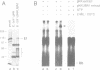Abstract
All known functions of ubiquitin are mediated through its covalent attachment to other proteins. The post-translational formation of ubiquitin--protein conjugates is preceded by an ATP-requiring step in which the carboxyl terminus of ubiquitin is adenylated and subsequently joined, through a thiolester bond, to a cysteine residue in the ubiquitin-activating enzyme, also known as E1. We report the isolation and functional analysis of the gene (UBA1) for the ubiquitin-activating enzyme of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. UBA1 encodes a 114 kd protein whose amino acid sequence contains motifs characteristic of nucleotide-binding sites. Expression of catalytically active UBA1 protein in E. coli, which lacks the ubiquitin system, confirmed that the yeast UBA1 gene encodes a ubiquitin-activating enzyme. Deletion of the UBA1 gene is lethal, demonstrating that the formation of ubiquitin--protein conjugates is essential for cell viability.
Full text
PDF








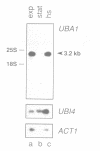
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold J. E., Gevers W. Auto-ubiquitination of ubiquitin-activating enzymes from chicken breast muscle. Biochem J. 1990 May 1;267(3):751–757. doi: 10.1042/bj2670751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmair A., Finley D., Varshavsky A. In vivo half-life of a protein is a function of its amino-terminal residue. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):179–186. doi: 10.1126/science.3018930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker T. A., Grossman A. D., Gross C. A. A gene regulating the heat shock response in Escherichia coli also affects proteolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6779–6783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balzi E., Choder M., Chen W. N., Varshavsky A., Goffeau A. Cloning and functional analysis of the arginyl-tRNA-protein transferase gene ATE1 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7464–7471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel B., Wünning I., Varshavsky A. The recognition component of the N-end rule pathway. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3179–3189. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07516.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Lupski J. R. Plasmids for the selection and analysis of prokaryotic promoters. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:54–68. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chau V., Tobias J. W., Bachmair A., Marriott D., Ecker D. J., Gonda D. K., Varshavsky A. A multiubiquitin chain is confined to specific lysine in a targeted short-lived protein. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1576–1583. doi: 10.1126/science.2538923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Elias S., Heller H., Hershko A. "Covalent affinity" purification of ubiquitin-activating enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2537–2542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanover A., Heller H., Elias S., Haas A. L., Hershko A. ATP-dependent conjugation of reticulocyte proteins with the polypeptide required for protein degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1365–1368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Glynias M. J., Merrick W. C. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Roberts N. A., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M., Perkins R. E., Conroy S. C., Fothergill L. A. Conservation of high efficiency promoter sequences in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2625–2637. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eki T., Enomoto T., Miyajima A., Miyazawa H., Murakami Y., Hanaoka F., Yamada M., Ui M. Isolation of temperature-sensitive cell cycle mutants from mouse FM3A cells. Characterization of mutants with special reference to DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):26–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Bartel B., Varshavsky A. The tails of ubiquitin precursors are ribosomal proteins whose fusion to ubiquitin facilitates ribosome biogenesis. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):394–401. doi: 10.1038/338394a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
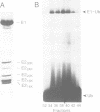
