Abstract
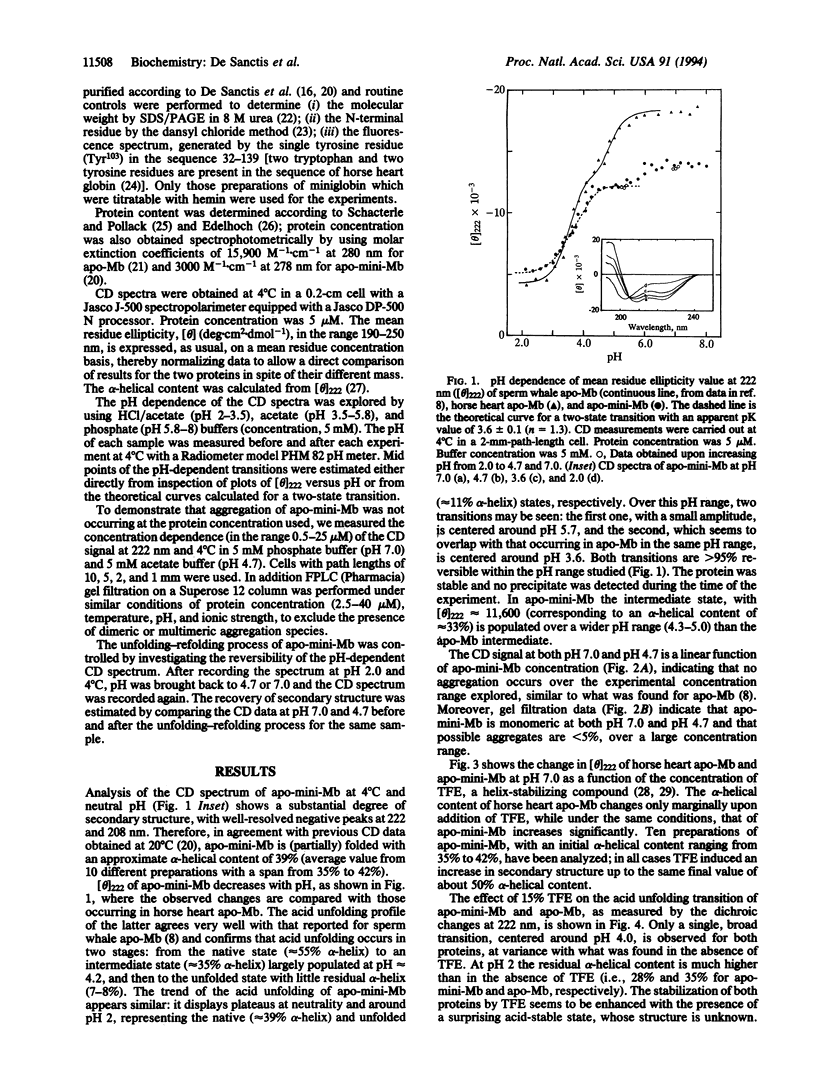
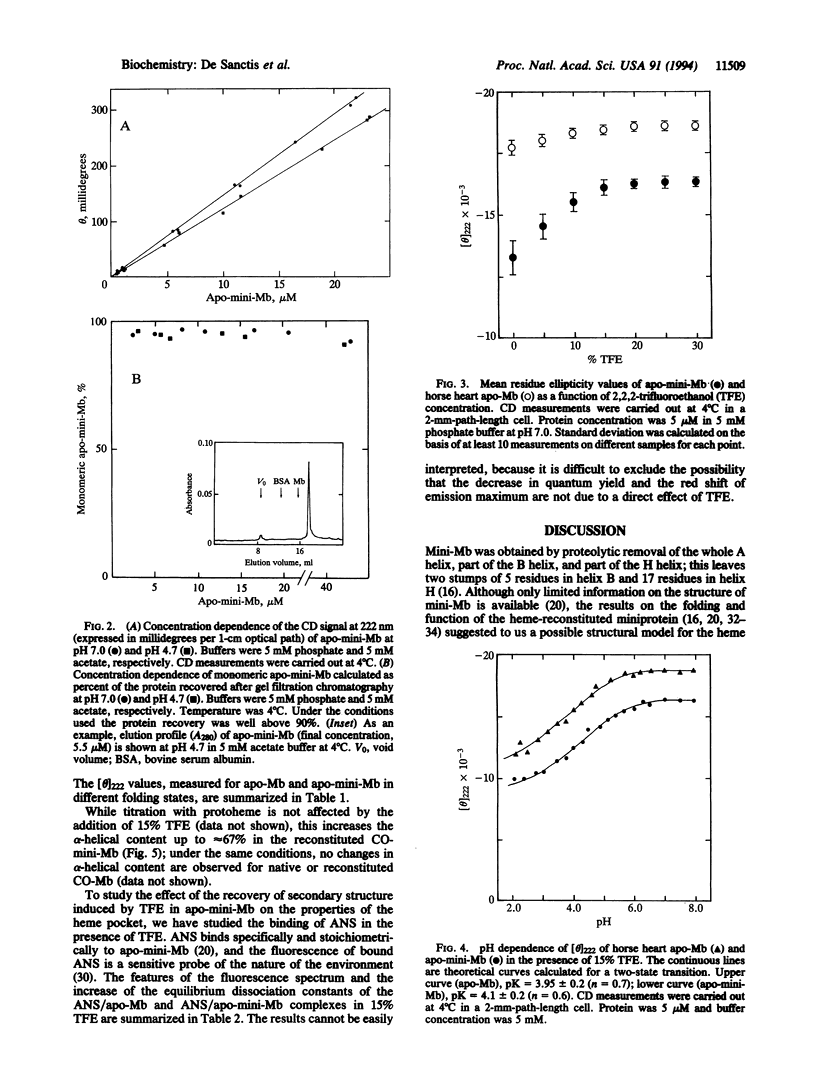
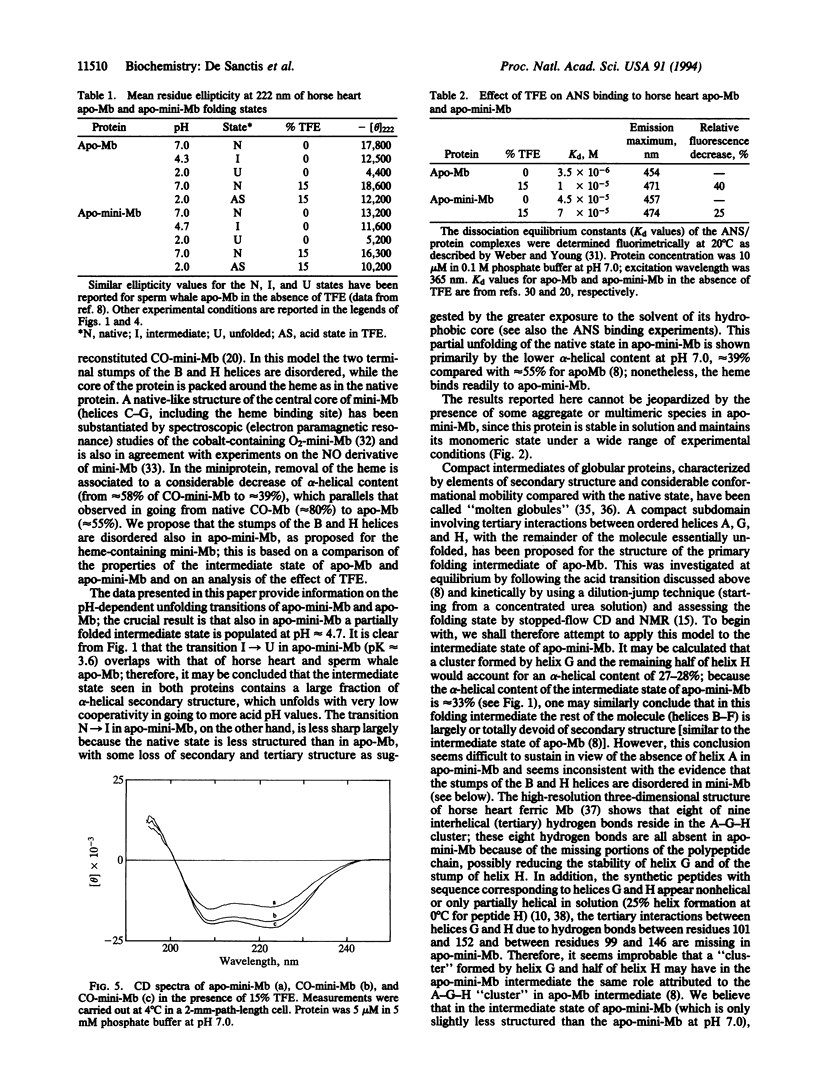
The acid unfolding pathway of apominimyoglobin (apo-mini-Mb), a 108-aa fragment (aa 32-139) of horse heart apomyoglobin has been studied by means of circular dichroism, in comparison with the native apoprotein. Similar to sperm whale apomyoglobin [Hughson, F. M., Wright, P. E. & Baldwin, R. L. (1990) Science 249, 1544-1548], a partly folded intermediate (alpha-helical content approximately 35%) is populated at pH 4.2 for horse heart apomyoglobin. For this intermediate, Hughson et al. proposed a structural model with a compact subdomain involving tertiary interactions between the folded A, G, and H helices, with the remainder of the protein essentially unfolded. As described in this paper, a folding intermediate with an alpha-helical content of approximately 33% is populated at pH 4.3-5.0 also in apo-mini-Mb. The acid unfolding pathway is similarly affected in both the native and the mini apoprotein by 15% trifluoroethanol, a helix-stabilizing compound. Thus, the folding of the apo-mini-Mb intermediate is similar to that observed for the native apoprotein, in spite of the absence in the miniprotein of the A helix and of a large part of the H helix, which are crucial for the stability of apo-Mb intermediate. Our results suggest that acquisition of a folded state in apo-mini-Mb occurs through an alternative pathway, which may or may not be shared also by apo-Mb.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin R. L. How does protein folding get started? Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Jul;14(7):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrick D., Baldwin R. L. Stein and Moore Award address. The molten globule intermediate of apomyoglobin and the process of protein folding. Protein Sci. 1993 Jun;2(6):869–876. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrow C. J., Yasuda A., Kenny P. T., Zagorski M. G. Solution conformations and aggregational properties of synthetic amyloid beta-peptides of Alzheimer's disease. Analysis of circular dichroism spectra. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jun 20;225(4):1075–1093. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90106-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchetot A., Price M., Jeffreys A. J. The mouse myoglobin gene. Characterisation and sequence comparison with other mammalian myoglobin genes. