Abstract
The three-dimensional structure of the activation domain isolated from porcine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase B was determined using 1H NMR spectroscopy. A group of 20 conformers is used to describe the solution structure of this 81 residue polypeptide chain, which has a well-defined backbone fold from residues 11-76 with an average root mean square distance for the backbone atoms of 1.0 +/- 0.1 A relative to the mean of the 20 conformers. The molecular architecture contains a four-stranded beta-sheet with the polypeptide segments 11-17, 36-39, 50-56 and 75-76, two well defined alpha-helices from residues 20-30 and 60-70, and a 3(10) helix from residues 43-46. The three helices are oriented almost exactly antiparallel to each other, are all on the same side of the beta-sheet, and the helix axes from an angle of approximately 45 degrees relative to the direction of the beta-strands. Three segments linking beta-strands and helical secondary structures, with residues 32-35, 39-43 and 56-61, are significantly less well ordered than the rest of the molecule. In the three-dimensional structure two of these loops (residues 32-35 and 56-61) are located close to each other near the protein surface, forming a continuous region of increased mobility, and the third disordered loop is separated from this region only by the peripheral beta-strand 36-39 and precedes the short 3(10) helix.
Full text
PDF

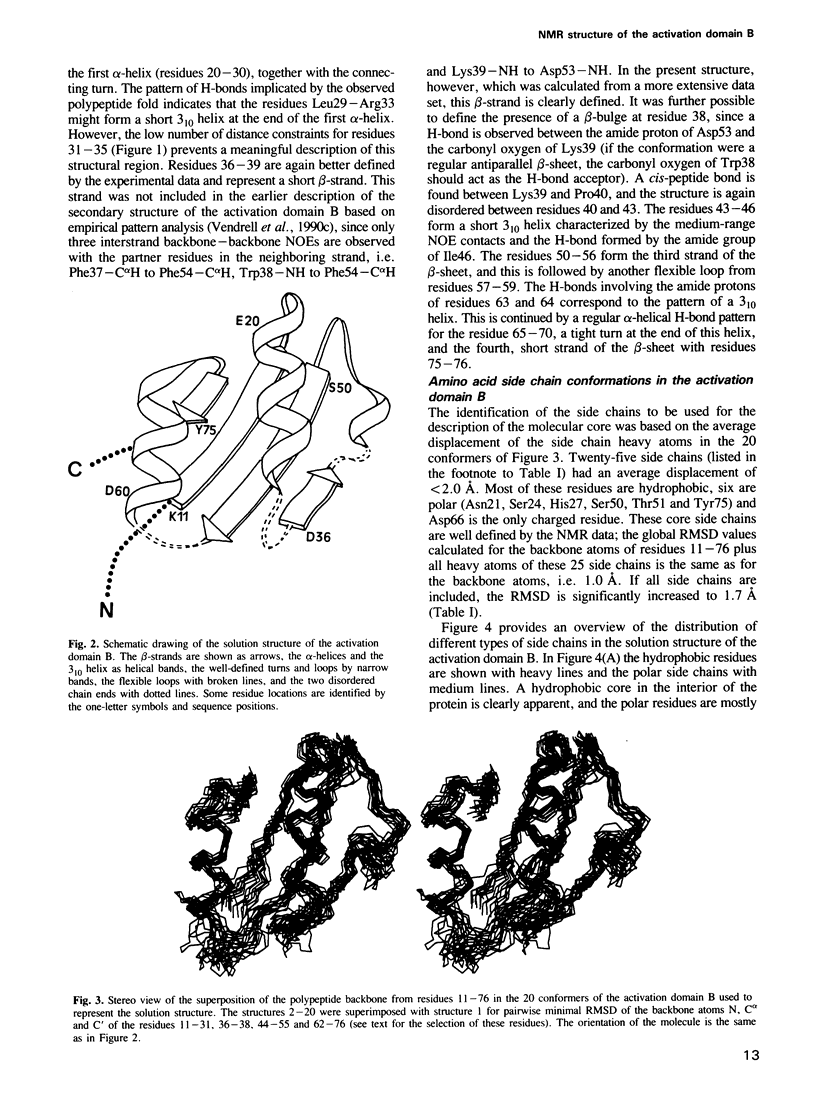

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avilés F. X., Segundo B. S., Vilanova M., Cuchillo C. M., Turner C. The activation segment of procarboxypeptidase A from porcine pancreas constitutes a folded structural domain. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 29;149(2):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81112-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Qian Y., Otting G., Müller M., Gehring W. J., Wüthrich K. Determination of the three-dimensional structure of the Antennapedia homeodomain from Drosophila in solution by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jul 5;214(1):183–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90155-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clauser E., Gardell S. J., Craik C. S., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Structural characterization of the rat carboxypeptidase A1 and B genes. Comparative analysis of the rat carboxypeptidase gene family. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17837–17845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coll M., Guasch A., Avilés F. X., Huber R. Three-dimensional structure of porcine procarboxypeptidase B: a structural basis of its inactivity. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglizzo E., Bonicel J., Kerfelec B., Granon S., Chapus C. Primary structure of the activation peptide from bovine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 18;954(2):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(88)90070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinto C., Quiroga M., Swain W. F., Nikovits W. C., Jr, Standring D. N., Pictet R. L., Valenzuela P., Rutter W. J. Rat preprocarboxypeptidase A: cDNA sequence and preliminary characterization of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):31–35. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.31. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Ruiz J. M., Lopez-Lacomba J. L., Mateo P. L., Vilanova M., Serra M. A., Aviles F. X. Analysis of the thermal unfolding of porcine procarboxypeptidase A and its functional pieces by differential scanning calorimetry. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):225–230. