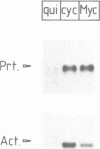Abstract
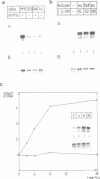
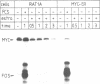
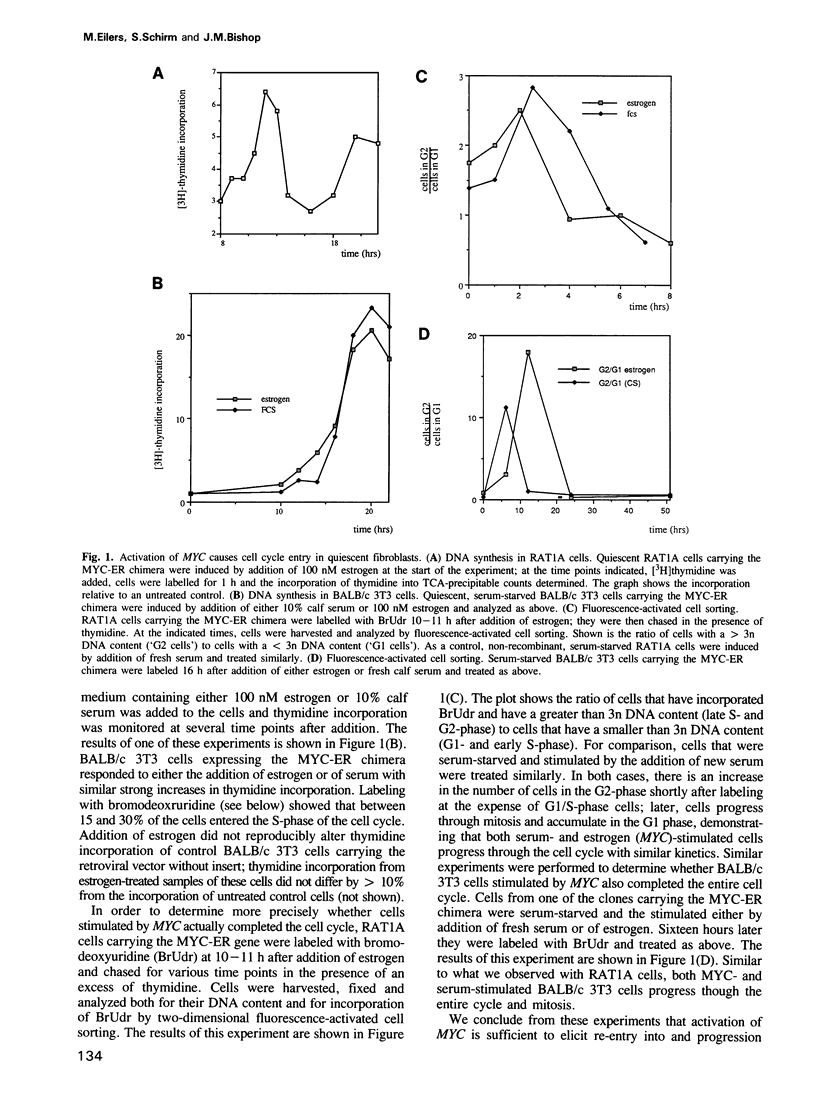
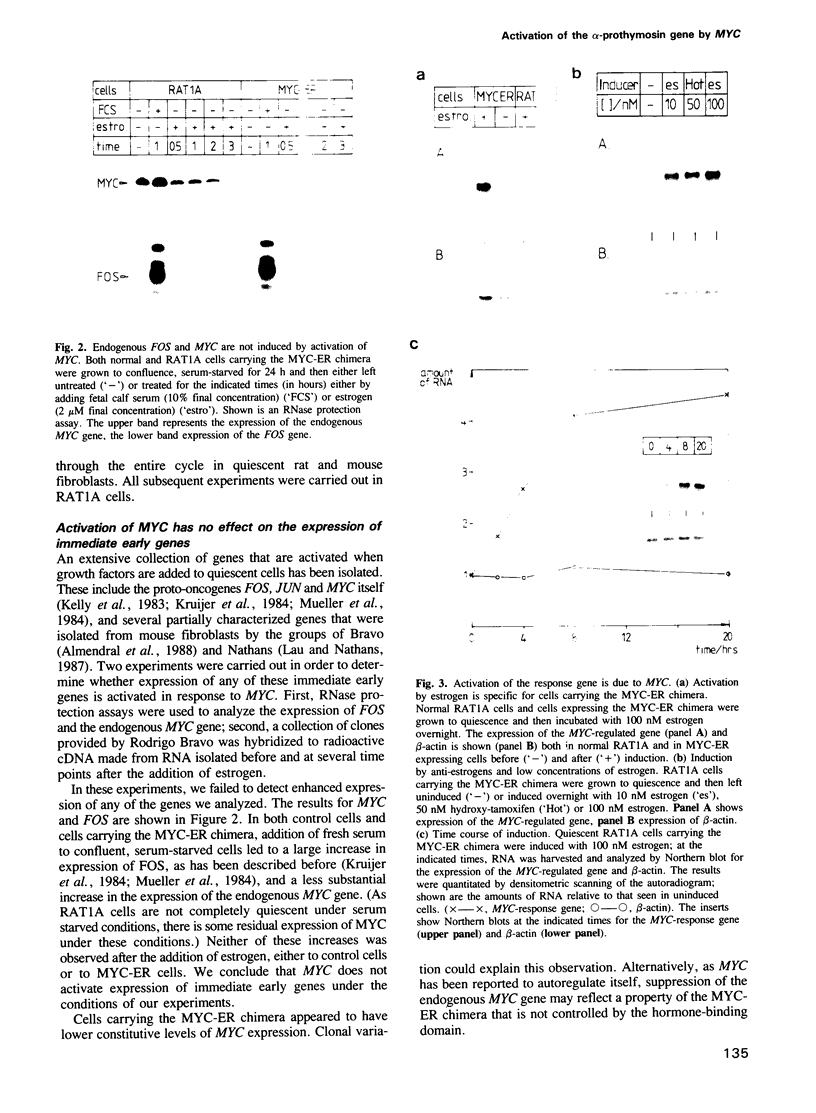
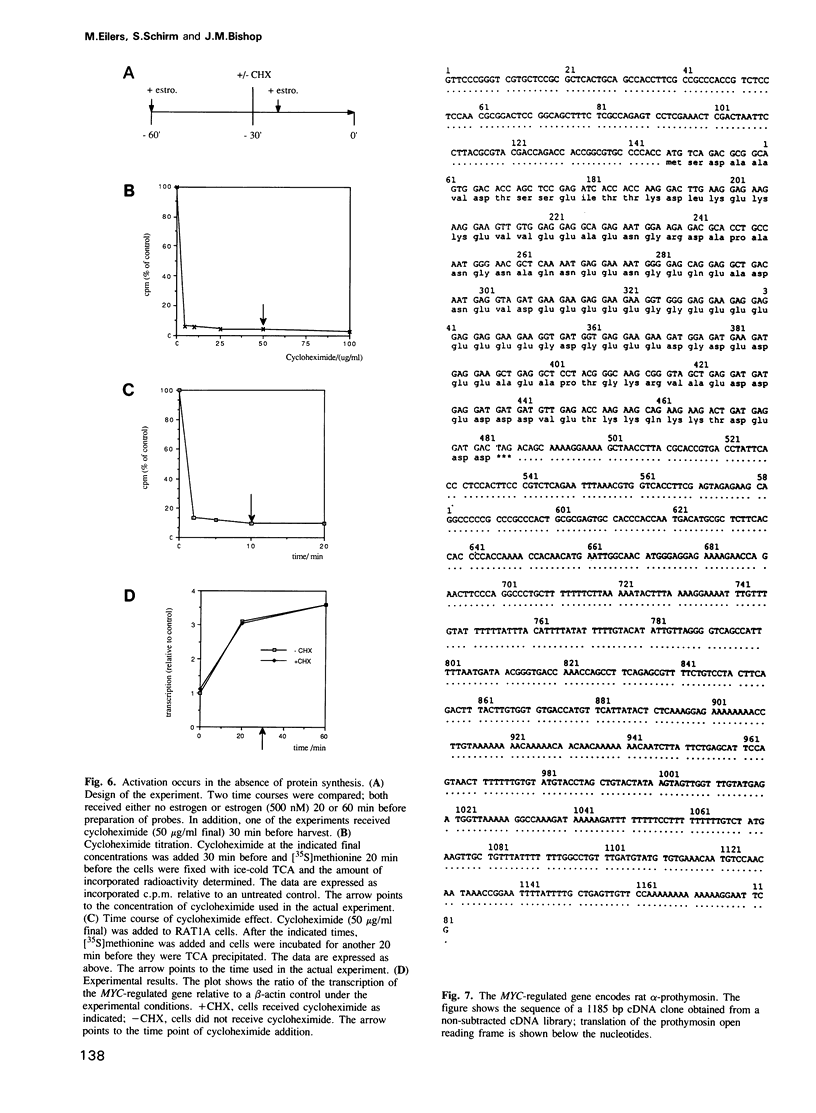
The proto-oncogene MYC encodes a nuclear protein whose biochemical and physiological functions remain uncertain. We used an estrogen-regulated version of the MYC protein to explore these functions. Activation of MYC in quiescent rat and mouse fibroblasts elicited re-entry into and progression through the cell cycle, bypassing early events that would follow stimulation of the cells with serum. Activation of MYC led to a rapid increase in transcription of the alpha-prothymosin gene, even in the absence of protein synthesis. We conclude that the product of MYC acts directly on transcription, in accord with inferences based on the structure of the MYC protein. The function of alpha-prothymosin is not known, but our results suggest that the protein may play a role in the proliferation of mammalian cells.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Sommer D., Macdonald-Bravo H., Burckhardt J., Perera J., Bravo R. Complexity of the early genetic response to growth factors in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2140–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxevanis C. N., Reclos G. J., Panneerselvam C., Papamichail M. Enhancement of human T lymphocyte functions by prothymosin alpha. I. Augmentation of mixed lymphocyte culture reactions and soluble protein-induced proliferative responses. Immunopharmacology. 1988 Mar-Apr;15(2):73–84. doi: 10.1016/0162-3109(88)90054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonne-Andrea C., Harper F., Sobczak J., De Recondo A. M. Rat liver HMG1: a physiological nucleosome assembly factor. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1193–1199. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavalieri F., Goldfarb M. Growth factor-deprived BALB/c 3T3 murine fibroblasts can enter the S phase after induction of c-myc gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3554–3560. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clinton M., Frangou-Lazaridis M., Panneerselvam C., Horecker B. L. Prothymosin alpha and parathymosin: mRNA and polypeptide levels in rodent tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 15;269(1):256–263. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Lee W. M., Williams P. W., Giels G. M., Williams L. T. c-myc gene expression is stimulated by agents that activate protein kinase C and does not account for the mitogenic effect of PDGF. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):243–251. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90029-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dang C. V., McGuire M., Buckmire M., Lee W. M. Involvement of the 'leucine zipper' region in the oligomerization and transforming activity of human c-myc protein. Nature. 1989 Feb 16;337(6208):664–666. doi: 10.1038/337664a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Cheng P. F., Lassar A. B., Weintraub H. The MyoD DNA binding domain contains a recognition code for muscle-specific gene activation. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):733–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90088-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolbeare F., Gratzner H., Pallavicini M. G., Gray J. W. Flow cytometric measurement of total DNA content and incorporated bromodeoxyuridine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5573–5577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner P., Greiser-Wilke I., Moelling K. Nuclear localization and DNA binding of the transforming gene product of avian myelocytomatosis virus. Nature. 1982 Mar 18;296(5854):262–269. doi: 10.1038/296262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M. Chimaeras of myc oncoprotein and steroid receptors cause hormone-dependent transformation of cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):66–68. doi: 10.1038/340066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erard M. S., Belenguer P., Caizergues-Ferrer M., Pantaloni A., Amalric F. A major nucleolar protein, nucleolin, induces chromatin decondensation by binding to histone H1. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Aug 15;175(3):525–530. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14224.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Berger S. L. The human prothymosin alpha gene is polymorphic and induced upon growth stimulation: evidence using a cloned cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9403–9407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eschenfeldt W. H., Manrow R. E., Krug M. S., Berger S. L. Isolation and partial sequencing of the human prothymosin alpha gene family. Evidence against export of the gene products. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7546–7555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Márquez J., Segade F., Dosil M., Pichel J. G., Bustelo X. R., Freire M. The expression of prothymosin alpha gene in T lymphocytes and leukemic lymphoid cells is tied to lymphocyte proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8451–8454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Márquez J., Segade F. Prothymosin alpha is a nuclear protein. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 4;226(2):217–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81425-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hann S. R., Thompson C. B., Eisenman R. N. c-myc oncogene protein synthesis is independent of the cell cycle in human and avian cells. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):366–369. doi: 10.1038/314366a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Kiji Y., Ariga H. Possible function of the c-myc product: promotion of cellular DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Okazaki T., Itani T., Ogata M., Sato Y., Ariga H. An initiation site of DNA replication with transcriptional enhancer activity present upstream of the c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3135–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Admon A., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Nucleolar transcription factor hUBF contains a DNA-binding motif with homology to HMG proteins. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):830–836. doi: 10.1038/344830a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaddurah-Daouk R., Greene J. M., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Kingston R. E. Activation and repression of mammalian gene expression by the c-myc protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Jun;1(4):347–357. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.4.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Siebenlist U. The regulation and expression of c-myc in normal and malignant cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:317–338. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruijer W., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid but transient expression of the c-fos gene and protein. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):711–716. doi: 10.1038/312711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau L. F., Nathans D. Expression of a set of growth-related immediate early genes in BALB/c 3T3 cells: coordinate regulation with c-fos or c-myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1182–1186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Zakut R., Shani M., Neuman S., Levy Z., Yaffe D. The nucleotide sequence of the rat cytoplasmic beta-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1759–1771. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olden K., Yamada K. M. Mechanism of the decrease in the major cell surface protein of chick embryo fibroblasts after transformation. Cell. 1977 Aug;11(4):957–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prendergast G. C., Cole M. D. Posttranscriptional regulation of cellular gene expression by the c-myc oncogene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):124–134. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Nacar E. Q. Nucleotide sequence of the first exon of the rat c-myc gene: proviral insertions in murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas do not affect exon 1. Virology. 1988 May;164(1):55–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90619-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone J., de Lange T., Ramsay G., Jakobovits E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H., Lee W. Definition of regions in human c-myc that are involved in transformation and nuclear localization. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1697–1709. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt R. A., Shatzman A. R., Rosenberg M. Expression and characterization of the human c-myc DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;5(3):448–456. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.3.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watts J. D., Cary P. D., Crane-Robinson C. Prothymosin alpha is a nuclear protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80182-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N. J., Green S., Jin J. R., Chambon P. The hormone-binding domains of the estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors contain an inducible transcription activation function. Cell. 1988 Jul 15;54(2):199–207. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90552-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Bishop J. M. DNA sequences that mediate attenuation of transcription from the mouse protooncogene myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(2):505–509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.2.505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]