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):469–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanchetot A., Wilson V., Wood D., Jeffreys A. J. The seal myoglobin gene: an unusually long globin gene. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):732–734. doi: 10.1038/301732a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks C. L., 3rd Characterization of "native" apomyoglobin by molecular dynamics simulation. J Mol Biol. 1992 Sep 20;227(2):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90893-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Martinez H. M. Determination of the secondary structures of proteins by circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4120–4131. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen H., Pain R. H. Molten globule intermediates and protein folding. Eur Biophys J. 1991;19(5):221–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00183530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocco M. J., Kao Y. H., Phillips A. T., Lecomte J. T. Structural comparison of apomyoglobin and metaquomyoglobin: pH titration of histidines by NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 21;31(28):6481–6491. doi: 10.1021/bi00143a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocco M. J., Lecomte J. T. Characterization of hydrophobic cores in apomyoglobin: a proton NMR spectroscopy study. Biochemistry. 1990 Dec 18;29(50):11067–11072. doi: 10.1021/bi00502a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sanctis G., Falcioni G., Giardina B., Ascoli F., Brunori M. Mini-myoglobin. The structural significance of haem-ligand interactions. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):725–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90483-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sanctis G., Falcioni G., Giardina B., Ascoli F., Brunori M. Mini-myoglobin: preparation and reaction with oxygen and carbon monoxide. J Mol Biol. 1986 Mar 5;188(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90481-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sanctis G., Falcioni G., Grelloni F., Desideri A., Polizio F., Giardina B., Ascoli F., Brunori M. Mini-myoglobin. Electron paramagnetic resonance and reversible oxygenation of the cobalt derivative. J Mol Biol. 1991 Dec 5;222(3):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90501-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Sanctis G., Falcioni G., Polizio F., Desideri A., Giardina B., Ascoli F., Brunori M. Mini-myoglobin: native-like folding of the NO-derivative. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Jan 11;1204(1):28–32. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(94)90028-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Iorio E. E., Yu W., Calonder C., Winterhalter K. H., De Sanctis G., Falcioni G., Ascoli F., Giardina B., Brunori M. Protein dynamics in minimyoglobin: is the central core of myoglobin the conformational domain? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):2025–2029. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.2025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dill K. A., Fiebig K. M., Chan H. S. Cooperativity in protein-folding kinetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Mar 1;90(5):1942–1946. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.5.1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson H. J., Rance M., Houghten R. A., Wright P. E., Lerner R. A. Folding of immunogenic peptide fragments of proteins in water solution. II. The nascent helix. J Mol Biol. 1988 May 5;201(1):201–217. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90447-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelhoch H. Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1948–1954. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. V., Brayer G. D. High-resolution study of the three-dimensional structure of horse heart metmyoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):885–897. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80270-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fersht A. R., Matouschek A., Serrano L. The folding of an enzyme. I. Theory of protein engineering analysis of stability and pathway of protein folding. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 5;224(3):771–782. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90561-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griko Y. V., Privalov P. L., Venyaminov S. Y., Kutyshenko V. P. Thermodynamic study of the apomyoglobin structure. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90525-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughson F. M., Barrick D., Baldwin R. L. Probing the stability of a partly folded apomyoglobin intermediate by site-directed mutagenesis. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 30;30(17):4113–4118. doi: 10.1021/bi00231a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughson F. M., Wright P. E., Baldwin R. L. Structural characterization of a partly folded apomyoglobin intermediate. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1544–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.2218495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings P. A., Wright P. E. Formation of a molten globule intermediate early in the kinetic folding pathway of apomyoglobin. Science. 1993 Nov 5;262(5135):892–896. doi: 10.1126/science.8235610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim P. S., Baldwin R. L. Intermediates in the folding reactions of small proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:631–660. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranker A., Radford S. E., Karplus M., Dobson C. M. Demonstration by NMR of folding domains in lysozyme. Nature. 1991 Feb 14;349(6310):633–636. doi: 10.1038/349633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain R. H. Molecular biology. Brevity is the soul of wit. Nature. 1986 Mar 20;320(6059):216–217. doi: 10.1038/320216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptitsyn O. B., Pain R. H., Semisotnov G. V., Zerovnik E., Razgulyaev O. I. Evidence for a molten globule state as a general intermediate in protein folding. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 12;262(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schacterle G. R., Pollack R. L. A simplified method for the quantitative assay of small amounts of protein in biologic material. Anal Biochem. 1973 Feb;51(2):654–655. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90523-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. The interaction of a naphthalene dye with apomyoglobin and apohemoglobin. A fluorescent probe of non-polar binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):482–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirado-Rives J., Jorgensen W. L. Molecular dynamics simulations of the unfolding of apomyoglobin in water. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 27;32(16):4175–4184. doi: 10.1021/bi00067a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEBER G., YOUNG L. B. FRAGMENTATION OF BOVINE SERUM ALBUMIN BY PEPSIN. I. THE ORIGIN OF THE ACID EXPANSION OF THE ALBUMIN MOLECULE. J Biol Chem. 1964 May;239:1415–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller P., Jeffreys A. J., Wilson V., Blanchetot A. Organization of the human myoglobin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):439–446. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward C. Is the slow exchange core the protein folding core? Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Oct;18(10):359–360. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