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid M. F., Herriott J. R. Structure of carboxypeptidase B at 2-8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 5;103(1):175–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90058-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segundo B. S., Martínez M. C., Vilanova M., Cuchillo C. M., Avilés F. X. The severed activation segment of porcine pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A is a powerful inhibitor of the active enzyme. Isolation and characterisation of the activation peptide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Sep 22;707(1):74–80. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90398-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell J., Avilés F. X., Genescà E., San Segundo B., Soriano F., Méndez E. Primary structure of the activation segment of procarboxypeptidase A from porcine pancreas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Dec 15;141(2):517–523. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80203-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell J., Avilés F. X., Vilanova M., Turner C. H., Crane-Robinson C. 1H-n.m.r. studies of the isolated activation segment from pig procarboxypeptidase A. Biochem J. 1990 Apr 1;267(1):213–220. doi: 10.1042/bj2670213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell J., Cuchillo C. M., Avilés F. X. The tryptic activation pathway of monomeric procarboxypeptidase A. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6949–6953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendrell J., Wider G., Avilés F. X., Wüthrich K. Sequence-specific 1H NMR assignments and determination of the secondary structure for the activation domain isolated from pancreatic procarboxypeptidase B. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 14;29(32):7515–7522. doi: 10.1021/bi00484a600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilanova M., Vendrell J., López M. T., Cuchillo C. M., Avilés F. X. Preparative isolation of the two forms of pig pancreatic pro-(carboxypeptidase A) and their monomeric carboxypeptidases A. Biochem J. 1985 Aug 1;229(3):605–609. doi: 10.1042/bj2290605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wade R. D., Hass G. M., Kumar S., Walsh K. A., Neurath H. The amino acid sequence of the activation peptide of bovine pro-carboxypeptidase A. Biochimie. 1988 Sep;70(9):1137–1142. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widmer H., Billeter M., Wüthrich K. Three-dimensional structure of the neurotoxin ATX Ia from Anemonia sulcata in aqueous solution determined by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proteins. 1989;6(4):357–371. doi: 10.1002/prot.340060403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson M. P., Havel T. F., Wüthrich K. Solution conformation of proteinase inhibitor IIA from bull seminal plasma by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance and distance geometry. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 20;182(2):295–315. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90347-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K., Billeter M., Braun W. Polypeptide secondary structure determination by nuclear magnetic resonance observation of short proton-proton distances. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):715–740. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90034-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich K. Protein structure determination in solution by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Science. 1989 Jan 6;243(4887):45–50. doi: 10.1126/science.2911719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]