein-Barr virus EBNA2. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;16(3):952–959. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.3.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarriault S., Brou C., Logeat F., Schroeter E. H., Kopan R., Israel A. Signalling downstream of activated mammalian Notch. Nature. 1995 Sep 28;377(6547):355–358. doi: 10.1038/377355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansen K. M., Fehon R. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. The notch gene product is a glycoprotein expressed on the cell surface of both epidermal and neuronal precursor cells during Drosophila development. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2427–2440. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. S., Raines R. T. Ribonuclease S-peptide as a carrier in fusion proteins. Protein Sci. 1993 Mar;2(3):348–356. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodoyianni V., Maine E. M., Kimble J. Molecular basis of loss-of-function mutations in the glp-1 gene of Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol Biol Cell. 1992 Nov;3(11):1199–1213. doi: 10.1091/mbc.3.11.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooh P. J., Fehon R. G., Muskavitch M. A. Implications of dynamic patterns of Delta and Notch expression for cellular interactions during Drosophila development. Development. 1993 Feb;117(2):493–507. doi: 10.1242/dev.117.2.493. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopan R., Nye J. S., Weintraub H. The intracellular domain of mouse Notch: a constitutively activated repressor of myogenesis directed at the basic helix-loop-helix region of MyoD. Development. 1994 Sep;120(9):2385–2396. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.9.2385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopan R., Schroeter E. H., Weintraub H., Nye J. S. Signal transduction by activated mNotch: importance of proteolytic processing and its regulation by the extracellular domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 20;93(4):1683–1688. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.4.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambie E. J., Kimble J. Two homologous regulatory genes, lin-12 and glp-1, have overlapping functions. Development. 1991 May;112(1):231–240. doi: 10.1242/dev.112.1.231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecourtois M., Schweisguth F. The neurogenic suppressor of hairless DNA-binding protein mediates the transcriptional activation of the enhancer of split complex genes triggered by Notch signaling. Genes Dev. 1995 Nov 1;9(21):2598–2608. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.21.2598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieber T., Kidd S., Alcamo E., Corbin V., Young M. W. Antineurogenic phenotypes induced by truncated Notch proteins indicate a role in signal transduction and may point to a novel function for Notch in nuclei. Genes Dev. 1993 Oct;7(10):1949–1965. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.10.1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mango S. E., Maine E. M., Kimble J. Carboxy-terminal truncation activates glp-1 protein to specify vulval fates in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1991 Aug 29;352(6338):811–815. doi: 10.1038/352811a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsunami N., Hamaguchi Y., Yamamoto Y., Kuze K., Kangawa K., Matsuo H., Kawaichi M., Honjo T. A protein binding to the J kappa recombination sequence of immunoglobulin genes contains a sequence related to the integrase motif. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):934–937. doi: 10.1038/342934a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mello C. C., Kramer J. M., Stinchcomb D., Ambros V. Efficient gene transfer in C.elegans: extrachromosomal maintenance and integration of transforming sequences. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3959–3970. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04966.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. S., Kopan R., Axel R. An activated Notch suppresses neurogenesis and myogenesis but not gliogenesis in mammalian cells. Development. 1994 Sep;120(9):2421–2430. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.9.2421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nye J. S., Kopan R. Developmental signaling. Vertebrate ligands for Notch. Curr Biol. 1995 Sep 1;5(9):966–969. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priess J. R., Schnabel H., Schnabel R. The glp-1 locus and cellular interactions in early C. elegans embryos. Cell. 1987 Nov 20;51(4):601–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90129-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebay I., Fehon R. G., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Specific truncations of Drosophila Notch define dominant activated and dominant negative forms of the receptor. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90423-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roehl H., Kimble J. Control of cell fate in C. elegans by a GLP-1 peptide consisting primarily of ankyrin repeats. Nature. 1993 Aug 12;364(6438):632–635. doi: 10.1038/364632a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence A. M., Coulson A., Hodgkin J. The product of fem-1, a nematode sex-determining gene, contains a motif found in cell cycle control proteins and receptors for cell-cell interactions. Cell. 1990 Mar 23;60(6):981–990. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90346-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl G., Fitzgerald K., Greenwald I. Intrinsic activity of the Lin-12 and Notch intracellular domains in vivo. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90424-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura K., Taniguchi Y., Minoguchi S., Sakai T., Tun T., Furukawa T., Honjo T. Physical interaction between a novel domain of the receptor Notch and the transcription factor RBP-J kappa/Su(H). Curr Biol. 1995 Dec 1;5(12):1416–1423. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(95)00279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tax F. E., Yeargers J. J., Thomas J. H. Sequence of C. elegans lag-2 reveals a cell-signalling domain shared with Delta and Serrate of Drosophila. Nature. 1994 Mar 10;368(6467):150–154. doi: 10.1038/368150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yochem J., Greenwald I. glp-1 and lin-12, genes implicated in distinct cell-cell interactions in C. elegans, encode similar transmembrane proteins. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):553–563. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90436-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yochem J., Weston K., Greenwald I. The Caenorhabditis elegans lin-12 gene encodes a transmembrane protein with overall similarity to Drosophila Notch. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):547–550. doi: 10.1038/335547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Amo F. F., Gendron-Maguire M., Swiatek P. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Gridley T. Cloning, analysis, and chromosomal localization of Notch-1, a mouse homolog of Drosophila Notch. Genomics. 1993 Feb;15(2):259–264. doi: 10.1006/geno.1993.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]