Abstract
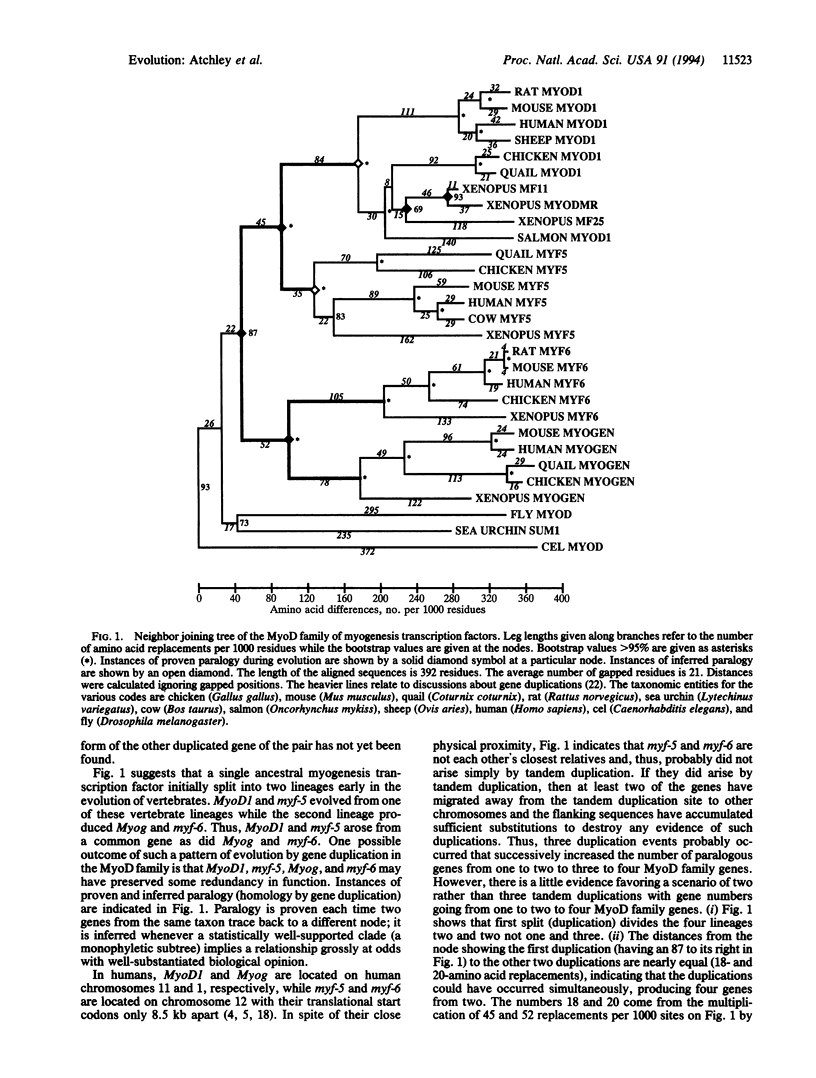
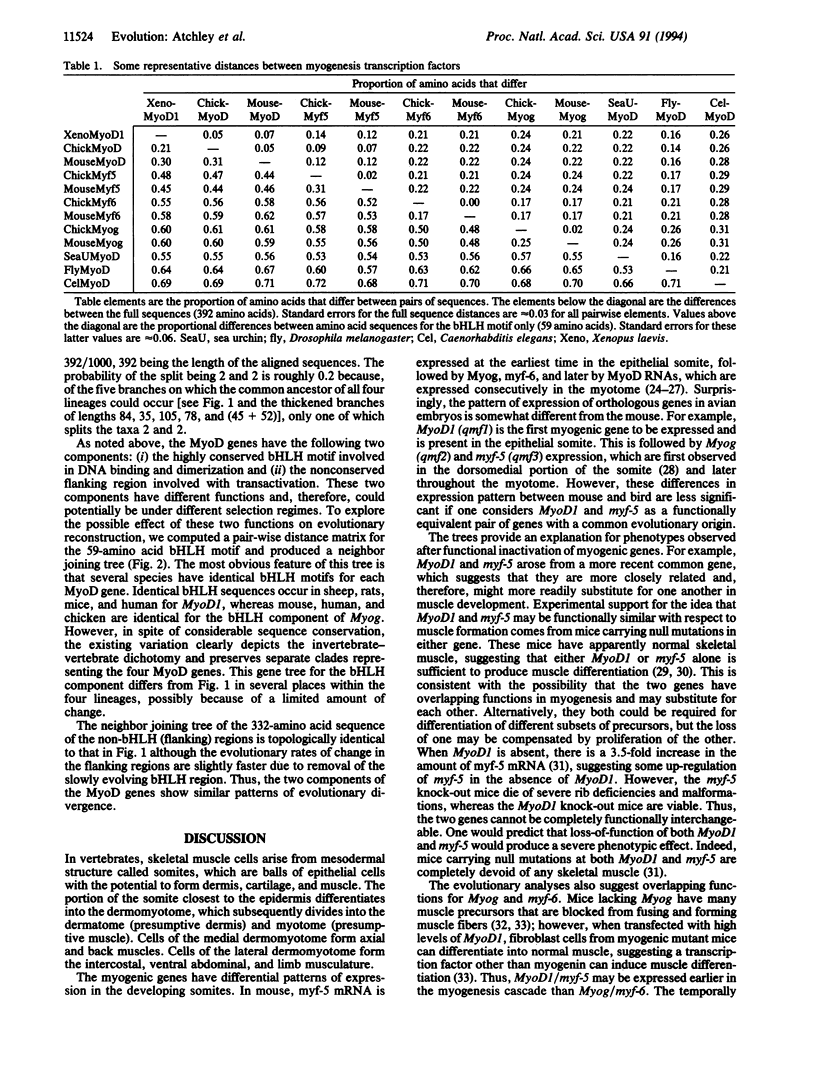
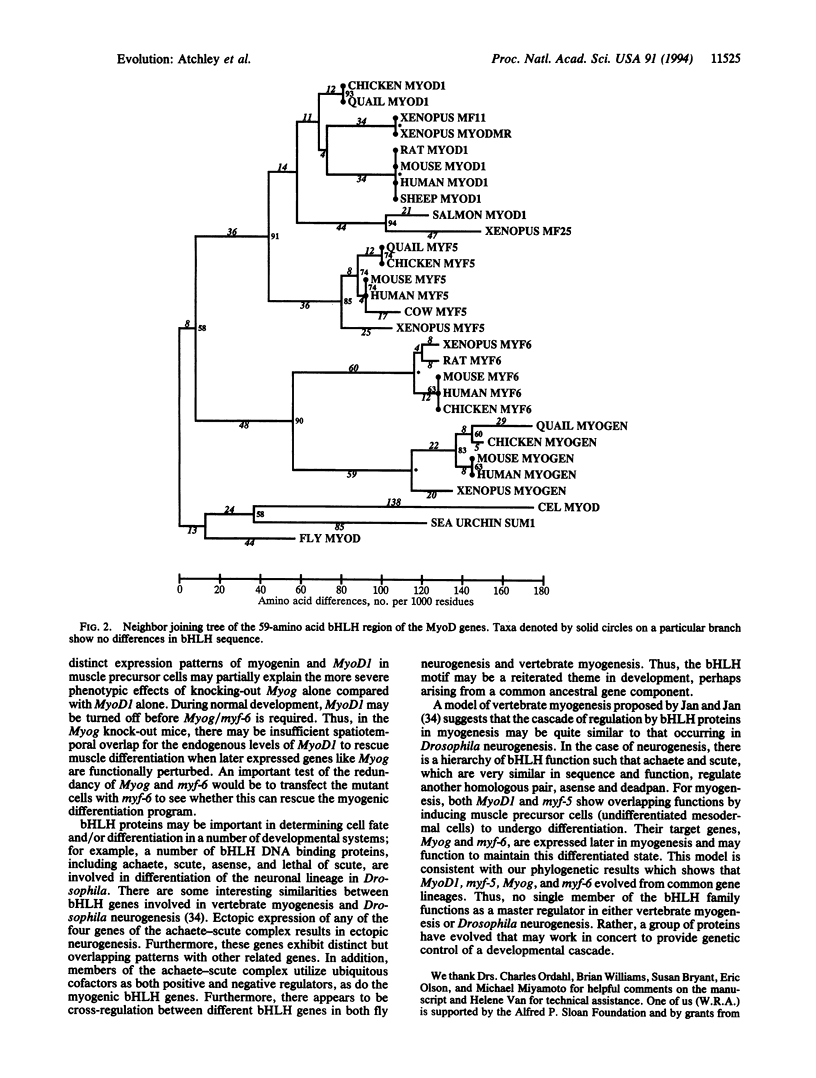
Myogenesis in skeletal muscle is a cascade of developmental events whose initiation involves the MyoD family of transcription factors. Evolutionary analyses of amino acid sequences of this family of transcriptional activators suggest that the vertebrate genes MyoD1, myf-5, Myog (myogenin), and myf-6 were derived by gene duplications from a single ancestral gene. A common genetic origin predicts some functional redundancy between MyoD1 and myf-5 and between Myog and myf-6. Experimental studies have suggested that these pairs of genes can substitute for each other during myogenesis. Separate analyses of the conserved basic helix-loop-helix and nonconserved flanking elements yield similar branching sequences but show evolutionary change in the basic helix-loop-helix region has occurred at a much slower rate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bober E., Lyons G. E., Braun T., Cossu G., Buckingham M., Arnold H. H. The muscle regulatory gene, Myf-6, has a biphasic pattern of expression during early mouse development. J Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;113(6):1255–1265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.6.1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Arnold H. H. The four human muscle regulatory helix-loop-helix proteins Myf3-Myf6 exhibit similar hetero-dimerization and DNA binding properties. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5645–5651. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Buschhausen-Denker G., Kohtz S., Grzeschik K. H., Arnold H. H., Kotz S. Differential expression of myogenic determination genes in muscle cells: possible autoactivation by the Myf gene products. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3617–3625. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Bober E., Winter B., Rosenthal N., Arnold H. H. Myf-6, a new member of the human gene family of myogenic determination factors: evidence for a gene cluster on chromosome 12. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):821–831. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Buschhausen-Denker G., Bober E., Tannich E., Arnold H. H. A novel human muscle factor related to but distinct from MyoD1 induces myogenic conversion in 10T1/2 fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):701–709. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03429.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun T., Rudnicki M. A., Arnold H. H., Jaenisch R. Targeted inactivation of the muscle regulatory gene Myf-5 results in abnormal rib development and perinatal death. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi J., Costa M. L., Mermelstein C. S., Chagas C., Holtzer S., Holtzer H. MyoD converts primary dermal fibroblasts, chondroblasts, smooth muscle, and retinal pigmented epithelial cells into striated mononucleated myoblasts and multinucleated myotubes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7988–7992. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. A gene with homology to the myc similarity region of MyoD1 is expressed during myogenesis and is sufficient to activate the muscle differentiation program. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):628–640. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmondson D. G., Olson E. N. Helix-loop-helix proteins as regulators of muscle-specific transcription. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):755–758. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon K., Smith C. K., 2nd, Bales K. R., Santerre R. F. Temporal and quantitative analysis of myogenic regulatory and growth factor gene expression in the developing mouse embryo. Dev Biol. 1992 May;151(1):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasty P., Bradley A., Morris J. H., Edmondson D. G., Venuti J. M., Olson E. N., Klein W. H. Muscle deficiency and neonatal death in mice with a targeted mutation in the myogenin gene. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):501–506. doi: 10.1038/364501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinterberger T. J., Mays J. L., Konieczny S. F. Structure and myofiber-specific expression of the rat muscle regulatory gene MRF4. Gene. 1992 Aug 15;117(2):201–207. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90730-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan Y. N., Jan L. Y. HLH proteins, fly neurogenesis, and vertebrate myogenesis. Cell. 1993 Dec 3;75(5):827–830. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90525-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Fire A., Harrison S. W., Priess J., Weintraub H. CeMyoD accumulation defines the body wall muscle cell fate during C. elegans embryogenesis. Cell. 1990 Nov 30;63(5):907–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90494-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Abmayr S. M., Bate M., Arias A. M., Maniatis T. Expression of a MyoD family member prefigures muscle pattern in Drosophila embryos. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2086–2097. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miner J. H., Wold B. Herculin, a fourth member of the MyoD family of myogenic regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Hanaoka K., Hayasaka M., Esumi E., Li S., Nonaka I., Nabeshima Y. Myogenin gene disruption results in perinatal lethality because of severe muscle defect. Nature. 1993 Aug 5;364(6437):532–535. doi: 10.1038/364532a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. MyoD family: a paradigm for development? Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1454–1461. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N. Regulation of muscle transcription by the MyoD family. The heart of the matter. Circ Res. 1993 Jan;72(1):1–6. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Bober E., Lyons G., Arnold H., Buckingham M. Early expression of the myogenic regulatory gene, myf-5, in precursor cells of skeletal muscle in the mouse embryo. Development. 1991 Apr;111(4):1097–1107. doi: 10.1242/dev.111.4.1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patapoutian A., Miner J. H., Lyons G. E., Wold B. Isolated sequences from the linked Myf-5 and MRF4 genes drive distinct patterns of muscle-specific expression in transgenic mice. Development. 1993 May;118(1):61–69. doi: 10.1242/dev.118.1.61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pownall M. E., Emerson C. P., Jr Sequential activation of three myogenic regulatory genes during somite morphogenesis in quail embryos. Dev Biol. 1992 May;151(1):67–79. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes S. J., Konieczny S. F. Identification of MRF4: a new member of the muscle regulatory factor gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2050–2061. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Braun T., Hinuma S., Jaenisch R. Inactivation of MyoD in mice leads to up-regulation of the myogenic HLH gene Myf-5 and results in apparently normal muscle development. Cell. 1992 Oct 30;71(3):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90508-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnicki M. A., Schnegelsberg P. N., Stead R. H., Braun T., Arnold H. H., Jaenisch R. MyoD or Myf-5 is required for the formation of skeletal muscle. Cell. 1993 Dec 31;75(7):1351–1359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90621-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassoon D., Lyons G., Wright W. E., Lin V., Lassar A., Weintraub H., Buckingham M. Expression of two myogenic regulatory factors myogenin and MyoD1 during mouse embryogenesis. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):303–307. doi: 10.1038/341303a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venuti J. M., Goldberg L., Chakraborty T., Olson E. N., Klein W. H. A myogenic factor from sea urchin embryos capable of programming muscle differentiation in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6219–6223. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Dwarki V. J., Verma I., Davis R., Hollenberg S., Snider L., Lassar A., Tapscott S. J. Muscle-specific transcriptional activation by MyoD. Genes Dev. 1991 Aug;5(8):1377–1386. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.8.1377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Sassoon D. A., Lin V. K. Myogenin, a factor regulating myogenesis, has a domain homologous to MyoD. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):607–617. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90583-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Brousse F. C., Emerson C. P., Jr Localized expression of a myogenic regulatory gene, qmf1, in the somite dermatome of avian embryos. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):567–581. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



