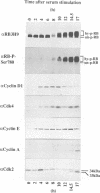
Abstract
Cyclin D-Cdk4/6 and cyclin A/E-Cdk2 are suggested to be involved in phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein (pRB) during the G1/S transition of the cell cycle. However, it is unclear why several Cdks are needed and how they are different from one another. We found that the consensus amino acid sequence for phosphorylation by cyclin D1-Cdk4 is different from S/T-P-X-K/R, which is the consensus sequence for phosphorylation by cyclin A/E-Cdk2 using various synthetic peptides as substrates. Cyclin D1-Cdk4 efficiently phosphorylated the G1 peptide, RPPTLS780PIPHIPR that contained a part of the sequence of pRB, while cyclins E-Cdk2 and A-Cdk2 did not. To determine the phosphorylation state of pRB in vitro and in vivo, we raised the specific antibody against phospho-Ser780 in pRB. We confirmed that cyclin D1-Cdk4, but not cyclin E-Cdk2, phosphorylated Ser780 in recombinant pRB. The Ser780 in pRB was phosphorylated in the G1 phase in a cell cycle-dependent manner. Furthermore, we found that pRB phosphorylated at Ser780 cannot bind to E2F-1 in vivo. Our data show that cyclin D1-Cdk4 and cyclin A/E Cdk2 phosphorylate different sites of pRB in vivo.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldin V., Lukas J., Marcote M. J., Pagano M., Draetta G. Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 1993 May;7(5):812–821. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.5.812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates S., Bonetta L., MacAllan D., Parry D., Holder A., Dickson C., Peters G. CDK6 (PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3) are a distinct subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases that associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene. 1994 Jan;9(1):71–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beijersbergen R. L., Carlée L., Kerkhoven R. M., Bernards R. Regulation of the retinoblastoma protein-related p107 by G1 cyclin complexes. Genes Dev. 1995 Jun 1;9(11):1340–1353. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.11.1340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durfee T., Becherer K., Chen P. L., Yeh S. H., Yang Y., Kilburn A. E., Lee W. H., Elledge S. J. The retinoblastoma protein associates with the protein phosphatase type 1 catalytic subunit. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):555–569. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynlacht B. D., Flores O., Lees J. A., Harlow E. Differential regulation of E2F transactivation by cyclin/cdk2 complexes. Genes Dev. 1994 Aug 1;8(15):1772–1786. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.15.1772. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Sluss H. K., Sherr C. J., Matsushime H., Kato J., Livingston D. M. Functional interactions of the retinoblastoma protein with mammalian D-type cyclins. Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):487–497. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90136-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewen M. E., Xing Y. G., Lawrence J. B., Livingston D. M. Molecular cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of the cDNA for p107, a retinoblastoma gene product-related protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1155–1164. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90038-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. A., Raden D. L., Davis R. J. Identification of substrate recognition determinants for human ERK1 and ERK2 protein kinases. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22159–22163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Jenkins C. W., Li Y., Nichols M. A., Wu X., O'Keefe C. L., Matera A. G., Xiong Y. Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function. Genes Dev. 1994 Dec 15;8(24):2939–2952. doi: 10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel P. A., Gill R. M., Phillips R. A., Gallie B. L. Regions controlling hyperphosphorylation and conformation of the retinoblastoma gene product are independent of domains required for transcriptional repression. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):693–701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helin K., Ed H. The retinoblastoma protein as a transcriptional repressor. Trends Cell Biol. 1993 Feb;3(2):43–46. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(93)90150-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Suzuki-Takahashi I., Saitoh S., Segawa K., Taya Y., Okuyama A., Nishimura S., Kitagawa M. Cyclin-dependent kinase-2 (Cdk2) forms an inactive complex with cyclin D1 since Cdk2 associated with cyclin D1 is not phosphorylated by Cdk7-cyclin-H. Eur J Biochem. 1996 Apr 15;237(2):460–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1996.0460k.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higashi H., Suzuki-Takahashi I., Taya Y., Segawa K., Nishimura S., Kitagawa M. Differences in substrate specificity between Cdk2-cyclin A and Cdk2-cyclin E in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1995 Nov 13;216(2):520–525. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1995.2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Mittnacht S., Dulic V., Arnold A., Reed S. I., Weinberg R. A. Regulation of retinoblastoma protein functions by ectopic expression of human cyclins. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):993–1006. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90249-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Q. J., Dyson N., Harlow E. The regions of the retinoblastoma protein needed for binding to adenovirus E1A or SV40 large T antigen are common sites for mutations. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1147–1155. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08221.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamb A. Cell-cycle regulators and cancer. Trends Genet. 1995 Apr;11(4):136–140. doi: 10.1016/s0168-9525(00)89027-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J., Matsushime H., Hiebert S. W., Ewen M. E., Sherr C. J. Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4. Genes Dev. 1993 Mar;7(3):331–342. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.3.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Higashi H., Suzuki-Takahashi I., Segawa K., Hanks S. K., Taya Y., Nishimura S., Okuyama A. Phosphorylation of E2F-1 by cyclin A-cdk2. Oncogene. 1995 Jan 19;10(2):229–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Higashi H., Takahashi I. S., Okabe T., Ogino H., Taya Y., Hishimura S., Okuyama A. A cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, butyrolactone I, inhibits phosphorylation of RB protein and cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 1994 Sep;9(9):2549–2557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Okabe T., Ogino H., Matsumoto H., Suzuki-Takahashi I., Kokubo T., Higashi H., Saitoh S., Taya Y., Yasuda H. Butyrolactone I, a selective inhibitor of cdk2 and cdc2 kinase. Oncogene. 1993 Sep;8(9):2425–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa M., Saitoh S., Ogino H., Okabe T., Matsumoto H., Okuyama A., Tamai K., Ohba Y., Yasuda H., Nishimura S. cdc2-like kinase is associated with the retinoblastoma protein. Oncogene. 1992 Jun;7(6):1067–1074. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krek W., Ewen M. E., Shirodkar S., Arany Z., Kaelin W. G., Jr, Livingston D. M. Negative regulation of the growth-promoting transcription factor E2F-1 by a stably bound cyclin A-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1994 Jul 15;78(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90582-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lees J. A., Buchkovich K. J., Marshak D. R., Anderson C. W., Harlow E. The retinoblastoma protein is phosphorylated on multiple sites by human cdc2. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4279–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb05006.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J., Bartkova J., Rohde M., Strauss M., Bartek J. Cyclin D1 is dispensable for G1 control in retinoblastoma gene-deficient cells independently of cdk4 activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2600–2611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas J., Parry D., Aagaard L., Mann D. J., Bartkova J., Strauss M., Peters G., Bartek J. Retinoblastoma-protein-dependent cell-cycle inhibition by the tumour suppressor p16. Nature. 1995 Jun 8;375(6531):503–506. doi: 10.1038/375503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Ewen M. E., Strom D. K., Kato J. Y., Hanks S. K., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Identification and properties of an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type G1 cyclins. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):323–334. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90360-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsushime H., Quelle D. E., Shurtleff S. A., Shibuya M., Sherr C. J., Kato J. Y. D-type cyclin-dependent kinase activity in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2066–2076. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayol X., Garriga J., Graña X. Cell cycle-dependent phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma-related protein p130. Oncogene. 1995 Aug 17;11(4):801–808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medema R. H., Herrera R. E., Lam F., Weinberg R. A. Growth suppression by p16ink4 requires functional retinoblastoma protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6289–6293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyerson M., Harlow E. Identification of G1 kinase activity for cdk6, a novel cyclin D partner. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):2077–2086. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittnacht S., Lees J. A., Desai D., Harlow E., Morgan D. O., Weinberg R. A. Distinct sub-populations of the retinoblastoma protein show a distinct pattern of phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):118–127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Mumberg D., Lucibello F. C. Signals and genes in the control of cell-cycle progression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Aug 23;1155(2):151–179. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(93)90003-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigg E. A. Targets of cyclin-dependent protein kinases. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;5(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90101-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Roberts J. M. Cyclin-dependent regulation of G1 in mammalian fibroblasts. Science. 1993 Mar 26;259(5103):1908–1912. doi: 10.1126/science.8384376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Theodoras A. M., Schumacher J., Roberts J. M., Pagano M. Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 May;15(5):2612–2624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.5.2612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Lukas J., Baldin V., Ansorge W., Bartek J., Draetta G. Regulation of the cell cycle by the cdk2 protein kinase in cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):101–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pines J. Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: take your partners. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Jun;18(6):195–197. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90185-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quelle D. E., Ashmun R. A., Shurtleff S. A., Kato J. Y., Bar-Sagi D., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Overexpression of mouse D-type cyclins accelerates G1 phase in rodent fibroblasts. Genes Dev. 1993 Aug;7(8):1559–1571. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.8.1559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Gossen M., Bujard H., Reed S. I. Acceleration of the G1/S phase transition by expression of cyclins D1 and E with an inducible system. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1669–1679. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnitzky D., Reed S. I. Different roles for cyclins D1 and E in regulation of the G1-to-S transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1995 Jul;15(7):3463–3469. doi: 10.1128/mcb.15.7.3463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblatt J., Gu Y., Morgan D. O. Human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is activated during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and associates with cyclin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2824–2828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M. F., Theodoras A. M., Pagano M., Sherr C. J. Rescue of defective mitogenic signaling by D-type cyclins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 18;92(15):6837–6841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.15.6837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saijo M., Kato M. V., Sasaki M. S., Ishizaki K., Taya Y. Inactivation of oncoprotein binding by a single Cys706-to-Tyr substitution in the retinoblastoma protein. FEBS Lett. 1994 Mar 7;340(3):181–184. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80133-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. D-type cyclins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 May;20(5):187–190. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89005-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J., Roberts J. M. Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev. 1995 May 15;9(10):1149–1163. doi: 10.1101/gad.9.10.1149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skapek S. X., Rhee J., Spicer D. B., Lassar A. B. Inhibition of myogenic differentiation in proliferating myoblasts by cyclin D1-dependent kinase. Science. 1995 Feb 17;267(5200):1022–1024. doi: 10.1126/science.7863328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki-Takahashi I., Kitagawa M., Saijo M., Higashi H., Ogino H., Matsumoto H., Taya Y., Nishimura S., Okuyama A. The interactions of E2F with pRB and with p107 are regulated via the phosphorylation of pRB and p107 by a cyclin-dependent kinase. Oncogene. 1995 May 4;10(9):1691–1698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taya Y., Yasuda H., Kamijo M., Nakaya K., Nakamura Y., Ohba Y., Nishimura S. In vitro phosphorylation of the tumor suppressor gene RB protein by mitosis-specific histone H1 kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Oct 16;164(1):580–586. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91759-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai L. H., Lees E., Faha B., Harlow E., Riabowol K. The cdk2 kinase is required for the G1-to-S transition in mammalian cells. Oncogene. 1993 Jun;8(6):1593–1602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Makino S., Kitagawa M., Nishimura S., Taya Y., Hata T. Chemical synthesis of phosphopeptides using the arylthio group for protection of phosphate: application to identification of cdc2 kinase phosphorylation sites. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1995 Aug;46(2):106–112. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1995.tb01325.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Prives C. Increased and altered DNA binding of human p53 by S and G2/M but not G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Nature. 1995 Jul 6;376(6535):88–91. doi: 10.1038/376088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. The retinoblastoma protein and cell cycle control. Cell. 1995 May 5;81(3):323–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimmel A., Lucibello F. C., Sewing A., Adolph S., Müller R. Inducible acceleration of G1 progression through tetracycline-regulated expression of human cyclin E. Oncogene. 1994 Mar;9(3):995–997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu L., van den Heuvel S., Helin K., Fattaey A., Ewen M., Livingston D., Dyson N., Harlow E. Inhibition of cell proliferation by p107, a relative of the retinoblastoma protein. Genes Dev. 1993 Jul;7(7A):1111–1125. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.7a.1111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel S., Harlow E. Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science. 1993 Dec 24;262(5142):2050–2054. doi: 10.1126/science.8266103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]