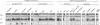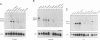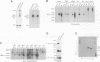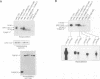Abstract
In mammalian cells, a specific stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK/JNK) pathway is activated in response to inflammatory cytokines, injury from heat, chemotherapeutic drugs and UV or ionizing radiation. The mechanisms that link these stimuli to activation of the SAPK/JNK pathway in different tissues remain to be identified. We have developed and applied a PCR-based subtraction strategy to identify novel genes that are differentially expressed at specific developmental points in hematopoiesis. We show that one such gene, hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1 (hpk1), encodes a serine/threonine kinase sharing similarity with the kinase domain of Ste20. HPK1 specifically activates the SAPK/JNK pathway after transfection into COS1 cells, but does not stimulate the p38/RK or mitogen-activated ERK signaling pathways. Activation of SAPK requires a functional HPK1 kinase domain and HPK1 signals via the SH3-containing mixed lineage kinase MLK-3 and the known SAPK activator SEK1. HPK1 therefore provides an example of a cell type-specific input into the SAPK/JNK pathway. The developmental specificity of its expression suggests a potential role in hematopoietic lineage decisions and growth regulation.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altschul S. F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E. W., Lipman D. J. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990 Oct 5;215(3):403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagrodia S., Taylor S. J., Creasy C. L., Chernoff J., Cerione R. A. Identification of a mouse p21Cdc42/Rac activated kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 29;270(39):22731–22737. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.39.22731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird T. A., Kyriakis J. M., Tyshler L., Gayle M., Milne A., Virca G. D. Interleukin-1 activates p54 mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/stress-activated protein kinase by a pathway that is independent of p21ras, Raf-1, and MAP kinase kinase. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 16;269(50):31836–31844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady G., Billia F., Knox J., Hoang T., Kirsch I. R., Voura E. B., Hawley R. G., Cumming R., Buchwald M., Siminovitch K. Analysis of gene expression in a complex differentiation hierarchy by global amplification of cDNA from single cells. Curr Biol. 1995 Aug 1;5(8):909–922. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(95)00181-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady G., Iscove N. N. Construction of cDNA libraries from single cells. Methods Enzymol. 1993;225:611–623. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)25039-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. L., Stowers L., Baer M., Trejo J., Coughlin S., Chant J. Human Ste20 homologue hPAK1 links GTPases to the JNK MAP kinase pathway. Curr Biol. 1996 May 1;6(5):598–605. doi: 10.1016/s0960-9822(02)00546-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbelo P. D., Drechsel D., Hall A. A conserved binding motif defines numerous candidate target proteins for both Cdc42 and Rac GTPases. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 8;270(49):29071–29074. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.49.29071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano E., Mahadevan L. C. Parallel signal processing among mammalian MAPKs. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Mar;20(3):117–122. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88978-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D. The hematopoietin receptor superfamily. Cytokine. 1993 Mar;5(2):95–106. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(93)90047-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coso O. A., Chiariello M., Yu J. C., Teramoto H., Crespo P., Xu N., Miki T., Gutkind J. S. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1137–1146. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80018-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumano A., Paige C. J., Iscove N. N., Brady G. Bipotential precursors of B cells and macrophages in murine fetal liver. Nature. 1992 Apr 16;356(6370):612–615. doi: 10.1038/356612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfee T., Becherer K., Chen P. L., Yeh S. H., Yang Y., Kilburn A. E., Lee W. H., Elledge S. J. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):555–569. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dérijard B., Raingeaud J., Barrett T., Wu I. H., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., Davis R. J. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science. 1995 Feb 3;267(5198):682–685. doi: 10.1126/science.7839144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezoe K., Lee S. T., Strunk K. M., Spritz R. A. PTK1, a novel protein kinase required for proliferation of human melanocytes. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):935–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J., Nikawa J., Broek D., MacDonald B., Rodgers L., Wilson I. A., Lerner R. A., Wigler M. Purification of a RAS-responsive adenylyl cyclase complex from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by use of an epitope addition method. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2159–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallo K. A., Mark M. R., Scadden D. T., Wang Z., Gu Q., Godowski P. J. Identification and characterization of SPRK, a novel src-homology 3 domain-containing proline-rich kinase with serine/threonine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1994 May 27;269(21):15092–15100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs C. S., Zoller M. J. Rational scanning mutagenesis of a protein kinase identifies functional regions involved in catalysis and substrate interactions. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8923–8931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Sakakeeny M. A., Humphries R. K., Eaves C. J., Eckner R. J. Demonstration of permanent factor-dependent multipotential (erythroid/neutrophil/basophil) hematopoietic progenitor cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):2931–2935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.2931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Bibbs L., Ulevitch R. J. A MAP kinase targeted by endotoxin and hyperosmolarity in mammalian cells. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):808–811. doi: 10.1126/science.7914033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J., Lee J. D., Jiang Y., Li Z., Feng L., Ulevitch R. J. Characterization of the structure and function of a novel MAP kinase kinase (MKK6). J Biol Chem. 1996 Feb 9;271(6):2886–2891. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.6.2886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. MAP kinase pathways in yeast: for mating and more. Cell. 1995 Jan 27;80(2):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90402-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S., Izawa M., Osada S., Spyrou G., Ohno S. Activation of the JNK pathway by distantly related protein kinases, MEKK and MUK. Oncogene. 1996 Feb 1;12(3):641–650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ing Y. L., Leung I. W., Heng H. H., Tsui L. C., Lassam N. J. MLK-3: identification of a widely-expressed protein kinase bearing an SH3 domain and a leucine zipper-basic region domain. Oncogene. 1994 Jun;9(6):1745–1750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iscove N. N., Fagg B., Keller G. A soluble activity from adherent marrow cells cooperates with IL 3 in stimulating growth of pluripotential hematopoietic precursors. Blood. 1988 Apr;71(4):953–957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz P., Whalen G., Kehrl J. H. Differential expression of a novel protein kinase in human B lymphocytes. Preferential localization in the germinal center. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jun 17;269(24):16802–16809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Pandey P., Ren R., Mayer B., Zon L., Kufe D. c-Abl activation regulates induction of the SEK1/stress-activated protein kinase pathway in the cellular response to 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30278–30281. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kharbanda S., Ren R., Pandey P., Shafman T. D., Feller S. M., Weichselbaum R. R., Kufe D. W. Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents. Nature. 1995 Aug 31;376(6543):785–788. doi: 10.1038/376785a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus U. G., Morris S., Dong H. J., Chernoff J., Bokoch G. M. Regulation of human leukocyte p21-activated kinases through G protein--coupled receptors. Science. 1995 Jul 14;269(5221):221–223. doi: 10.1126/science.7618083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6 in vitro transcription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7057–7070. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyriakis J. M., Banerjee P., Nikolakaki E., Dai T., Rubie E. A., Ahmad M. F., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. The stress-activated protein kinase subfamily of c-Jun kinases. Nature. 1994 May 12;369(6476):156–160. doi: 10.1038/369156a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma W., Hu Z. B., Drexler H. G. Sensitivity of different methods for the detection of myeloperoxidase in leukemia cells. Leukemia. 1994 Feb;8(2):336–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda T., Takekawa M., Saito H. Activation of yeast PBS2 MAPKK by MAPKKKs or by binding of an SH3-containing osmosensor. Science. 1995 Jul 28;269(5223):554–558. doi: 10.1126/science.7624781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus S., Polverino A., Chang E., Robbins D., Cobb M. H., Wigler M. H. Shk1, a homolog of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae Ste20 and mammalian p65PAK protein kinases, is a component of a Ras/Cdc42 signaling module in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jun 20;92(13):6180–6184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.13.6180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., Claret F. X., Abo A., Karin M. Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1147–1157. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minden A., Lin A., McMahon M., Lange-Carter C., Dérijard B., Davis R. J., Johnson G. L., Karin M. Differential activation of ERK and JNK mitogen-activated protein kinases by Raf-1 and MEKK. Science. 1994 Dec 9;266(5191):1719–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.7992057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P. R., Coleman T. R., Kumagai A., Dunphy W. G. Myt1: a membrane-associated inhibitory kinase that phosphorylates Cdc2 on both threonine-14 and tyrosine-15. Science. 1995 Oct 6;270(5233):86–90. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5233.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paige C. J., Kincade P. W., Ralph P. Murine B cell leukemia line with inducible surface immunoglobulin expression. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):641–647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patriotis C., Makris A., Bear S. E., Tsichlis P. N. Tumor progression locus 2 (Tpl-2) encodes a protein kinase involved in the progression of rodent T-cell lymphomas and in T-cell activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 15;90(6):2251–2255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.6.2251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):573–580. doi: 10.1038/373573a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pombo C. M., Kehrl J. H., Sánchez I., Katz P., Avruch J., Zon L. I., Woodgett J. R., Force T., Kyriakis J. M. Activation of the SAPK pathway by the human STE20 homologue germinal centre kinase. Nature. 1995 Oct 26;377(6551):750–754. doi: 10.1038/377750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raingeaud J., Whitmarsh A. J., Barrett T., Dérijard B., Davis R. J. MKK3- and MKK6-regulated gene expression is mediated by the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 1996 Mar;16(3):1247–1255. doi: 10.1128/mcb.16.3.1247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramer S. W., Davis R. W. A dominant truncation allele identifies a gene, STE20, that encodes a putative protein kinase necessary for mating in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):452–456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salmeron A., Ahmad T. B., Carlile G. W., Pappin D., Narsimhan R. P., Ley S. C. Activation of MEK-1 and SEK-1 by Tpl-2 proto-oncoprotein, a novel MAP kinase kinase kinase. EMBO J. 1996 Feb 15;15(4):817–826. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez I., Hughes R. T., Mayer B. J., Yee K., Woodgett J. R., Avruch J., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I. Role of SAPK/ERK kinase-1 in the stress-activated pathway regulating transcription factor c-Jun. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):794–798. doi: 10.1038/372794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T. Cytokine signaling through nonreceptor protein tyrosine kinases. Science. 1995 Apr 14;268(5208):251–255. doi: 10.1126/science.7716517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbles L. A., Ing Y. L., Kiefer F., Chan J., Iscove N., Woodgett J. R., Lassam N. J. MLK-3 activates the SAPK/JNK and p38/RK pathways via SEK1 and MKK3/6. EMBO J. 1996 Dec 16;15(24):7026–7035. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verheij M., Bose R., Lin X. H., Yao B., Jarvis W. D., Grant S., Birrer M. J., Szabo E., Zon L. I., Kyriakis J. M. Requirement for ceramide-initiated SAPK/JNK signalling in stress-induced apoptosis. Nature. 1996 Mar 7;380(6569):75–79. doi: 10.1038/380075a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. Q., Grigoriadis A. E., Möhle-Steinlein U., Wagner E. F. A novel target cell for c-fos-induced oncogenesis: development of chondrogenic tumours in embryonic stem cell chimeras. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2437–2450. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07783.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L., Moore M. A., Metcalf D. A transplantable myelomonocytic leukemia in BALB-c mice: cytology, karyotype, and muramidase content. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1969 Oct;43(4):963–982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodgett J. R., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Zon L. I., Zanke B., Templeton D. J. Reconstitution of novel signalling cascades responding to cellular stresses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1996 Feb 29;351(1336):135–142. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1996.0009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yan M., Dai T., Deak J. C., Kyriakis J. M., Zon L. I., Woodgett J. R., Templeton D. J. Activation of stress-activated protein kinase by MEKK1 phosphorylation of its activator SEK1. Nature. 1994 Dec 22;372(6508):798–800. doi: 10.1038/372798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S., Han J., Sells M. A., Chernoff J., Knaus U. G., Ulevitch R. J., Bokoch G. M. Rho family GTPases regulate p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase through the downstream mediator Pak1. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 13;270(41):23934–23936. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.41.23934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]