- Finley D., Ciechanover A., Varshavsky A. Thermolability of ubiquitin-activating enzyme from the mammalian cell cycle mutant ts85. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):43–55. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90299-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley D., Ozkaynak E., Varshavsky A. The yeast polyubiquitin gene is essential for resistance to high temperatures, starvation, and other stresses. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):1035–1046. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90711-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goebl M. G., Yochem J., Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A., Byers B. The yeast cell cycle gene CDC34 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Science. 1988 Sep 9;241(4871):1331–1335. doi: 10.1126/science.2842867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda D. K., Bachmair A., Wünning I., Tobias J. W., Lane W. S., Varshavsky A. Universality and structure of the N-end rule. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16700–16712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregori L., Poosch M. S., Cousins G., Chau V. A uniform isopeptide-linked multiubiquitin chain is sufficient to target substrate for degradation in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 25;265(15):8354–8357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas A. L., Rose I. A. The mechanism of ubiquitin activating enzyme. A kinetic and equilibrium analysis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10329–10337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannink M., Donoghue D. J. Lysine residue 121 in the proposed ATP-binding site of the v-mos protein is required for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7894–7898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield P. M., Callis J., Vierstra R. D. Cloning of ubiquitin activating enzyme from wheat and expression of a functional protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 15;265(26):15813–15817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Heller H., Elias S., Ciechanover A. Components of ubiquitin-protein ligase system. Resolution, affinity purification, and role in protein breakdown. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8206–8214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A. Ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15237–15240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast DNA repair gene RAD6 encodes a ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):131–134. doi: 10.1038/329131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jentsch S., Seufert W., Sommer T., Reins H. A. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes: novel regulators of eukaryotic cells. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 May;15(5):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90161-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. E., Rajagopalan K. V. Involvement of chlA, E, M, and N loci in Escherichia coli molybdopterin biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):117–125. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.117-125.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulka R. G., Raboy B., Schuster R., Parag H. A., Diamond G., Ciechanover A., Marcus M. A Chinese hamster cell cycle mutant arrested at G2 phase has a temperature-sensitive ubiquitin-activating enzyme, E1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15726–15731. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madura K., Prakash S., Prakash L. Expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA repair gene RAD6 that encodes a ubiquitin conjugating enzyme, increases in response to DNA damage and in meiosis but remains constant during the mitotic cell cycle. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):771–778. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer A., Gropper R., Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A. Purification, characterization, and rapid inactivation of thermolabile ubiquitin-activating enzyme from the mammalian cell cycle mutant ts85. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2060–2068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Varshavsky A. The yeast STE6 gene encodes a homologue of the mammalian multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. Nature. 1989 Aug 3;340(6232):400–404. doi: 10.1038/340400a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D., Contopoulou C. R., Kans J. A. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, edition 10. Yeast. 1989 Sep-Oct;5(5):321–403. doi: 10.1002/yea.320050503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick P., Osmond B. C., Botstein D. Suppressors of yeast actin mutations. Genetics. 1989 Apr;121(4):659–674. doi: 10.1093/genetics/121.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Nishimoto T. The gene coding a ubiquitin-activating enzyme may locate on X chromosome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1173–1178. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)81351-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozkaynak E., Finley D., Solomon M. J., Varshavsky A. The yeast ubiquitin genes: a family of natural gene fusions. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1429–1439. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02384.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Xiao H., Lis J. T. Stable binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to head-to-head and tail-to-tail repeats of a conserved 5 bp recognition unit. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickart C. M., Rose I. A. Functional heterogeneity of ubiquitin carrier proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1573–1581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss Y., Kaim D., Hershko A. Specificity of binding of NH2-terminal residue of proteins to ubiquitin-protein ligase. Use of amino acid derivatives to characterize specific binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2693–2698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Prakash S., Prakash L. The rhp6+ gene of Schizosaccharomyces pombe: a structural and functional homolog of the RAD6 gene from the distantly related yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1423–1430. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schatz P. J., Solomon F., Botstein D. Genetically essential and nonessential alpha-tubulin genes specify functionally interchangeable proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3722–3733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R., Eckerskorn C., Lottspeich F., Schweiger M. The human ubiquitin carrier protein E2(Mr = 17,000) is homologous to the yeast DNA repair gene RAD6. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1431–1435. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08259.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., Jentsch S. Ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes UBC4 and UBC5 mediate selective degradation of short-lived and abnormal proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):543–550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seufert W., McGrath J. P., Jentsch S. UBC1 encodes a novel member of an essential subfamily of yeast ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes involved in protein degradation. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4535–4541. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07905.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. The codon Adaptation Index--a measure of directional synonymous codon usage bias, and its potential applications. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1281–1295. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Haber J. E., Botstein D. Lethal disruption of the yeast actin gene by integrative DNA transformation. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):371–373. doi: 10.1126/science.7046050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
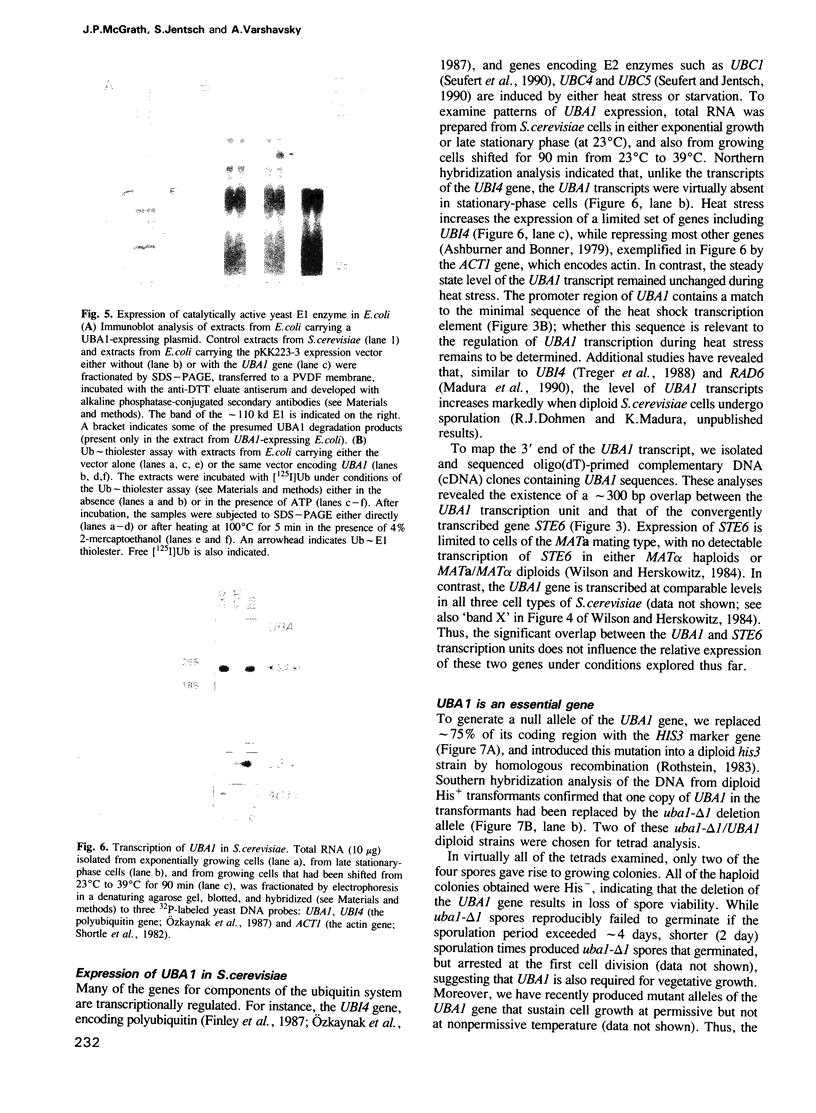
- Sullivan M. L., Vierstra R. D. A ubiquitin carrier protein from wheat germ is structurally and functionally similar to the yeast DNA repair enzyme encoded by RAD6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9861–9865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treger J. M., Heichman K. A., McEntee K. Expression of the yeast UB14 gene increases in response to DNA-damaging agents and in meiosis. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1132–1136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wierenga R. K., Hol W. G. Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):842–844. doi: 10.1038/302842a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson K. D., Lee K. M., Deshpande S., Duerksen-Hughes P., Boss J. M., Pohl J. The neuron-specific protein PGP 9.5 is a ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase. Science. 1989 Nov 3;246(4930):670–673. doi: 10.1126/science.2530630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. L., Herskowitz I. Negative regulation of STE6 gene expression by the alpha 2 product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2420–2427. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacksenhaus E., Sheinin R. Molecular cloning, primary structure and expression of the human X linked A1S9 gene cDNA which complements the ts A1S9 mouse L cell defect in DNA replication. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2923–2929. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07483.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Paluh J. L., van Cleemput M., Moye W. S., Yanofsky C. Nucleotide sequence of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genes TRP2 and TRP3 encoding bifunctional anthranilate synthase: indole-3-glycerol phosphate synthase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3985–3992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]